pathology
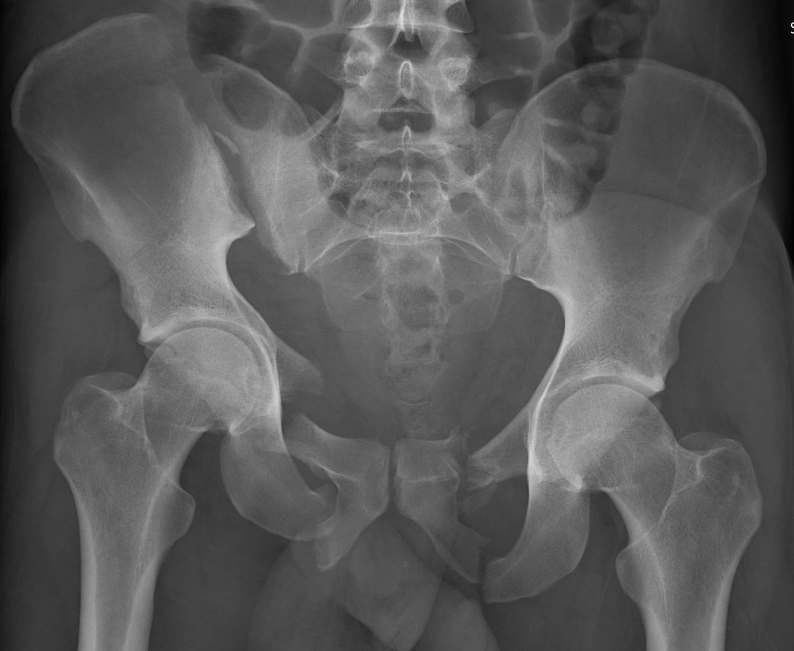
Vertical Shear
Definition
Unstable injuries
Complete disruption of both the anterior and posterior ring
5 - 20% of pelvic fractures
Mechanism
Axial load
Motor vehicle accident
Fall from height
Pathology
Anterior ring
Osteoblastoma
Epidemiology
Uncommon
< 1% Primary bone tumour
Young boys
- second decade
Location
Similar to OO
Spine 30%
- especially posterior elements
Long bones 35%
Clinical
Back or limb pain
- pain less severe than OO
Sternoclavicular Pathology
Condensing Osteitis
Epidemiology
- seen in women over 40
Xray
- sclerotic and overgrown
CT
Congenital Vertical Talus
Definition
Rockerbottom foot / Persian Slipper Foot
Epidemiology
Uncommon
50% bilateral
Doesn't delay walking
- may present in toddler with callus under talus head
Associations
Congenital anomalies
- CNS disorders
- spina bifida & diastematomyelia ~10%
- arthrogryposis
- neurofibromatosis
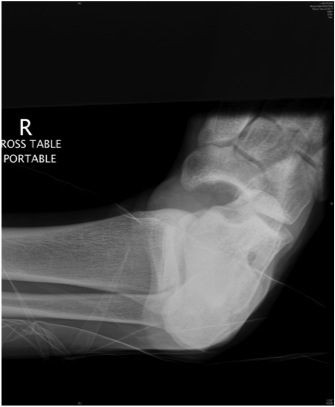
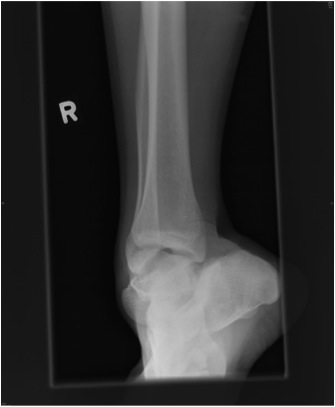
Subtalar Dislocation
Epidemiology
Rare
Types
Medial
- 80%
- calcaneum dislocated medially
Lateral
- 20%
- higher energy injury
Central Cord Syndrome
Epidemiology
Most common pattern cord injury
Hyper-extension injury in middle aged man with osteoarthritic spine
Usually C3/4 and C4/5
Mechanism
Most common type / in older patient with pre-existing spondylosis / OPLL
- hyperextension injury
- compression of the cord
- anteriorly by osteophytes
- posteriorly by infolded ligamentum flavum
Great toe dislocation
Epidemiology
Uncommon
- dancers
- athletes
Aetiology
Hyperdorsiflexion of the MTPJ
Pathology
MT head dislocates plantar
- may buttonhole through capsule
- can prevent closed reduction
Blocks to Reduction
1. Sesamoids
2. Conjoint tendon
3. Intersesamoid Ligament
Flexor Tendon Background
Anatomy
Fascicles of long, spiraling bundles
- tenocytes & Type I collagen
- synovial cells & fibroblasts present
Endotenon
- surrounds the individual collagen bundles
Epitenon
- fine fibrous outer layer, highly cellular, continuous with endotenon
- contains most of the blood vessels & capillaries
Background
Definition 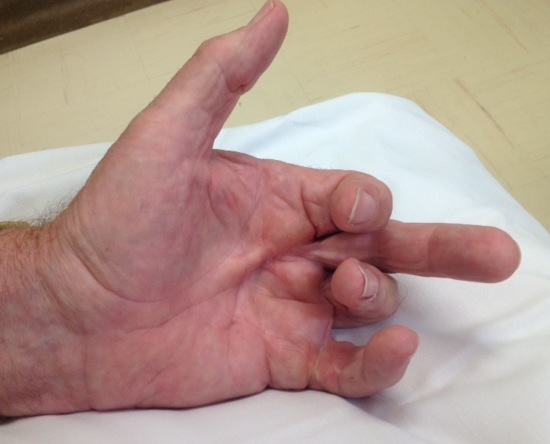
Palmar Fibromatosis
Aetiology
AD with variable penetration
Pathogenesis
Murrell's Theory of Pathogenesis
1. Microvascular ischaemia