Open approach
A. Posterior approach to Knee
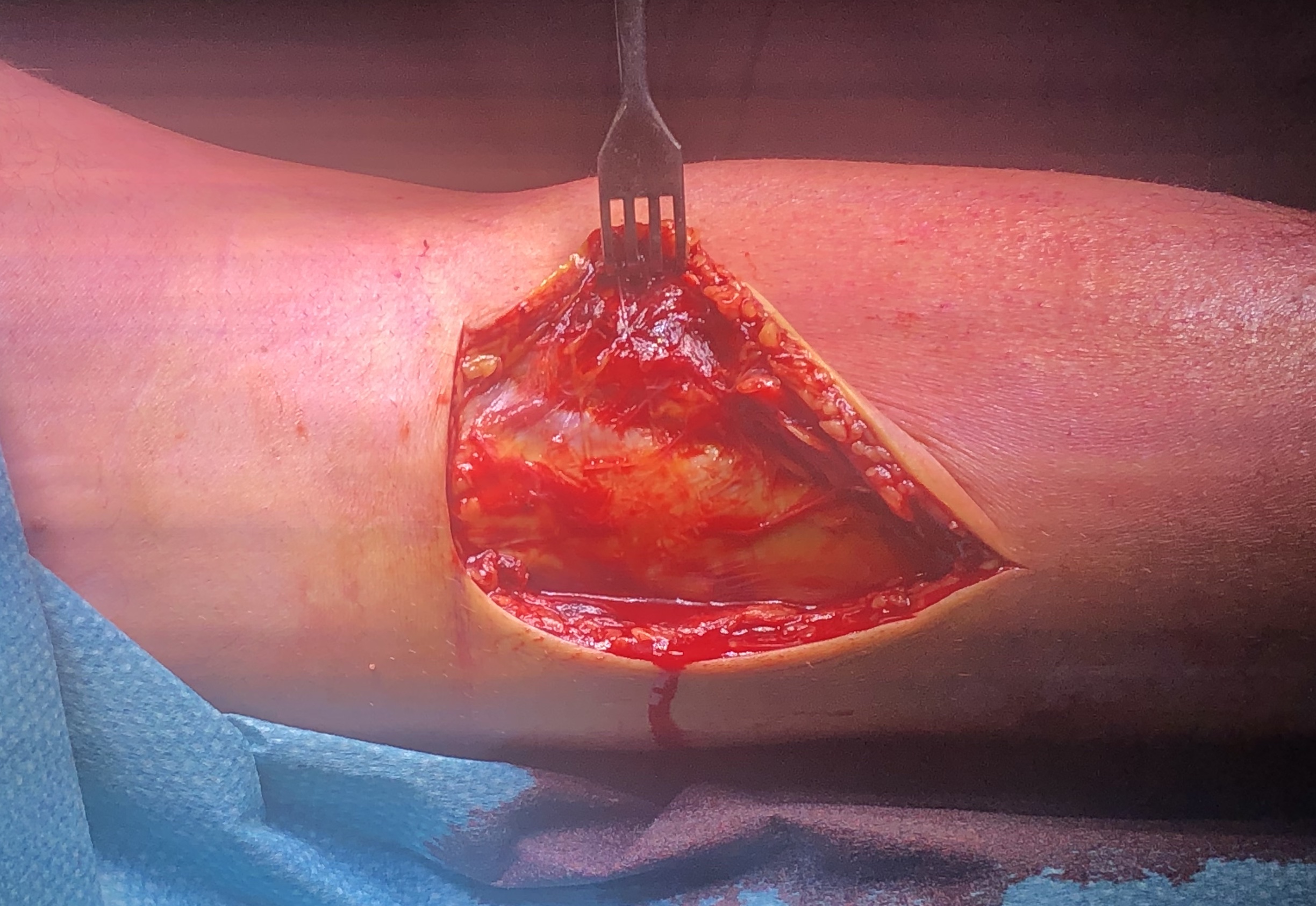
S shaped incision
- lateral proximally to medial distally
Superficial dissection
- small saphenous vein and medial sural nerve identified midline distally
- open deep fascia
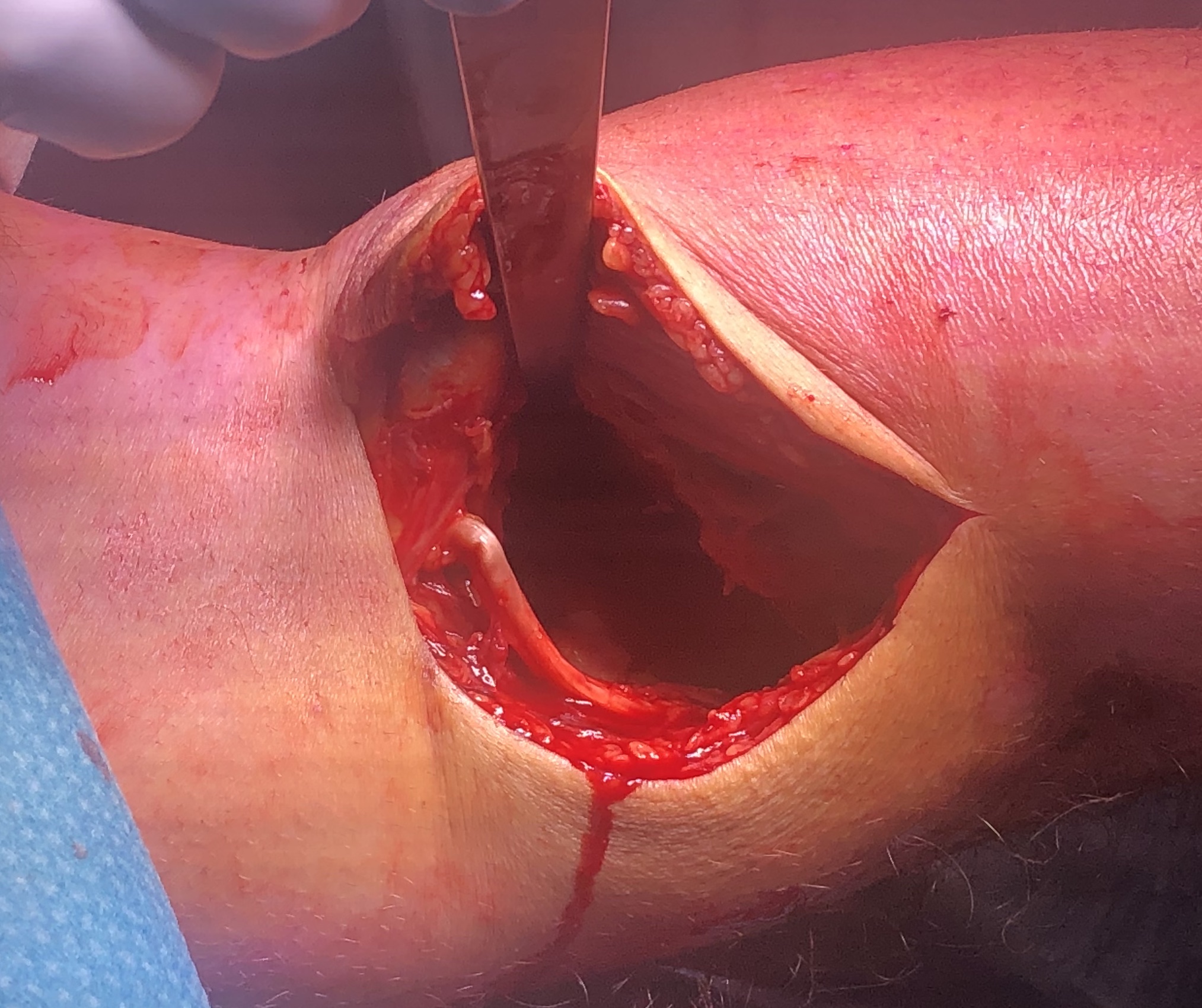
Deep dissection
- popliteal fossa
- superiorly: semimebranosus & semitendinosus medial, biceps femoris lateral
- inferiorly: medial and lateral gastrocnemius
- popliteal artery deep and medial
- vein in middle, tibial nerve lateral
- common peroneal nerve laterally with biceps
Find and protect medial sural nerve
- track to tibial nerve
Identify and ligate middle genicular artery
- allows mobilisation of vessel
- retract neurovascular structures laterally
Open capsule
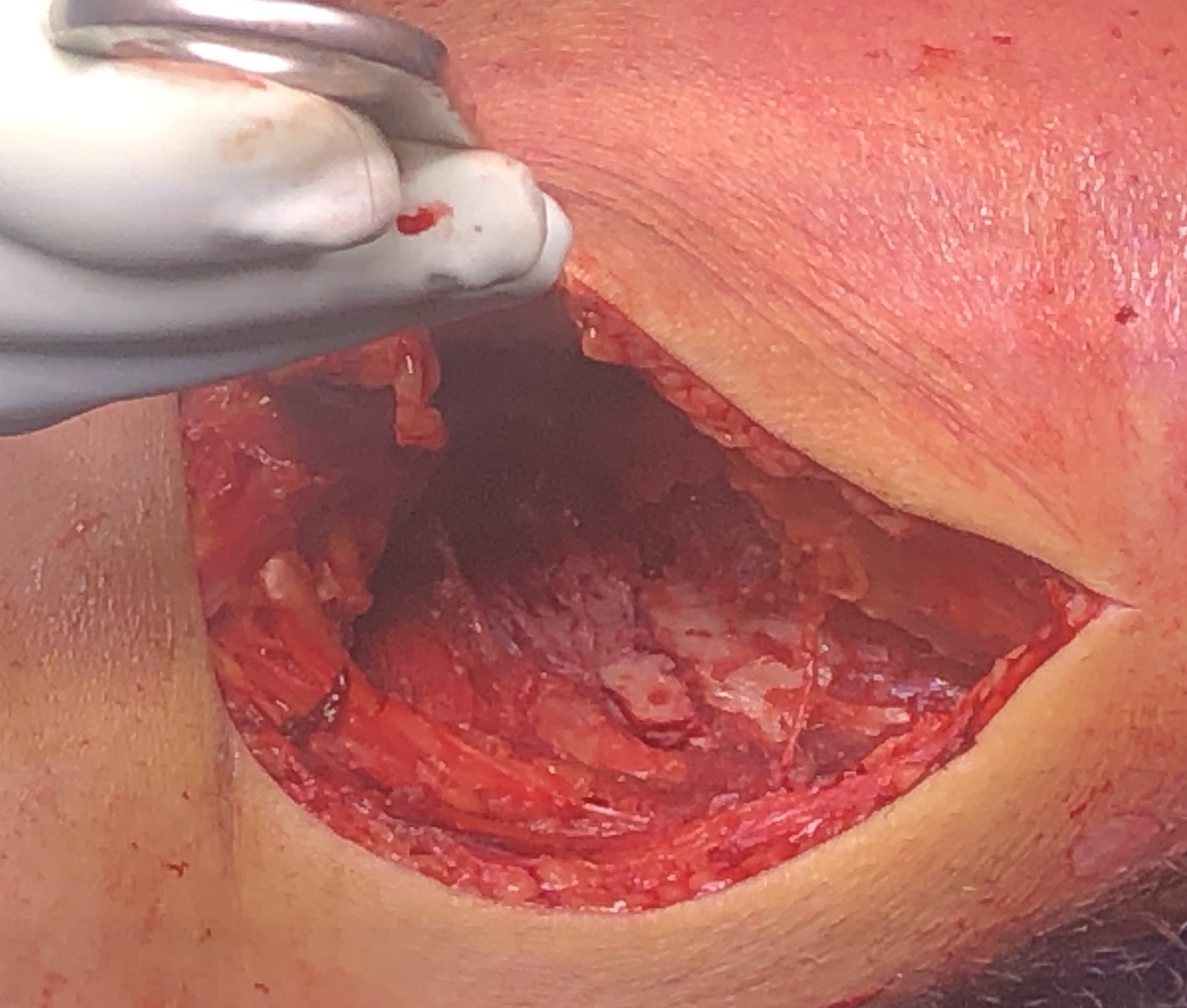
B. Burk modified posterior approach / Posteromedial approach
Advantages
- avoids major neurovascular bundle
Interval between semimembranosus and medial gastrocnemius
- semimembranosus medially
- medial head gastrocnemius laterally / can be released
- release popliteus from medial tibia and reflect laterally
- place blunt homan across tibia
- open capsule
AO foundation surgical approach
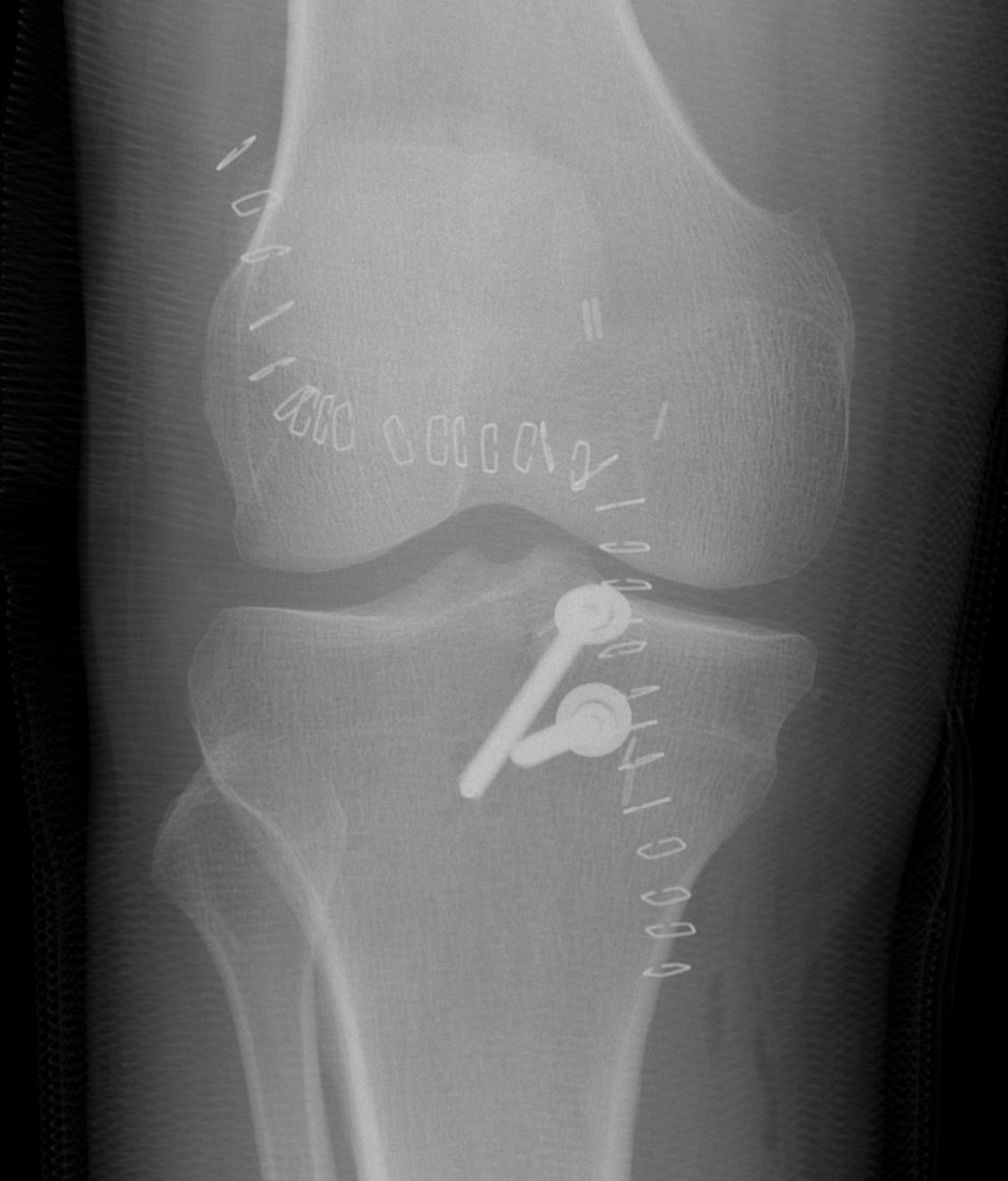
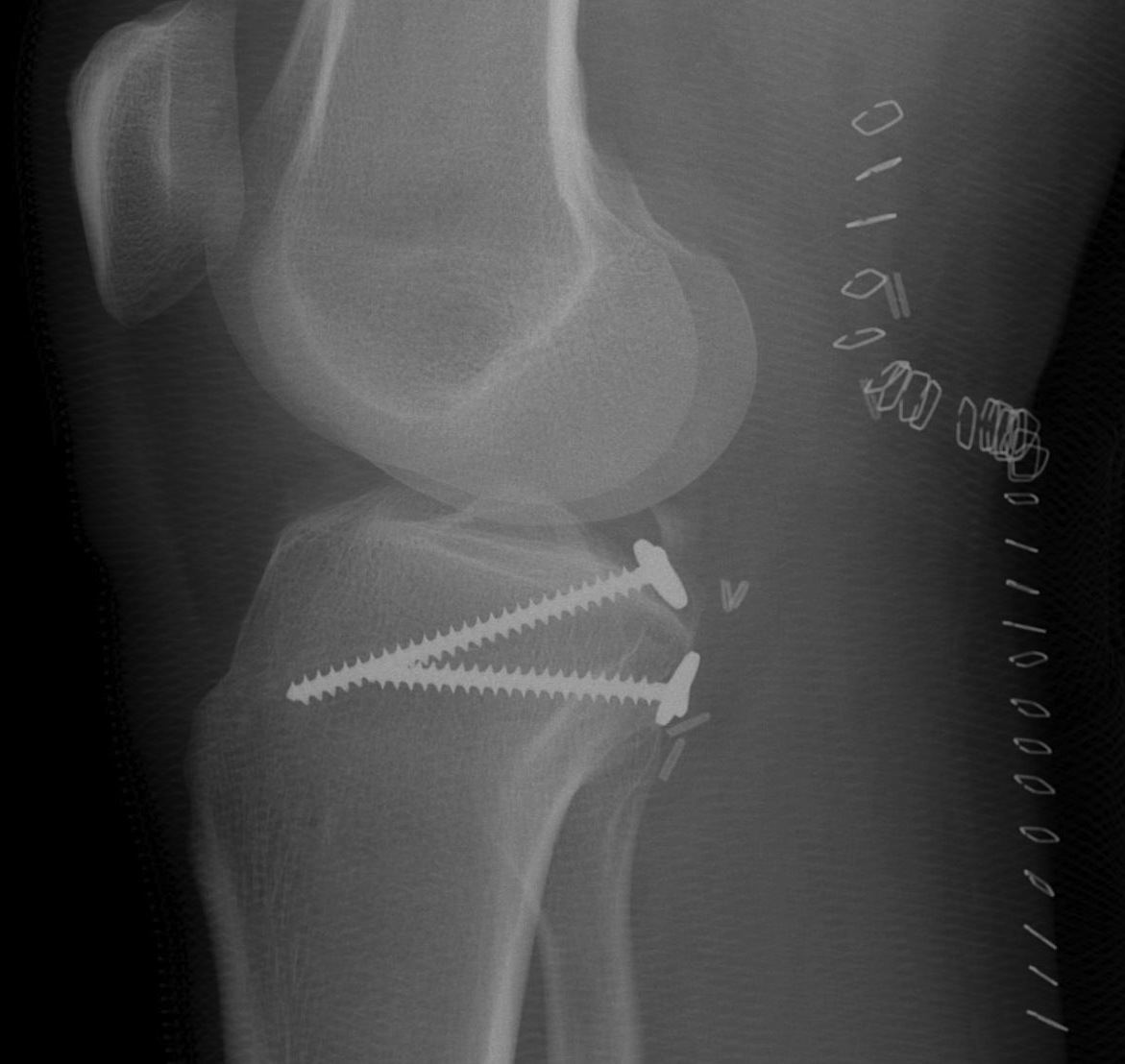
Fixation options
- size dependent
- screw / staple