Definition
Schwannoma - benign tumour of nerve sheath
Epidemiology
Middle age
Solitary lesion
Upper limb > lower limb
Less common than neurofibroma
Multiple
- Neurofibromatosis Type II
- Schwannomatosis
Schwannomatosis
- rare condition
- multiple schwannomas
- no manifestations of Neurofibromatosis
Clinical
Painful tender lump
Positive Tinel's sign
Paresthesia
Location
Sayed et al Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 2022
- 150 cases of schwannoma excision
- most common posterior tibial nerve and median nerve
Pathology
Usually located eccentrically within nerve
- compared with neurofibroma which are fusiform swellings of the nerve
Well encapsulated
- capsule consists of epineurium
- bulges from originating fascicles & pushes aside adjacent fascicles
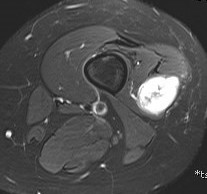
MRI
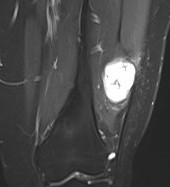

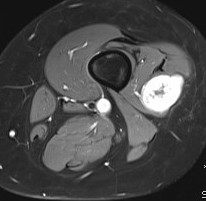
Show lesion on nerve periphery compared with neurofibroma which is in center of nerve
Differential
- neurofibroma
- schwanomma
- malignant tumour of nerve sheath
Istefan et al BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2023
- sensitivity MRI for schwannoma 85%
- specificity 50%
MRI features of nerve tumours PDF
Histology
Contain spindled Schwann cells
Arranged in alternating hypercellular (Antoni A) & hypocellular (Antoni B) regions
Stains S-100 positive
Management
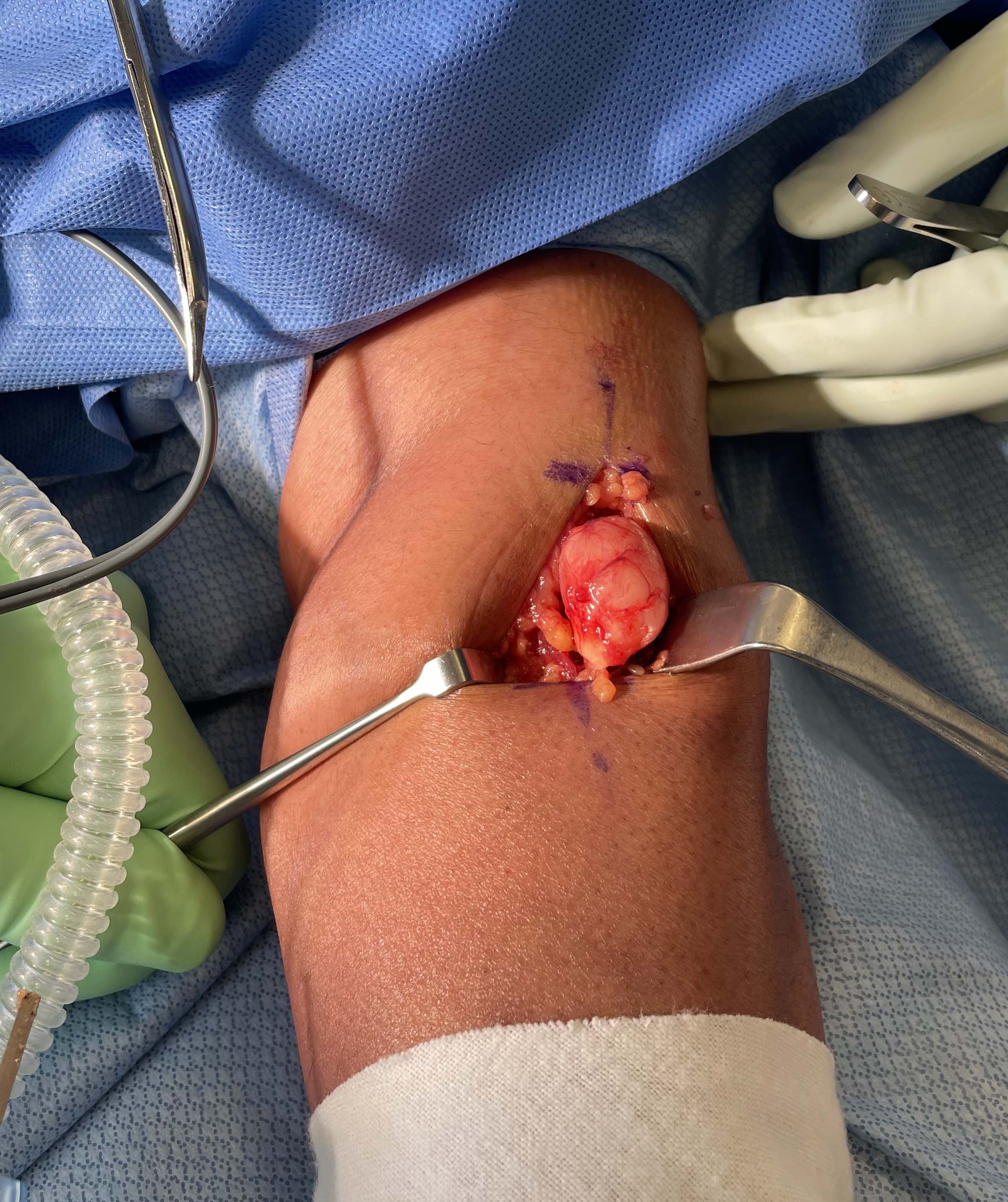
Operative excision

Enucleation / intra-capsular excision
- open epineurium and capsule
- preserve nerve fascicles
- remove schwannoma
Vumedi schwannoma sciatic nerve
Vumedi brachial plexus schwannoma
Results
Fujibuchi et al J Clin Neurosci 2017
- surgical excision of 98 schwannomas
- postoperative neurological complications in 18%
- higher risk with preoperative neurological symptoms
- higher risk with more proximal nerve lesions
- 56 cases of schwannoma excision upper limb
- postoperatively 73% had nerve injury symptoms and signs
- at 2 years 70% no neurological deficit
- 30% hypoaesthesia, paraesthesiae or mild motor weakness
