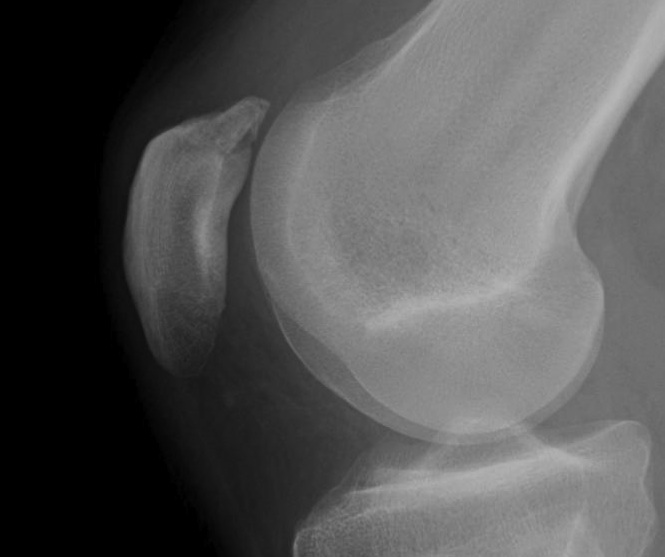
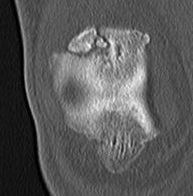
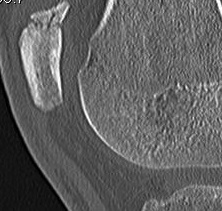
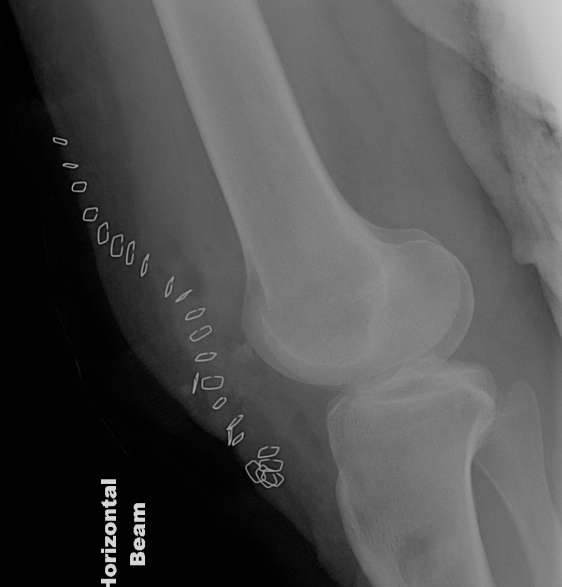
Mechanism
Direct blow
- most common
Indirect
- forced knee flexion with foot fixed / maximally contracted quadriceps
Types
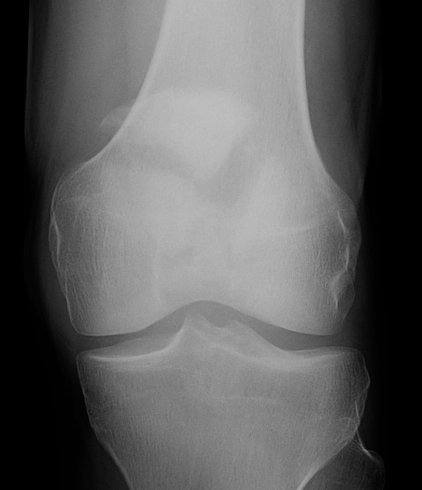
1. Vertical
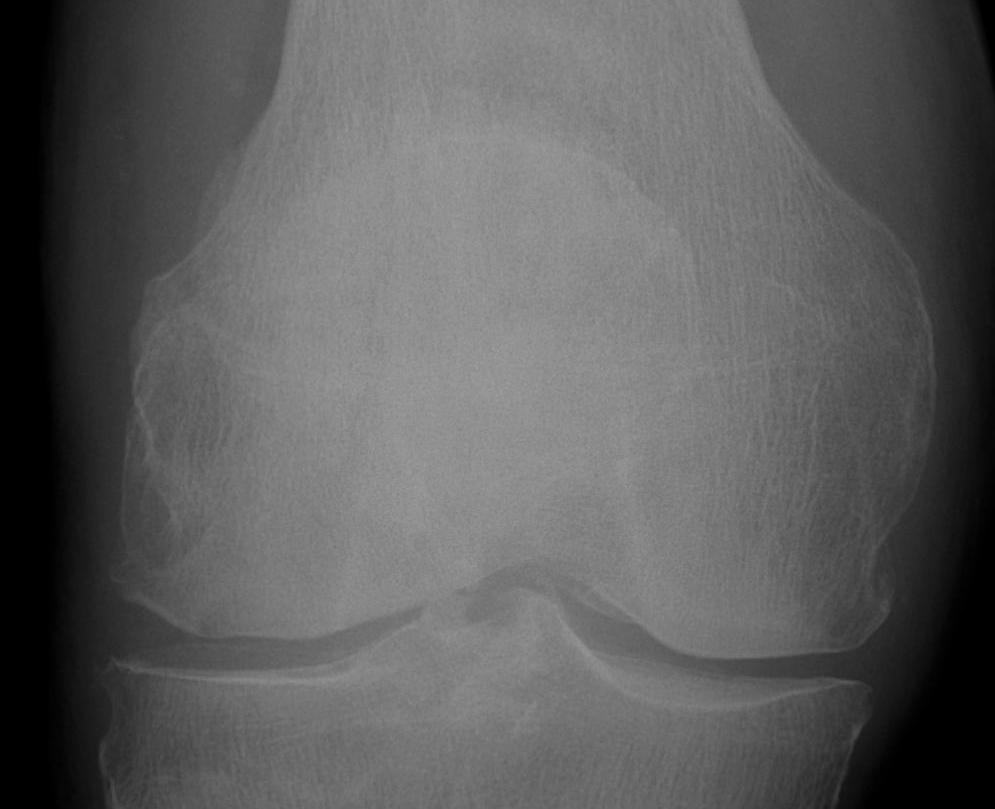
2. Transverse
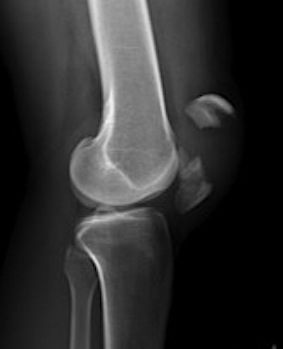
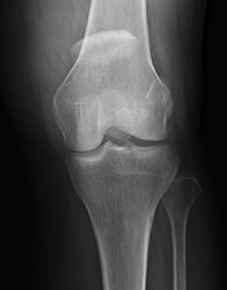
3. Burst / Stellate
Management
Non operative
Indications
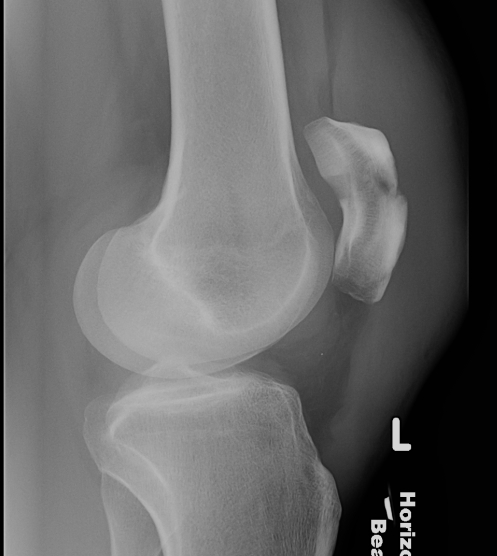
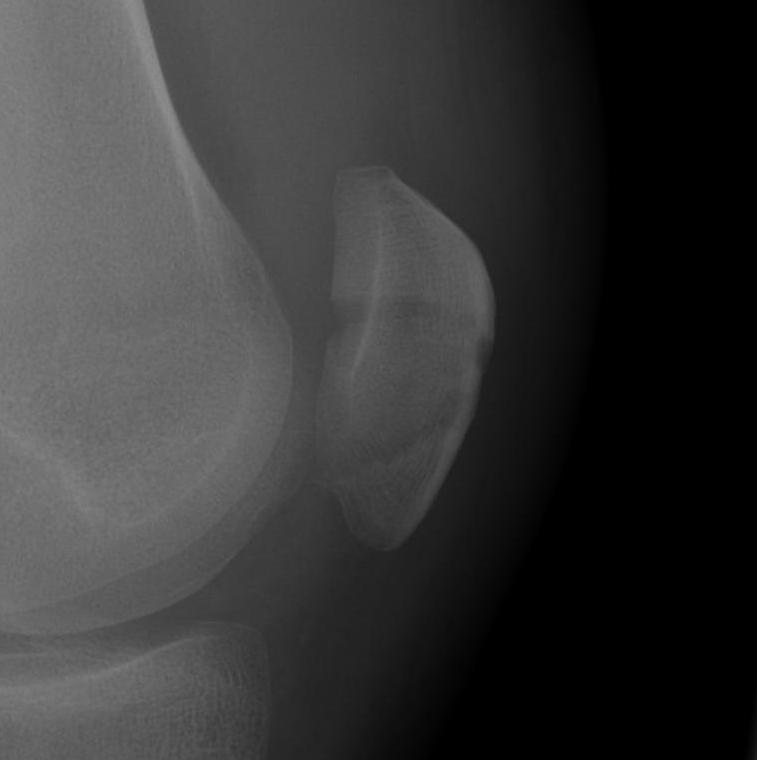
Vertical
- biomechanically stable
Undisplaced transverse fractures
- < 2mm
- extensor mechanism intact
- able to straight leg raise
Operative
Indications
Displaced transverse fractures
Techniques
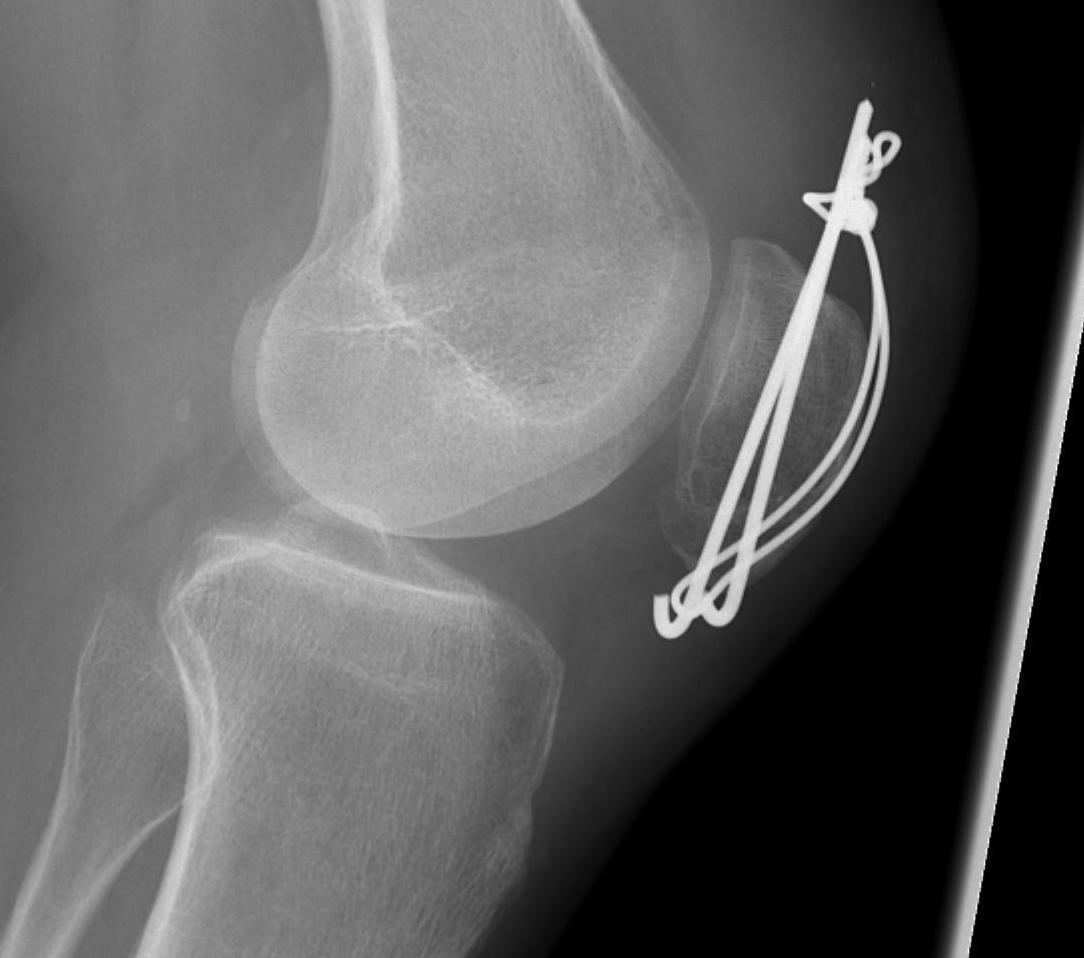
1. TBW
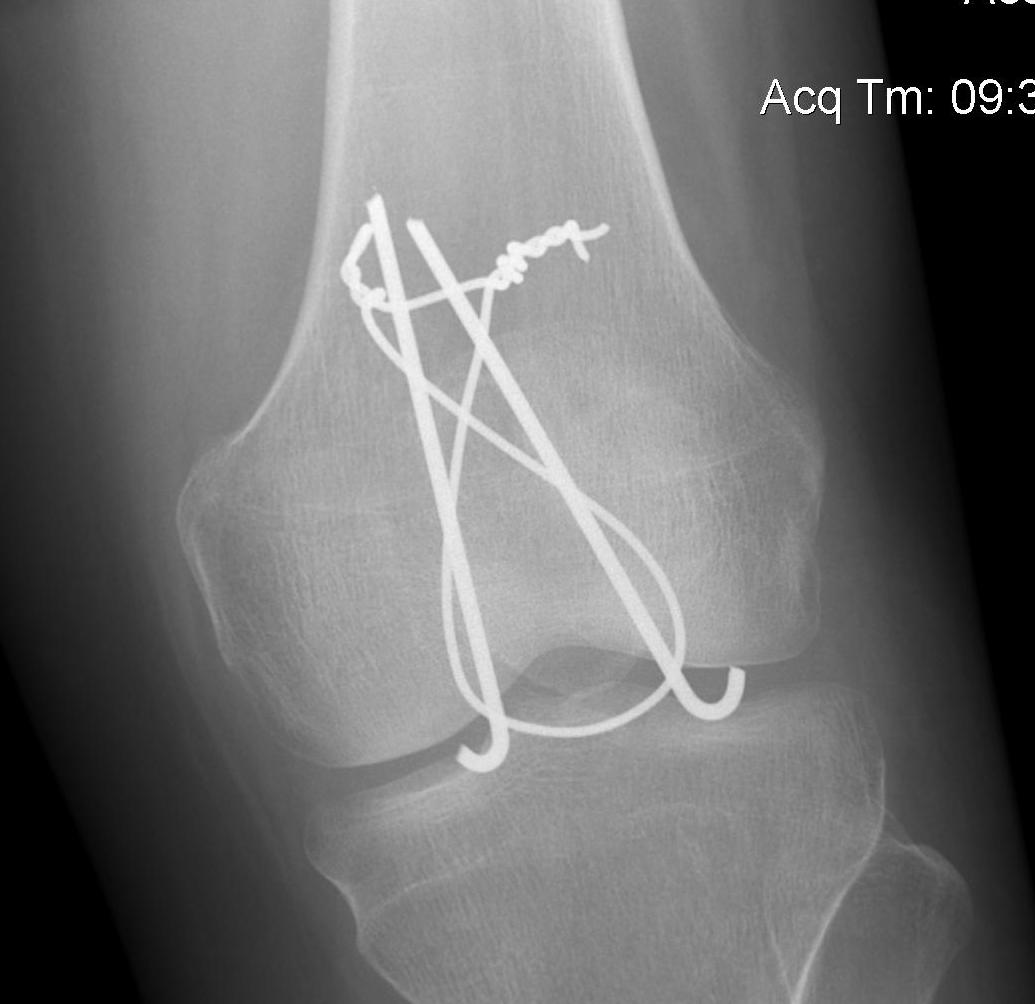
2. Cerclage wire +/- ORIF
- stellate fractures
3. Lag screws
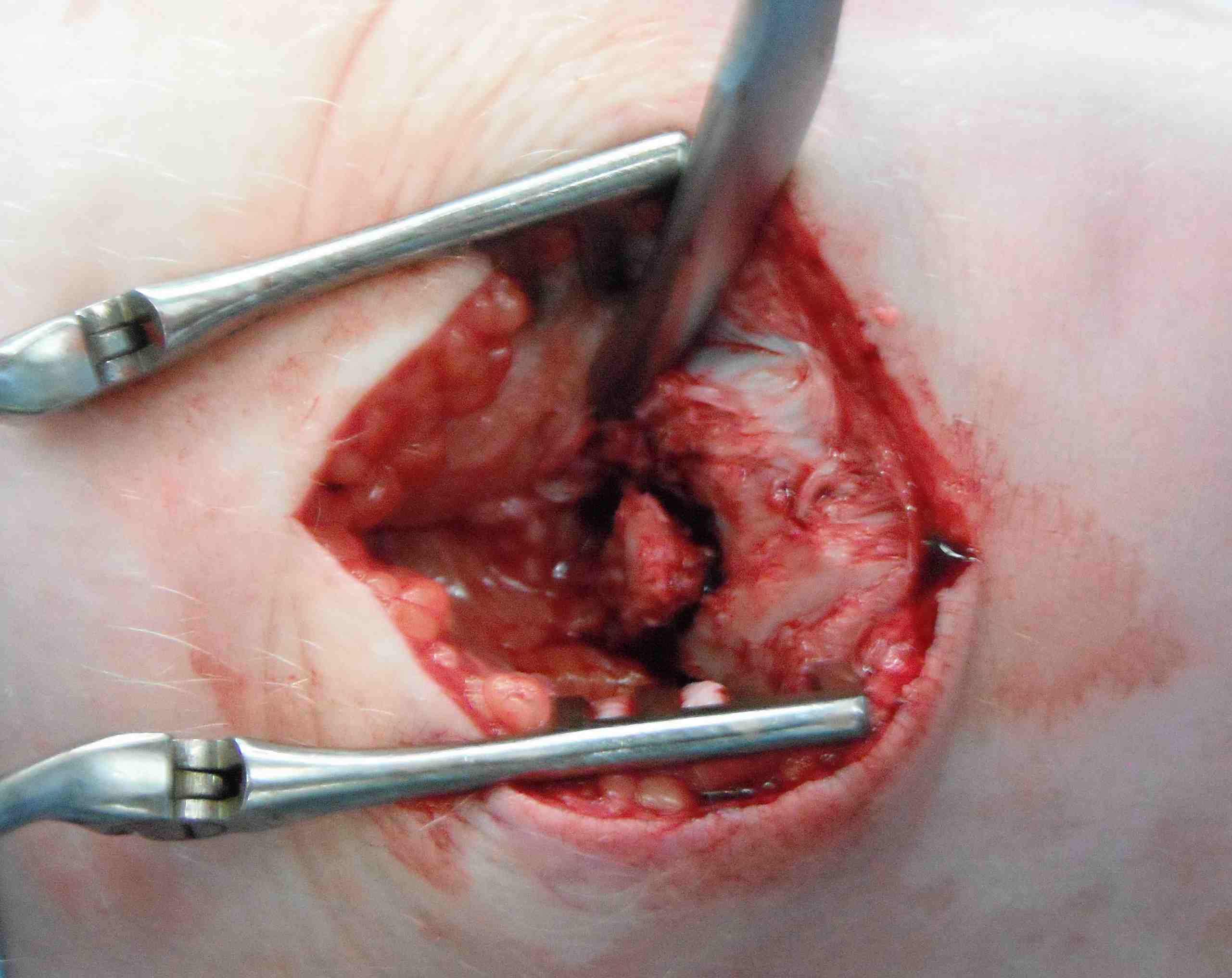
4. Patellectomy
Technique
Concept
Excise patella in full close retinaculum tightly with VMO advancement
Concerns
- extensor lag and weakness
- continued pain if trochlea lesions
- issues with later TKA
AO Surgery Reference Technique
Results
Outcomes
- patellectomy for OA in 20 knees
- 19/20 satisfied
- systematic review of 31 articles and 1400 patellectomies
- 85% good or excellent if extensor mechanism reinforcement is performed
Complications
- 12 patellectomies
- good function, but extensor weakness and ROM differences
Asopa et al J Orthop Surg Res 2015
- better results with disease confined to the patella
TKA and patellectomy
- systematic review of TKA after previous patellectomy
- reduced flexion and increased risk complications in patients with patellectomy
Indications
- unreconstructable fracture
Risks
- extension lag / weakness
- anterior instability
Gunal et al JBJS Br 1996
- patients with at least 5 fragments
- advocated VMO advancement
- additional medial parapatellar incision
- advance laterally and distally
- demonstrated improved strength and decreased lag
Late Management
Malunion Patella Fractures
Partial patellectomy
- remove part of medial or lateral facet
- good functional and pain relief
Non Union Patella Fragment