

Definition
Osteonecrosis / Avascular necrosis of metatarsal head
Epidemiology
Usually 2nd metatarsal (80%)
- occasionally third
- can occur in any
Age 10-15 years
- peak 15 year old girls
- F:M = 5:1
- occurs during the growth spurt at puberty
Bilateral < 10%
Etiology
Trauma / repetitive stress interrupts blood supply to epiphysis
2nd metatarsal prone to stress fracture & AVN
- long metatarsal / fixed base / thin shaft
Systemic disorders - diabetes / SLE / hypercoagulability
Clinical
Tender enlarged metatarsal head
Pain on dorsiflexion
Limited dorsiflexion due to synovitis or degenerative change
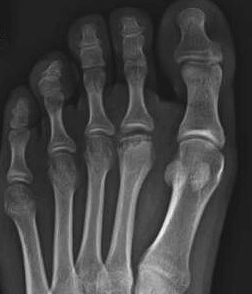
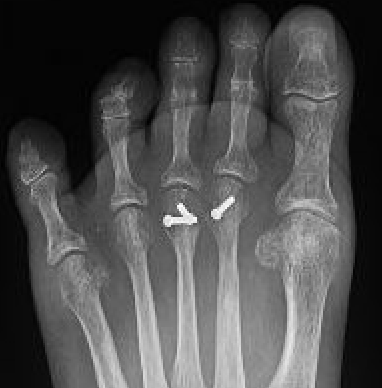
X-ray
Enlarged metatarsal head
Flattening / fragmentation / collapse



Smillie Classification
Stage 1 - normal xray, MRI positive
| Stage II | Stage III | Stage IV | Stage V |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Slight widening of joint space Sclerosis of epiphysis |
Flattening of epiphysis
|
Fragmentation of epiphysis Multiple loose bodies |
Osteoarthritis |
 |
 |
 |
 |
MRI
Non-operative management
Limit activities
Metatarsal bar / premetatarsal dome to unload MT head
Avoid high heels
Consider moonboot to reduce symptoms
Operative management
Options
Debridement
Osteotomy
- dorsal closing wedge osteotomy
- modified Weil osteotomy
Cartilage restoration procedure
- Osteochondral Autologous Transplantation (OATS)
- Autologous Matrix Induced Chondrogenesis (AMIC)
Interposition arthroplasty
Debridement
Synovectomy / osteophyte removal / removal loose bodies
Dorsal closing wedge osteotomy
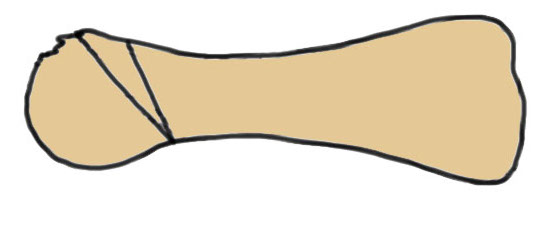
Concept
Most affected portion is dorsal
Redirects plantar articular surface
Results
Pereira et al Foot Ankle Int 2016
- 20 patients treated with osteotomy
- mean follow up 23 years
- 80% excellent, 20% good results
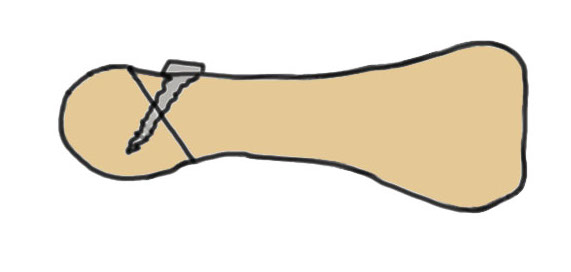
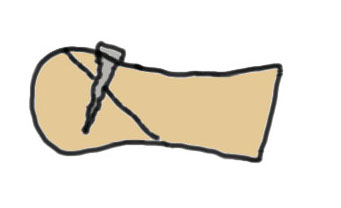
Modified Weil osteotomy

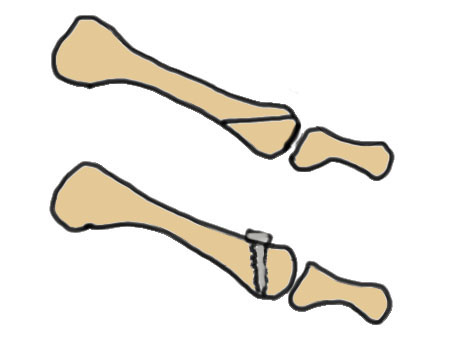
Modification
Take wedge of bone out dorsal
Dorsiflex metatarsal head

Results
Kim et al Clin Orthop Surg 2012
- Weil osteotomy for 20 cases Freibergs
- 95% good or excellent
Osteochondral Autologous Transplantation (OATS)
Indication
Focal osteochondral defect


Donor site
Lateral trochlea of knee
Lateral articular surface talus
Results
- RCT of osteotomy v OATS
- 27 patients
- equal outcome scores
Autologous Matrix Induced Chondrogenesis (AMIC)
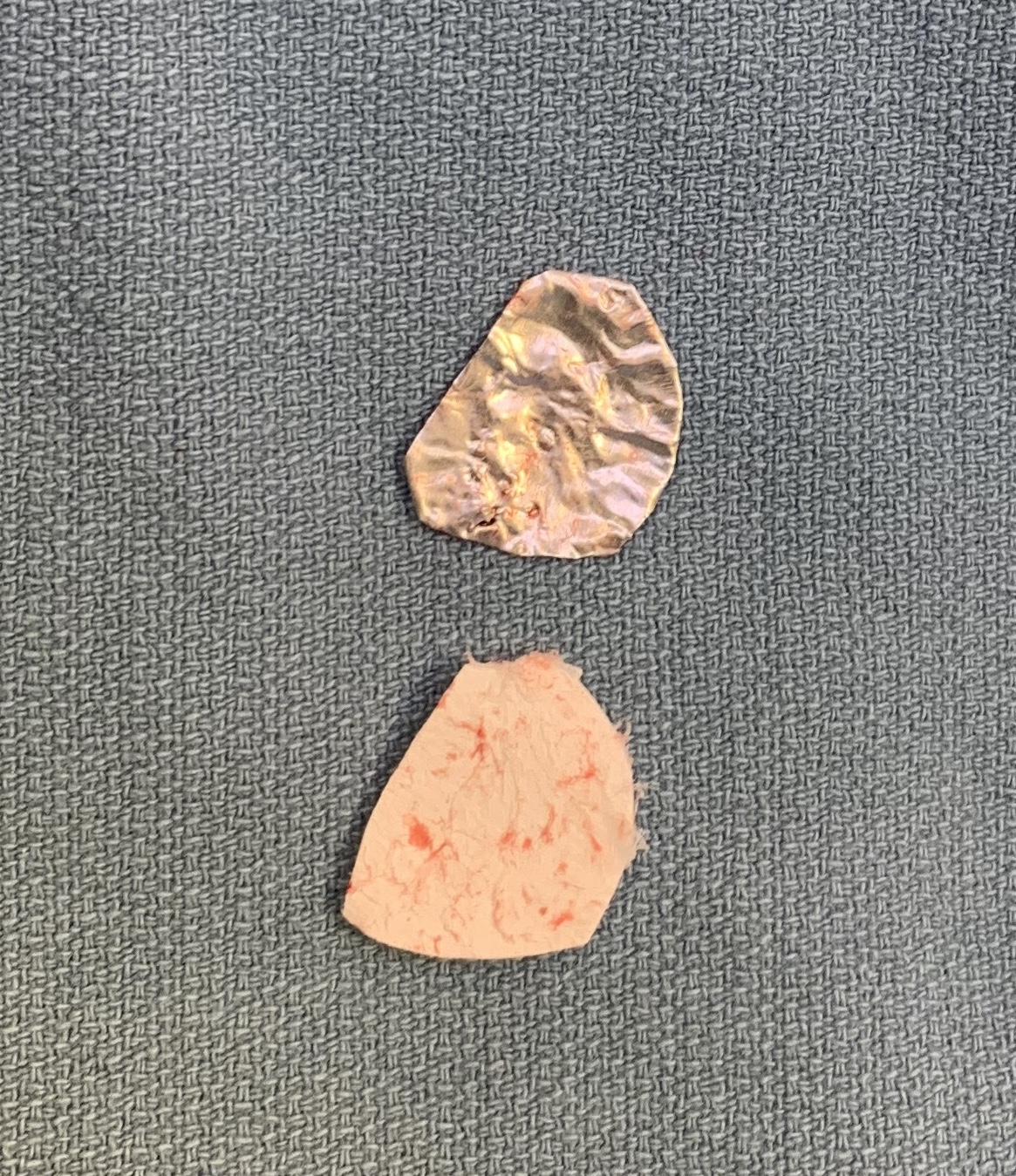

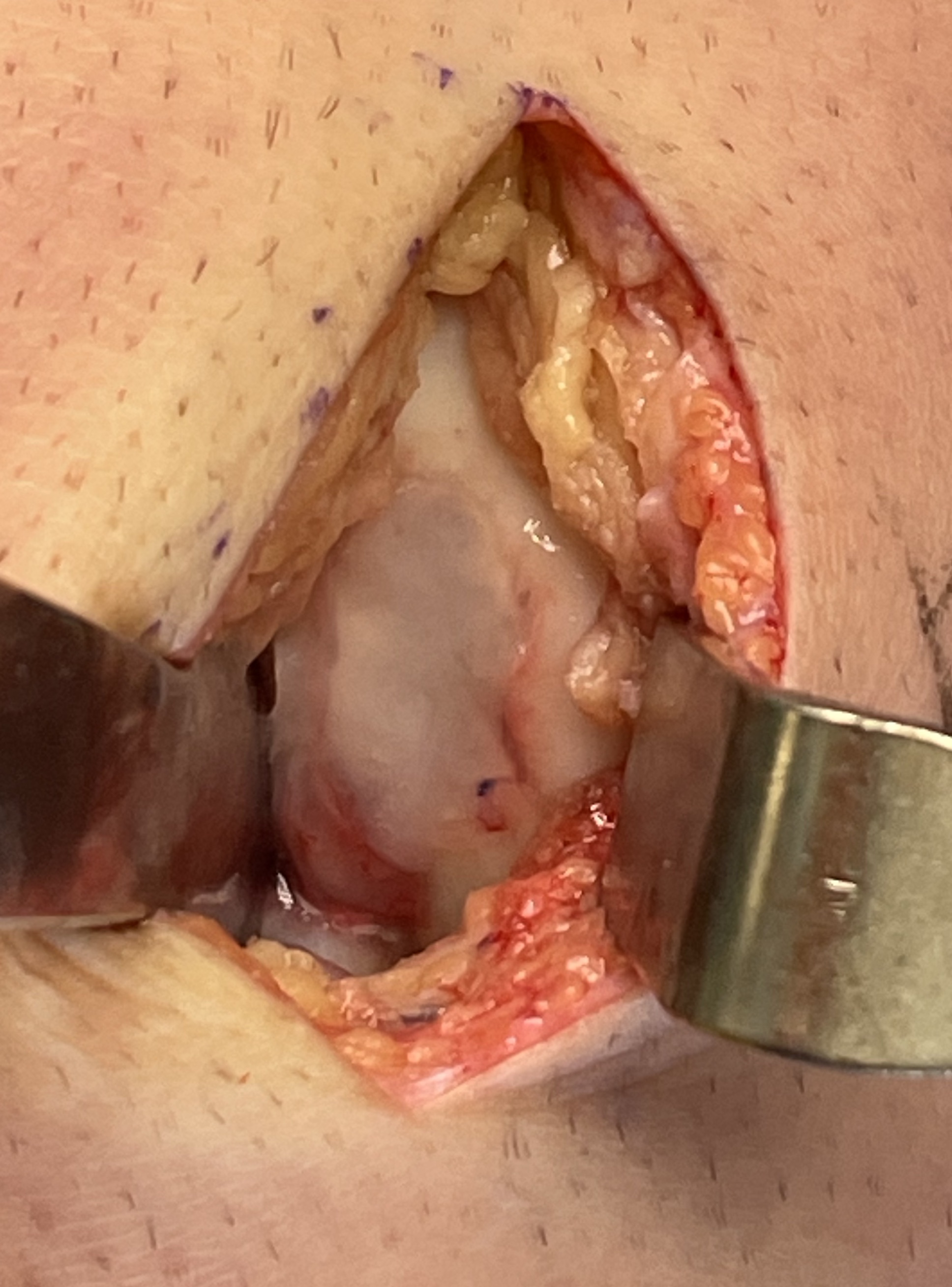
Concept
Microfracture with collagen patch
Results
Rajeev et al Foot Ankle Surg 2023
- 10 Freiberg patients treated with AMIC
- improvement in outcome scorew
Interposition arthroplasty
Results
Cevik et al Foot Ankle Int 2020
- 24 cases advanced stage Freibergs
- interposition arthroplasty with EDB tendon
- 9 very satisfied, 12 satisfied, 2 moderately satisfied, 1 dissatisfied



