Epidemiology
1/3 caucasian women > 64
Risk Factors
Insufficient bone mass at time of skeletal maturity
- peak bone mass is achieved at age 25
Rapid loss of bone after menopause
Low body weight / weight loss / history of smoking / steroids
Primary
Type 1
- postmenopausal
- high turnover / osteoclast mediated
- F x 6
Type 2
- age-related / senile
- low turnover / osteoblast mediated
- F x 2
Can have both
Secondary
DDD NICE
Disuse
- prolonged bed rest
- inactivity
- paralysis
- space travel
Diet
- low calcium, insufficient vitamin C
- anorexia nervosa
Drugs
- heparin
- methotrexate
- ethanol
- steroids
Neoplasms
- metastatic disease
- myeloma / lymphoma / leukemia
Idiopathic
- adolescent (10-18 years)
- middle-age men
Chronic Illness
- RA / cirrhosis / sarcoidosis
Endocrine Abnormalities
- DM
- pituitary hypersecretion
- adrenal cortex excess
- ovary- oestrogen deficiency
- testis - testosterone deficiency
- hyperparathyroidism
- hyperthyroidism
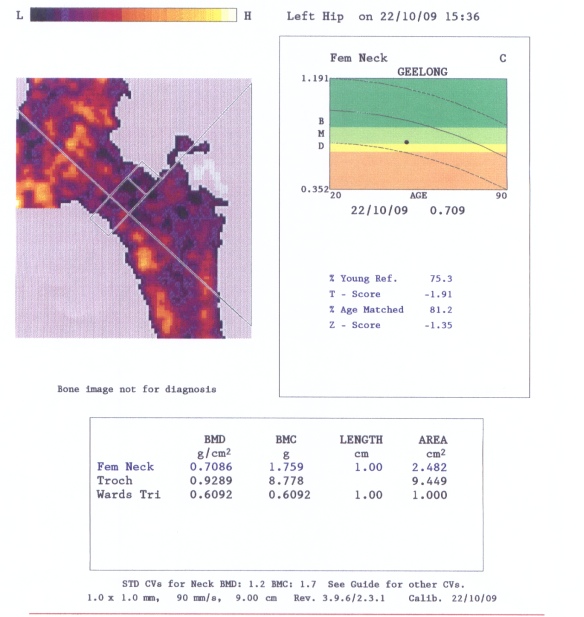
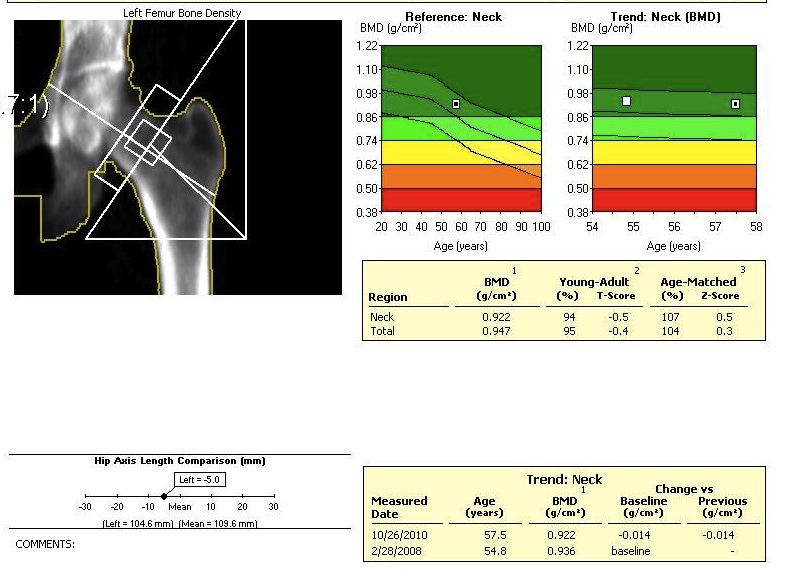
DEXA Screening
Definition
Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry
- hip and spine
Method
Compare bone mass values
- to ideal peak bone mass in pool of peers / young people
False negatives
- osteophytes in hip or spine
Grading
Within 1 SD of ideal
- normal
1 – 2.5 SD below ideal
- osteopenic
>2.5
- osteporotic
> 2.5 + fragility fracture
- severe, established osteoporosis
Scores
T score
- SD below young adult at peak bone density
Z score
- SD below average person of same age
Investigation
Exclude secondary causes
Neoplasm
- multiple myeloma (se electrophoresis)
Endocrine
- hyperparathyroidism (Ca, PO4, PTH)
- hyperthyroidism (TFT, T3, T4)
- Cushing’s / CRF (U&E)
- DM (glucose)
- osteomalacia (low Ca, Vit D)
- FSH / LH / T
Issues
Wrist fractures
Hip fractures
Vertebral fractures
Sacral insufficiency fractures
Management
Premenopausal
Adequate calcium and vit D
Adequate weight
Exercise
No smoking
Post menopausal
Calcium Carbonate
Basis
Quite often have inadequate calcium intake
- need 1500 mg / day
- patents develop osteomalacia with secondary hyperparathyroidism
Effect
Reduces rate of bone loss
- very cost effective
- supplement with vit D
Vitamin D
Physiology
- 25 hydroxy Vitamin D ingested
- alpha-hydroxylation in kidney to 1,25
- 1,25 dihyroxy D is active form
- enhances absorption of GIT calcium
Treatment
Calcitriol (1,25 dihyroxy Vit D)
Effect
Salovaara et al J Bone Mineral Research
- RCT of vit D3 and calcium v placebo in 3500 women > 60
- 3 year follow up
- reduced distal forearm fractures by 30%
- no effect on incidence lower limb fractures
Estrogen
Method
Osteoblasts have receptors for estrogen
Menopause
- skeletal bone loss increases 2% per year
- 8% cancellous
- 0.5% cortical
Results
PEARL trial of Lasofoxifene in postmenopausal women
- reduced risk of CAD and CVA
- reduced risk of breast cancer
- increased risk of thromboembolic events
Cummings et al N Eng J Med 2010
- RCT of 8550 women lasofoxifene v placebo
- significantly improved BMD
- reduced rates of vertebral and non vertebral fracture
- reduced rates breast cancer, CVA and MI
Calcitonin
Action
- binds to osteoclast
- decreases their number and activity
Administration
- nasal spray
Problems
- 22% people develop resistance
Effects
Kaskani et al Clin Rheumatol 2005
- RCT of calcitonin v vit D3
- calcitonin increased BMD at 1 year
Tascioglu et al Rheumatol Int 2005
- RCT of calcitonin v aledronate
- aledronate significantly better improvements in BMD
Bisphosphonates
Action
Pyrophosphate analogs
- bind to surface HA crystals
- inhibit osteoclast resorption
Indications
Low energy fracture
T score > 2.5 below
Side effects
Indigestion 30%
Occasional diarrhea
Bone pain (remedy by giving calcium at same time)
Very rarely jaw necrosis at high doses IV
Etidronate
- increases risk GI ulceration and bleeding
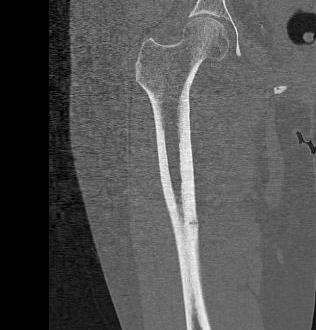
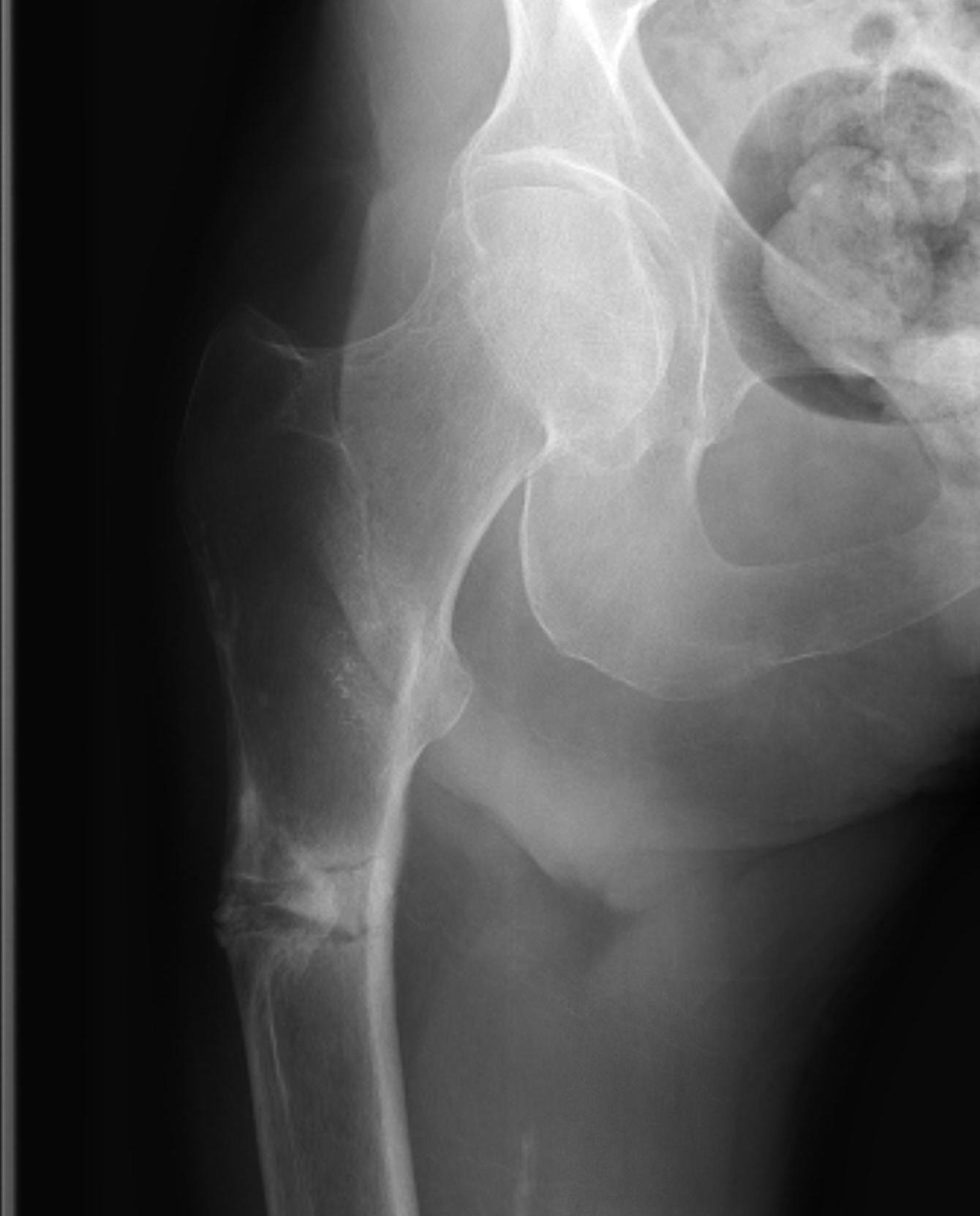
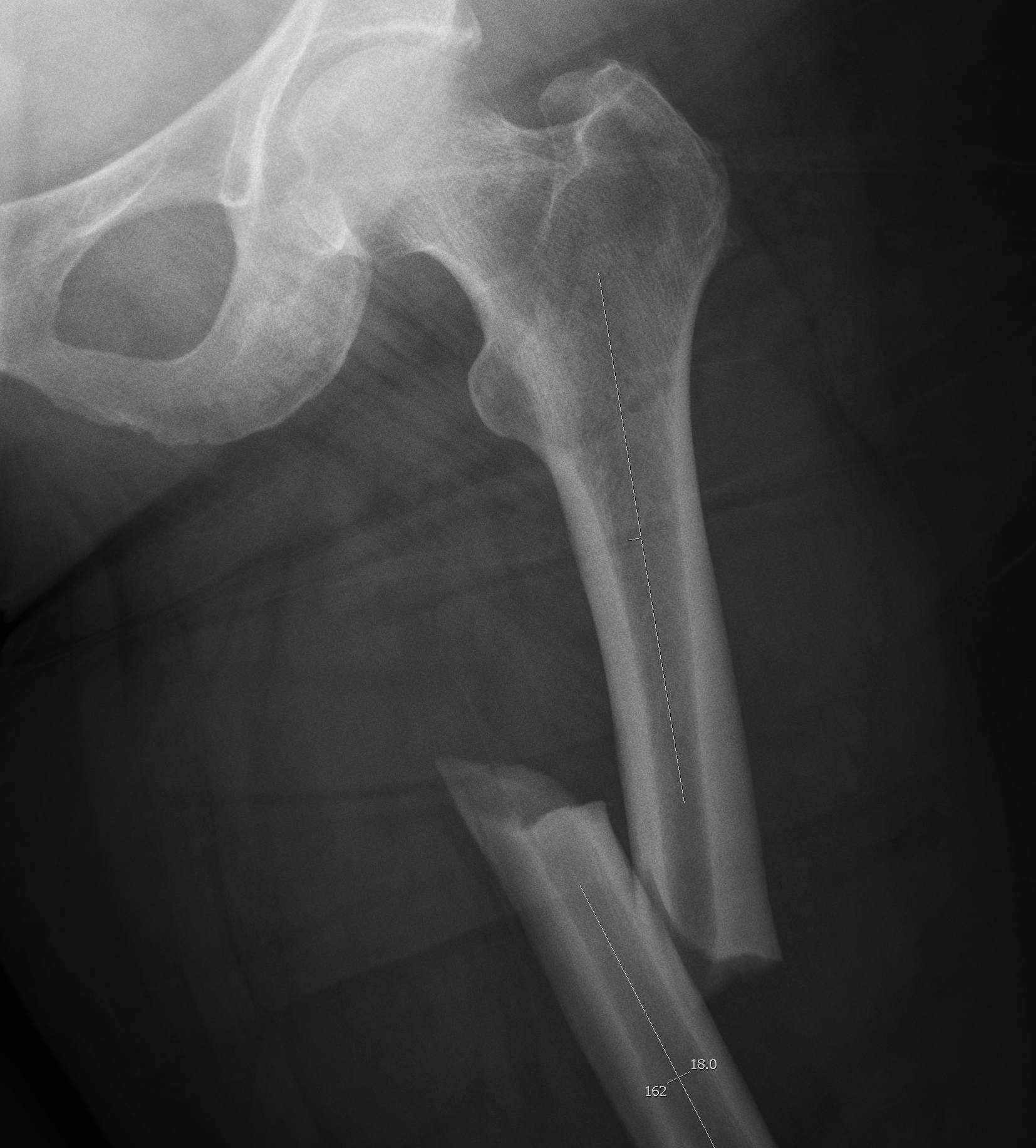
Atypical femoral fracture related to bisphosphonates
- reports of atraumatic bilateral femoral fracture
- seen in women taking bisphosphonates for more than 5 years
- insufficiency fracture
- characterised by short oblique subtrochanteric and diaphyseal fractures
- typically see lateral cortical thickening / sclerosis / beaking before the fracture
- must check contralateral femur if have a fracture
- xray any patient complaining of thigh pain
- recommend drug holidays to prevent this complication
Doses
Aledronate / fosamax 70 mg weekly
- must take on empty stomach, with no food for one hour
IV risedronate
- take only once per year
Results
Harris et al JAMA 1999
- RCT of oral risedronate v placebo 2500 women with history vertebral fracture
- reduced risk of vertebral fracture by 40%
- reduced risk of non vertebral fracture by 40%
- increases BMD at vertebrae by 5%
- prevents loss of BMD at femoral neck