Differential Diagnosis of the Painful TKA
Surgical Diagnosis
1. Prosthetic loosening and failure
2. Infection
3. Patellofemoral tracking problems
4. Instability
5. Recurrent intra-articular soft-tissue impingement / Component overhang
Nonsurgical Diagnoses
1. Referred pain - Hip / Back
2. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
3. Bursitis-tendonitis - Pes anserine / patella / popliteal bursitis
4. Persistent crystalline deposition - Gout / pseuodogout
5. Neurovascular problems - Neuropathy / Radiculopathy / Vascular claudication / Thrombophlebitis / DVT
6. Expectation / Result mismatch - Multiply operated knee / Secondary gain issues / Unrealistic expectations
7. Psychiatric disorders and depression
Infection v Loosening
History
Postoperative course
- infection / course of antibiotics / persistent drainage post operatively
Nature of Pain
°Pain-free interval
- indolent infection
- pathology elsewhere (pain same as pre-op)
Pain-free interval
- loosening / infection / implant failure
Mechanical pain
- loosening
Rest pain / night pain
- infection
Start up pain
- loosening
- as implant settles then pain subsides
Examination
Knee painful
Signs infection
Effusion
- able to aspirate
Careful examination of spine / hip / vascular status
Xray
Problems
- may be normal in face of pathology
- can't DDx infection vs loosening on XR
- serial comparison very important
Bone Scan
Problems
- very sensitive, poor specificity
- can have increased vascularity for several months
- 1 year post cemented TKR
- 18 months post uncemented TKR
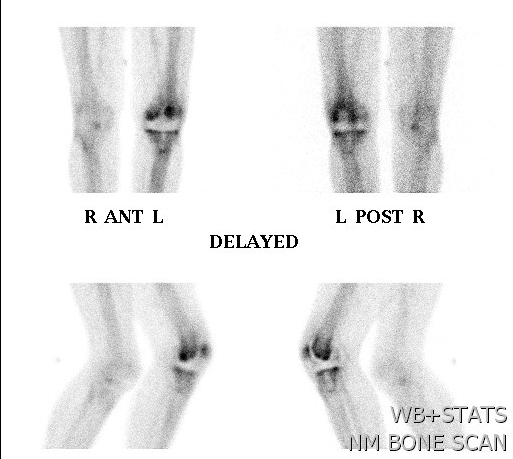
Advantage
- pathology unlikely if negative
Infection
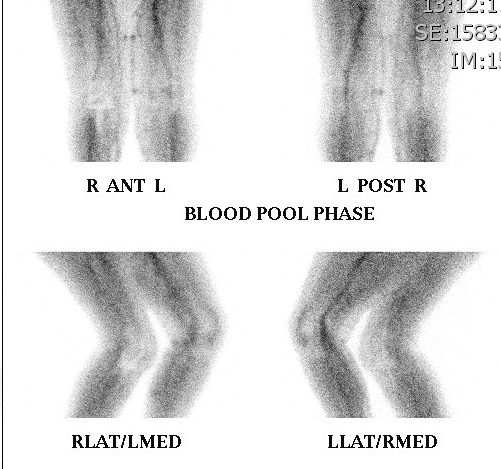
- diffuse uptake all 3 phases (blood flow, early and delayed bone phase)
Loosening
- focal uptake unless whole prosthesis loose
- nil increase on blood flow or blood pool
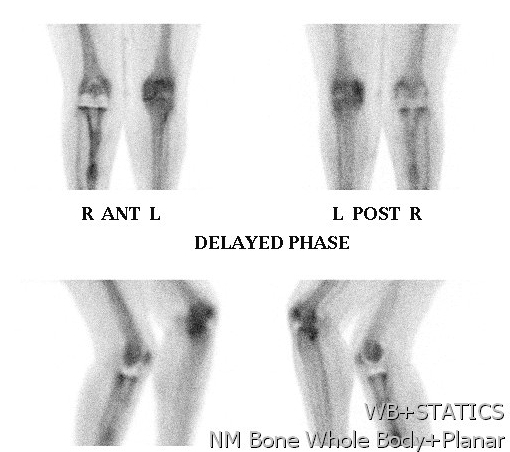
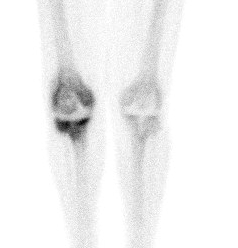
Also diagnose
- stress Fractures
- RSD
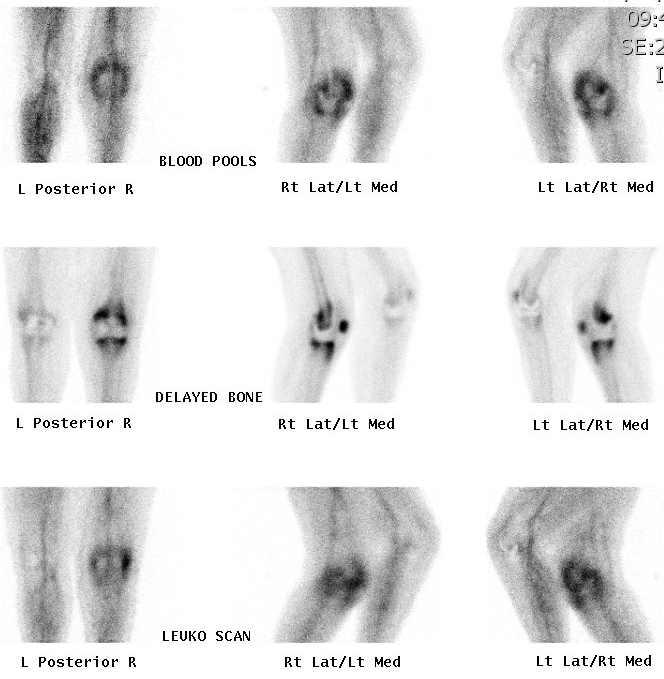
Technetium Labelled White Cell Scan
Uncertain role
- expensive, difficult to perform
- have to harvest WC, label with technicium
- alone not superior, use in conjunction with bone scan
- increase sensitivity if increase on bone phase in WC and bone scan
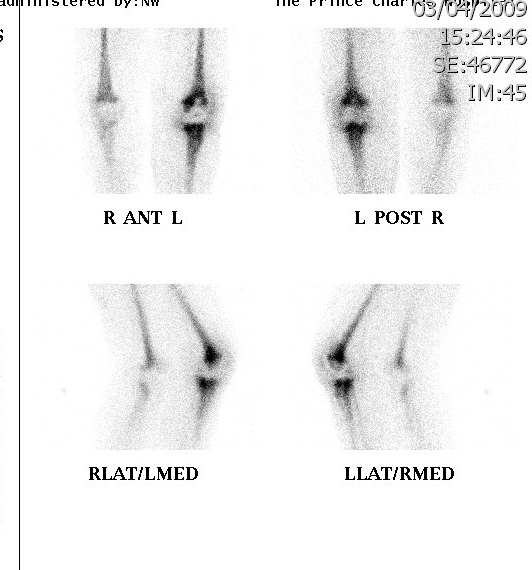
Van Acker et al Eur J Nuc Med 2001
- WCC 100% sensitive but 53% specific in infected TKR
Bloods
WCC
Little value
- increased in 15%
- raised only if very septic
ESR
> 30 mm
- 80% sensitivity & specific
Problem
- raised post operatively for up to 12 months
- remote pathology can elevate
- permanently raised in RA
- can be raised in aseptic loosening
CRP
> 10 mg/l
- 90% sensitive & specific
- negative predictive value 99%
Advantage
- more predictable response post OT
- peak at day 2 (~400), normal after 3 weeks
- rarely increased with loosening
Aspiration
Technique
- no antibiotics > 4 weeks
- no LA (bacteriostatic)
- if only 1 specimum positive then repeat
> 65% white cells very high risk for infection
> 1700 white cells per microlitre
Intra-Operative Frozen Section
PMN Cell Count per HPF / average over 10
> 5 per hpf
- 84% sensitive
- 96% specific
> 10 per hpf
- 84% sensitive
- 99% specific
Intraoperative gram stain & M/C/S
Sensitivity < 20%, but very specific
- 10% false positive
Surgical Opinion
Sensitivity 70%
Specificity 85%
