bone scan
March Fracture
Definition
Insufficiency fracture
- secondary to exceeding fatigue threshold
- usually of second or third MT shaft
Epidemiology
Onset of new and very intense / strenuous physical activity
- i.e. new army recruits / dancers
Women with postmenopausal osteoporosis
Association
Cavus feet
History
Paget's Disease
Definition
Chronic, non metabolic bone disorder
Characterised by increased bone resorption, bone formation and remodelling
Epidemiology
Rare < 40
1 – 3 % population over 60
M > F
Aetiology
Unknown
Paramyxovirus implicated
- measles
- RSV
- canine distemper virus
Electron Microscope
Accessory Navicular
Incidence
1 - 2 %
Anatomy
Medial Aspect of foot
- proximal to navicular
- part of T posterior tendon
Usually will fuse with navicular (50%)
Issues
1. Probably not a cause of flat foot
- excising accessory navicular / rerouting / reattaching tibialis posterior
- will not help pes planus
2. Pain
- may fracture
Painful TKR
Differential Diagnosis of the Painful TKA
Surgical Diagnosis
1. Prosthetic loosening and failure
2. Infection
3. Patellofemoral tracking problems
4. Instability
5. Recurrent intra-articular soft-tissue impingement / Component overhang
Nonsurgical Diagnoses
1. Referred pain - Hip / Back
Management
Incidence
Knee > Hip
- superficial position
- limited cover of well vascularised muscle
- watershed area of skin blood supply anterior to the skin incision
- much increased in fully constrained prosthesis
Ideal < 1%
Risk Factors
Increased with
- revision
- prior infection
- RA / Psoriatic arthropathy
- DM
Metastasis with Unknown Origin
Likely Origin / Hexagon / PBBLTK
Thyroid Breast
Background
Aim 
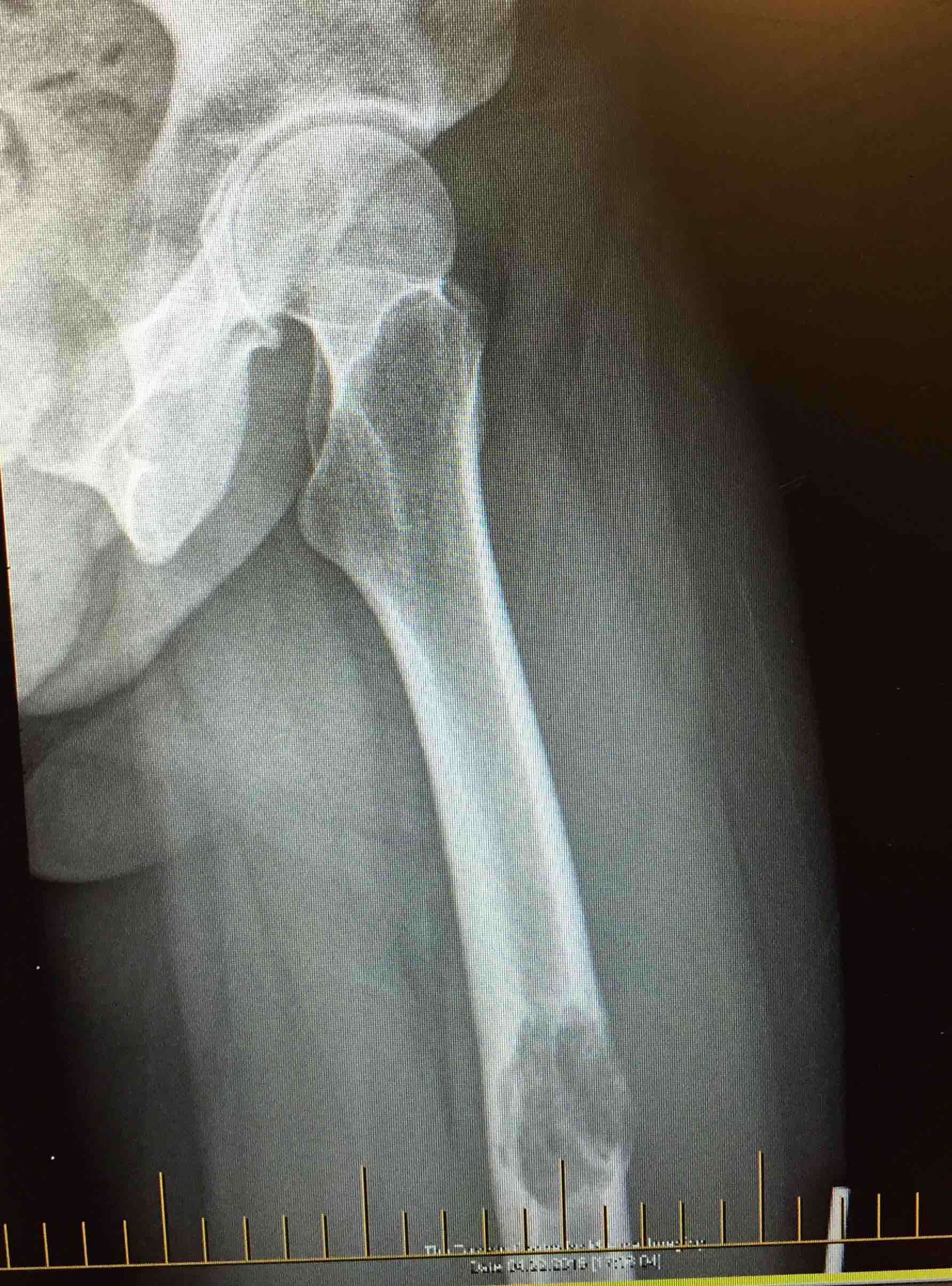
The identification of skeletal metastasis & fixation prior to fracture
Incidence
50% of new cancer cases have metastasis
- 1% have pathological fracture
- increasing with more aggressive palliative care
PVNS
Definition
Pigmented Villo-Nodular Synovitis
- benign inflammatory process that arises in synovial tissues
- contains significant amounts of hemosiderin
Epidemiology
Age: 20 - 50
Sex: M > F
Types
A. Diffuse
- throughout joint synovium
- more difficult to treat / excise fully