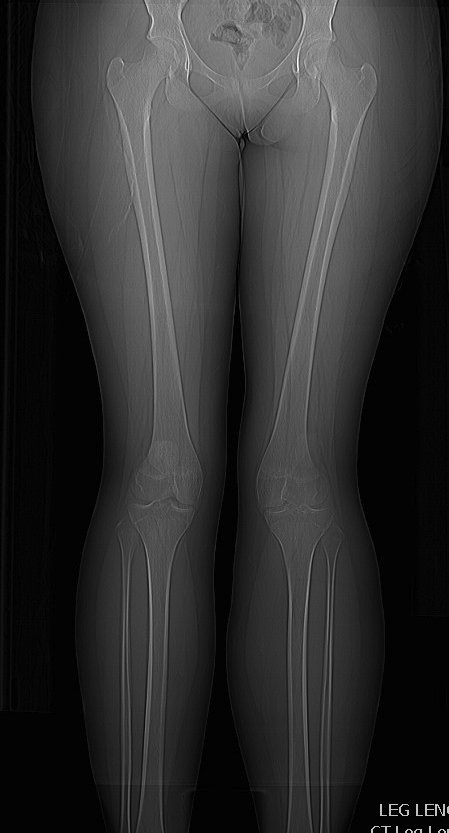
AP / Long Leg Views
Quantify Valgus Malalignment
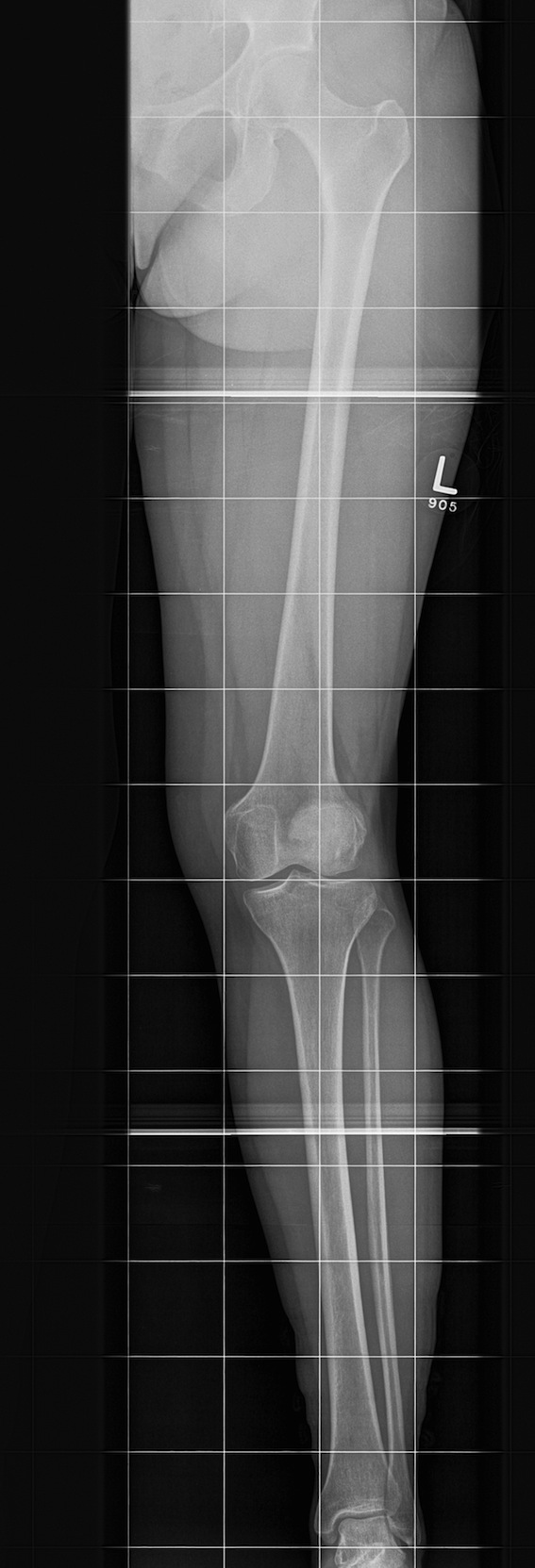
Lateral Xray
1. Assess Patella Alta
30o flexion
A. Blumensaat's line / Inaccurate
Knee flexed to 30o
- line should just touch inferior pole of patella
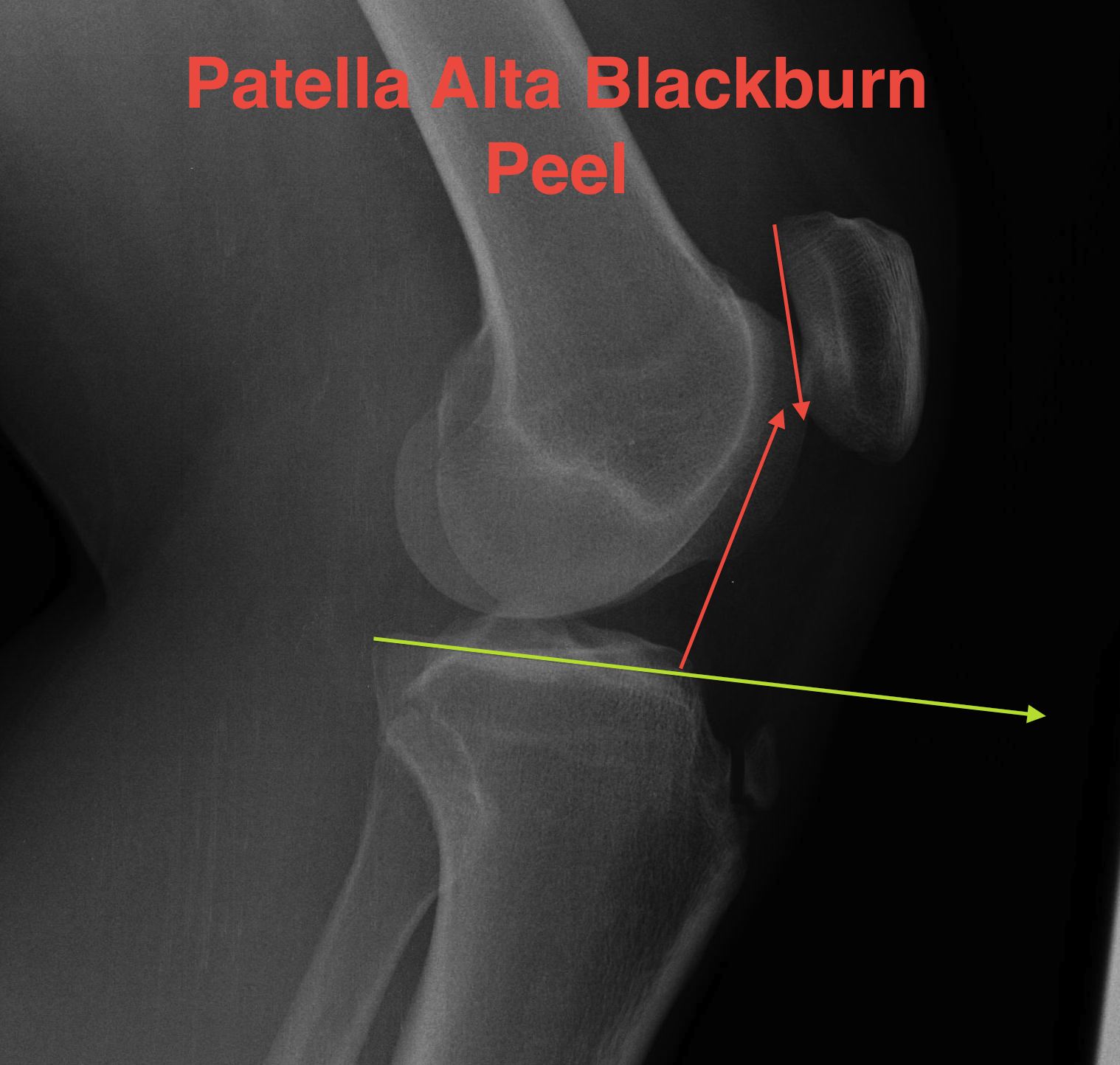
- pole above line - alta
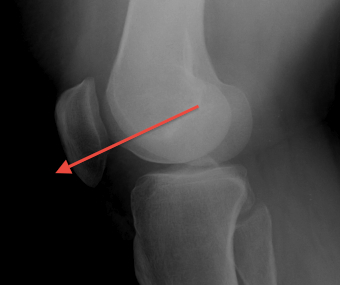
- pole below line - baja
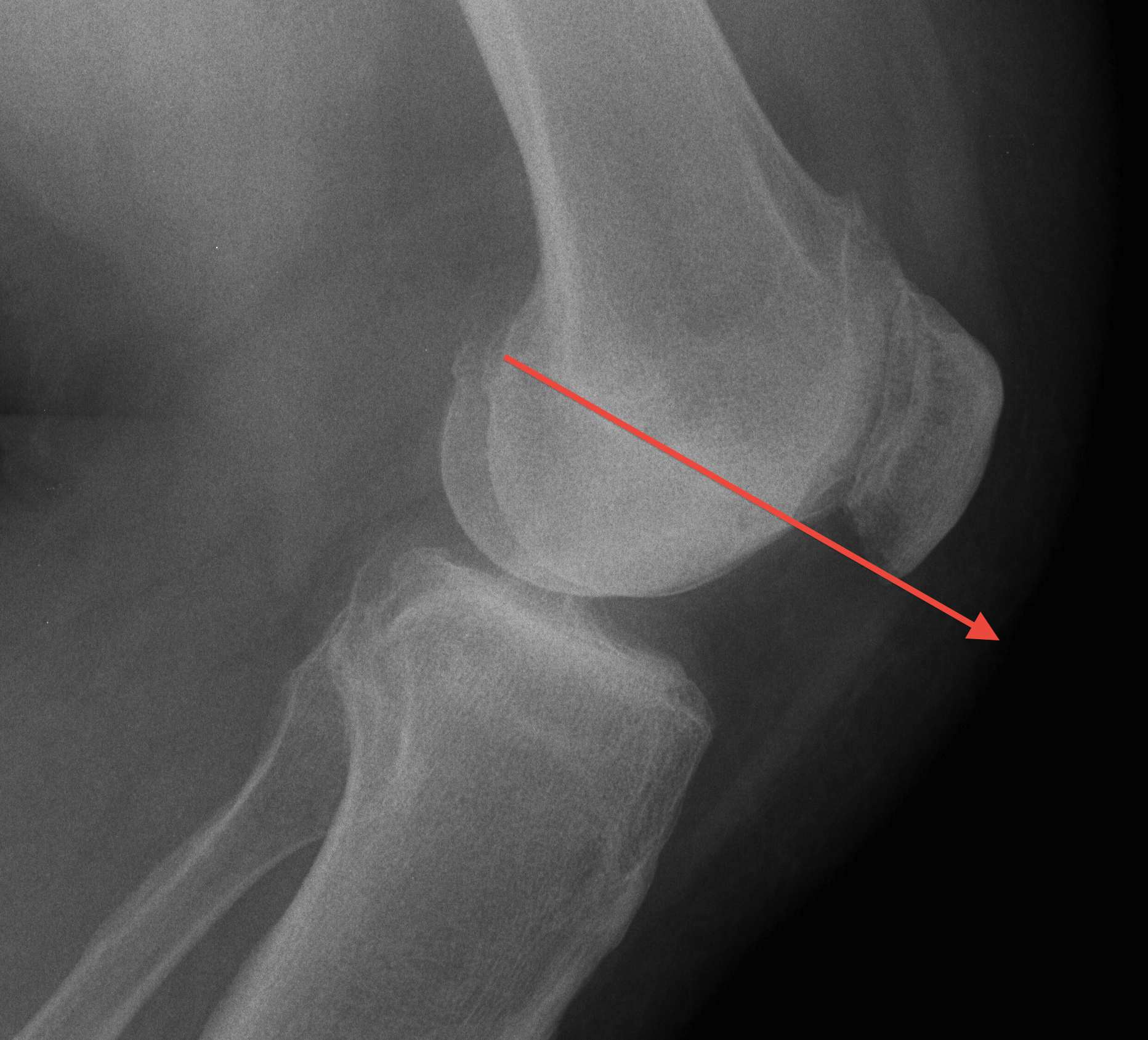
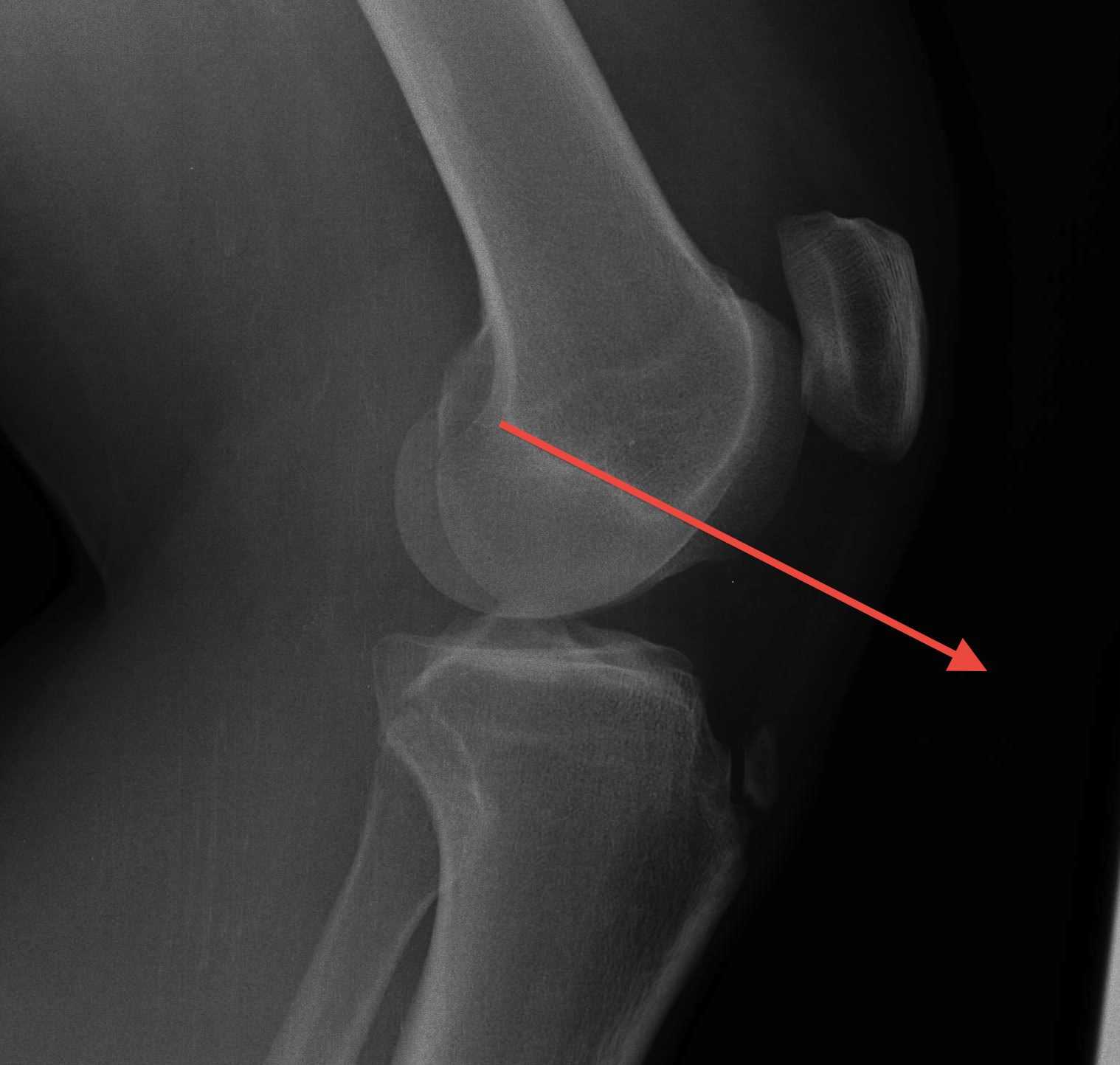
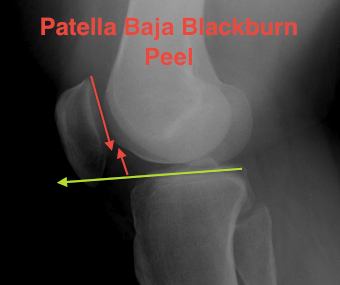
B. Blackburn-Peele ratio / Best and Most accurate
Distance between tibial and patella articular surface
- divided by patella articular surface
- patella alta > 1
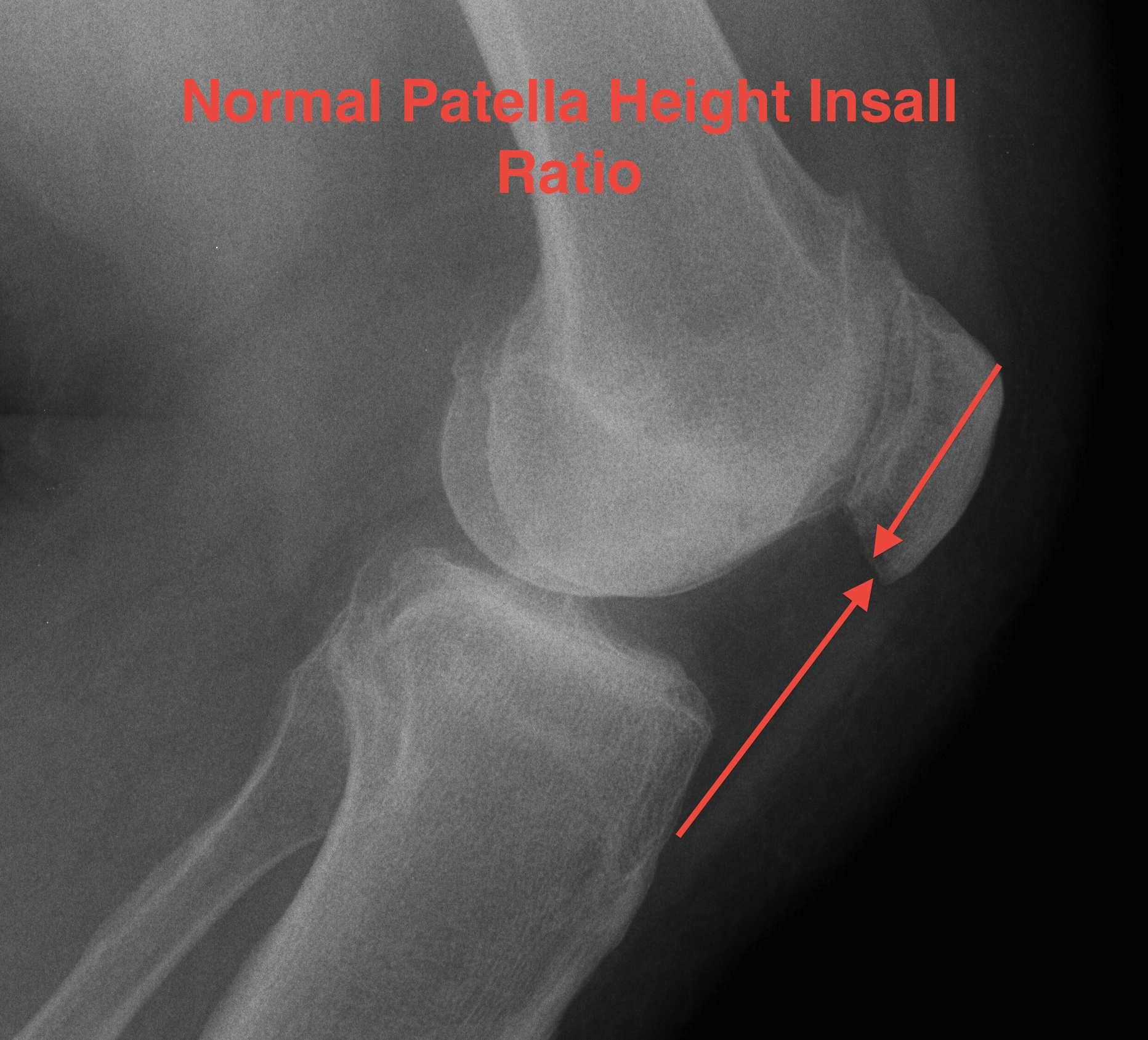
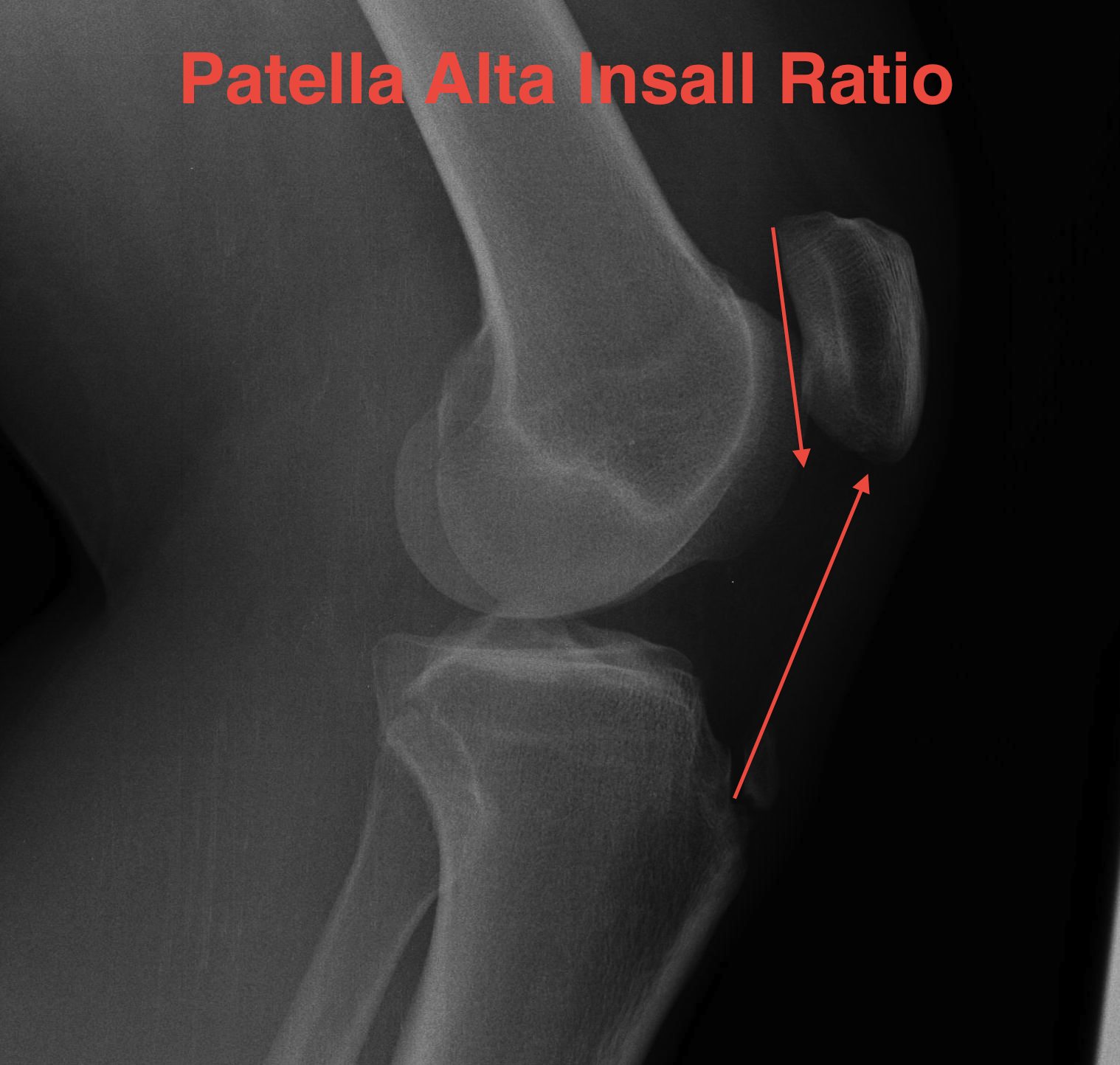
C. Insall ratio
- less accurate, probably because more difficult to measure
- ratios also difficult to remember and calculate
- length of patella tendon v length patella
- patella alta LT : LP 1.2
- patella baja LT : LP <1
2. Assess Trochlea Dysplasia
Dejour Crossover Sign
- lateral x-ray at 30o with condyles superimposed
- identify base of trochlea
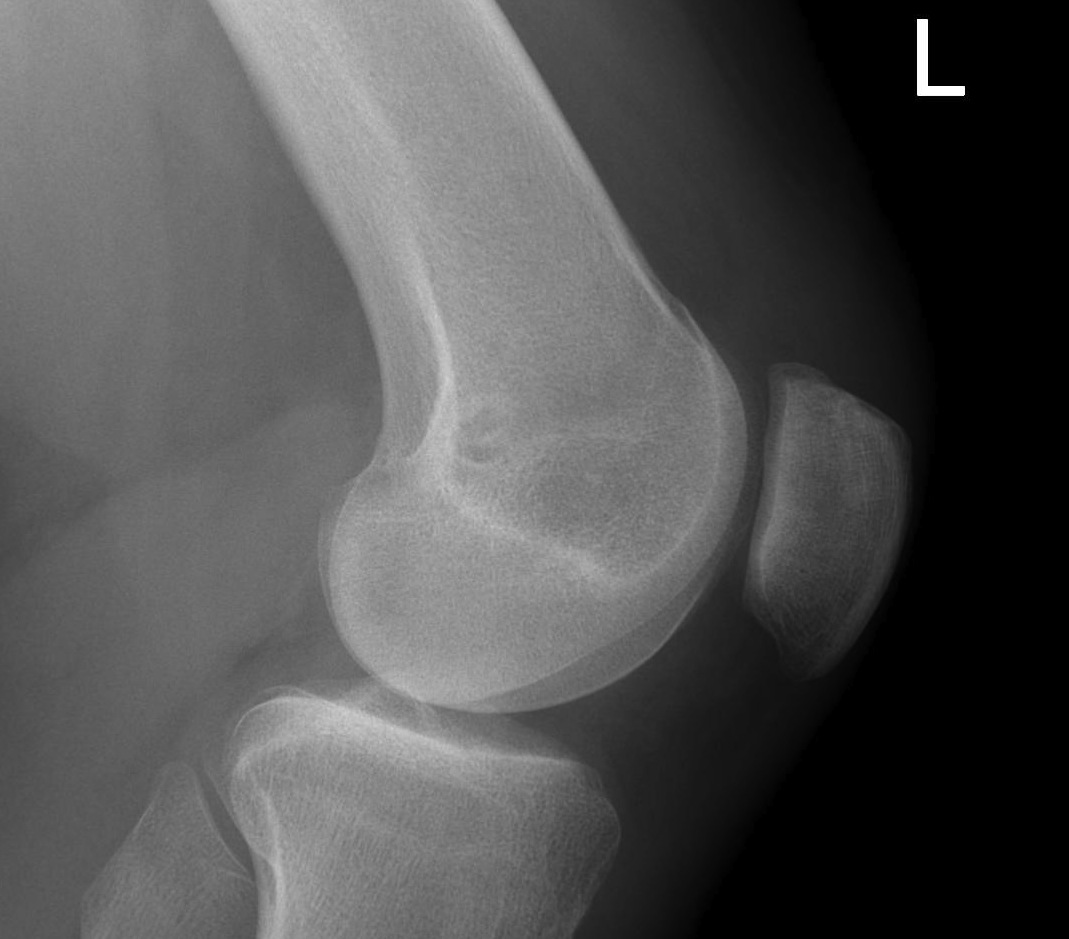
Normal
- clearly defined trochlea groove
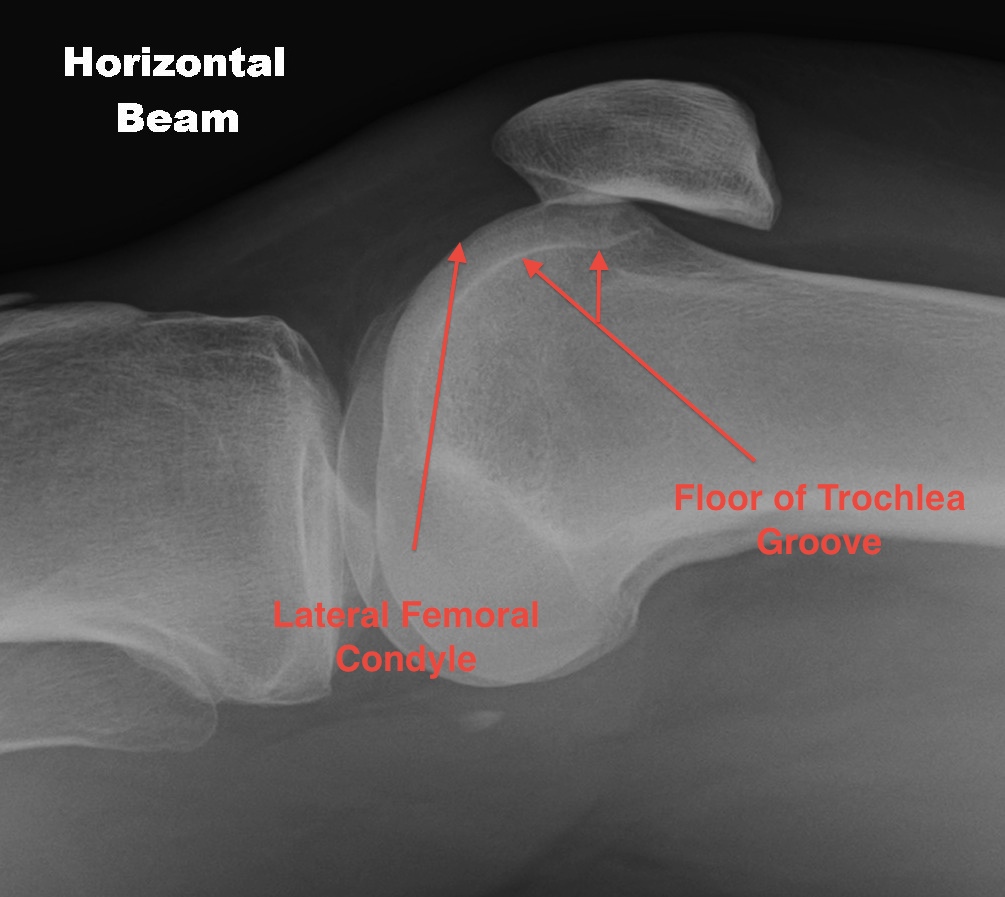
Abnormal / Crossover
- line of floor of trochlea crosses lateral lip of condyle
- indicates trochlea is deficient proximally
Trochlea depth
- < 8 mm shallow
Dejour grading system 1 - IV
Patellofemoral view
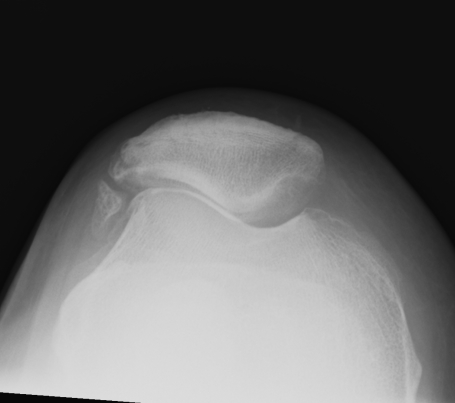
1. Skyline view
Technique
- 45o
- shoot throught film
Look for
- OCD
- bony avulsion MPFL
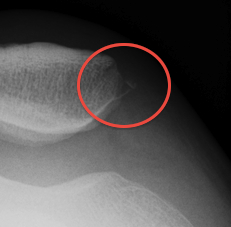
2. Laurin view / patella tilt
Technique
- knee 20o, camera at bottom
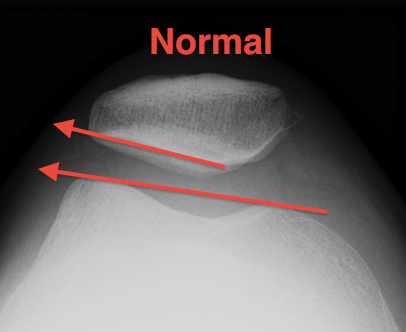
Assessment patella tilt
- first line anterior aspect both condyles
- line lateral facet
- should diverge laterally
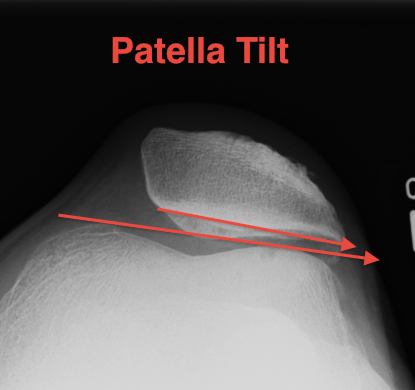
Patella tilt
- lines parallel or open medially
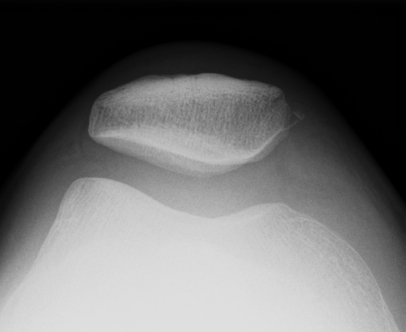
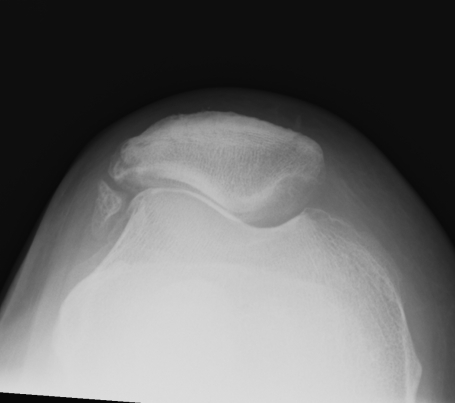
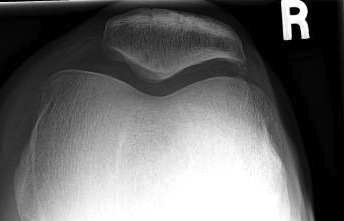
3. Merchant view / patella subluxation
Technique
- 40o flexion, beam from top
- patella should be well engaged
- central ridge should lie at or medial to bisector of the trochlea groove
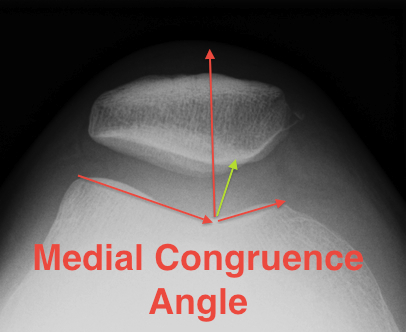
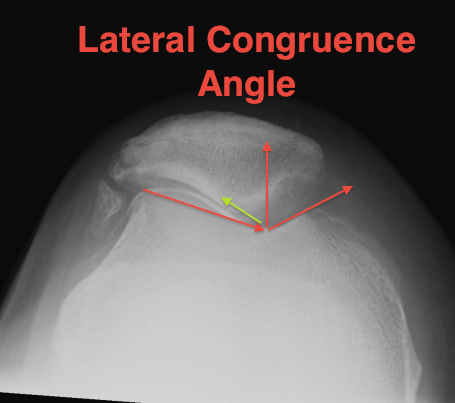
Congruence angle
- draw sulcus angle
- bisector of sulcus angle
- line to central ridge of patella
- should be - 10o (i.e. medial)
- lateral direction is positive
Normal
Subluxed
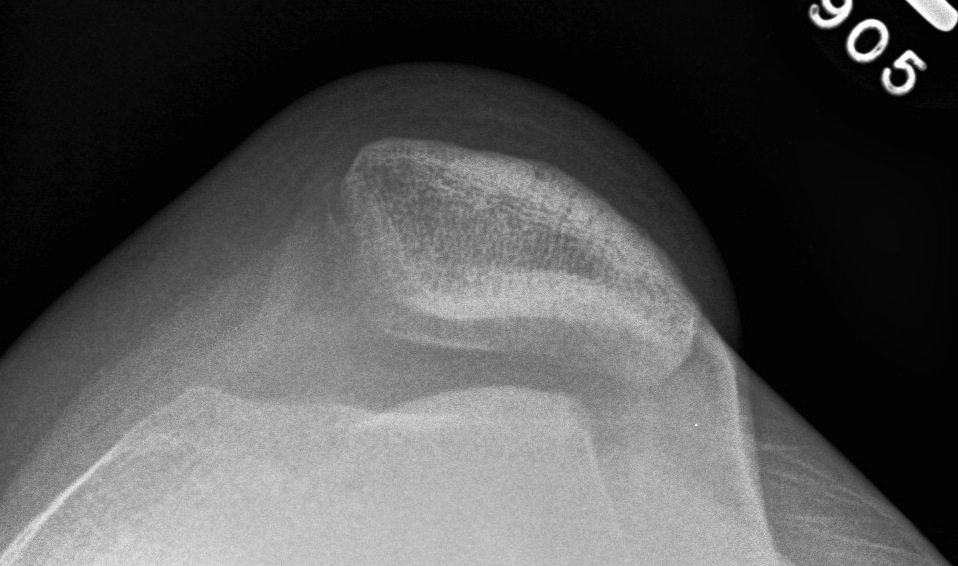
4. Trochlea dysplasia
Normal

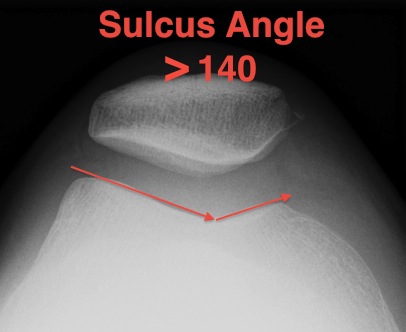
Sulcus angle
- > 140o flattened
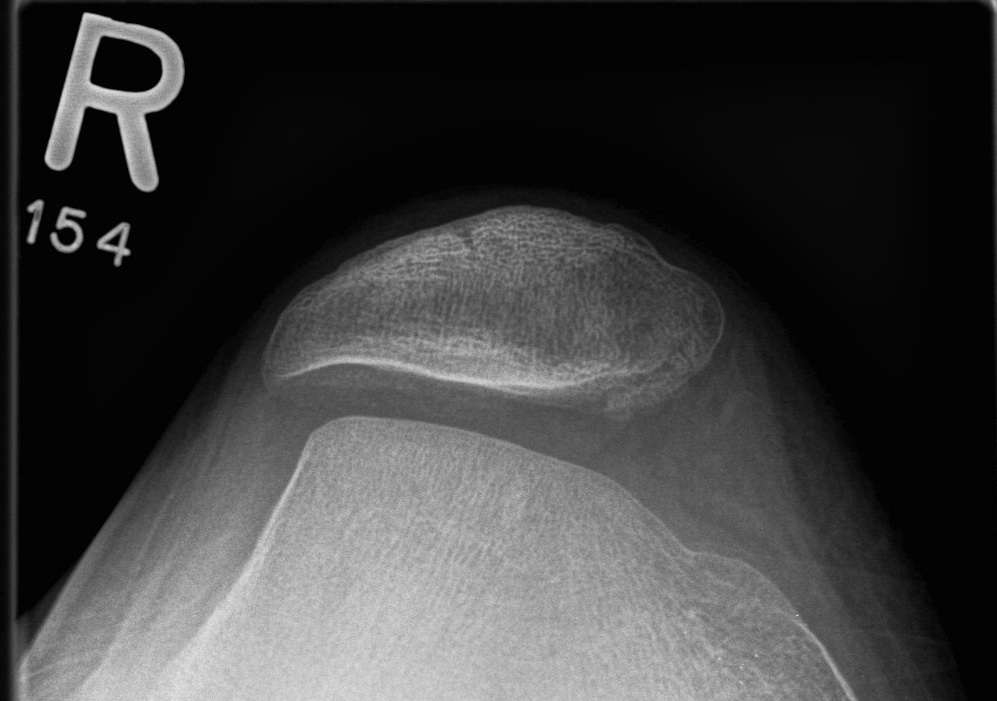
5. Excessive Lateral Pressure Syndrome
Ficat and Hungerford
A. Indirect signs of excessive lateral pressure
- thickened subchondral plate
- increased density lateral facet
- lateralisation of trochlea
- medial facet osteoporosis
- hypoplasia lateral condyle
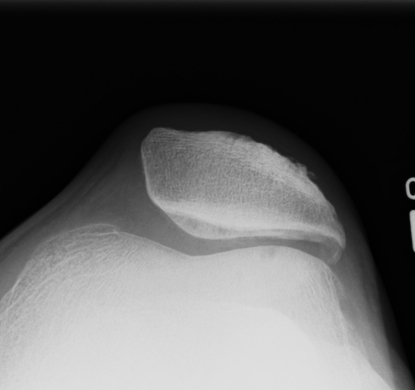
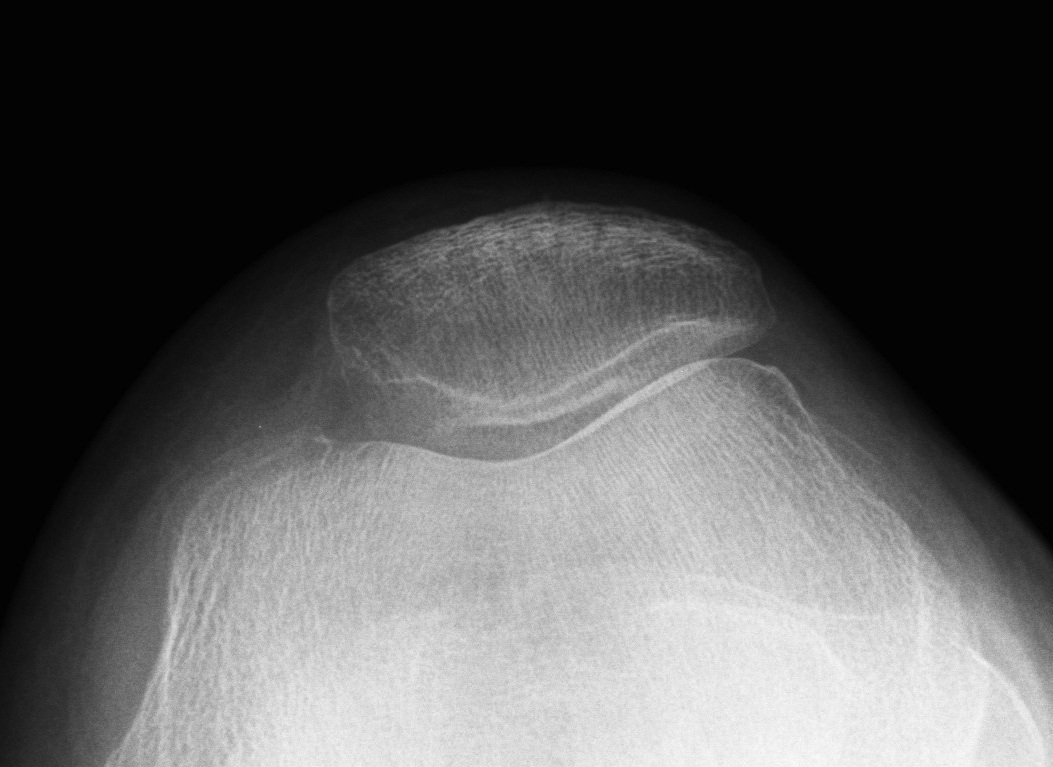
B. Indirect signs of excessive lateral ligament tension
- fibrosis lateral retinaculum
- calcification lateral retinaculum
- lateral osteophyte
- bipartite patella
- lateral facet hypoplasia
- medial compartment hypoplasia
CT
1. Skyline View
Assess for
- lateral tilt
- subluxation
- trochlea dysplasia
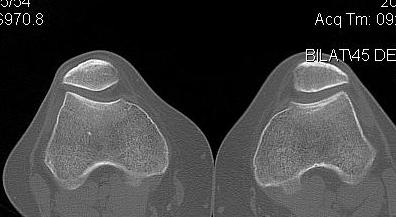
2. Lateralisation of tibial tuberosity
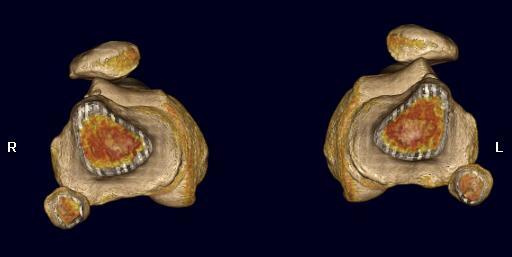
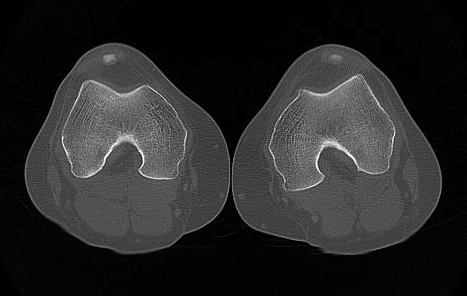
Jones et al Skeletal Radiology
Superimpose 2 axial slices
A. Axial slice of trochlea
- line of posterior condyles
- line perpendicular through trochlea
B. Slice through tibial tuberosity
- perpendicular line through TT
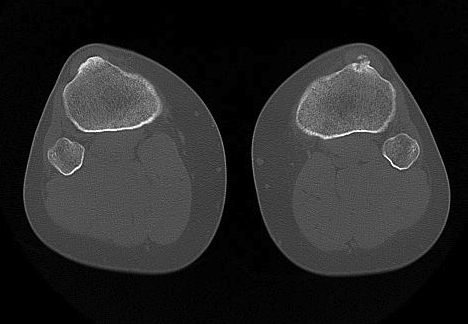
Calculate Distance between two points / TTTG
10 - 15 mm normal, > 15 abnormal
Pandit et al Int Orthop 2011
- normal 10 +/-1 on MRI
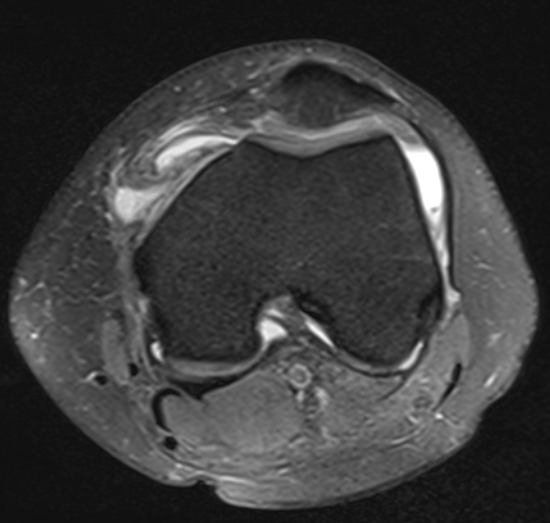
MRI
Articular Cartilage Damage
MPFL integrity
OCD
Loose Bodies
Arthroscopy
Assess chondral surfaces
Removal of Loose Bodies
Tracking
- not particularly valid
- patient is relaxed / knee filled with fluid
