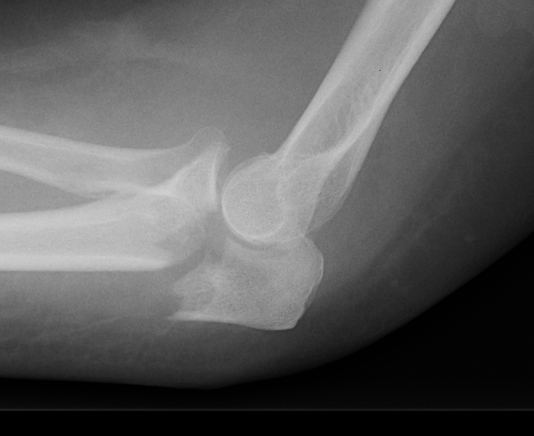
Definition
Intra-articular proximal ulna fracture
Anatomy
Articulates with trochlea
- may have a central bare area
Triceps insertion
- via broad aponeurosis which blends with anconeus and CEO
Management
Non operative Management
Undisplaced fracture
- need to ensure triceps mechanism is intact
- Long arm POP 3/52 in 90o flexion
Operative Management
Indications
1. Disruption of extensor mechanism
- any displaced fracture
2. Articular incongruity
Options
TBW
Plate
Excision fragment / triceps advancement
TBW Technique
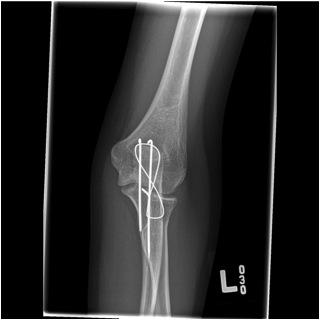
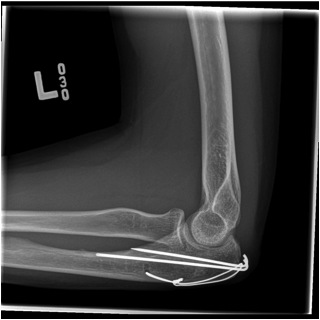
Goal
- convert the tensile distraction force of triceps into a compressive force at the articular surface
Options
- bi-cortical K wires
- intra-medullary k wires
- intramedullary screw
Contraindication
- fracture distal to centre of rotation / midpoint of trochlea notch
- highly comminuted fractures
- oblique fractures
- best to use plate in these situations
Technique
- lateral decubitus over bolster
- curvilinear incision to avoid prominence of olecranon
- clean and washout haematoma
- reduction (extend elbow to defunction triceps / place bone forcep)
- 2 x IM k wires (no need to bite anterior cortex / risk nerve injury)
- drill hole in ulna, pass 20 gauge wire
- form figure of 8 wire about wires, can pass under triceps
- twist via 2 knots
- bury end of K wires under triceps
Screw / TBW
Beware bow of proximal ulna
- may cause medial shift
- avoid long screw
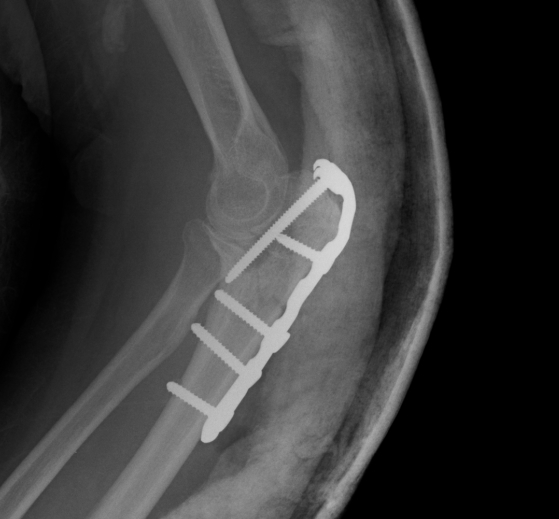
Plate
Indication
- fracture distal to centre of rotation
Main problem is hardware prominence
- precontoured low profile
- proximal hooks to grip triceps
- beware over compression articular surface in comminuted fractures
Excision fragment / triceps advancement
Indications
- elderly
- osteoporotic
- < 50% articular surface
- non reconstructable