Definition 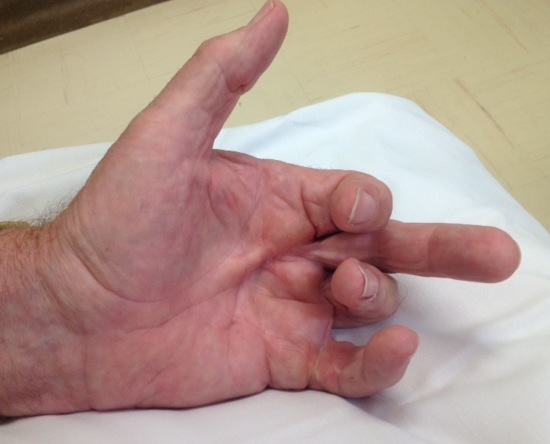
Palmar Fibromatosis
Aetiology
AD with variable penetration
Pathogenesis
Murrell's Theory of Pathogenesis
1. Microvascular ischaemia
2. Leads to conversion of
- ATP to Hypoxanthine
- Endothelial Xanthine Hydrogenase to Xanthine Oxidase
3. Xanthine Oxidase converts Hypoxanthine to Uric Acid
- gives off OH-
4 OH- releases Free Radicals
- stimulate fibroblast proliferation & increased Type III Collagen
5 Fibroblasts strangle microvessels
- Vicious Cycle
Luck's three stages of Dupuytren's contracture
1st stage (proliferative) stage
- increased cellularity
- number of large myofibroblasts
2nd (involutional) stage
- dense myofibroblast network aligned to long axis of collagen bundles
- the ratio of Type III collagen to Type I collagen is inc
3rd (residual) stage
- myofibroblasts disappear
- fibrocytes are dominant cell type
- dense collagen cord remains
Myofibroblasts
Cell of origin for the nodular myofibroblast is unknown
- fibroblast / smooth muscle cell / pericyte
- Contractile cell
- nodules composed of myofibroblasts
- No myofibroblasts in cords
Dupuytren's diathesis
Aggressive early-onset form of the disease which involves the multiple areas
- usually have family history
- disease recurs rapidly following treatment
Feet (Ledderhose, 1897)
Penis (Peyronie)
Garrod knuckle pads on dorsum PIPJs
Associations
Chronic alcoholism
- ? metabolic effect on fat and prostaglandin metabolism
Diabetes mellitus
- may be related to the diabetic microangiopathy
Epilepsy
- likely effect of antiepileptic drugs on collagen metabolism
Smoking
Chronic pulmonary disease
Occupational hand trauma
- controversial
- probably only aggravation due to traumatizing an early nodule
Epidemiology
Age 50-70
Male 7:1
Caucasians
- especially celtics / vikings heritage
- rare in blacks & asians
Anatomy
A. Involved anatomy
1. Pre-tendinous Bands
- part of the palmar aponeurosis in palm
- common site of disease
- palpable nodule is pathognomonic of Dupuytren's
2. Spiral Band
- continuation of pre-tendinous band into finger
- spirals deep to NV bundle then becomes superficial to bundle
3. Natatory Ligament
- pass between the web spaces
- frequently diseased and prevents abduction
4. Lateral Digital Sheet
- condensation of superficial fascia on either side of the finger
- receives fibres from the natatory ligament, spiral band, Grayson's and Cleland's ligaments
5. Grayson's Ligaments
- hold skin during flexion and extension
- pass from fibrous tendon sheath to the lateral digital sheet
- volar to the NV bundle
- almost always involved in Dupuytren's
B. Not involved anatomy
Skoog's fibres
- transverse palmar fibres
- run from flexor sheath to flexor sheath at the level of the A1 pulley
- the nerve is always deep to the fibres
- part of palmar aponeurosis
- deep to pre-tendinous band
- don't become diseased
Cleland's Ligaments
- hold skin during flexion and extension
- firm fascial structures
- pass from the side of the phalanges to the skin
- dorsal to the neurovascular bundle
- involved in Dupuytren's only through mingling with the lateral digital sheet
MEM: Dave Christie Goes Volar
(Dorsal Cleland's, Grayson's Volar)
Site
LF / RF most commonly affected
MF / IF are sometimes affected
1st web sometimes affected
Pathology
5 Major Pathological cords
1. Pretendinous cord
In palm / other 4 in finger
- diseased pretendinous band
- causes MCPJ deformity
2. Central cord
Diseased central fibrofatty tissue
- large nodule often present in cord just proximal to PIPJ
- causes PIPJ deformity
3. Spiral cord
Pathological spiral band
- usually connects to the P2 (bone and tendon sheath)
- displaces neurovascular bundle volarly
Difficult to predict presence
- associated with more severe contractures
4. Lateral Cord
Diseased lateral digital sheath
- intimately adherent to skin (sharp dissection required)
- contributes to DIPJ +/- PIPJ
5. Natatory Cord
Diseased Natatory ligament
- causes web contracture
3 Minor Cords
1. Retrovascular Cord
Involves longitudinal fibers dorsal to the bundle
- commonly seen in combination with other cords
- causes DIPJ extension with lateral cord
2. Abductor Digiti Minimi Cord
Cord arises from abductor digiti minimi
- from MT junction
- to ulnar side of the base of P2
- commonly adheres to the lateral skin
3. Intercommissural Cords / 1st Web
Pathological changes in
- pre-tendinous band (radial longitudinal fiber)
- superficial transverse fibers of the palm (proximal transverse commissural ligament)
- the first web natatory ligaments (Grapow's ligament)
Contractures
1. PIPJ Contracture
4 components
- Central cord
- Spiral cord
- Lateral cord
- Retrovascular cord
Correction sequence
- resection pathological cords
- capsulotomy, release check rein ligaments
- release of accessory collateral ligaments performed
- release of volar plate
2. MCPJ Contracture
Always correctable by removal of central band
- Flexion deformity does not lead to collateral shortening
3. DIPJ Hyperextension
Occurs in advanced disease
- contracture of retro-vascular + lateral cord
History
Usually mildly painful nodules to begin
- palm of RF and LF rays
- very short lived
Severe night pain
- suspect fibrosarcoma
Progressive contracture of MCP, then PIPJ
- nodule over PIPJ warning of impending PIPJ contracture
Difficulty putting hands in pockets
- difficult gripping
- poke themselves in the eye
Diasthesis
- foot, penis
Examination
Nodules / dimples / pits
- palm, fingers
Contractures
- MCPJ
- PIPJ
- DIPJ extension
- web space contractures / natatory cords
PIPJ Contracture
- Examine PIPJ with MCPJ flexed
- eliminate effect of cord
- establish if any joint contracture
Diasthesis
- feet, Garrod's pads
Hueston Table Top Test
- Royal Melbourne hospital
- palm down on table
- positive if can slide pen under
- MCPJ contracture 30-40o
