Aggressive Fibromatosis / Desmoid Tumours
Definition
Deep fibromatosis
- rare monoclonal fibroblastic proliferation
- aggressive, rapidly growing, locally invasive
Different from superficial fibromatosis
- small, slow growing
- palmar fibromatosis www.boneschool.com/dupuytrens
- plantar fibromatosis www.boneschool.com/plantar-fibromatosis
Deep / Desmoid tumours
Types
Intra- or Extra-abdominal
Primary / Sporadic
Associated with familial adenomatous polyposis / Gardener's syndrome
Epidemiology
3rd to 4th decade
Presentation
Mass
Neurological compression
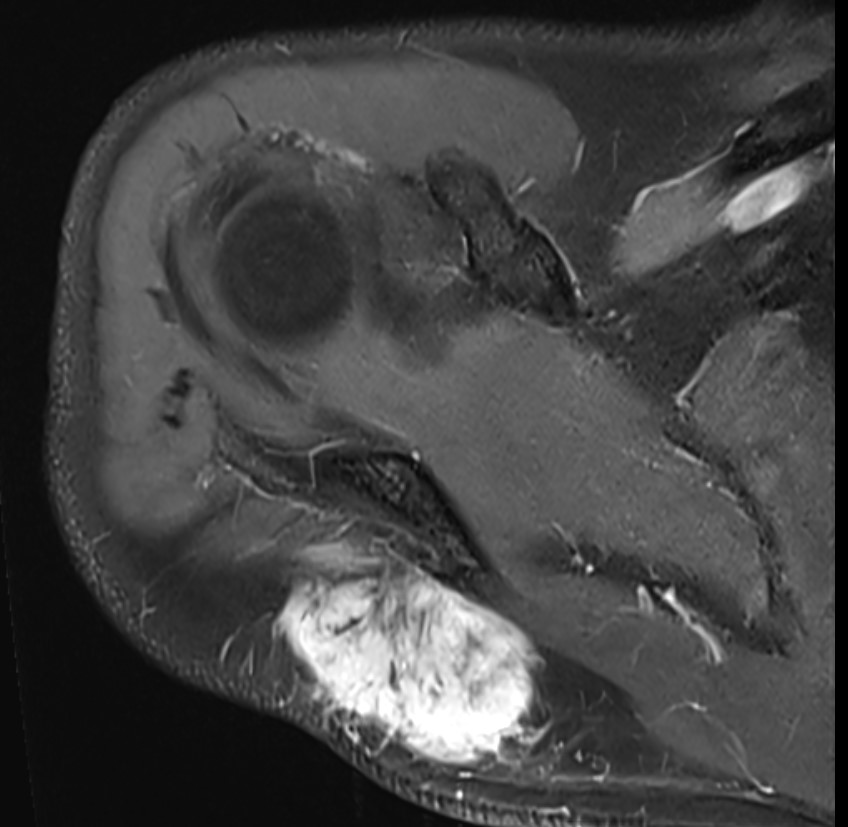
MRI
Soft tissue mass
Histology
Spindle shaped fibroblasts with plump nuclei & mildly eosinophilic cytoplasm
Management
Options
Desmoid tumour working group consensus 2018
- First line is surveillance
- Surgery if adjacent to the abdominal wall and failing surveillance
- Medical therapy if failing surveillance and not abdominal wall
- Ablation therapy (cryotherapy or radiotherapy) as an alternative to medical therapy, on a case-by-case basis
- Priority of treatment is pain control
Natural history
Bonvalot et al Ann Surg Oncol 2023
- 100 patients with desmoid tumours treated with observation
- 58% had tumour regression
- 48% had progression, with 28% requiring active treatment
Operative versus nonoperative
- 771 cases
- overall event free survival at 2 years 56%
- no difference between surgery or observation
Cryotherapy
- prospective study of cryotherapy in 50 patients with desmoid tumours
- non progressive disease in 86% with pain control and better functional status
Wide resection +/- radiotherapy
- systematic review
- local control surgery: 61%
- local control surgery + radiotherapy: 75%
- local control radiotherapy: 78%
