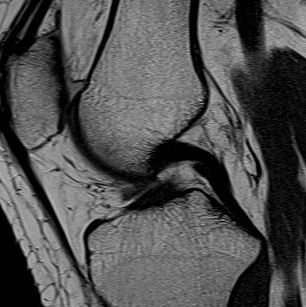
Anatomy
Size
Strength
- 2 x strong as ACL
Length
- about the same as ACL
- 38 mm
Cross sectional area
- 150% of ACL
- 13 mm diameter
2 Bundles
1. Anterolateral
- most important
- double the size of the posteromedial
- tight in flexion
- try to reconstruct this bundle
2. Posteromedial
- tight in extension
Femoral insertion
Half moon
- anterolateral aspect MFC
- much more anterior than the origin of ACL
- inserts 5mm posterior to articular margin of MFC
- midpoint is 1 cm posterior to articular margin of MFC
- 1 or 11 o'clock
Radiographic anatomy of femoral PCL insertion
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3874986/pdf/aob-21-323.pdf
Tibial insertion
PCL facet
- 1 cm below joint line
Radiographic anatomy of the tibial insertion of PCL insertion
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4519663/pdf/main.pdf
Menisco-femoral ligaments
Both insert onto femur with PCL
Originate from posterior horn lateral meniscus
At least one present in > half of all knees
Humphrey
- <1/3 diameter of PCL
- anterior
Wrisberg Ligament
- half the diameter of the PCL
- posterior to the PCL
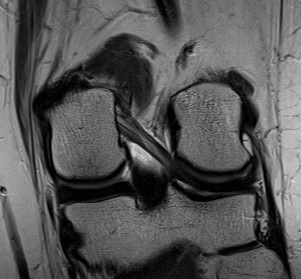
Ligament of Wrisberg MRI
Arterial supply
Middle genicular artery
Nerve Supply
Tibial nerve
Function
Primary restraint to posterior tibial translation
- secondary restraints are posterolateral corner
- posterior translation increased even further if PLC and PCL deficient
Secondary restraint to ER and varus
Incidence
10x less common ACL
Aetiology
Direct trauma
- posteriorly directed force on flexed knee
- dashboard injury
Indirect
- forced knee hyper-extension
Associated Injuries
Multi-ligament knee injury
- posterolateral corner
- posteromedial corner
- ACL
Clinical
Injury often unremarkable
- knee doesn't feel right
- don't feel pop or tear
- posterior knee pain
May complain of difficulties walking down stairs in chronic situation
Examination
Excessive Recurvatum
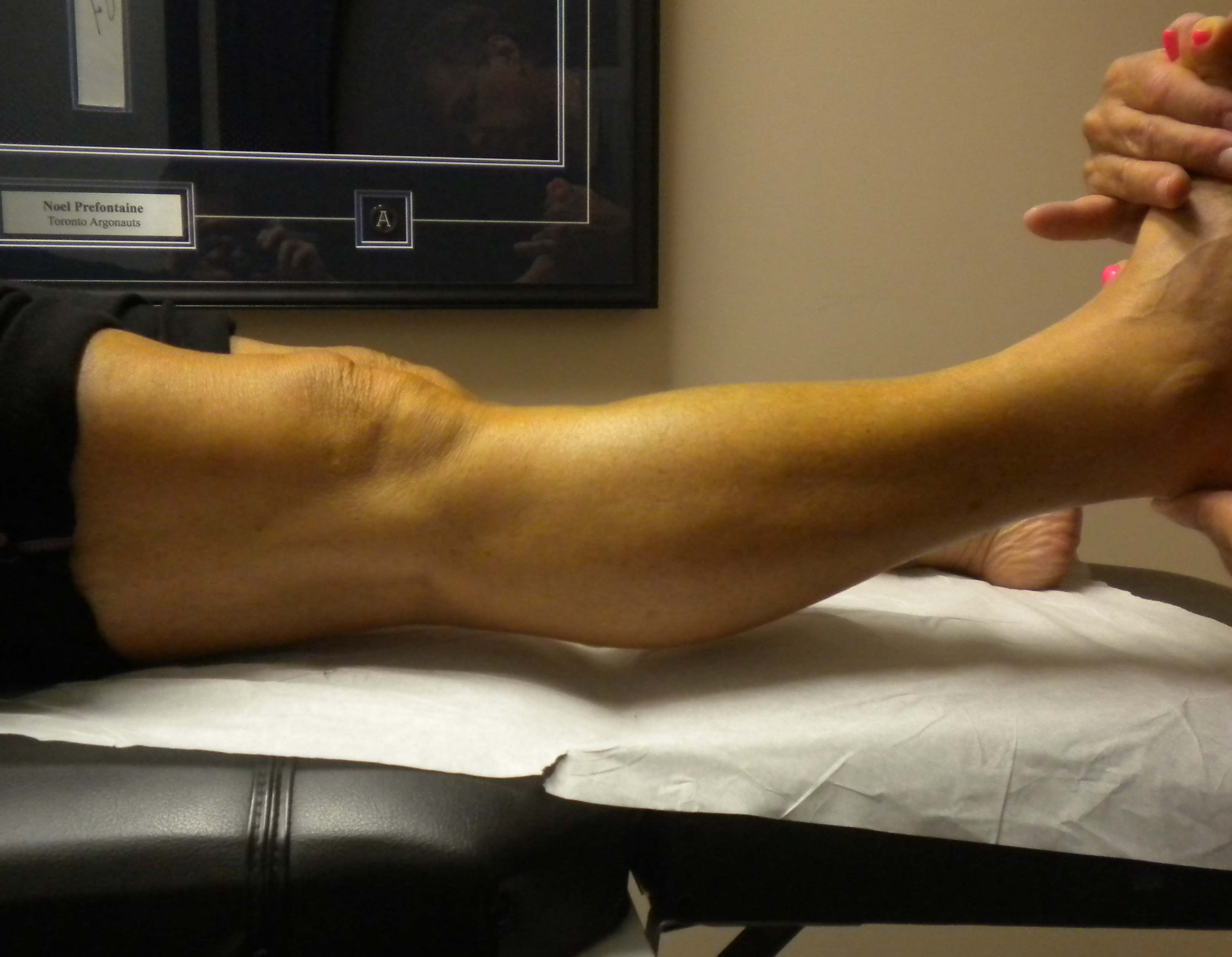
Positive Lachman's
Will be positive with both ACL and PCL
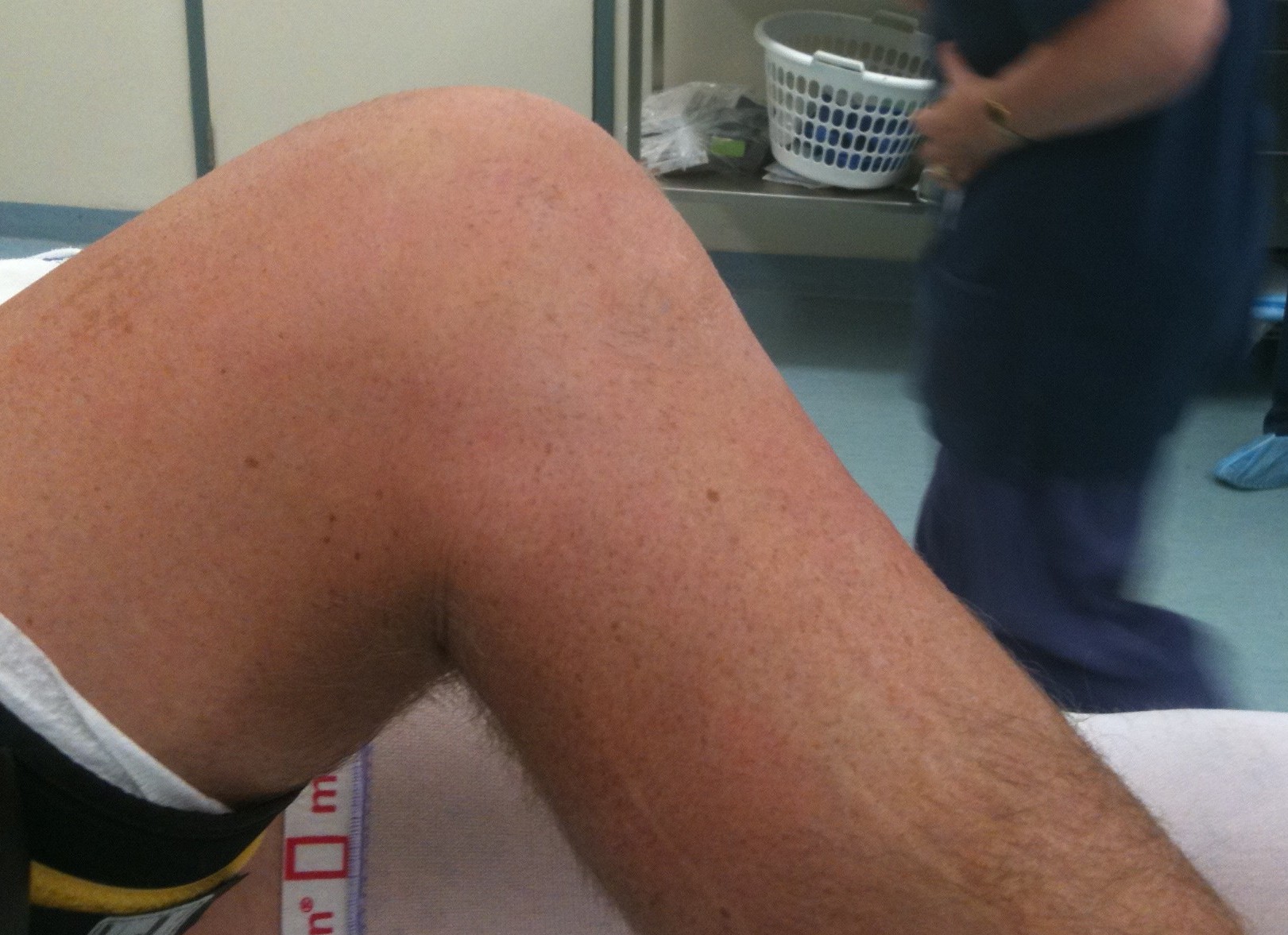
Posterior sag
- place knee at 90 degrees
- tibia will sag posteriorly
- loss of tibial step off (normal 1cm)
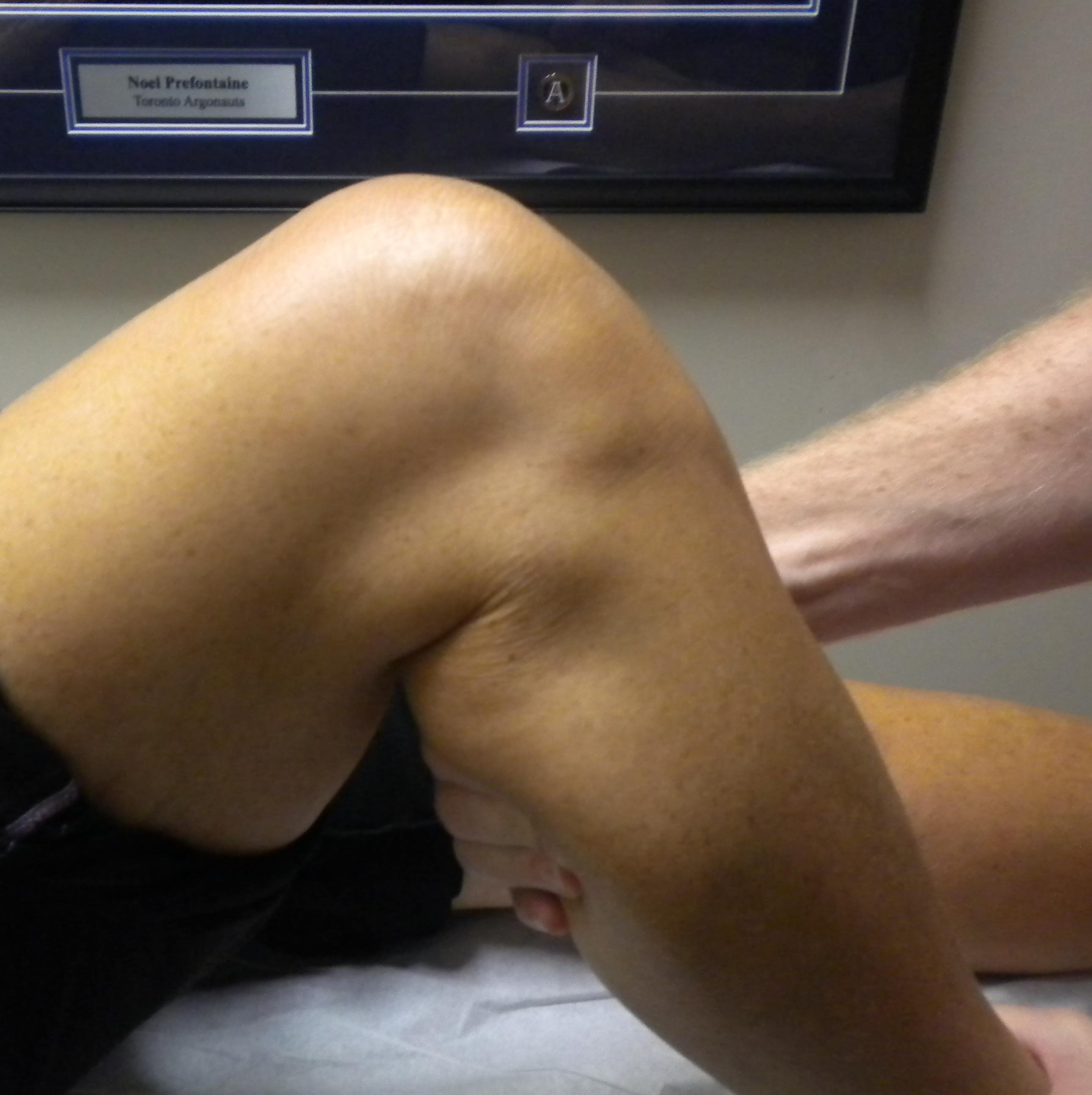
Posterior drawer
Restore step off first (tibia 1 cm anterior to femur) then push tibia back
- Grade 1: < 5mm
- Grade 2: 5 - 10mm
- Grade 3: > 10mm
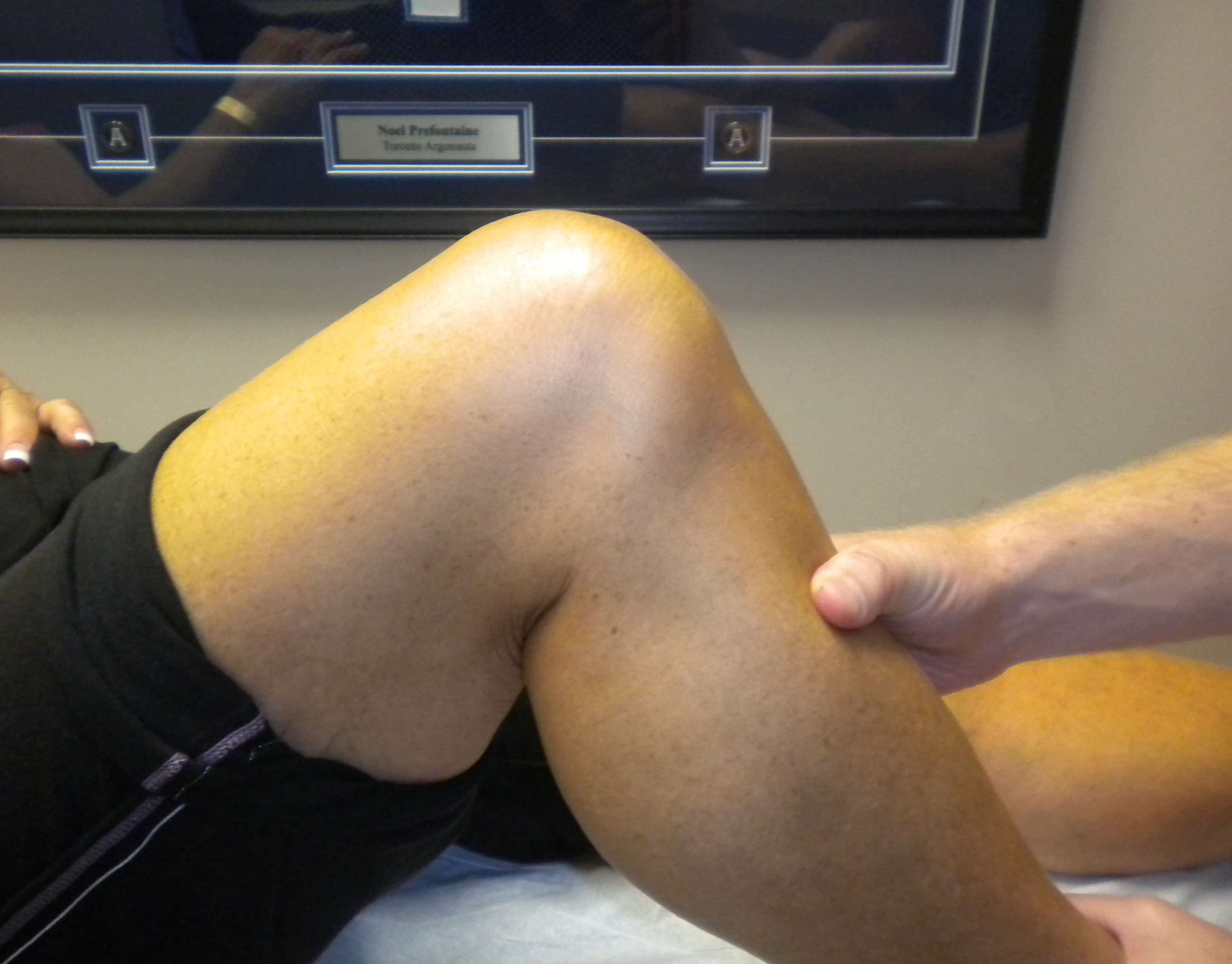
Quadriceps Active Test
- patients contracts quadriceps with foot stabilised
- the tibia is reduced anteriorly from its subluxed position by the quadriceps
Exclude Associated Ligament injury
PLC instability
1. Posterolateral draw with foot ER
2. Dial test
- patient prone, external rotation
- > 10 - 15o compared with other side abnormal
- asymmetry 30o posterolateral corner only
- asymmetry 30 and 90o, PCL and posterolateral corner
X-ray
Bony Avulsion
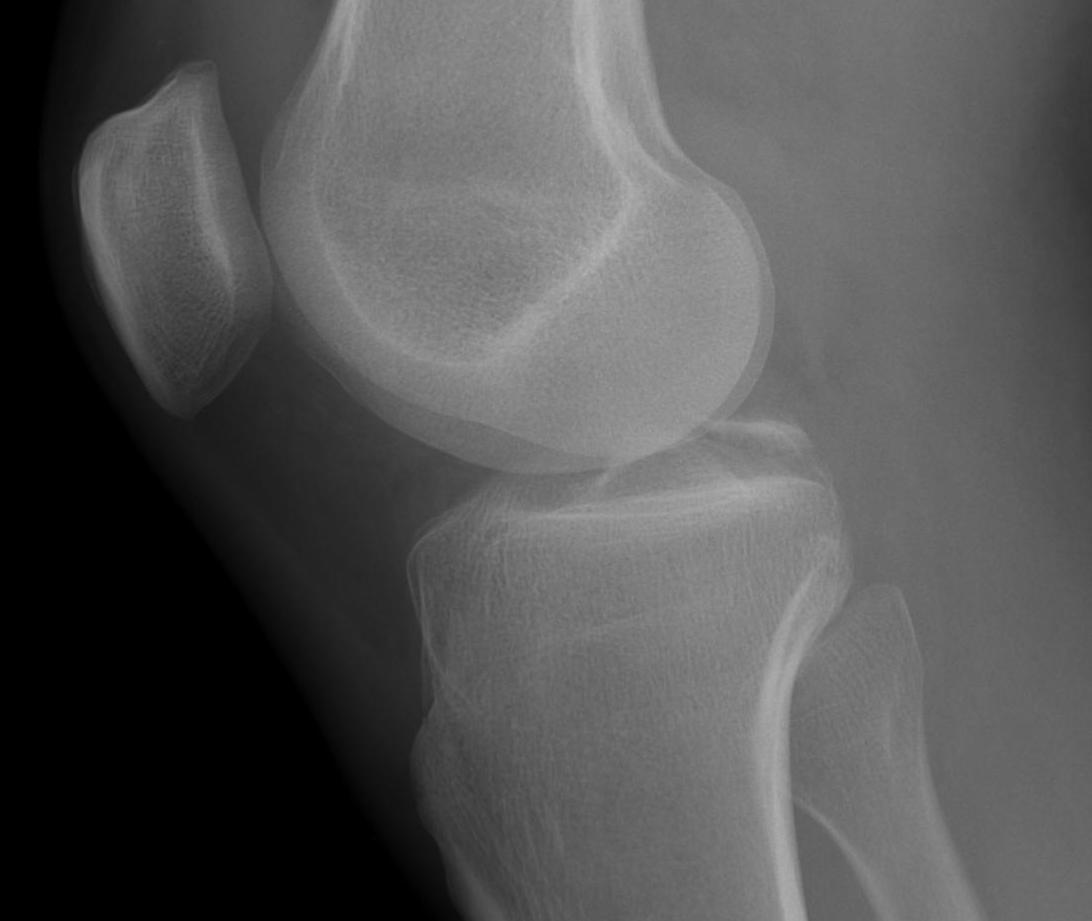
Posterior subluxation of tibia
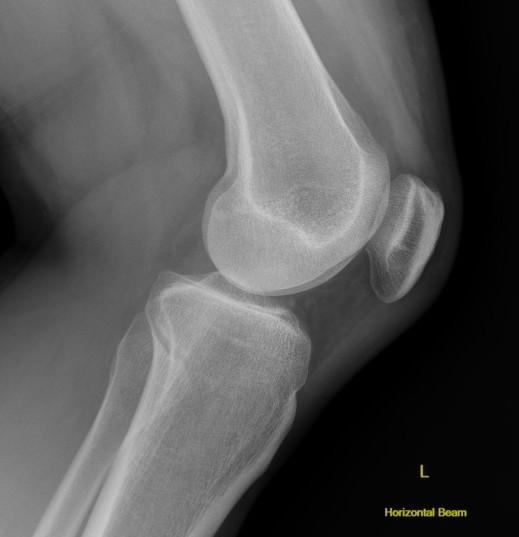
Grade 3 PCL disruption - posterior tibia subluxed behind posterior aspect femoral condyles
CT
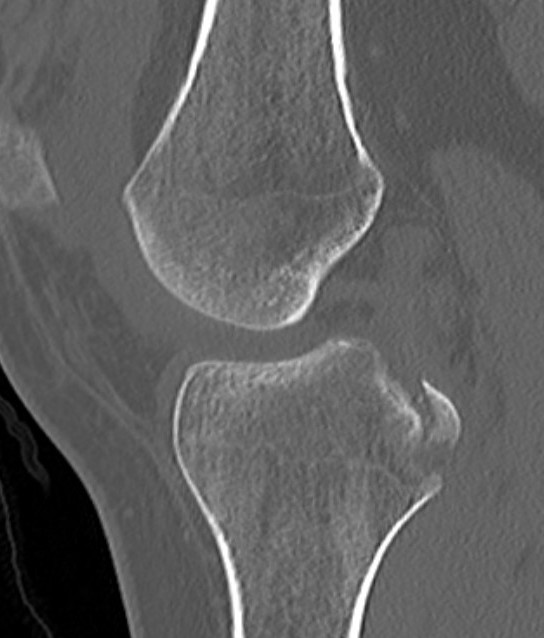
Bony avulsion PCL
MRI
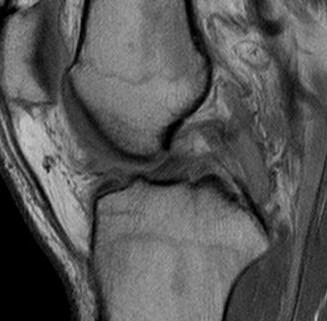
PCL completely torn
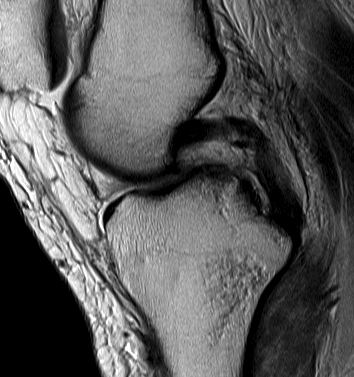
PCL midsubstance tear with lengthening
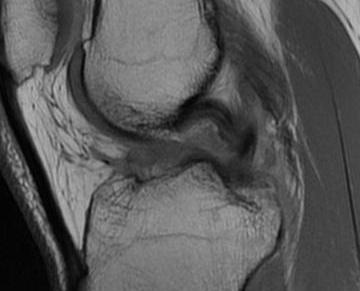
PCL tibial avulsion
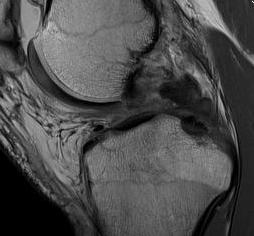
PCL femoral avulsion
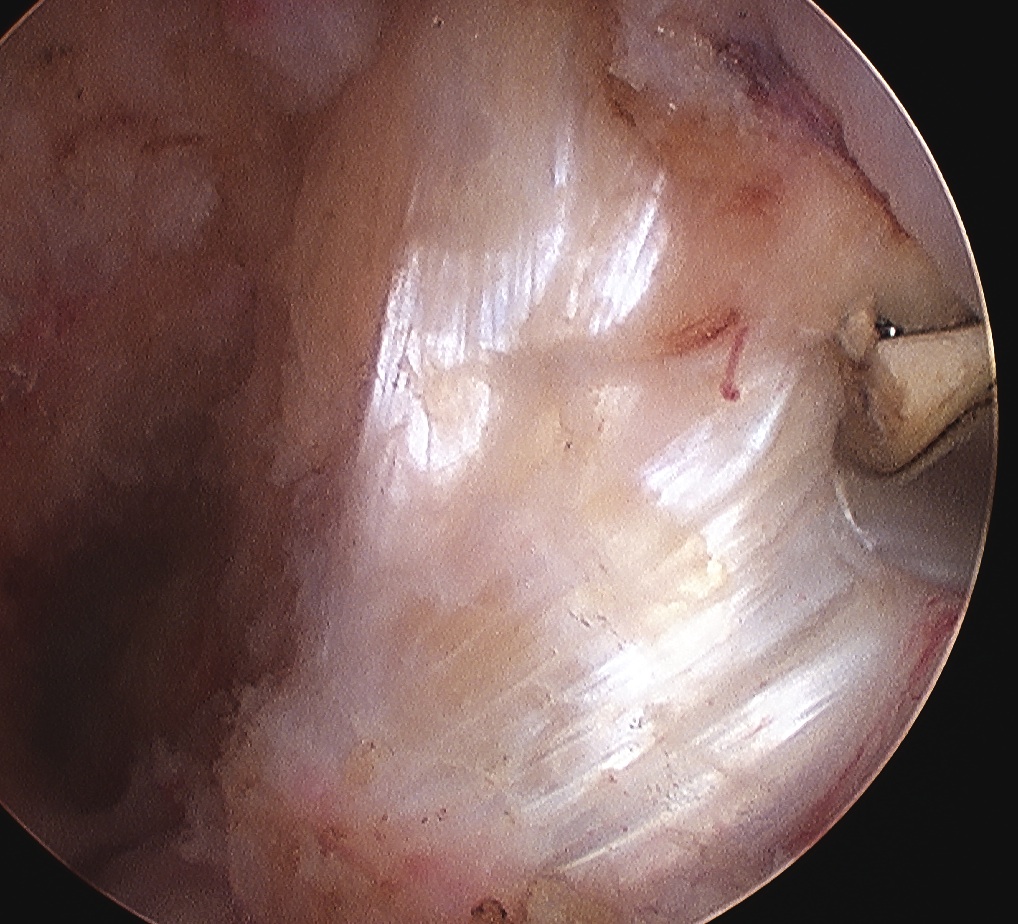
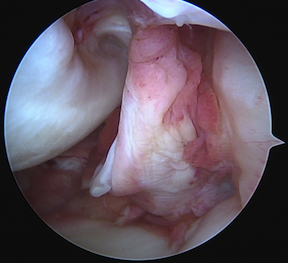
Arthroscopy
May miss tear as is extra-synovial
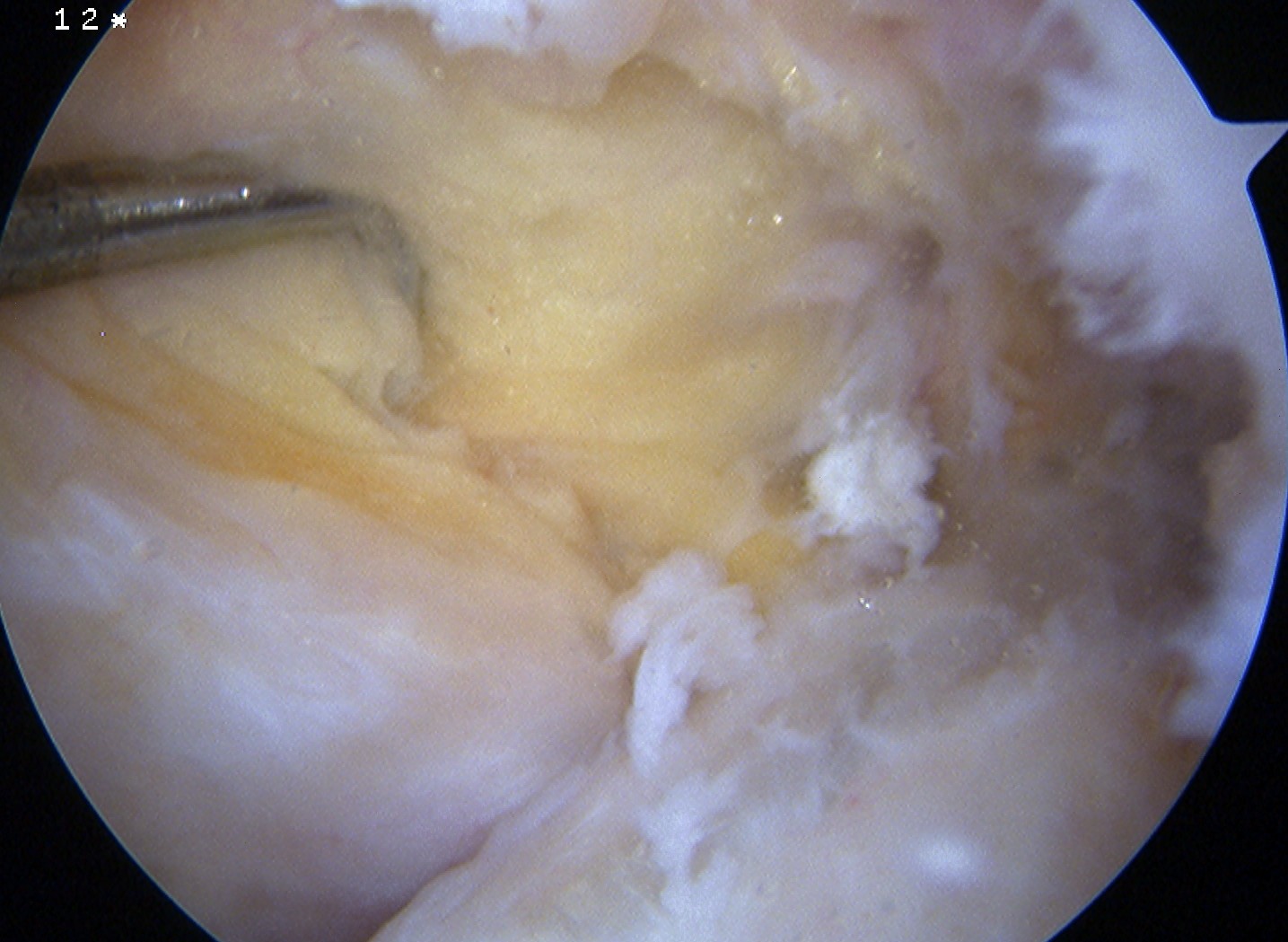
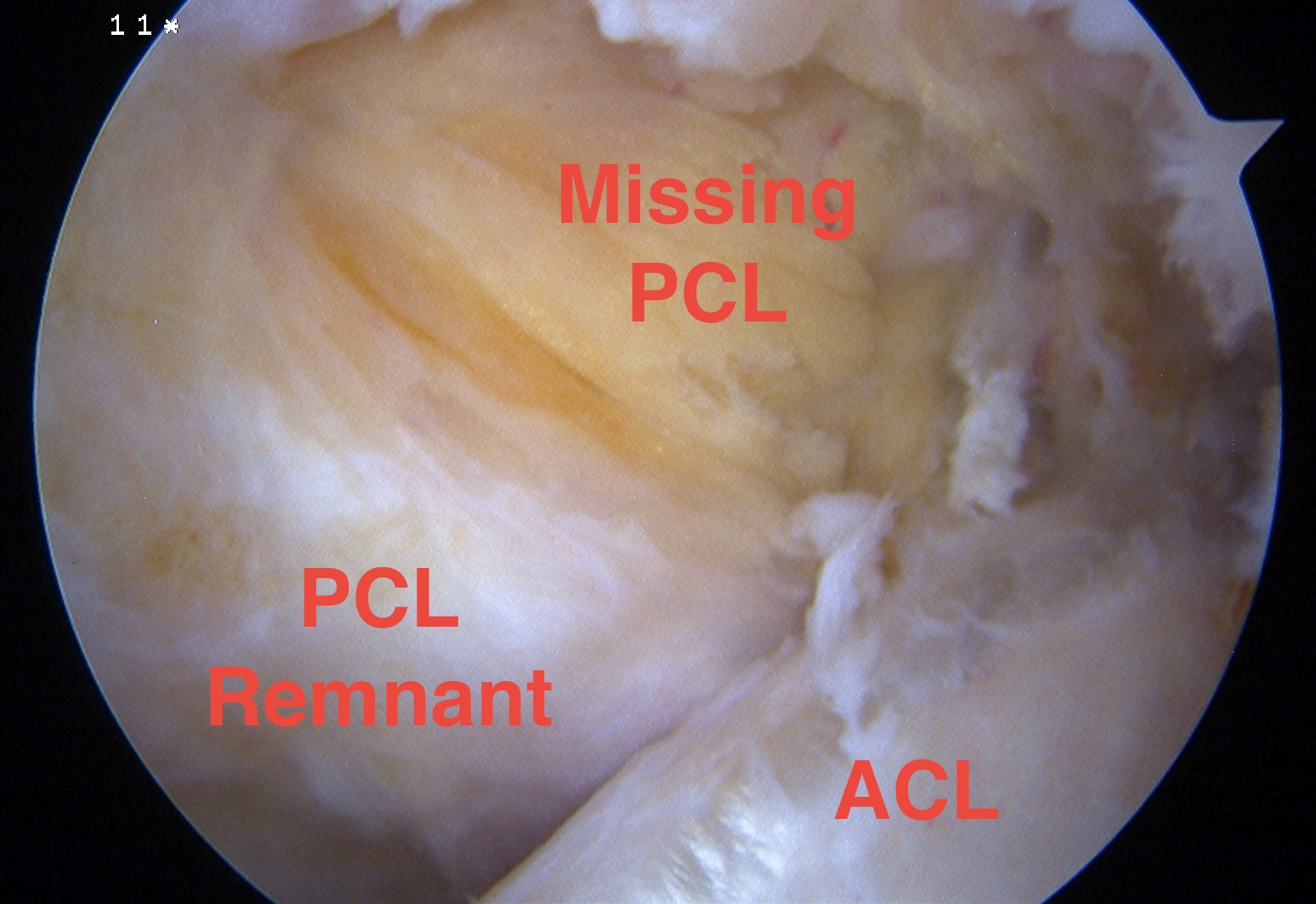
Chronic PCL tear from femur
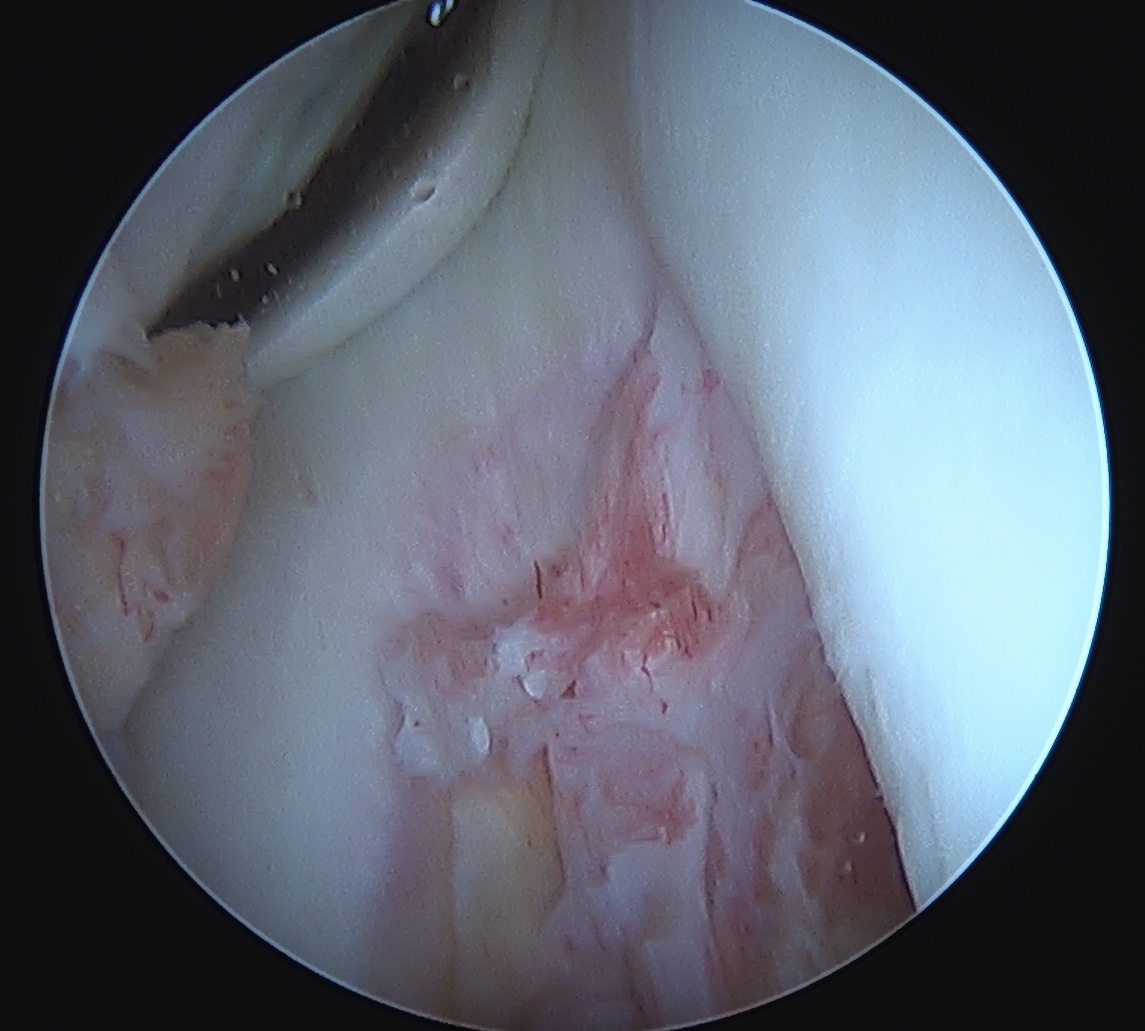
Acute PCL femoral avulsion
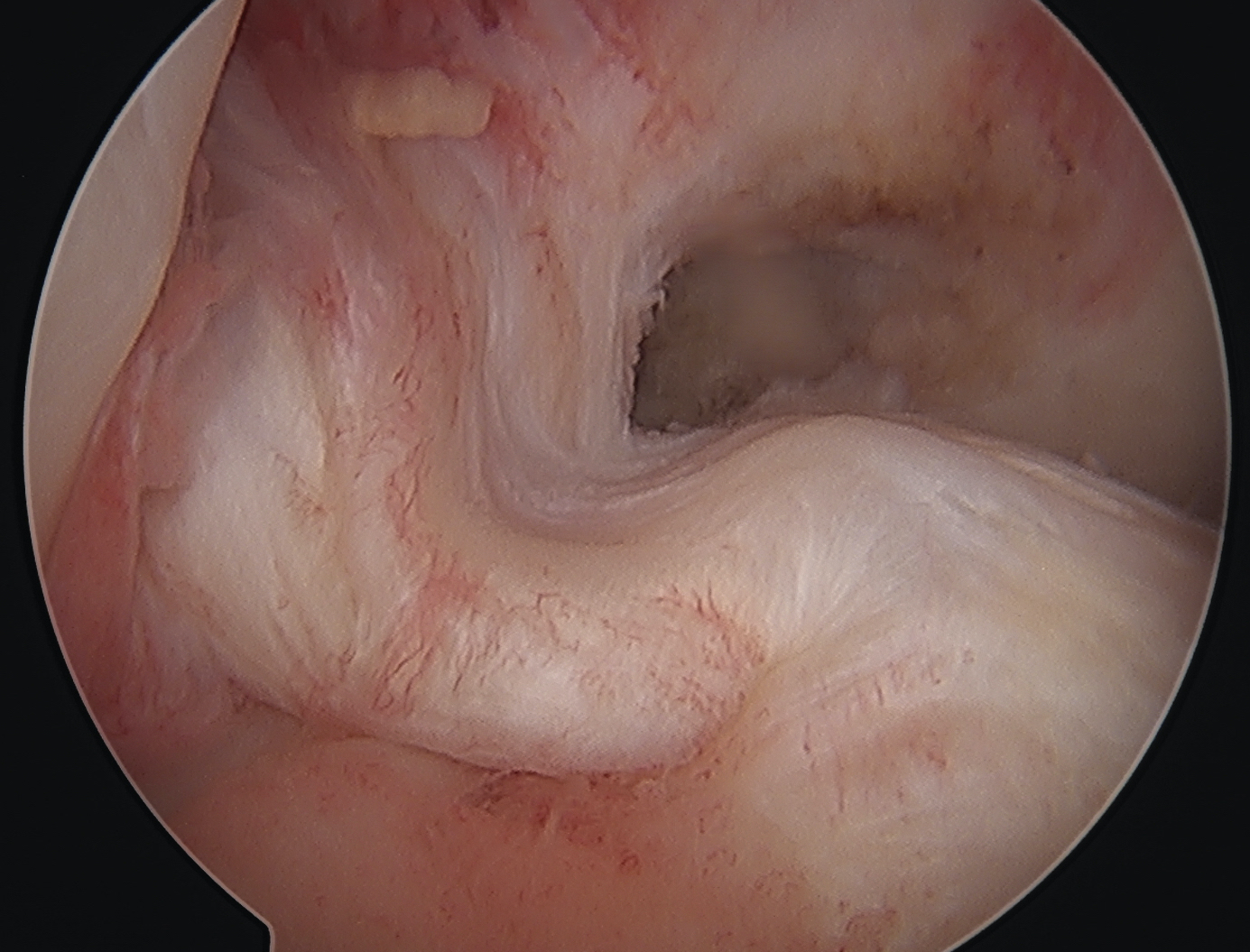
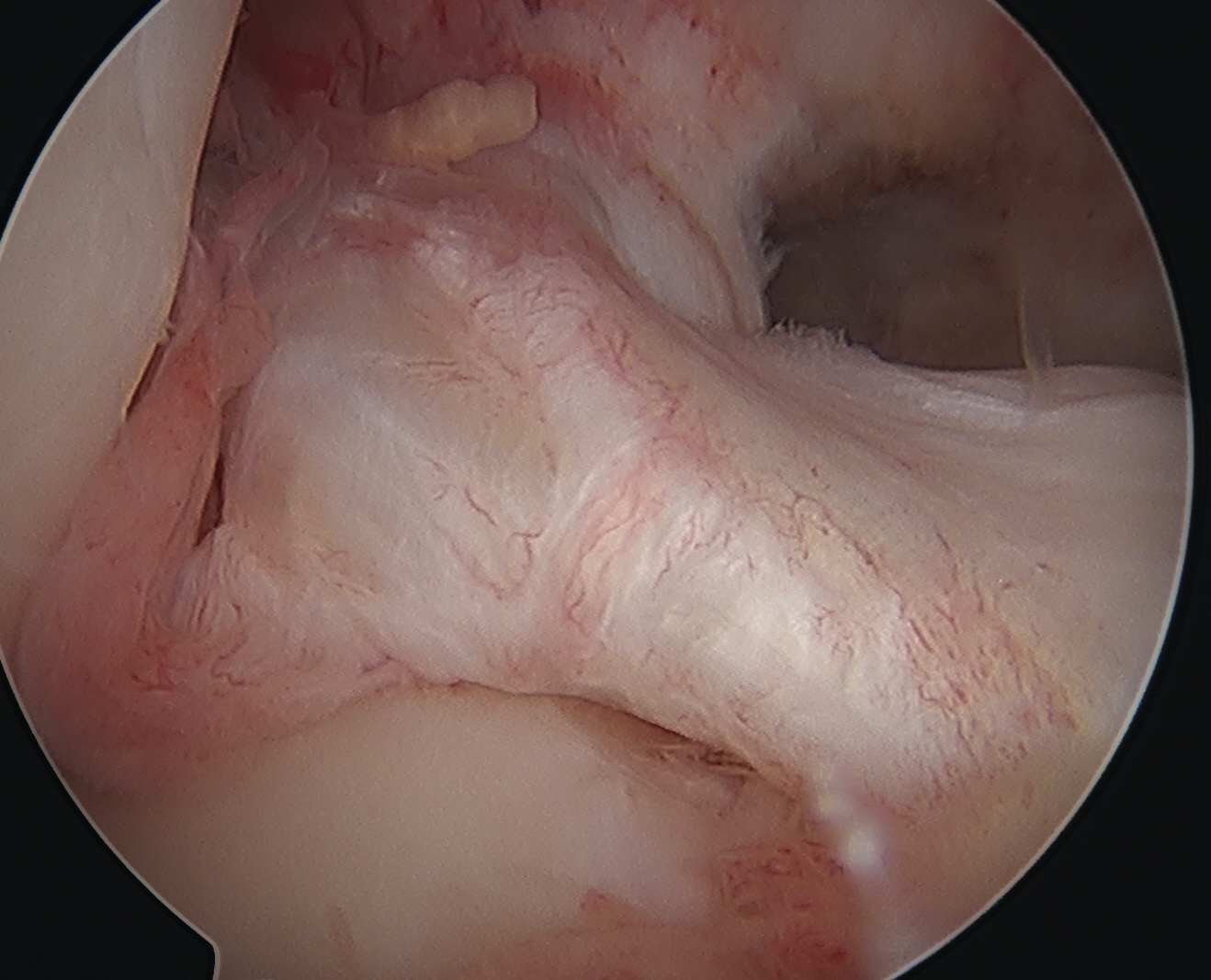
Apparent ACL laxity due to PCL tear and posterior tibial sag; ACL tension restored with anterior drawer