Arthroscopy
Results
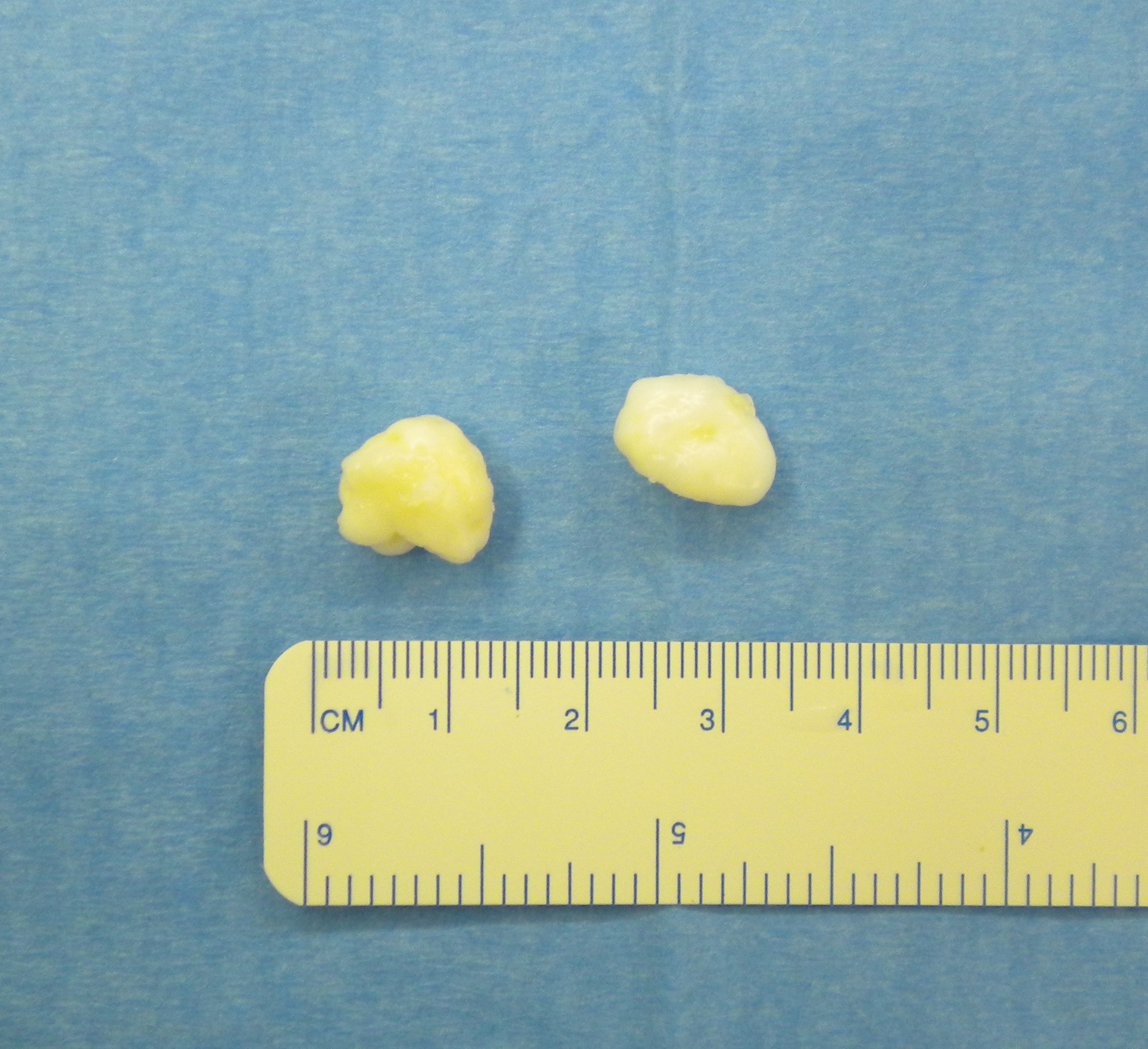
- 85 intra-articular ganglions
- 49 ACL, 16 PCL
- 12 from anterior horn meniscus, 3 posterior horn meniscus
- 3 from fat pad
Technique
Surgical technique PDF using trans-septal portal
Movement of iliopsoas tendon over femoral head / iliofemoral ridge / iliofemoral ligament
Arthroscope in lateral portal
Clear fat pad
Ensure can see entire dimensions of OCD
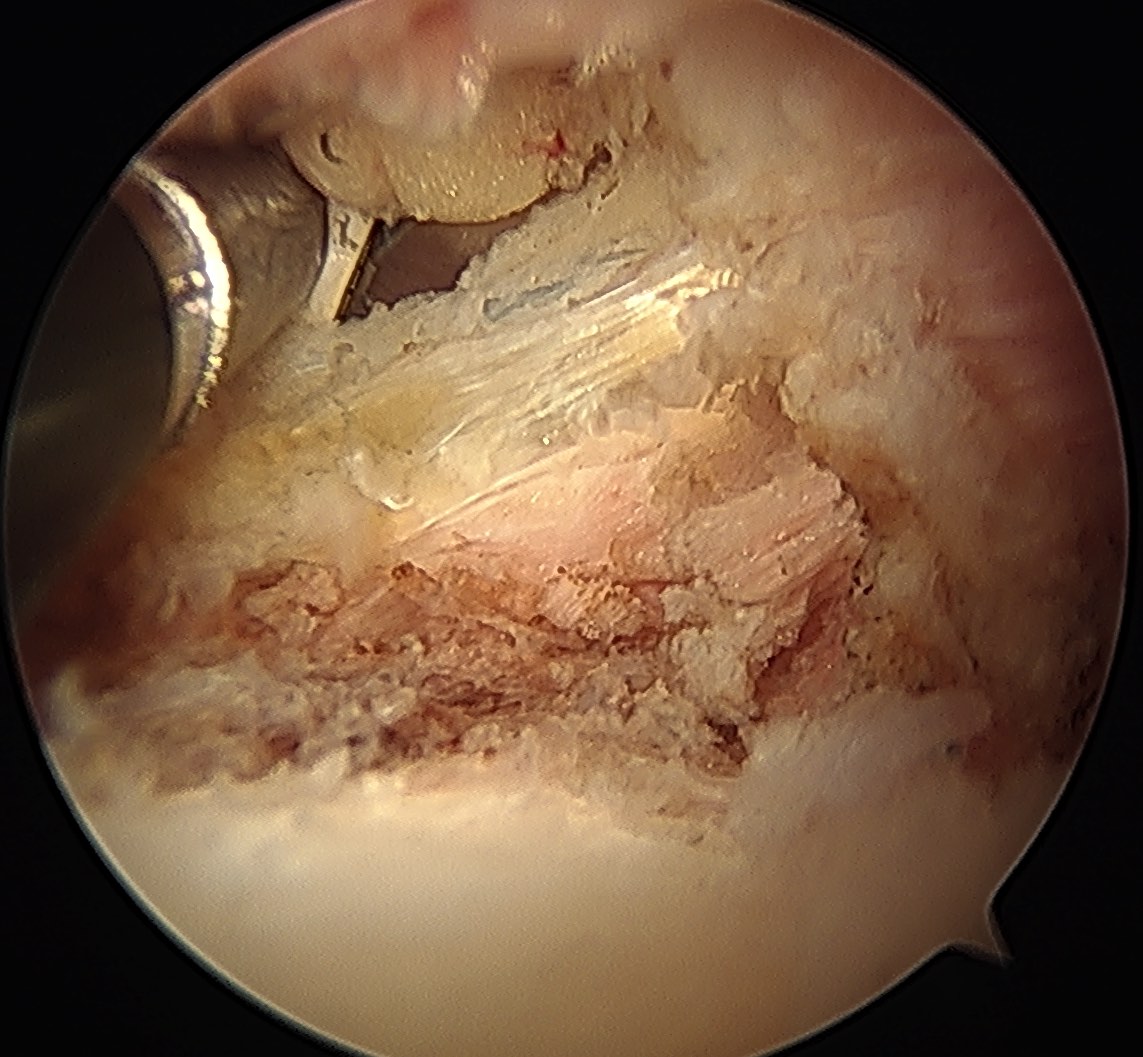
If fragment is displaced, reduce and pin with accessory K wire
Engaging Hill Sachs
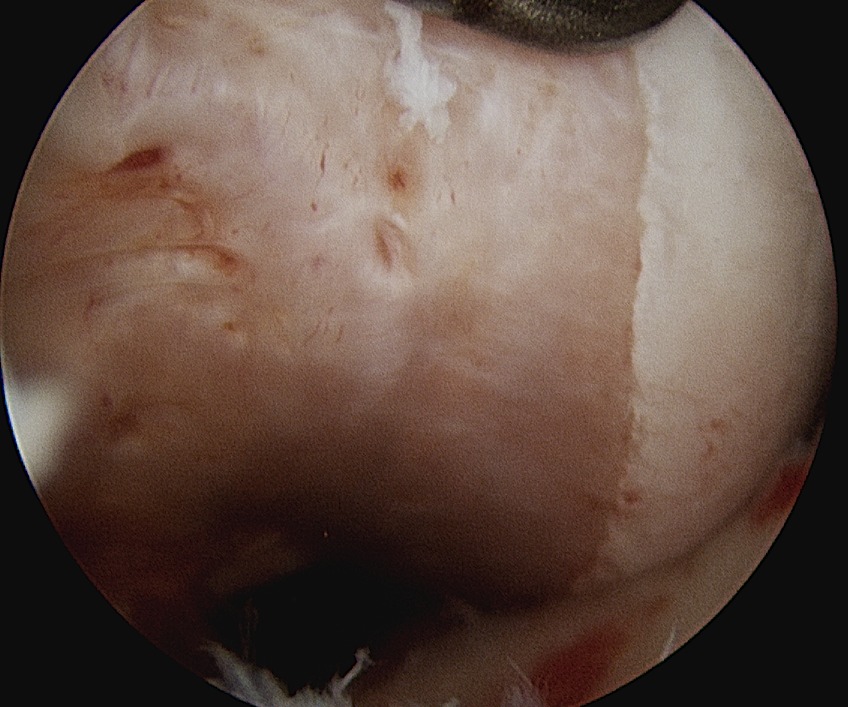
Pigmented Villo-Nodular Synovitis
- benign inflammatory process that arises in synovial tissues
- contains significant amounts of hemosiderin
Age: 20 - 50
Sex: M > F
A. Diffuse
- throughout joint synovium
- more difficult to treat / excise fully
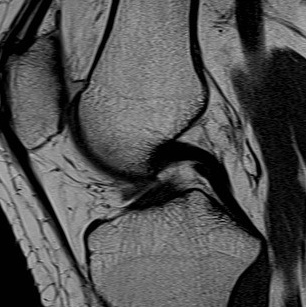
OCD
OA - Osteophytes
Meniscus
Pain
Locking
Clicking
Can cause chondral damage
OA Loose Bodies
Size
2 x as strong as ACL
About the same length as ACL 38 mm
Cross sectional area 150% of ACL
13 mm diameter (thicker)
2 Bundles
1. Anterolateral
- most important
- double the size of the posteromedial
- tight in flexion
- try to reconstruct this bundle
Most common
- fascia lata on greater trochanter
- iliopsoas on lesser trochanter
1. Intra-articular structures
- labrum
- ligamentum Teres
- loose bodies
- synovial chondromatosis
- osteochondoma
2. Extra-articular structures
- fascia lata on greater trochanter (common)