Epidemiology
Most common sarcoma - 20 - 25%
Rarely arise from lipoma
MRI
Deep to fascia / heterogenous
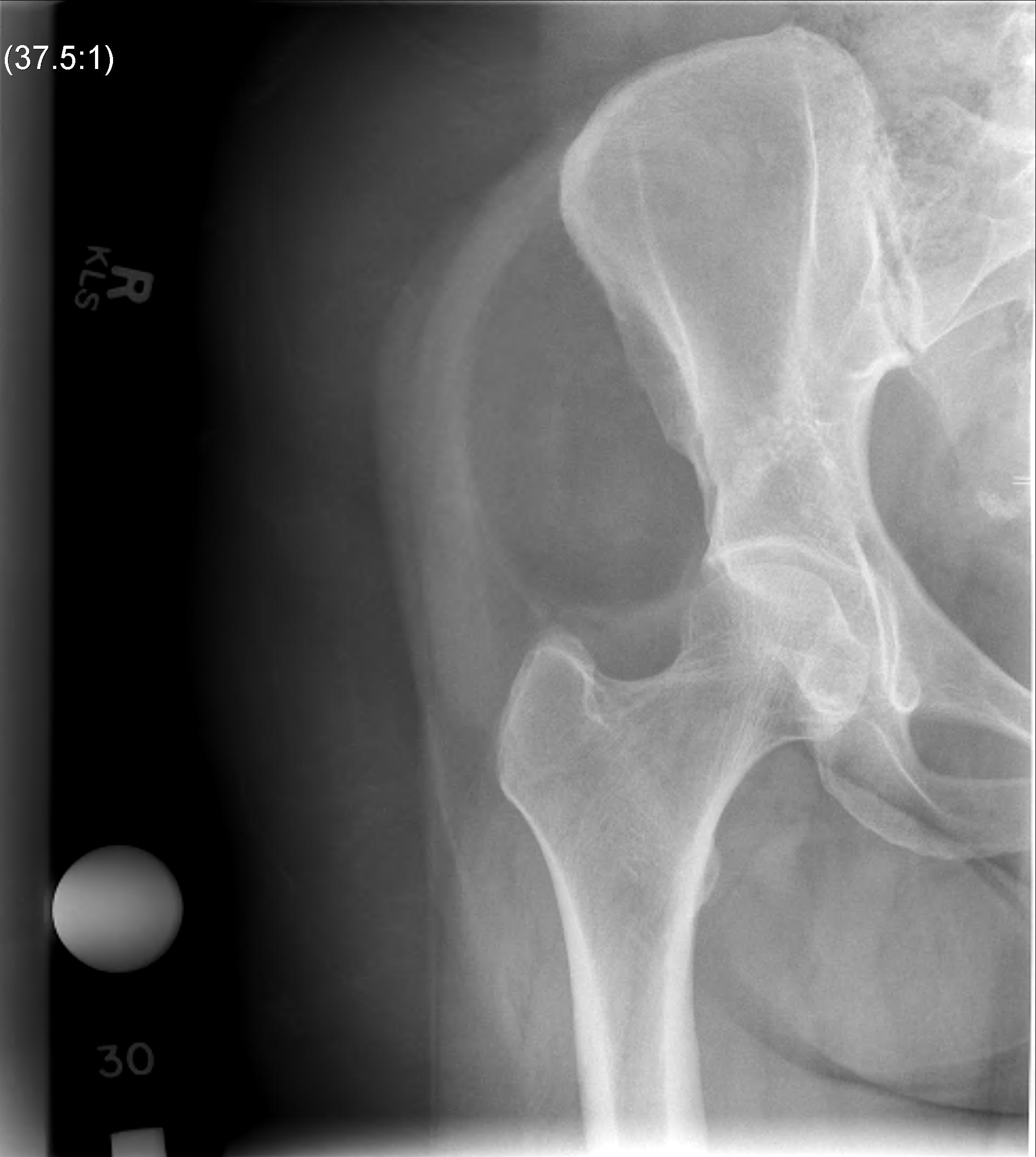
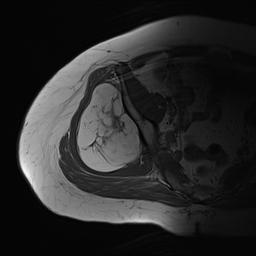
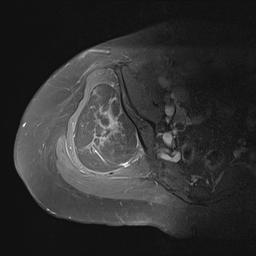
Liposarcoma pelvis
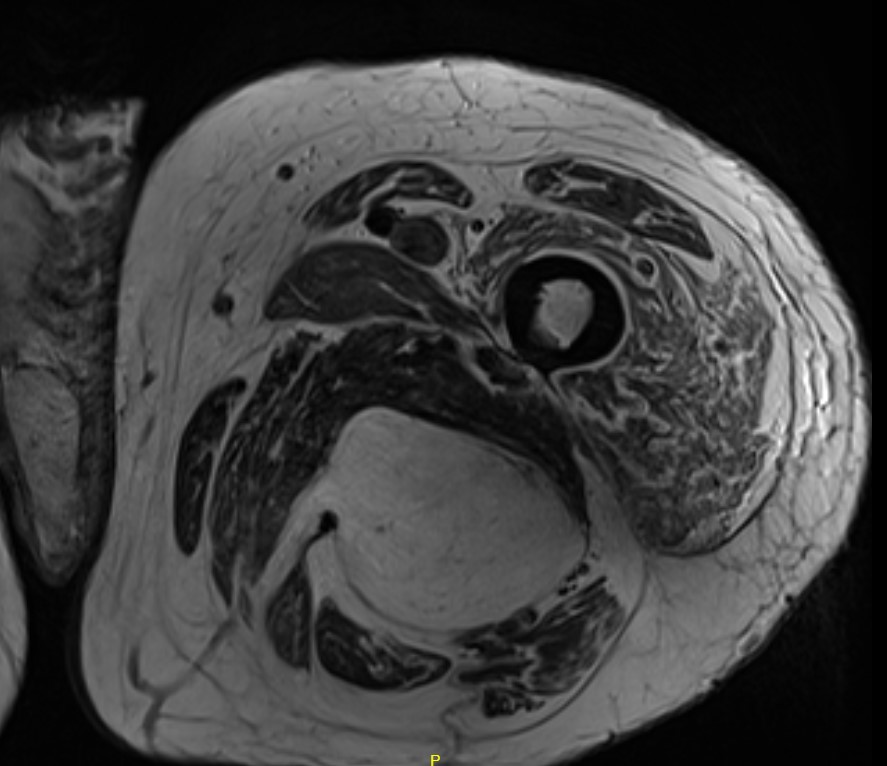
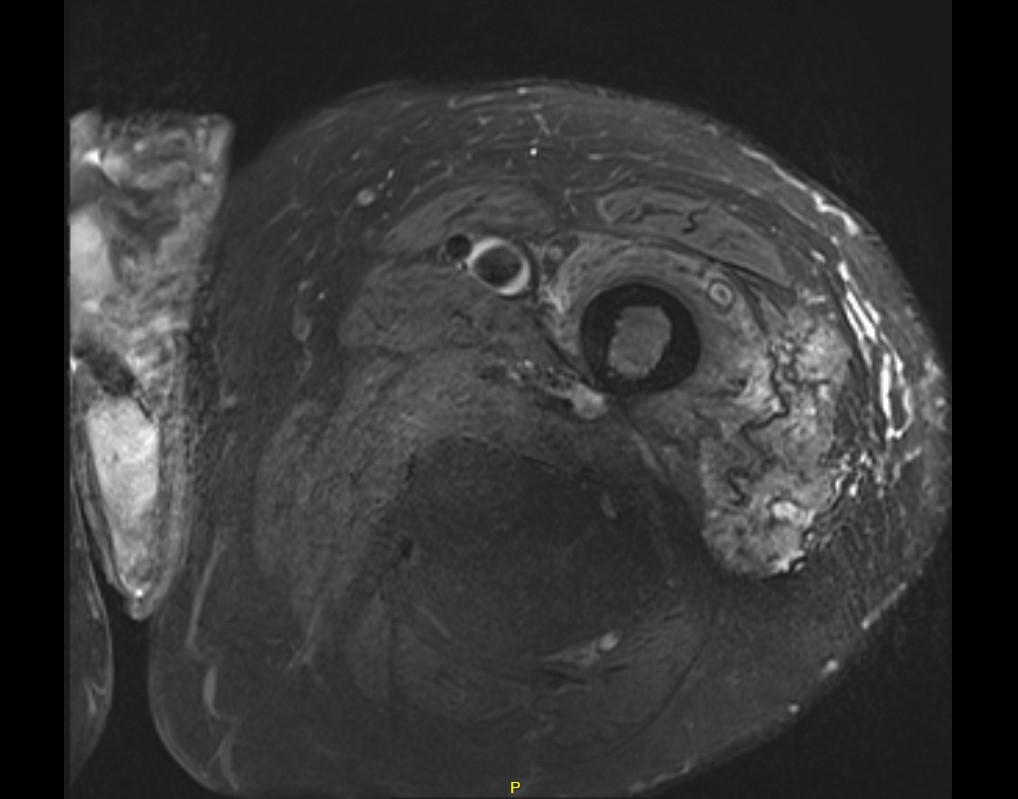
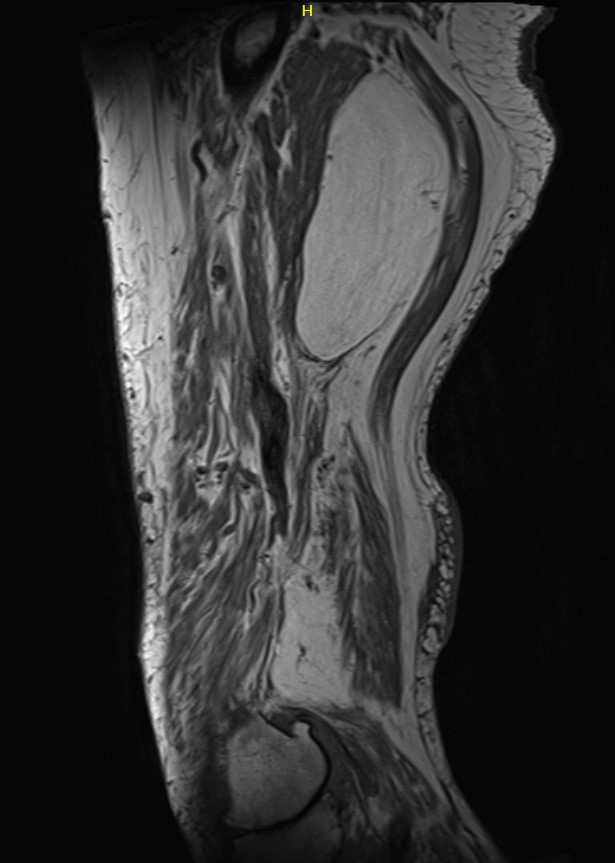
Liposarcoma posterior thigh
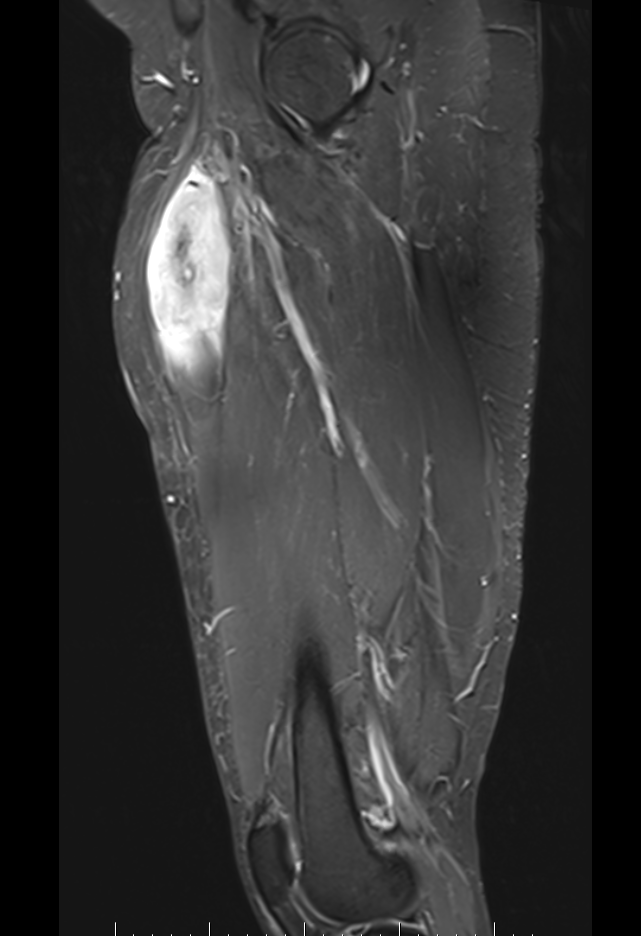
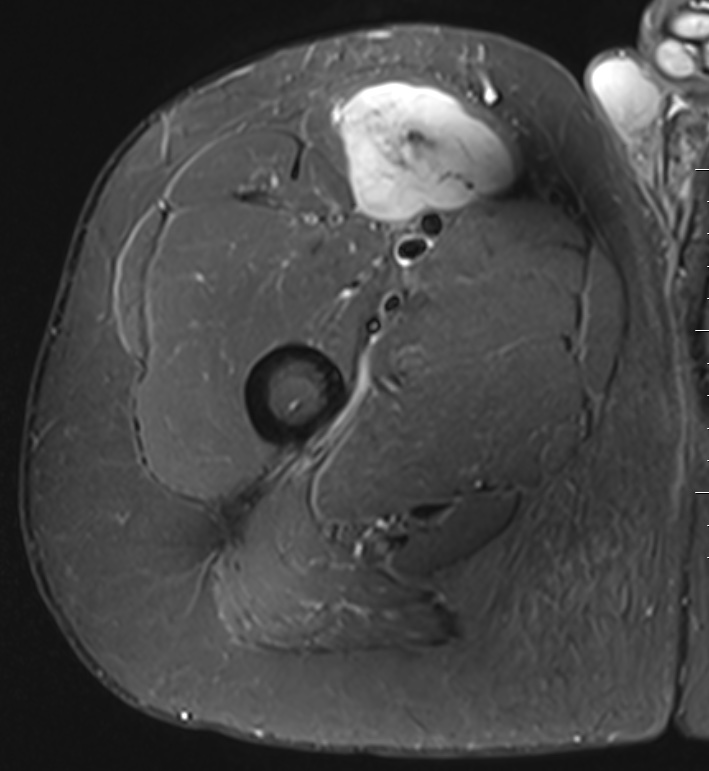
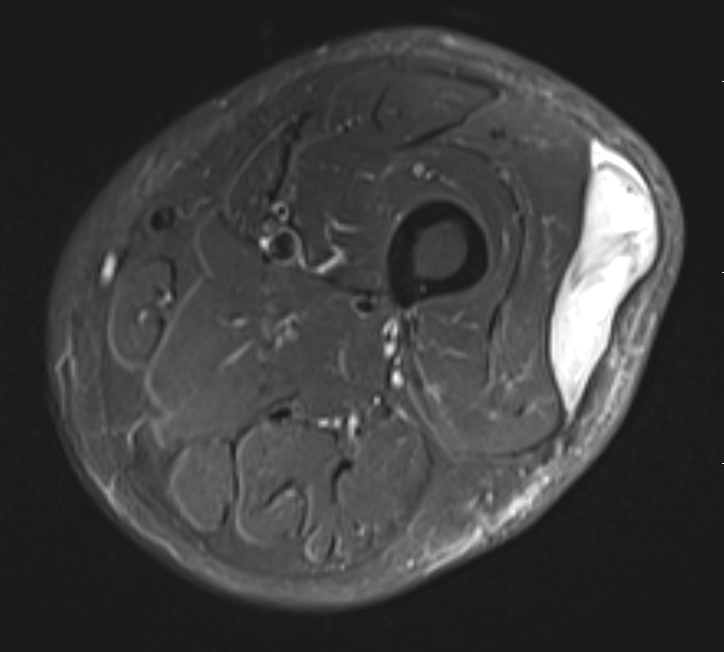
Liposarcoma anterior thigh
Differential diagnosis
Liposarcoma vs Atypical Lipoma
Liposarcoma
- > 5 cm
- rapidly growing
- deep to fascia
- non homogenous on MRI
Lipoma
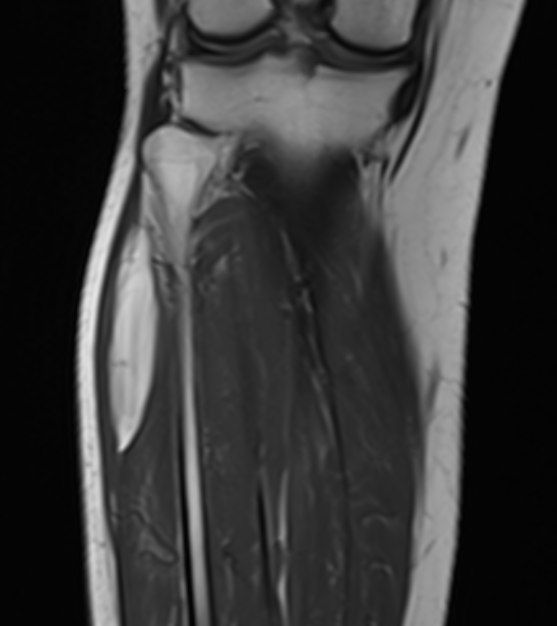
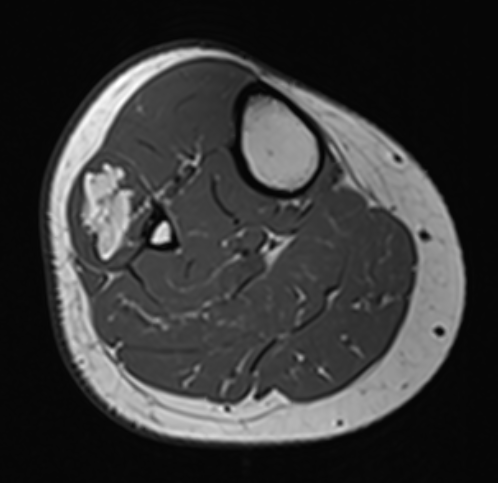
Lipoma tibia
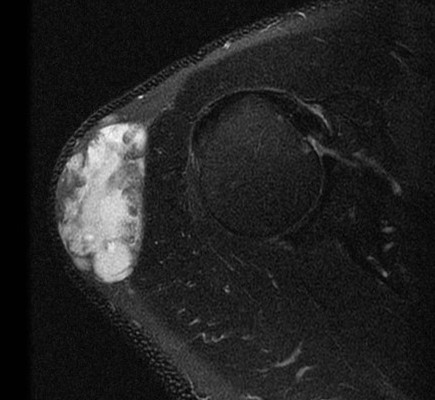
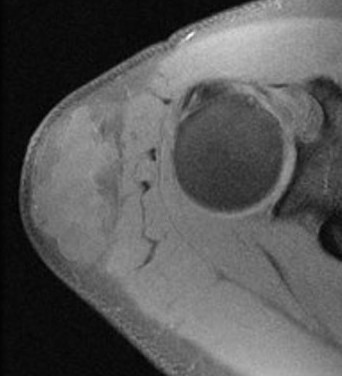
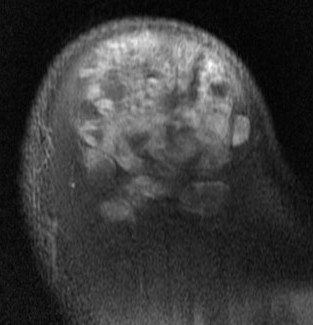
Lipoma shoulder - superficial to fascia
Prognosis
Depends on histological subtype
| Type | Genomics | Local recurrence | Metastasis | Chemo-sensitive | Radio-sensitive | 5 year survival |
| Well differentiated | Amplification oncogenes MDM2, CDK4, and HMGA2 | Low | Low | Low | Moderate | 93% |
| De-differentiated | Amplification oncogenes MDM2, CDK4, and HMGA2 | Moderate | Low | Low | Moderate | 44% |
| Myxoid | translocation of FUS and DDIT3 (CHOP) genes | Low | Low | High | High | 90% |
| Round | Translocation of FUS and DDIT3 (CHOP) genes | Moderate | High | High | High | 60% |
| Pleomorphic | Loss of tumor suppressors p53 and Rb | Moderate | High | High | Moderate | 50% |
Management
Primary disease
- Wide resection
- Neo-adjuvant treatment (XRT/Chemo) not indicated in primary disease
- De-differentiated liposarcoma is typically contained within lipoma, hence a positive fat margin can be accepted as long as not the malignant component
Metastatic disease
- Consider chemotherapy +/- XRT
Surveillance
- CXR + whole body STIR MRI
