Epidemiology
Aggressive malignancy with high recurrence and metastatic potential
5 - 10% sarcoma
Occurs younger
- peak age 3rd-4th decade
- same age group as other synovial pathology (primary synovial chondromatosis and PVNS)
- 2nd most common in children after rhabdomyosarcoma
Characteristic translocation in >95% cases - t(X:18)
Location
Occur near to but rarely within joint
- extremities particularly around the knee
- most common sarcoma of the foot
Can be slow growing compared to other sarcomas
X-ray
May have calcification
Differential soft tissue lump with calcification
Soft tissue sarcoma
Benign soft tissue tumour - hemangioma / AVM
Myositis Ossification
MRI
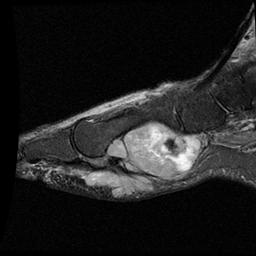
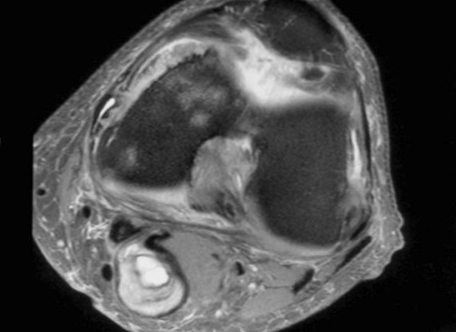
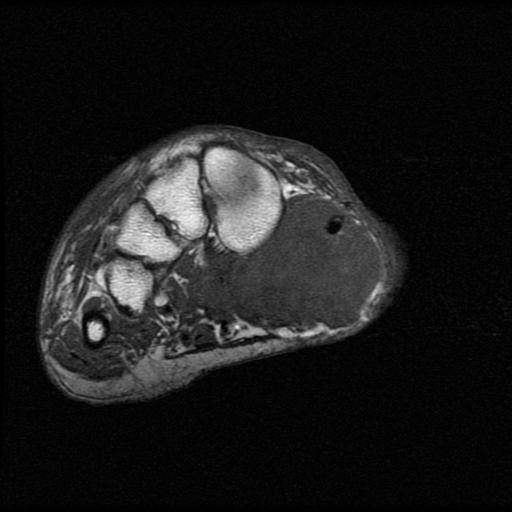
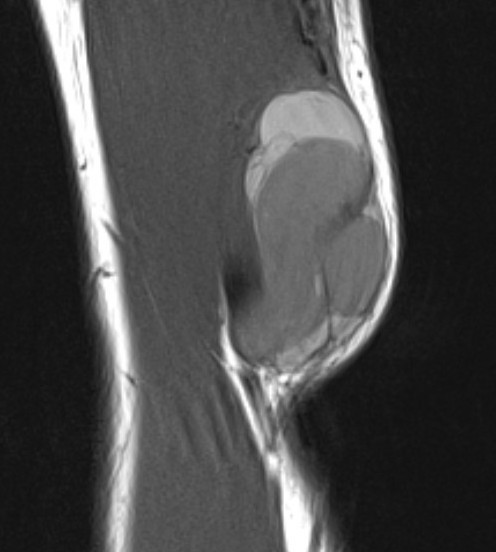
Heterogenous mass, low signal intensity T1, high signal intensity T2
- may have characteristic triple signal intensity
- area hyperintensity, isointensity and hypointensity
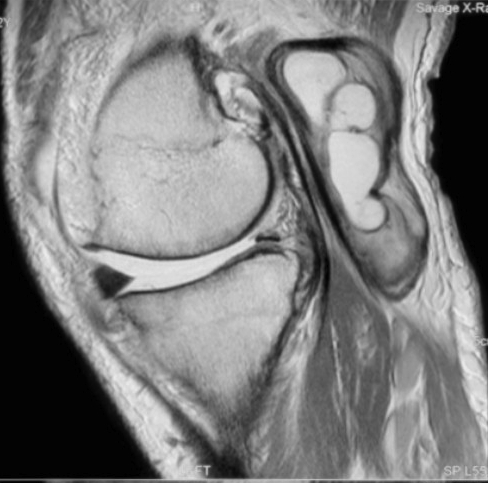
Knee
Heterogenous mass, not communicating with joint
DDx Baker's cyst
- semimembranosus
- communicates with joint
- between semimebranosus tendon and medial head gastrocnemius

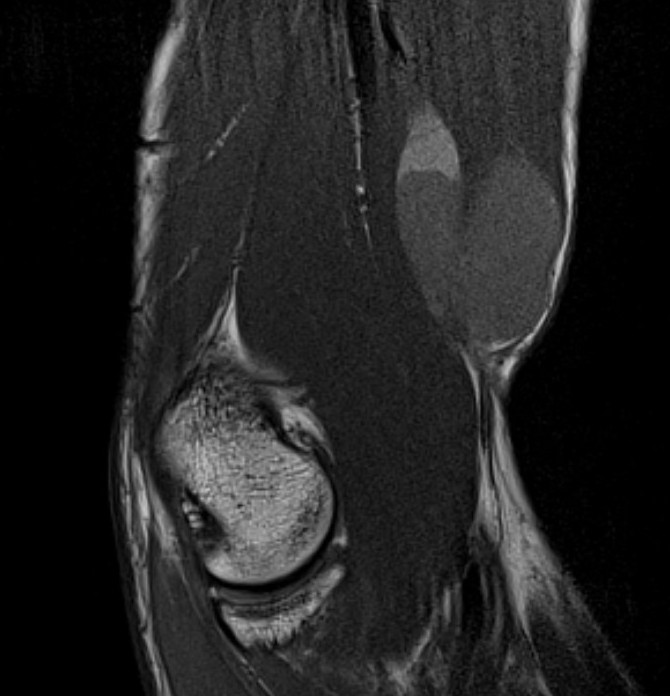
Foot

Elbow

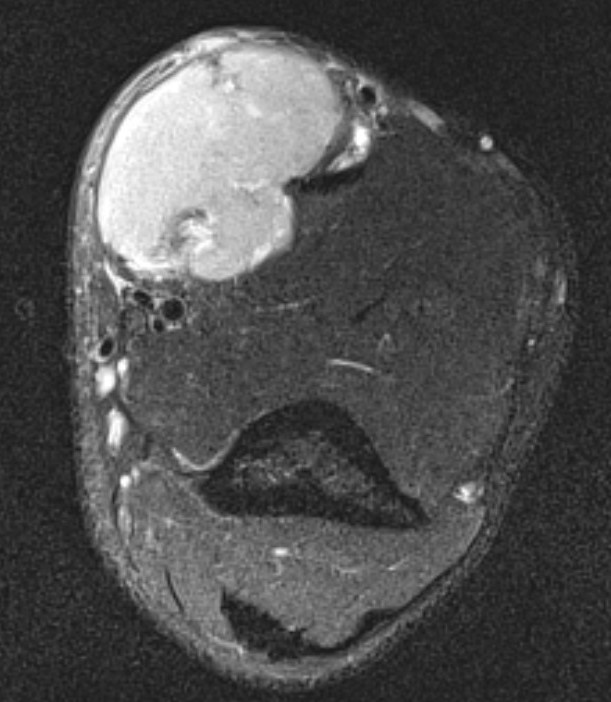
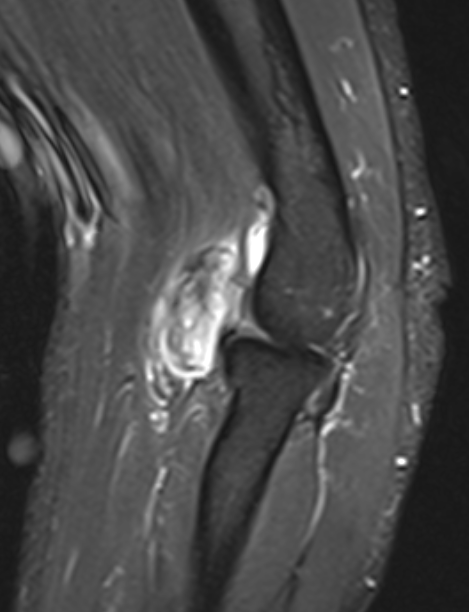
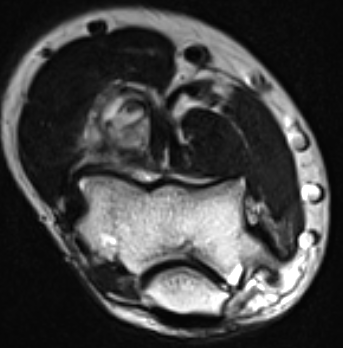
Buttock
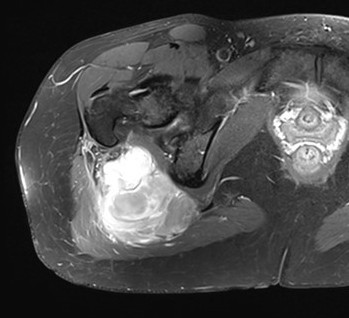
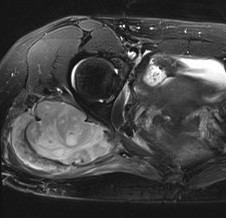
Management
Up to 50% present after unplanned excision
Wide resection + radiotherapy
Chemotherapy
- of benefit in children
- may be of benefit in adults
Prognosis
- 1268 cases of synovial sarcoma
- 5 year survival for adults 62%
- 5 year survival for children 83%
