patella
Acute Patella Dislocation
Mechanism
1. Direct lateral blow to patella
- usually with knee partly flexed and quadriceps relaxed
2. Indirect low energy injury
Background
Definition
Repeated dislocation of patella with minimal trauma
- 15-20% of paediatric acute patella dislocations
- more common girls
- often bilateral
Dislocation occurs unexpectedly when quadriceps contracted with knee in flexion
Direction
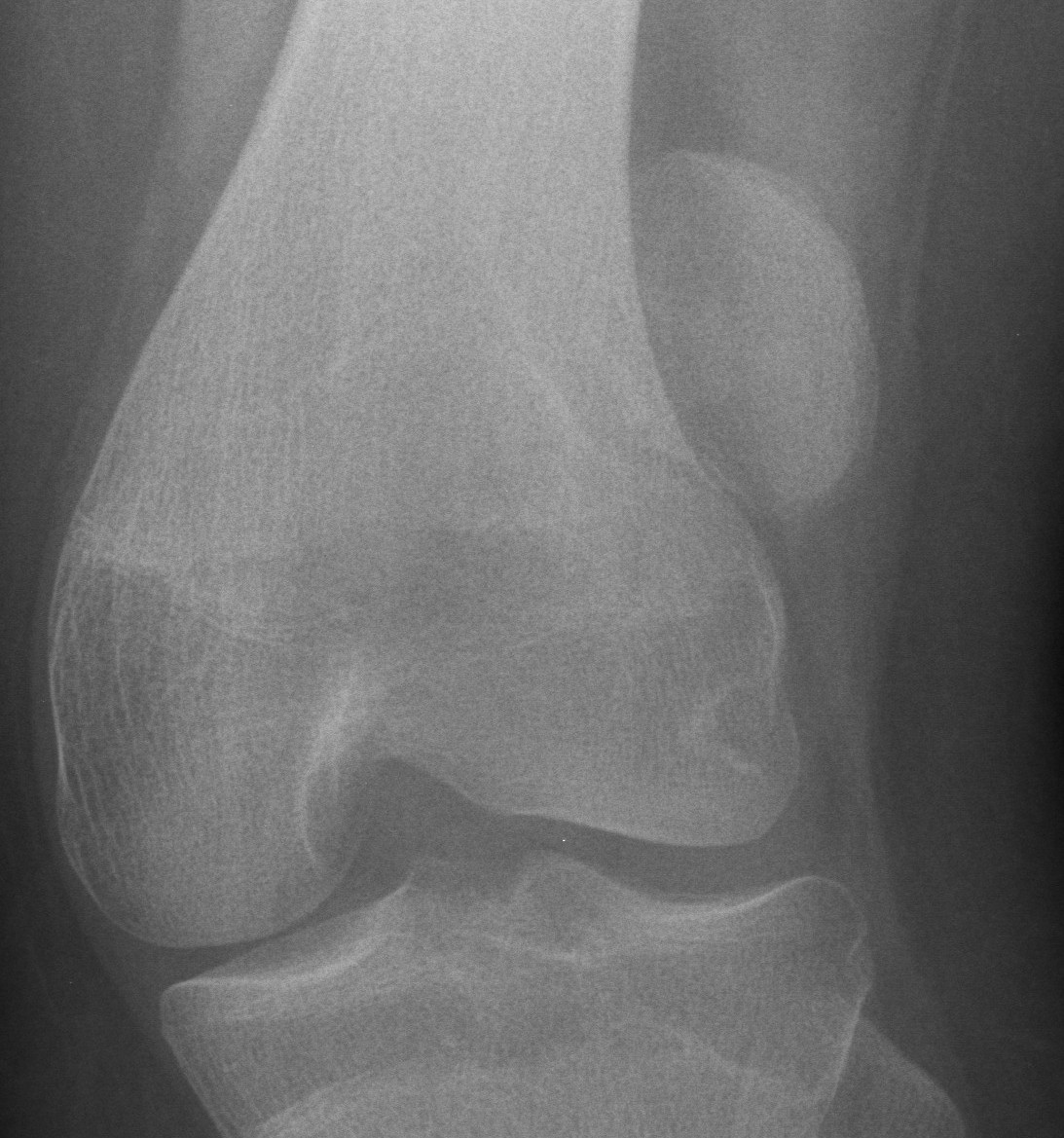
Patella Fracture
Mechanism
Direct blow
- most common
Indirect
- forced knee flexion with foot fixed / maximally contracted quadriceps
Types
1. Vertical
2. Transverse
Anatomical Approach to Biopsy
Region specific approaches
Theory
- want to traverse one muscle / one compartment
- keep away from NV bundle
- as a rule perform open biopsy through compartment the tumour is in
- this is the compartment that will require surgical removal in wide excision
- direct approach without going through muscle if possible i.e. tibia, distal ulna
Lower Limb
Thigh
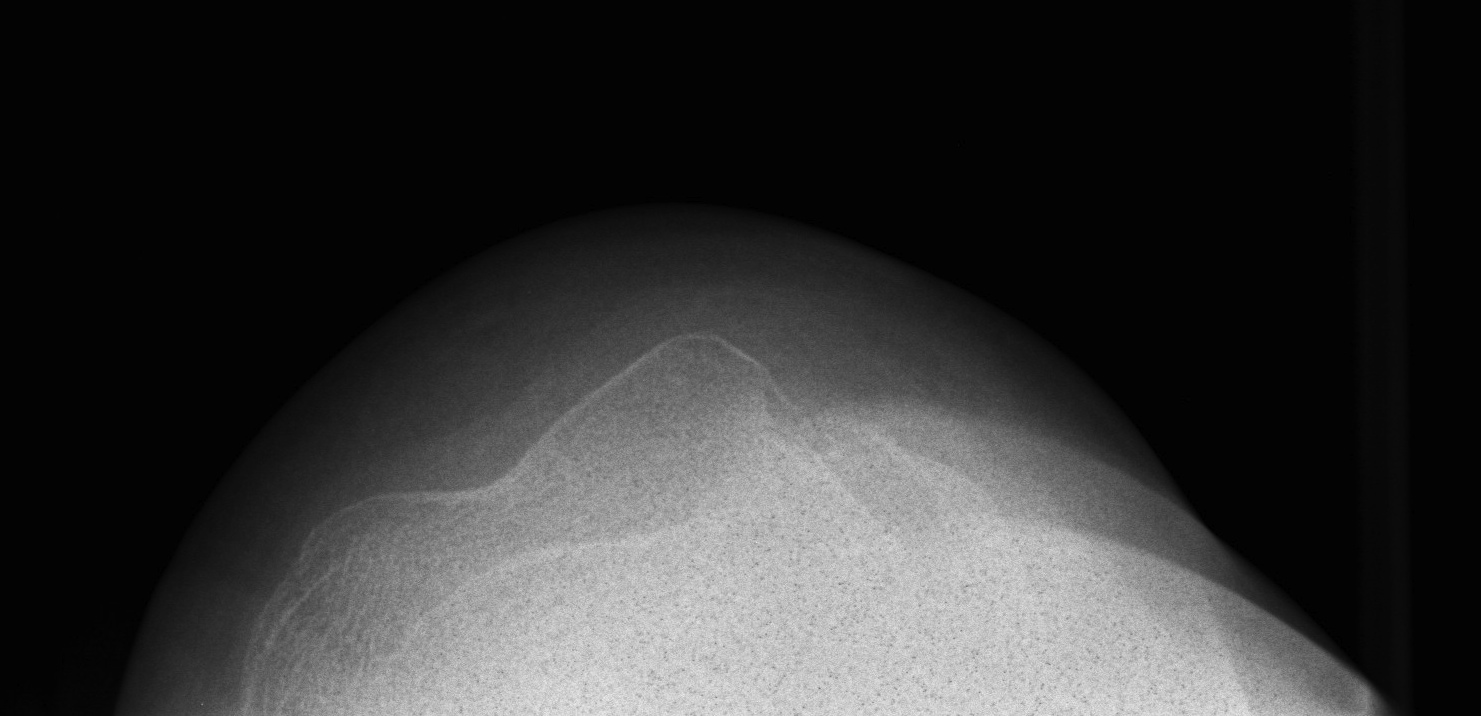
Bipartite Patella
Ossification
Patella may develop from one or multiple ossification centres at 3 years
Failure of centres to fuse may produce bipartite or tripartite patella
- usually bilateral and painless
Classically superolateral
Classification Saupe
I Inferior Pole 5%
II Lateral 20%
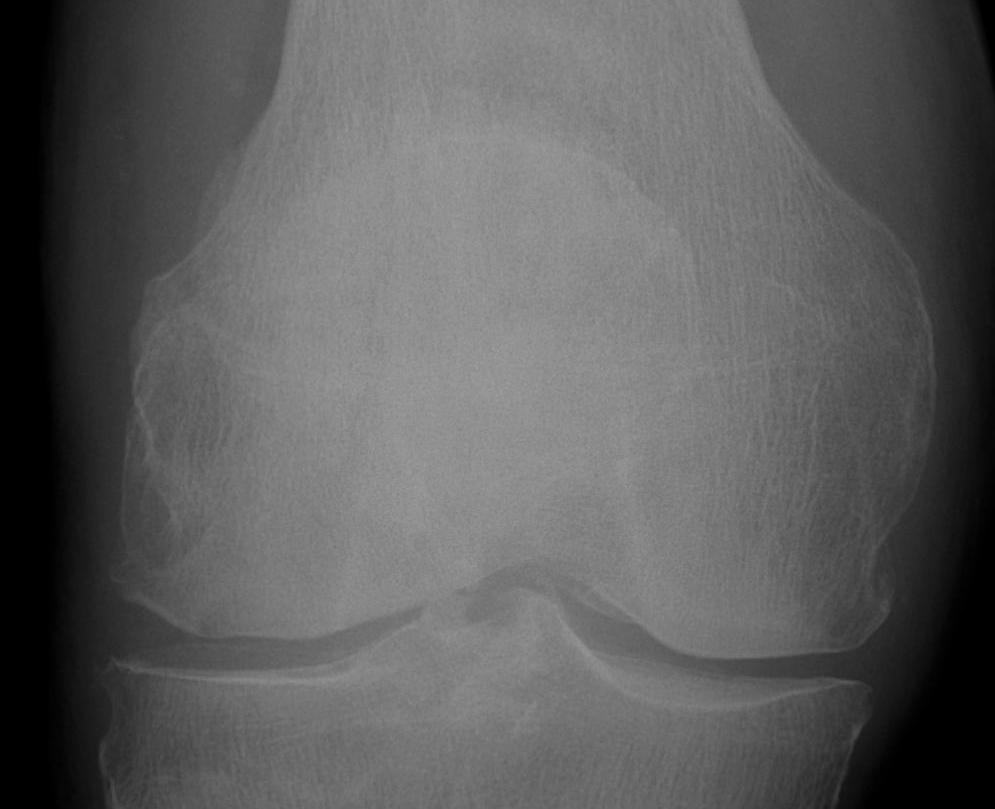
Sinding - Larson - Johanssen
Epidemiology
Active pre teen boy
- activity related pain
- common in high jumpers
Diagnosis
Fragmentation / calcification of inferior pole
- repetitive traction injury where PT inserts
- tender at this point
Stages
I Normal
II Ca inferior pole irregularity
III Coalesce Ca inferior pole
Patellar tendonitis
Definition
Patellar Tendinitis
Epidemiology
Most common in athletes
- especially if involved in running, jumping and kicking
- over use injury
Basketball players
Aetiology
Chronic overload v inferior patella impingement
Schmidt et al Am J Sports Med
- dynamic MRI in patients with jumper's knee v controls
- no evidence of impingemnt
Management
Non-operative
Results
90% respond
- very important
- 6 - 12 months minimum before offering surgery
Physiotherapy
1. Stretches
- quads stretches
- ITB
- lateral retinaculum
Investigation
AP / Long Leg Views
Quantify Valgus Malalignment
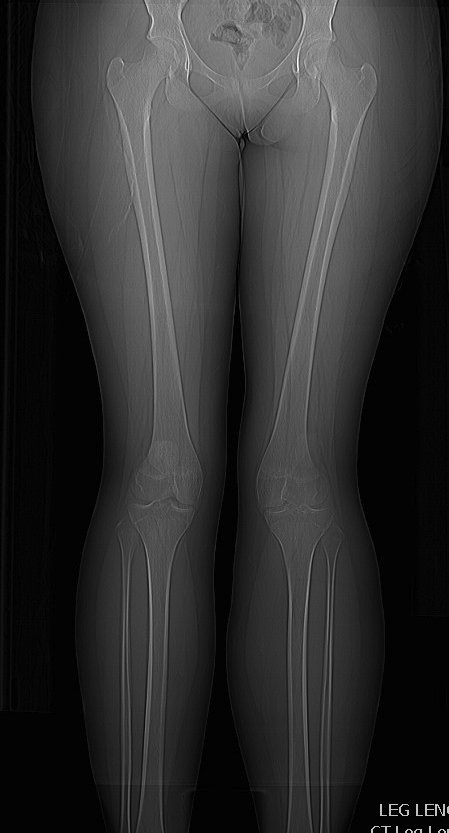
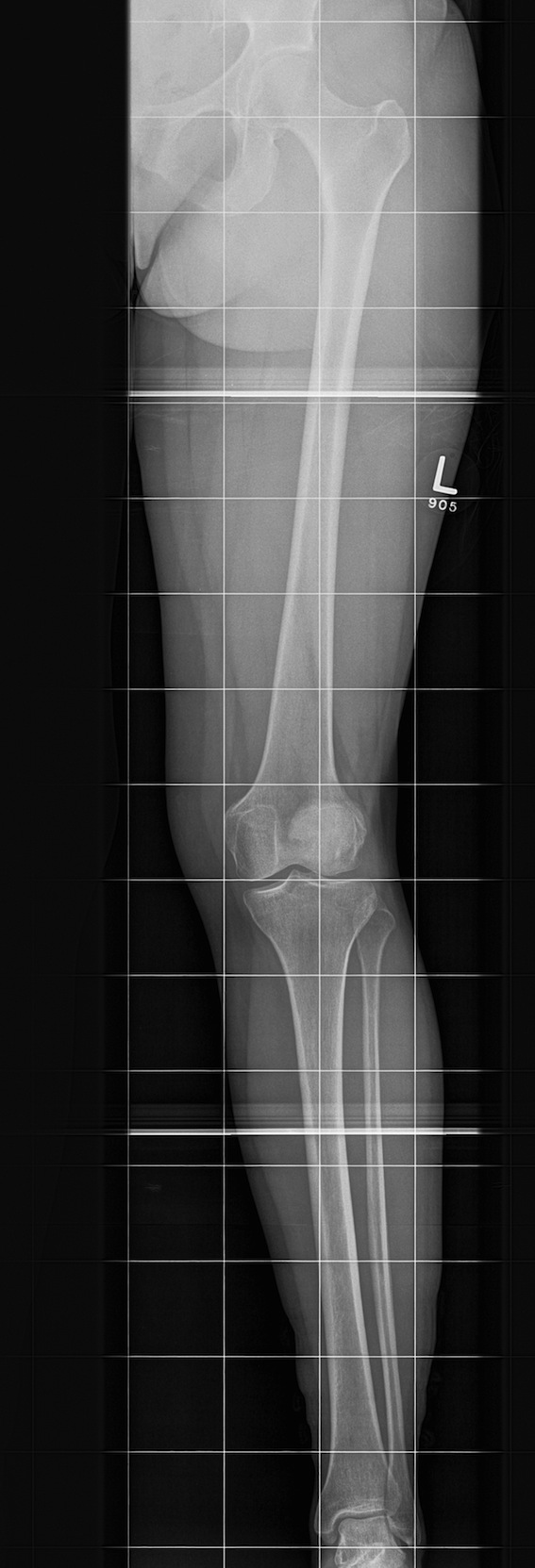
Lateral Xray
1. Assess Patella Alta
30o flexion