Definition
Skeletal disorder characterized by focal abnormalities of bone remodelling
Epidemiology
Incidence
Male > female
Caucasian
van Staa et al J Bone Miner Res 2002
- England database of 5 million patients
- 2500 patients with Paget's (0.3%)
- increasingly common with age
- increased incidence of back pain, OA, THA, TKA, fracture, hearing loss
- incidence sarcoma 0.3%
Declining prevalence
Poor et al J Bone Miner Res 2002
- reducing prevalence of Paget's disease in Britain over time
Etiology
Genetic factors
- family history / AD with incomplete penetrance
- genetic mutations lead to inability to bind ubiquitin, which activates osteoclasts
Environmental factors
- ? slow virus infection
- Paramyxovirus - measles / RSV
Pathophysiology
Primary abnormality
- intense focal resorption of normal bone by abnormal osteoclasts
- osteoclasts large, very active, numerous with excess nuclei
Response
- osteoblasts recruited and activity very rapid
- newly formed bone is not organized and remains irregular and woven in nature
- prone to deformity and fracture, especially in weight bearing extremities
3 phases
1. Initial short lived resorption phase
- burst of multinucleate osteoclastic activity / marked elevation of serum alkaline phosphatase
2. Mixed phase
- both osteoclastic and osteoblastic activity with structurally abnormal bone
3. Final sclerotic phase
- bone formation exceeds bone resorption
Site
Polyostotic 65% / Monostotic 35%
Location - pelvis (70%), spine (50%), femur, tibia, and skull
Xray
Findings
- mixed lysis and sclerosis
- cortical thickening
- bone expansion and deformity
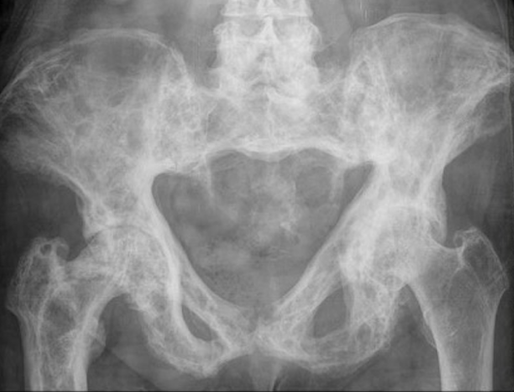
Pelvis
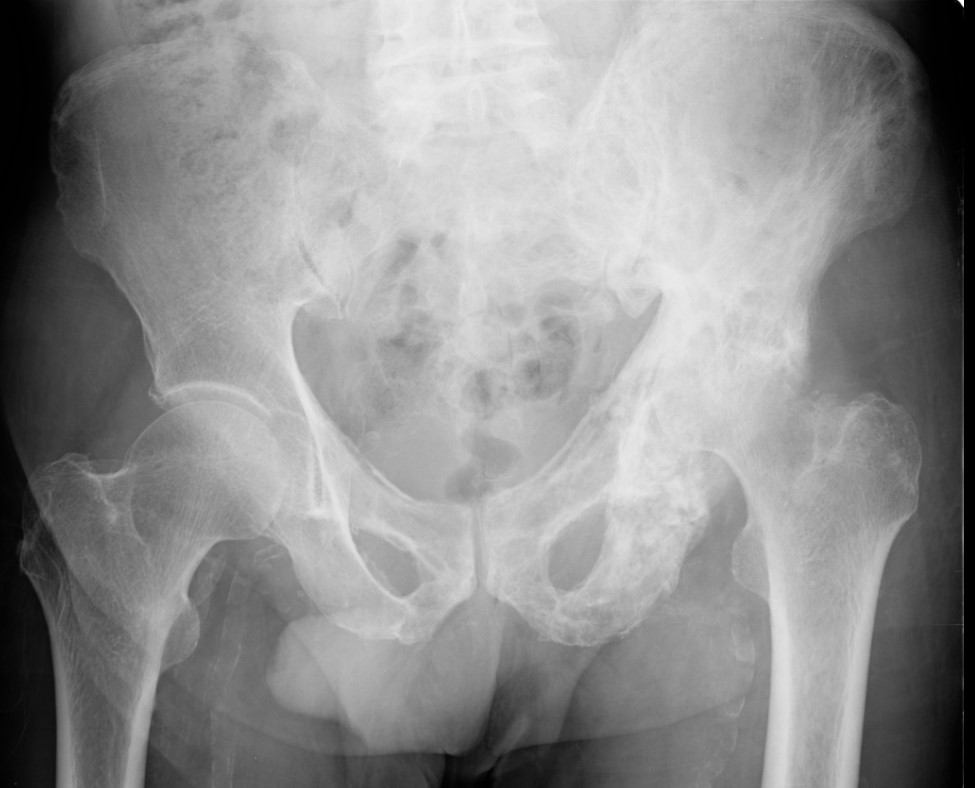

Coxa vara / protrusio / OA
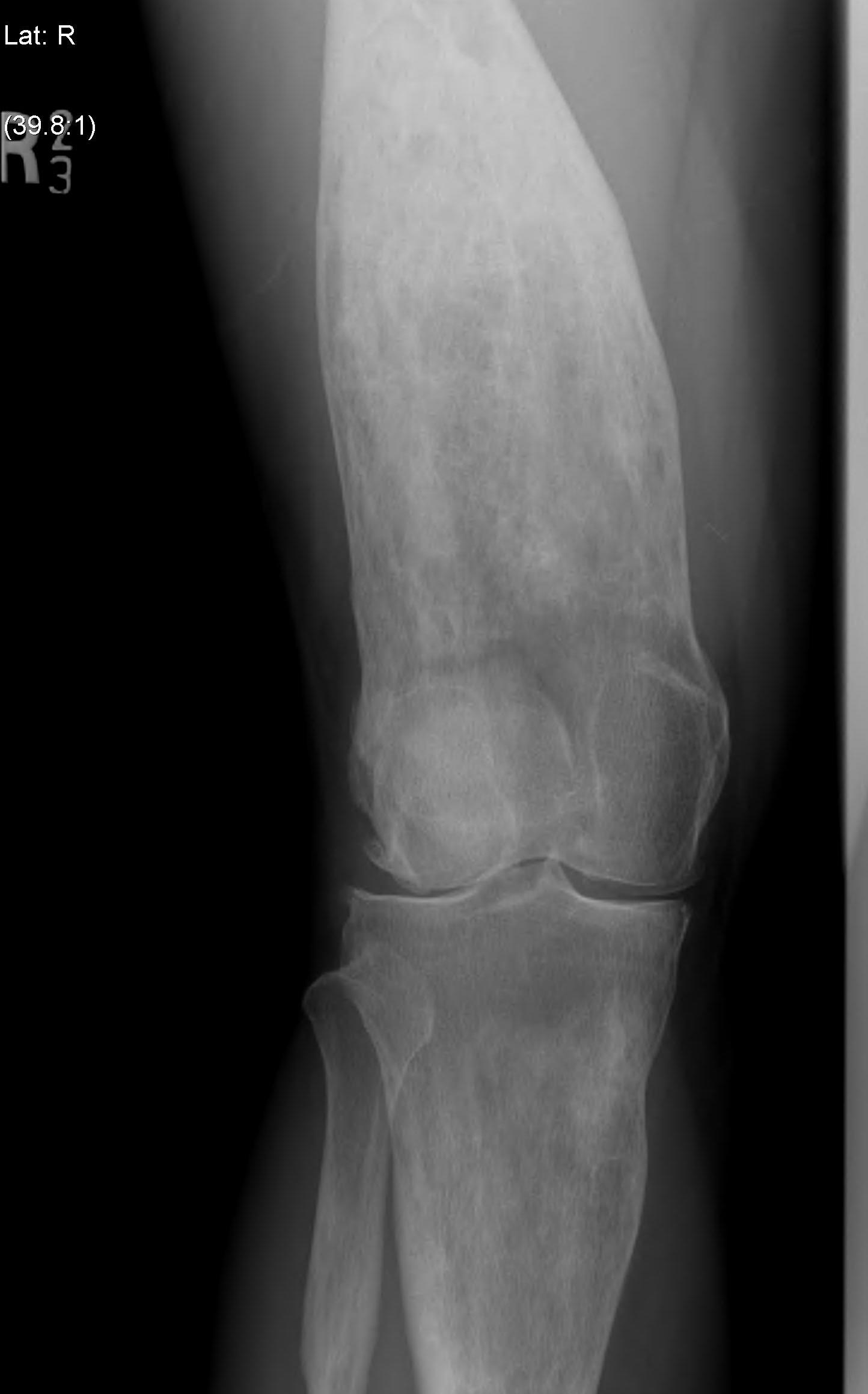
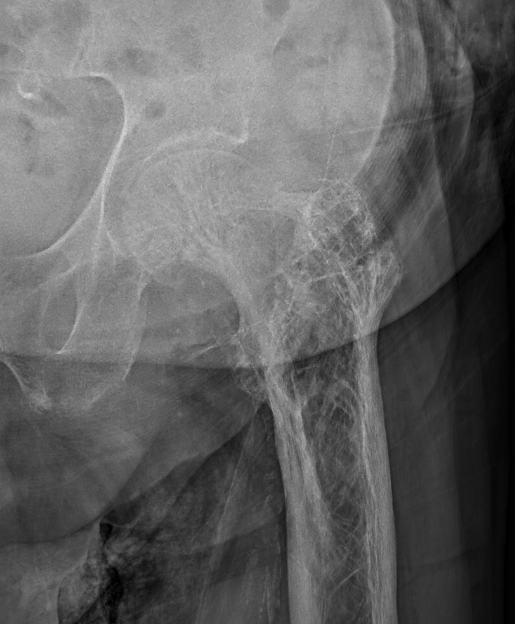
Femur

Tibia
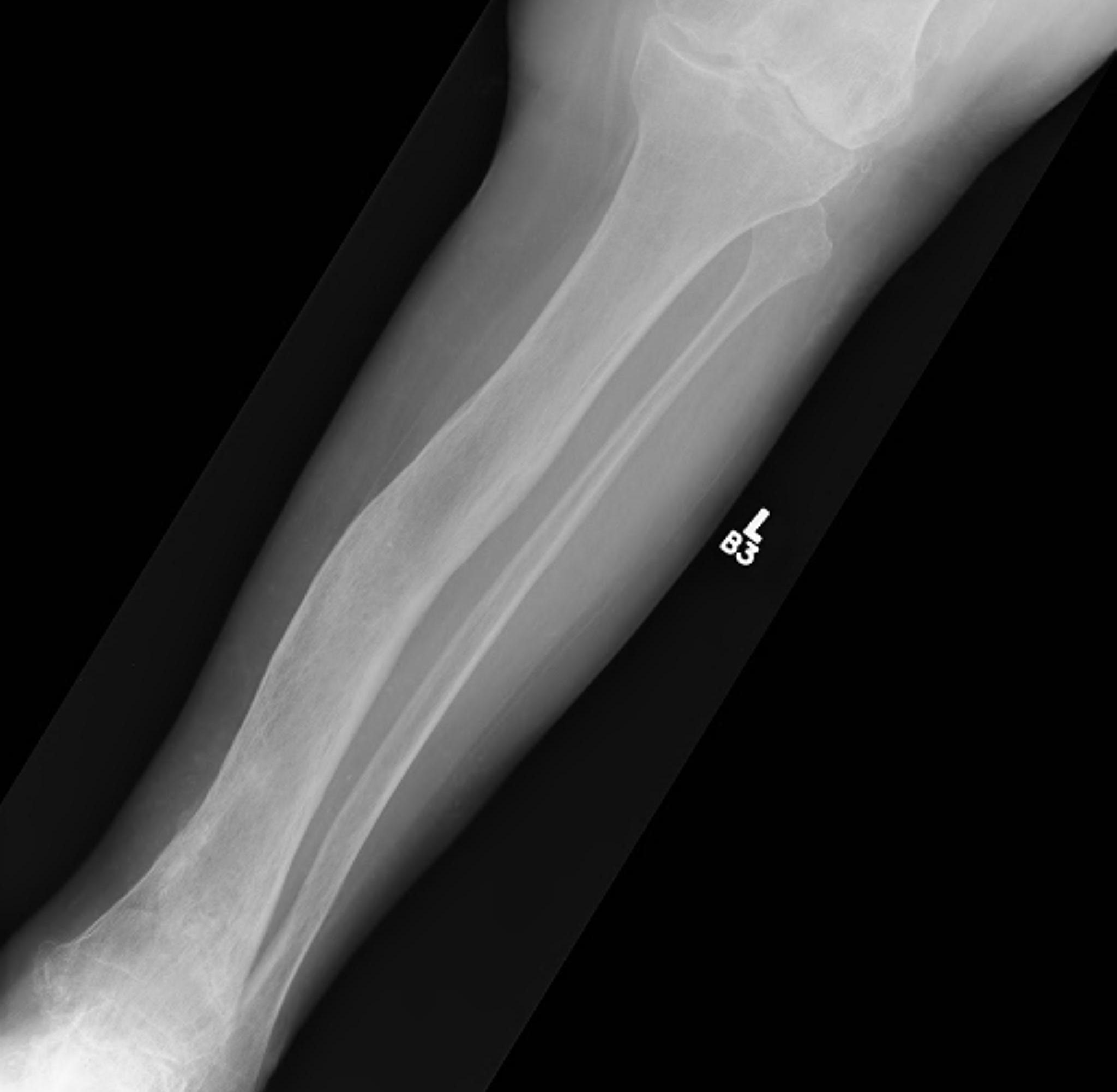
Tibia deformity - sabre tibia
Lumbosacral spine
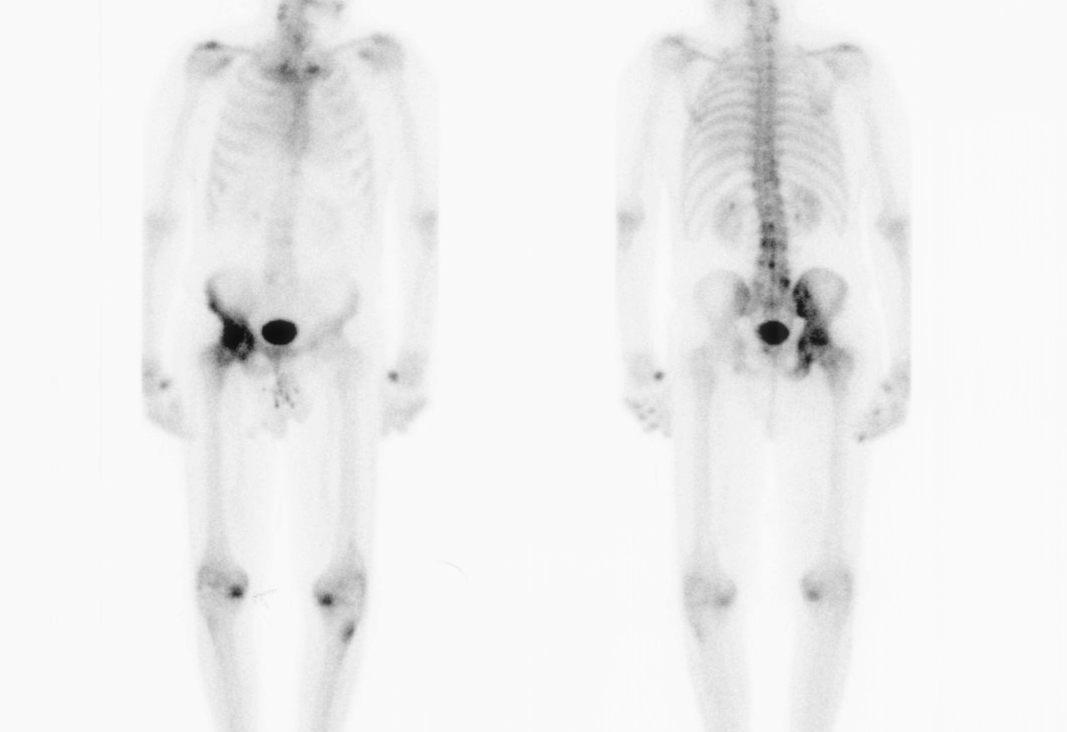
Bone scan
Shows increased uptake / will only detect active disease
Biochemistry
Diagnosis - urinary hydroxyproline levels
Serum alkaline phosphatase - good indicator of activity
Calcium - may be elevated after bed rest
ESR - may be elevated in malignant transformation
Histology
Biopsy - rarely needed and predisposes to fracture
Histology
- poorly organised lamellar bone
- multinucleated osteoclasts
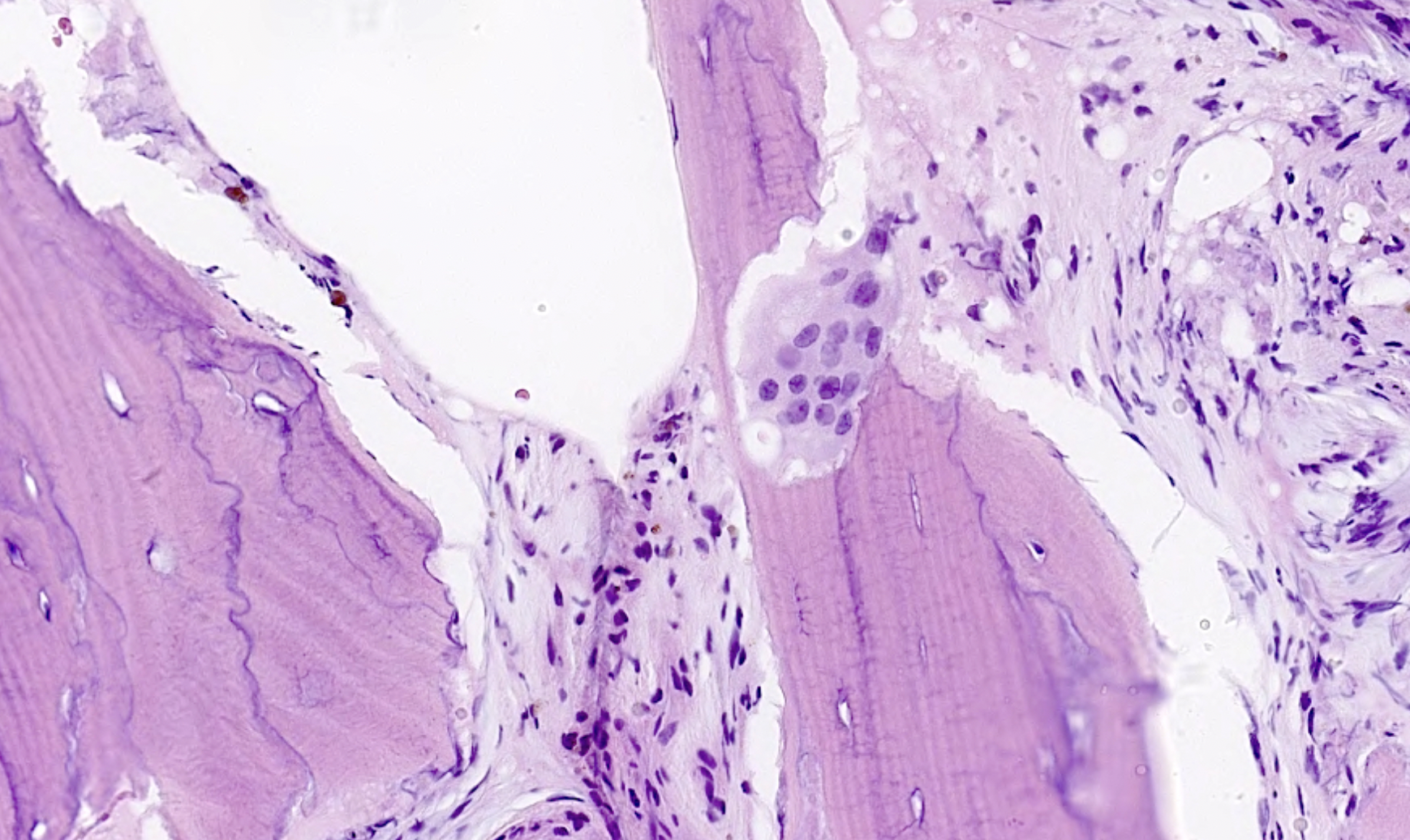
https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bonepagets.html
Clinical Presentation
Usually incidental finding on x-ray or elevated alk phosphatase
Tan et al Calcif Tissue Int 2014
- systematic review
- bone pain most common presentation 52%
- bone deformity 23%
- fracture 9%
- deafness 9%
Issues
Bone deformity and fractures
Hip osteoarthritis with coxa vara and protrusio
Leonine skull - deafness / cranial nerve palsy
Spinal cord compression
Sarcomatous transformation 0.3%
Management
Bisphosphonates
Indication
Bone pain
Results
Corral-Gudino et al Cochrance Database 2017
- 20 studies and 3200 patients
- good evidence that bisphosphonates reduce bone pain
Langston et al J Bone Miner Res 2010
- RCT of bisphosphonate in 1324 patients with Paget's
- 3 year follow up
- no difference in hearing / fractures / need for orthopedic surgery
Surgical issues
Bleeding
- hypervascular bone
- pre-operative medication indicated if possible
Medical
- systematic review of THA and TKA in Pagets
- 19 articles and 10,000 patients
- mortality 30% at 8 years
- increased medical complications
Hard bone
Parvizi et al PMR Summary article surgical management Pagets
Fracture
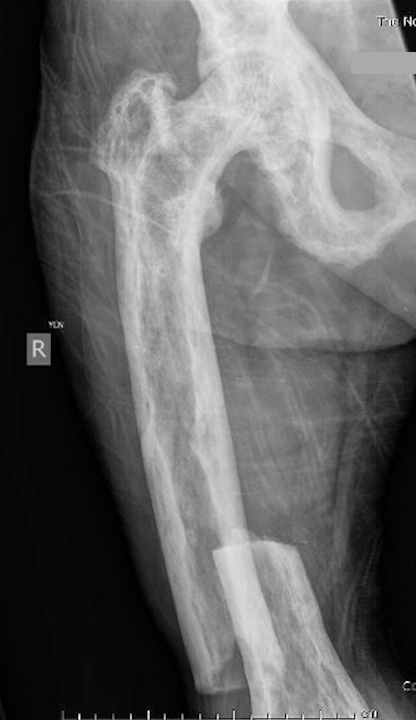
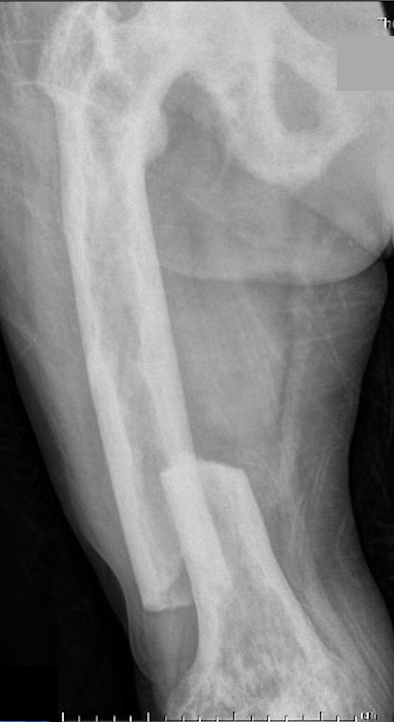
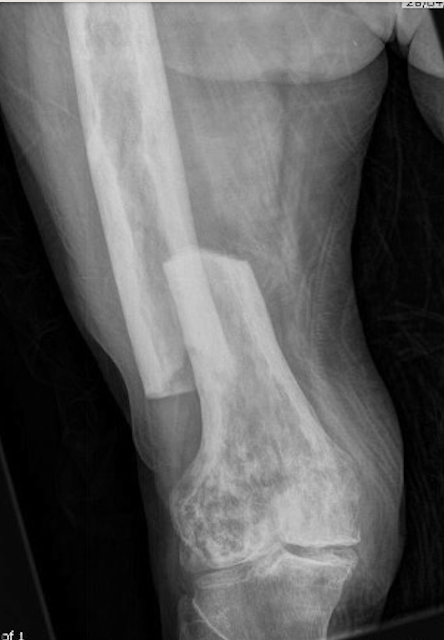
Issues
Paget's fractures likely have normal healing capacity
Hard bone - difficult entry points
Bleeding
Deformity - may require osteotomy prior to IM nails
THA
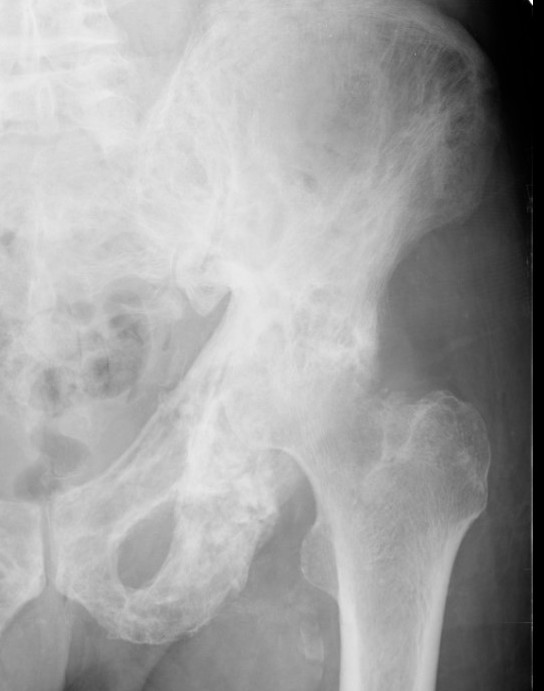
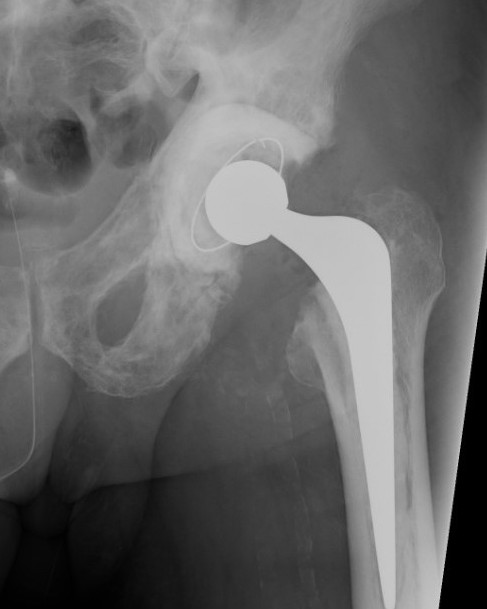
Technical issues
Bleeding
- preoperative calcitonin / bisphosphonates / EPO / Iron
- intra-operative blood salvage system
Acetabulum
- difficult reaming due to hard bone
- protrusio - consider medial bone graft / cages / lateral offset liners
- limited ability for cement interdigitation - uncemented cups may be preferrred
Femur
- coxa vara - risk varus femoral implants
- difficulty broaching femur - may need burrs
- femoral bowing - may need osteotomy
- poor cement interdigitation - uncemented stems may be preferred
- brittle bone - increased risk fracture
Heterotopic ossification
- high risk
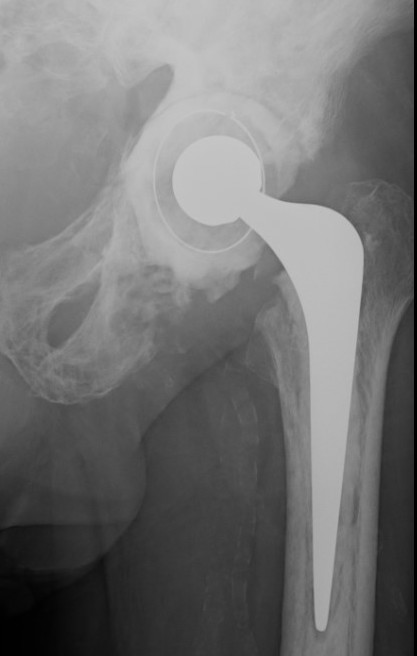
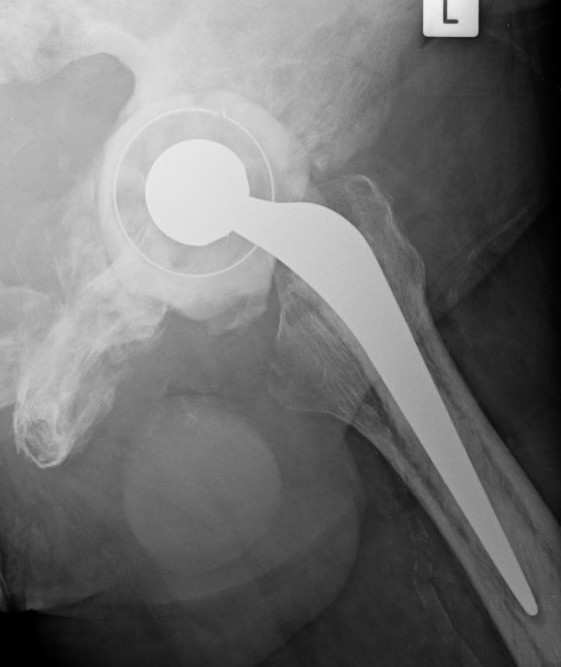
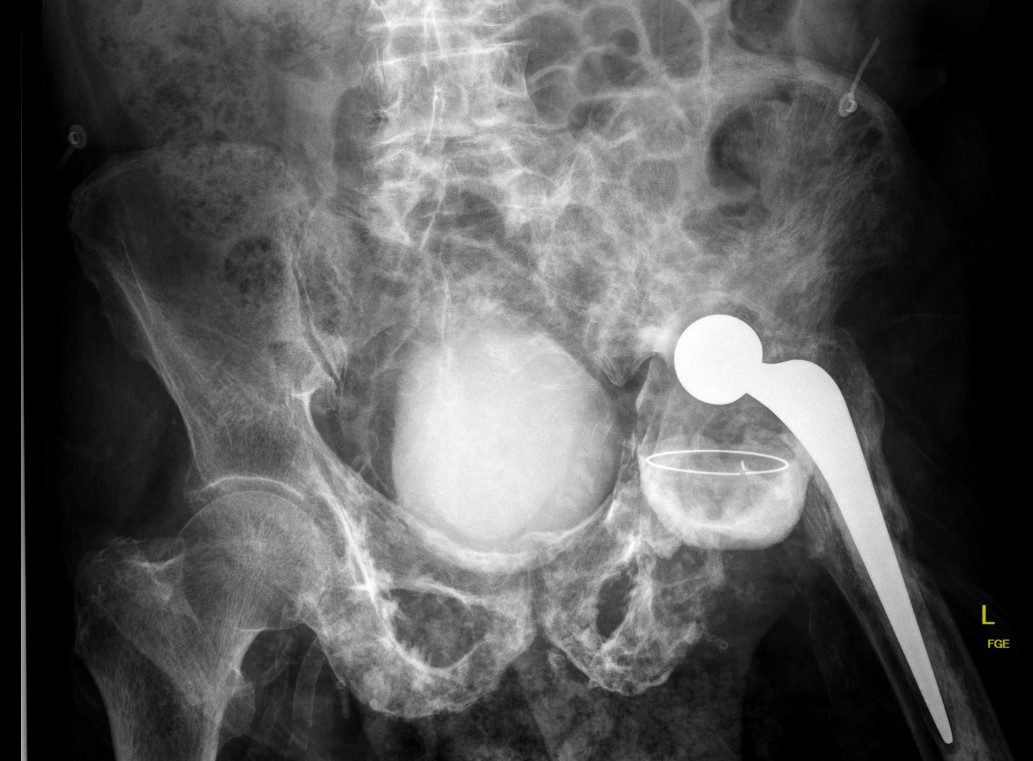
Progression of disease and loosening of cemented acetabular component
Results
Martino et al J Orthop Traumatol 2021
- 66 registry patients with Paget's undergoing THA: 10 year survival 90%
- 29 institution THA
- 50% HO, 14% varus stems, high transfusion rates
- systematic review of THA and TKA in Pagets
- 19 articles and 10,000 patients
- mortality 30% at 8 years
- revision rate 4% at 7 years
TKA


Technical issues
Exposure difficult
- patella enlarged
- risk patella tendon avulsion
Bone very hard and deformed (tibial and femoral bowing)
- difficulties with IM and EM jigs
- navigation may be advantageous
Enlarged bones
- difficult releases
- may need different femoral and tibial components
Results
- systematic review of THA and TKA in Pagets
- 19 articles and 10,000 patients
- mortality 30% at 8 years
- revision rate 2% at 7 years
Popat et al World J Orthop 2018
- 4 studies with 54 patients
- multiple intra-operative challenges: Malalignment, bone loss, soft tissue contractures
- 5% rate of patella tendon avulsion
Lumbar spine
Pathology
Lumbar (60%) / thoracic (45%) / cervical (14%)
Bony overgrowth
- foraminal compression - radiculopathy
- canal compression - spinal stenosis
Compression fractures
Xray
Sclerotic / Ivory vertebrae
- DDx: metastasis, lymphoma
Symptoms
Back pain
- Paget's
- degenerative changes
- fractures
- malignant transformation
Stenosis (33%)
Neural compression
Management
Calcitonin / bisphosphonates mainstay
Jorge-Mora Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 2016
- systematic review of 17%
- neurological decompression +/- fusion
- 44% major bleeding complication
Malignant Transformation
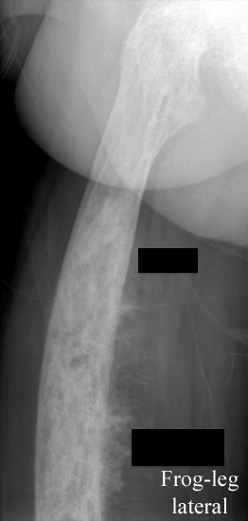
Results
- 26 patients with bone sarcoma arising from Paget's
- surgery +/- radiotherapy +/- chemotherapy
- 22/26 died at mean of 20 months
