Definition
Hyperextension of MTPJ and PIPJ / DIPJ flexion
- usually all toes affected
DDx
1. Complex hammer
- hammer toe with MTPJ extension
- hammer usually affects second toe
2. Curly toe
- normal MTPJ
- flexed PIPJ and DIPJ
Associations
Cavus foot
Compartment syndrome
Diabetic neuropathy
Rheumatoid arthritis
Pathology
Imbalance between intrinsics and extrinsics
- intrinsic weak (MCPJ flexion and IPJ extension)
- extrinsics strong
MTPJ
- extension strong
- flexion weak
IPJ
- extension weak
- flexion strong
P1 subluxes dorsally
- it pushes the MT head plantar-ward
- leading to metatarsalgia
Cavus foot
- claw occurs not only due to intrinsic weakness but because of plantar flexed MT's
- lead to dorsiflexion at MTPJ's
- results in flexion of IPJ's as seen above
- If claw flexible may correct if reduce MT's
History
Pain & callosities under MT heads (metatarsalgia)
Examination
Hindfoot
- cavus
- coleman block
Forefoot
- characteristic deformity
Calluses
- dorsum PIPJ
- bleow MTPJ
Mobile or fixed of MTPJ / PIPJ crucial
Flexible
- claw disappears with ankle PF
- returns with DF ankle (tight long flexors)
Cavus foot
- when DF to correct MT claw actually improves (tight plantar fascia)
Management
Non-operative
Extra width and depth toe box shoe
MT dome
Operative
Significant deformity of the hindfoot ± a cavus foot should be addressed first if symptomatic
Surgical Algorithm
1. Flexible Deformity PIPJ / MCPJ
Girdlestone Taylor FETT
- divide FDL in two and suture dorsally over P1
- +/- Extensor tenotomy & Dorsal MTPJ capsulotomy
2. Fixed PIPJ Deformity / Flexible MCPJ
A. Du Vries Excisional Arthroplasty PIPJ
- resection of head & neck of P1
- stabilise with K wire
- aiming for fibrous union
- ROM 15o
B. Extensor tenotomy + PIPJ Fusion
+/- Dorsal MTP capsulotomy MP joint
3. Fixed PIPJ / MCPJ
PIPJ arthrodesis + Extensor tendon tenotomy
+ dorsal MTPJ capsulotomy
+ MT neck osteotomy
4. Great toe involved
Jones procedure
- arthrodesis of IPJ
- EHL to MT neck
Metatarsal options
Persistent MTPJ DF main cause of failure
Options
1. Excision of MT head (Keller's)(RA)
2. Distal metatarsal oblique osteotomy (Weil)
3. Hibbs (if from cavovarus)
Techniques
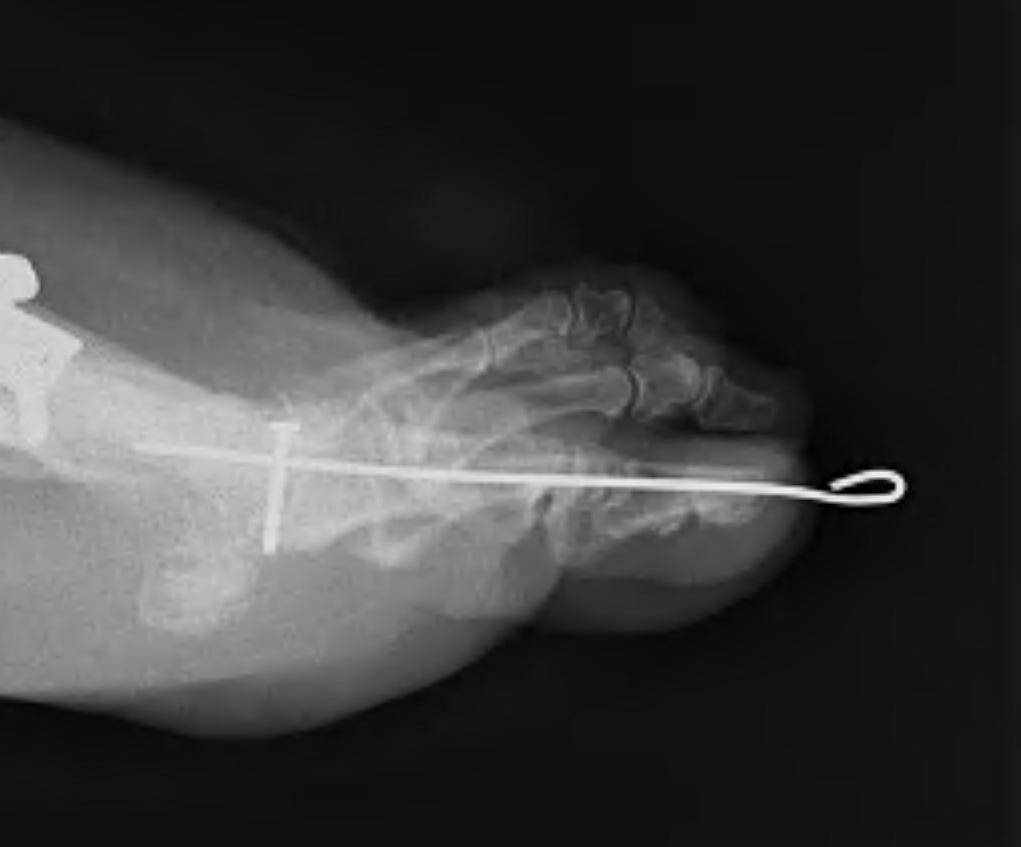
1. FETT Technique / Modified Girdlestone Taylor
A. Release FDL distally / divide into two
- 2 plantar incisions P2 and P3
- transverse incision plantar aspect P3
- divide FDL, protect NV bundles
- transverse incision plantar aspect P2
- harvest FDL and split in two
- can do single longitudinal plantar incision
B. Pass FDL over plantar aspect P1
- dorsal incision over P1
- place clamp each side of hood
- don't trap digital nerve
- bring tendon through incision slot in extensor tendon over P1 on each side
- if over P2 will not work
- toe placed in approximately 20 degrees of plantar flexion at the MTP joint
- suture to each other & ED
- if varus or valgus take whole FDL either side
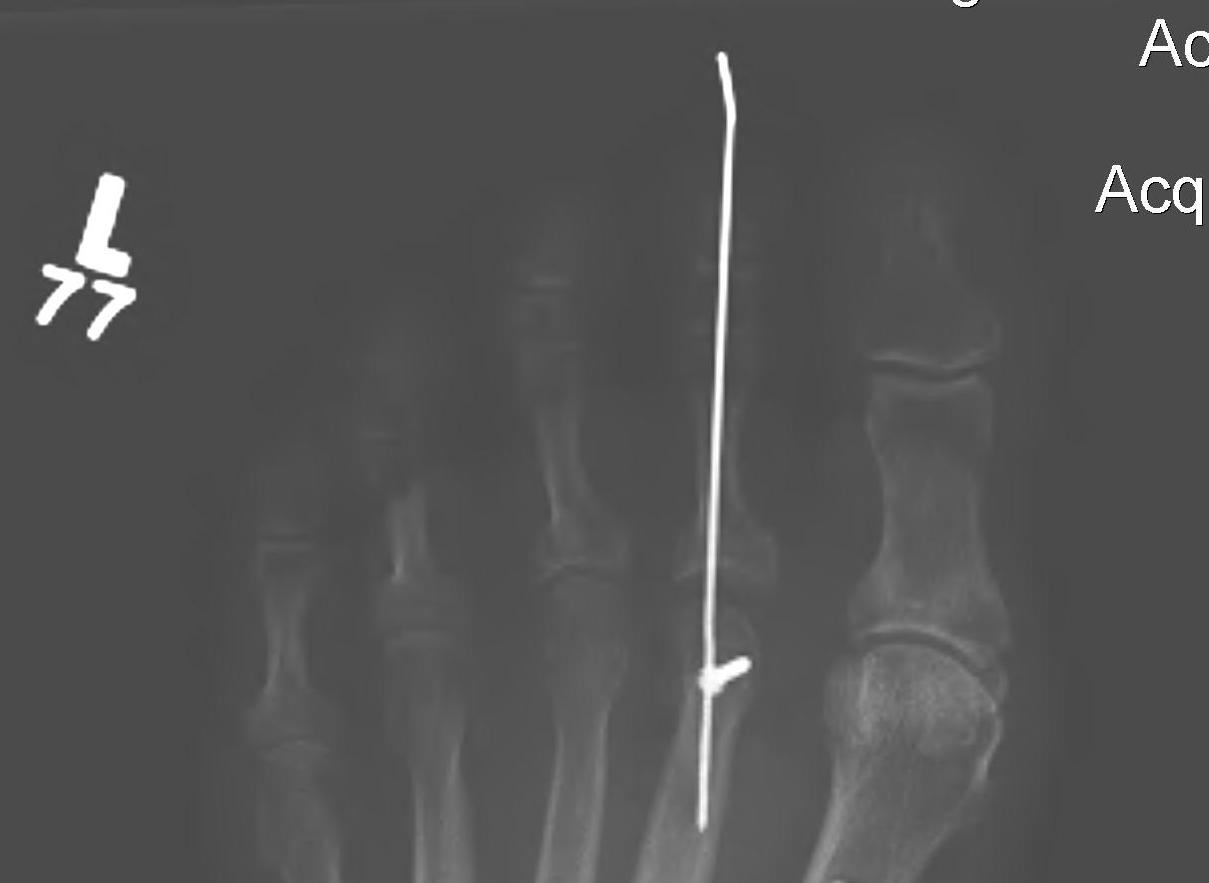
2. PIPJ fusion
Principles
- important to shorten the toe
Technique
- Ellipse of skin excised over dorsum PIPJ
- Extensor tendon taken in the ellipse
- release the collaterals so that P1 subluxes into operative field
- elevate volar plate off P1
- bone cutters to resect P1 condyles
- resect base P2
- retrograde K wire out through P2 and P3 first
- back through P1, rest against subchondral bone
- bend wire over and tape
Risk
- check blood supply at end of case
- if problematic
- release dressings / warm / increase BP
- can use antispasmodic
- will usually reperfuse over 5 minutes
- keep patient asleep in meantime
- need to have ischaemia as part of consent
3. Weil Osteotomy
Technique
- Dorsal metatarsal exposed
- web space incisions if doing multiple toes
- homan retractors each side of MT
- saw enters at edge of articular surface dorsally
- Blade angled as low / horizontal as possible
- When osteotomy complete the MT head slides back
- Needs to slide back at least 5mm
- Then fix with screw from dorsal to distal plantar
- Amputate leading edge of proximal fragment
- if have valgus or varus deformity then can correct for this