Definition
Hematological disease
- uncontrolled proliferation of single clone of plasma cells
- secrete monoclonal immunoglobulins
Epidemiology
10% of all hemotological diseases - cecond most common hemotological diease
Most common primary bone cancer
Median age 65 - 70
Twice as common in African Americans as in Caucasians
Pathology
Plasma cell malignancies
Genetically complex disease
- collection of several different cytogenetically distinct malignancies
- usually bone marrow of entire skeleton involved
Associated with abnormality of protein synthesis
- monoclonal M proteins (IgG,M,A,D,E) - cause hyperviscosity
- monoclonal free light chain proteins (Bence Jone proteins) - damage kidney
Morbidity due to end organ destruction
Predisease
Monoclonal Gammopathy of Unknown Significance (MGUS)
- 3% of white population > 50
- 6% of African-American population > 50
- risk of progression to multiple myeloma is 1% per year
Two Forms
1. Multiple Myeloma 95%
- disseminated disease
2. Plasmacytoma 5%
- solitary bone or soft tissue lesion
- usually axial skeleton
- usually disseminates to multiple myeloma in 5 - 10 years
International Myeloma Working Group Diagnostic Criteria
Plasmacytoma
1. Biopsy proven single osseous lesion
2. Normal bone marrow with no evidence of clonal plasma cells
3. Normal skeletal survey and MRI (or CT) of spine and pelvis
4. No end-organ damage such as hypercalcemia / renal insufficiency / anemia, or bone lesions (CRAB)
secondary to a lympho-plasma cell proliferative disorder
Multiple myeloma
Any one or more of:
1. 60% or greater clonal plasma cells on marrow examination
2. Serum involved/uninvolved free light chain ratio of 100 or greater AND involved light chains > 100mg/L
3. More than one focal lesion on MRI > 5mm in size
Location
Always spine
Common in skull, ribs, sternum and pelvis
History
Bone pain
- back / long bones / skull / pelvis
Low back pain
- worse at night
- worse supine
- resistant to simple analgesia
Fatigue / fever / night sweats
Infections
Peripheral neuropathy
Laboratory
Pancytopenia
Elevated ESR > 100
Hypercalcaemia
Chronic Renal Failure
Bence Jones Proteins in urine
- 24 hour urinalysis
- urine electrophoresis
Serum electrophoresis
- monoclonal antibody band/ M protein
- most sensitive
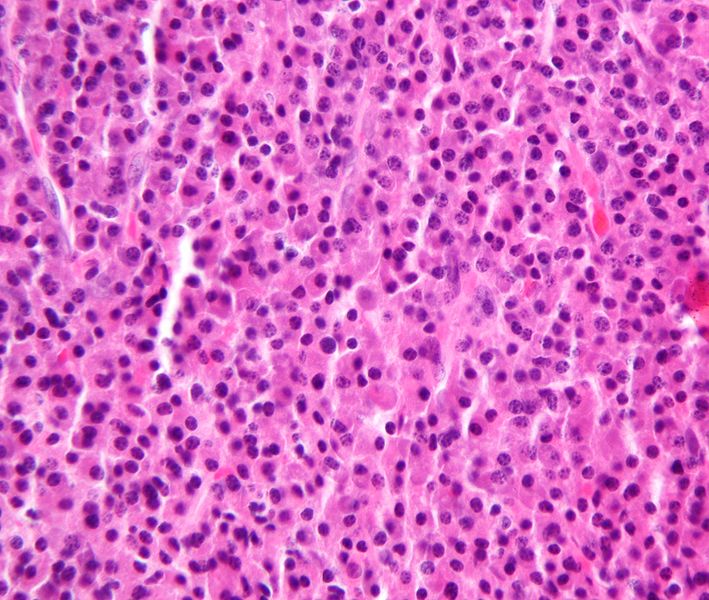
Bone Marrow Biopsy
Definitive diagnosis
Sheets of plasma cells
- clock-faced eccentric nuclei
- perinuclear clear area
- increased rER on electron microscopy
- no background stroma
Cellular atypia not prognostic
May see amyloid
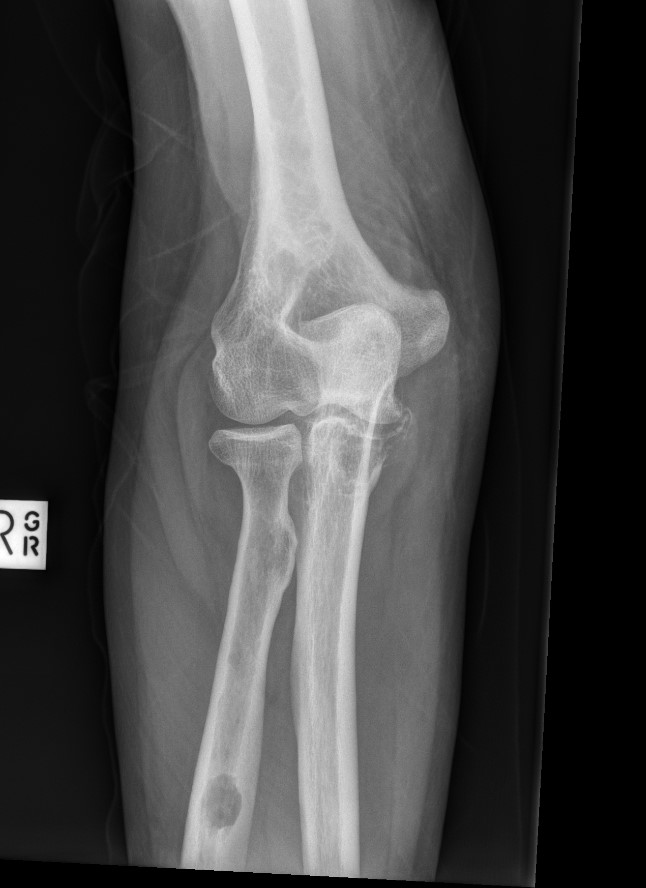
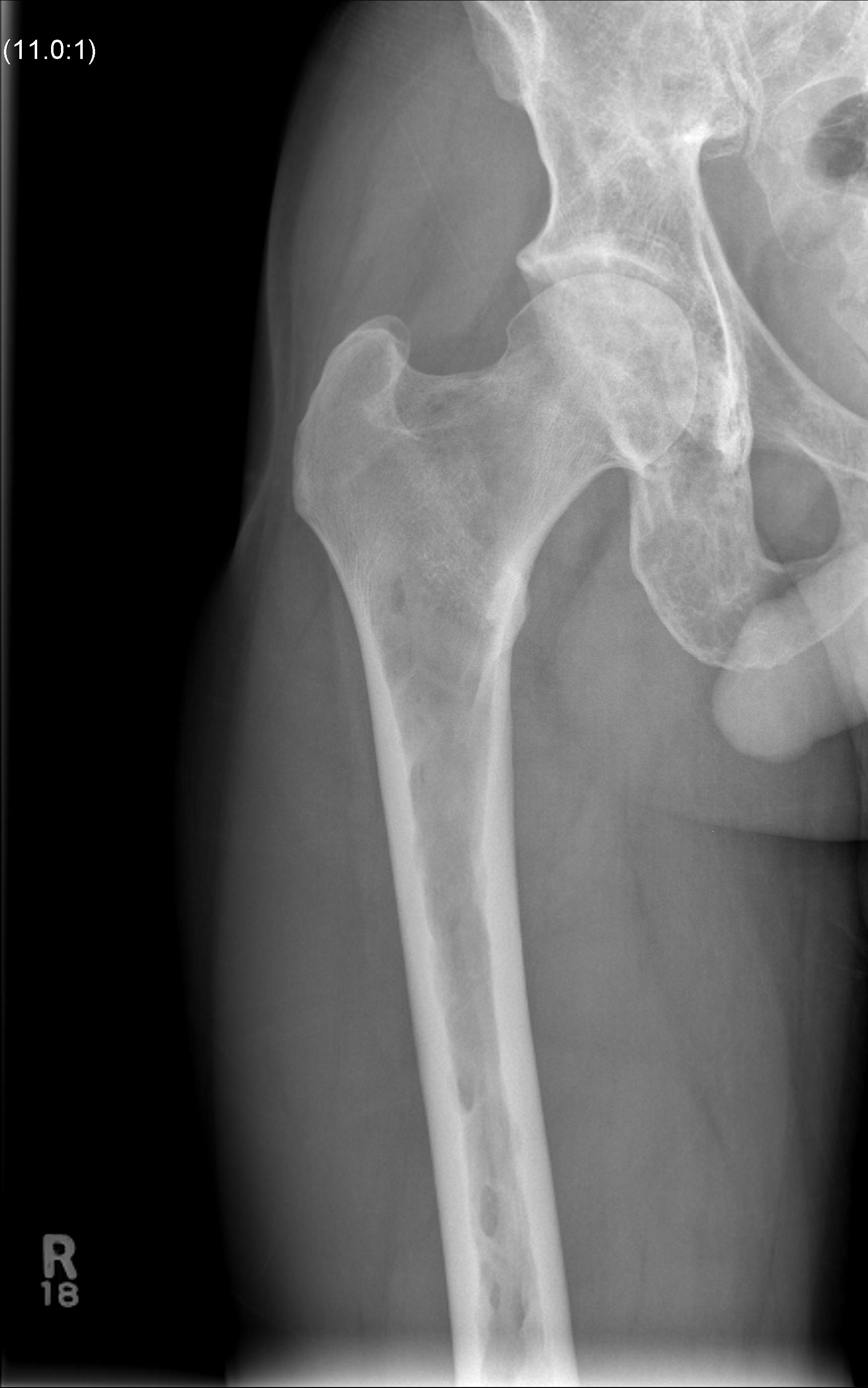
X-ray
1. Punched out lytic lesions
- axial and appendical skeleton
- widely disseminated
- soap bubble appearance
- no sclerotic reaction
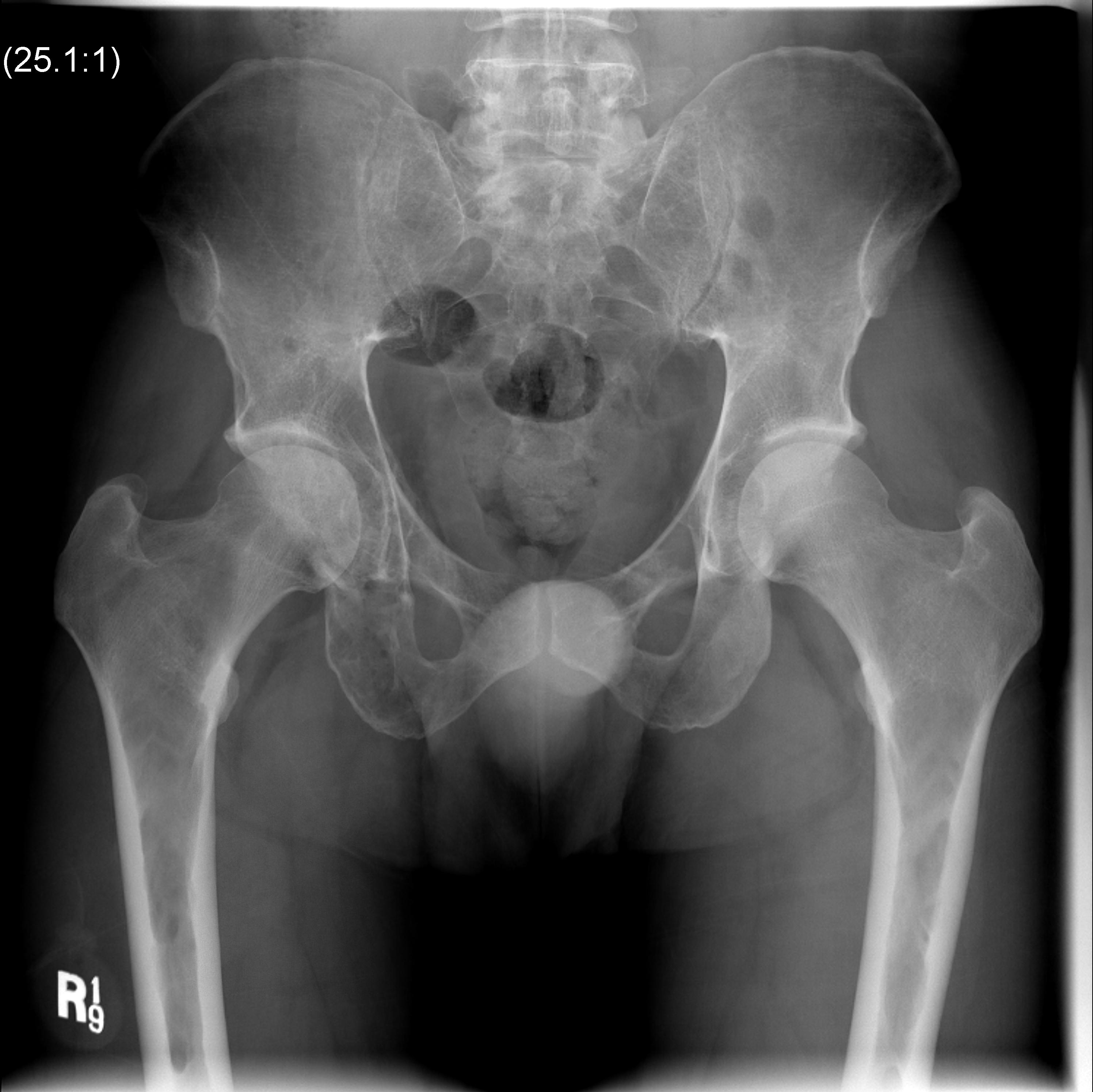
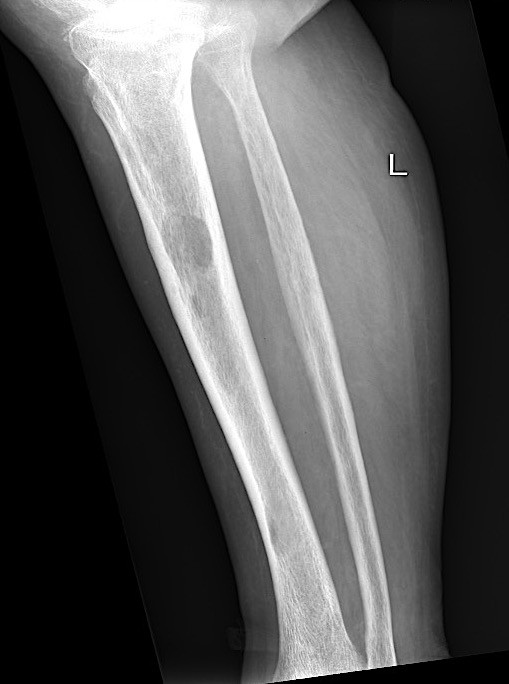
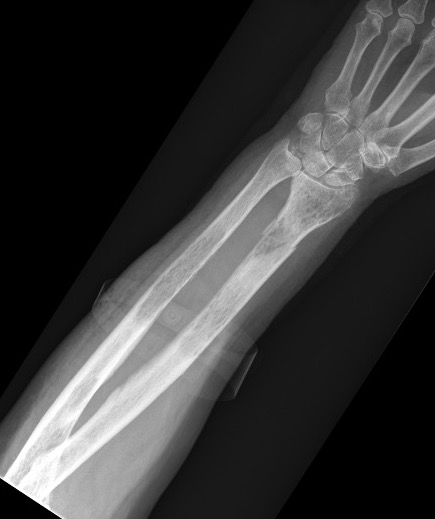
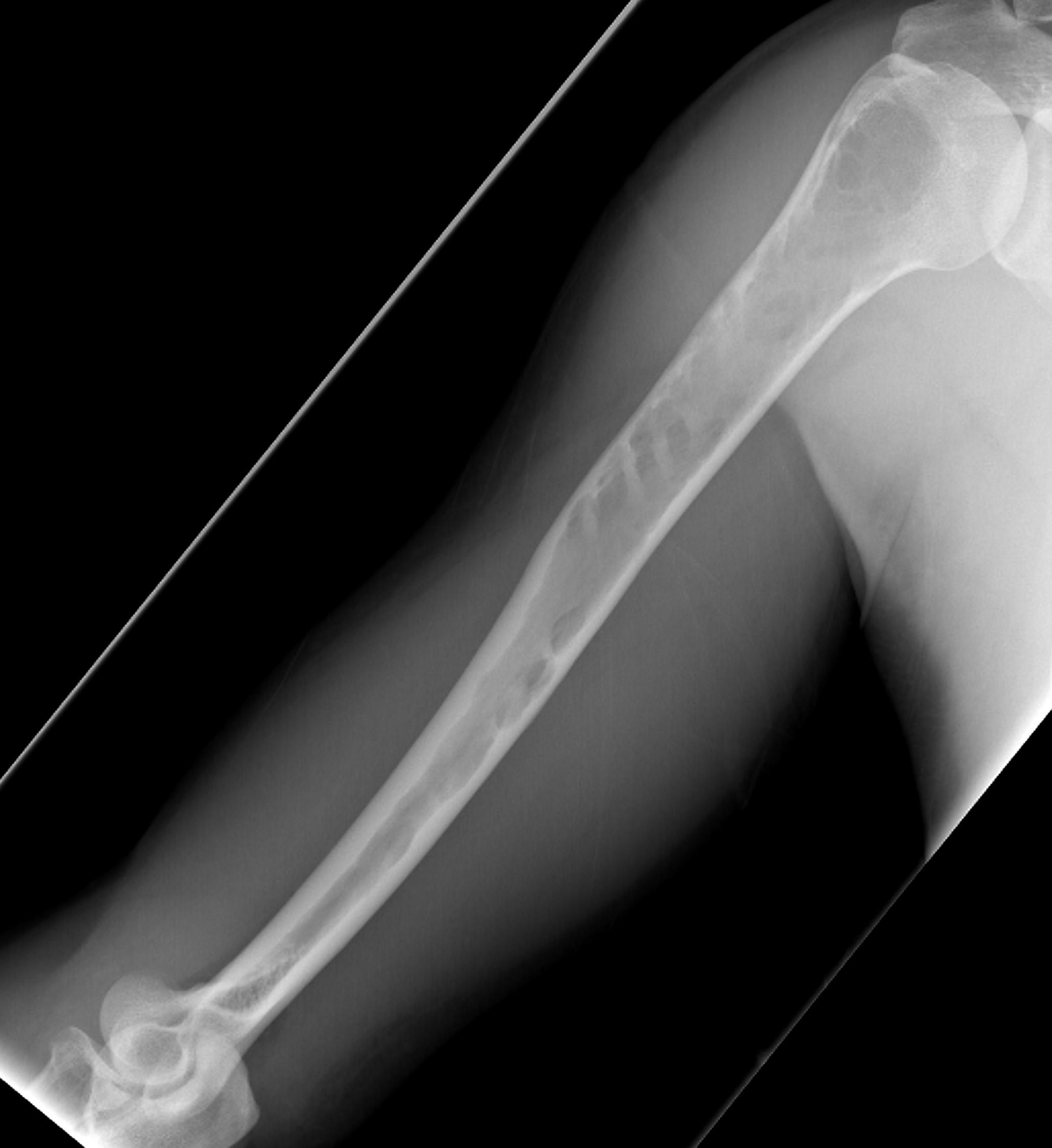
2. Diffuse osteopenia
- in 15% to 25% of patients, no discrete lysis occurs
- diffuse osteopenia and osteoporosis are the only skeletal manifestations
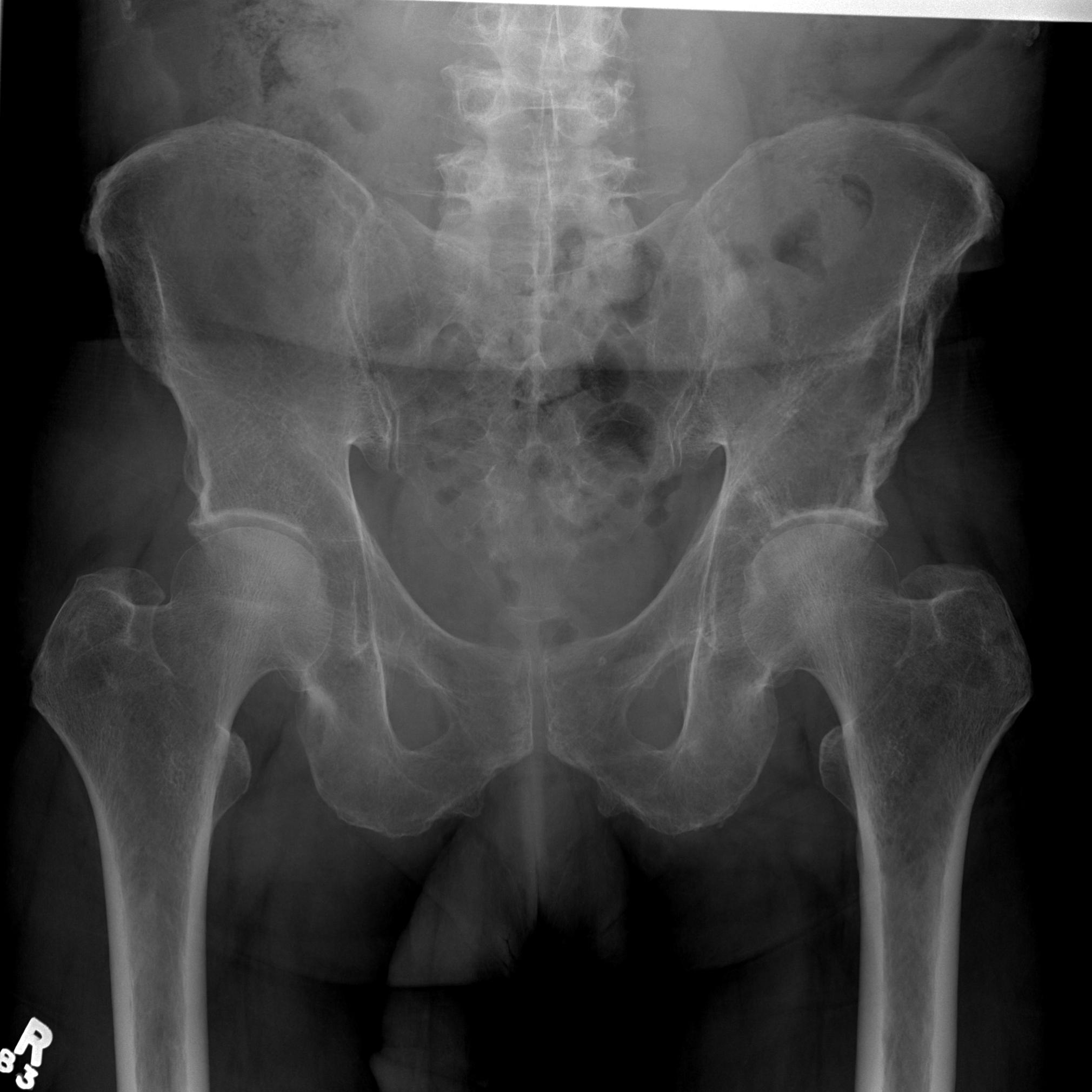
3. Vertebrae Plana
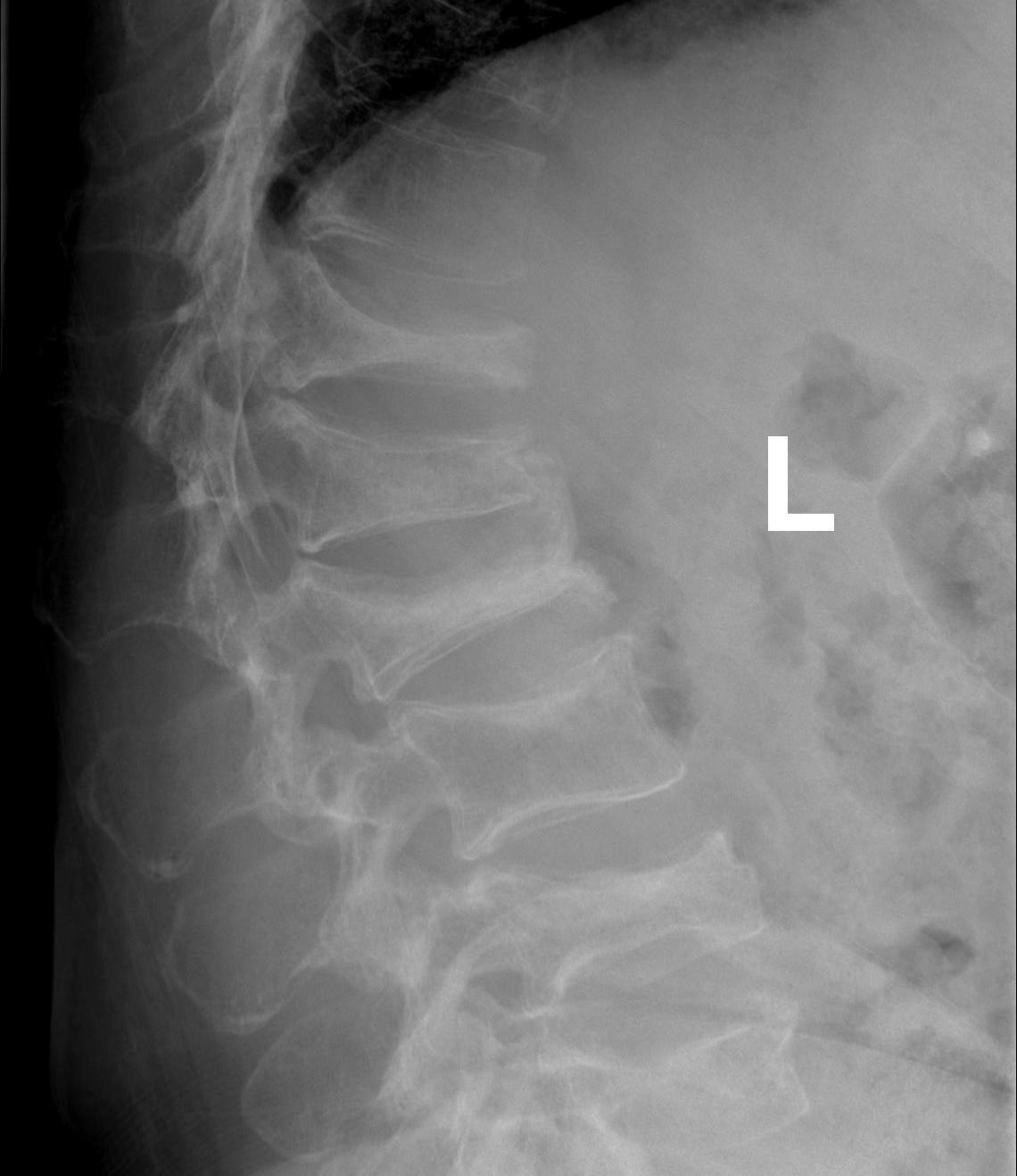
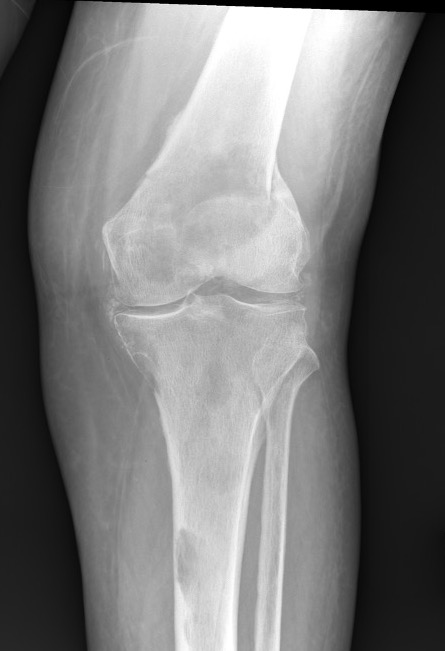
4. Pathological Fracture
5. Pepper pot skull
Bone Scan
25% negative - no malignant or reactive bone formation
Skeletal survey
Xray
- skull / spine / humerus / femurs / pelvis / chest & ribs
- low sensitivity
- only detect lesions with > 30% cortical destruction
Low dose whole body CT
- detects lesions < 5 mm
Whole body MRI
PET / CT
Management Multiple Myeloma
Systemic Problems
Anaemia - erythropoietin
Acute / chronic renal failure - dialysis
Hypercalcaemia
Coagulation defects - systemic anticoagulation
Amyloidosis
Gout
Bone fragility - bisphosphonates
Infection - frequent cause of death in elderly
Algorithm
Chemotherapy
Allogenic stem cell transplantation
Maintenance therapy
+/- immunotherapy / monoclonal antibody therapy (lenalidomide / daratumumab)
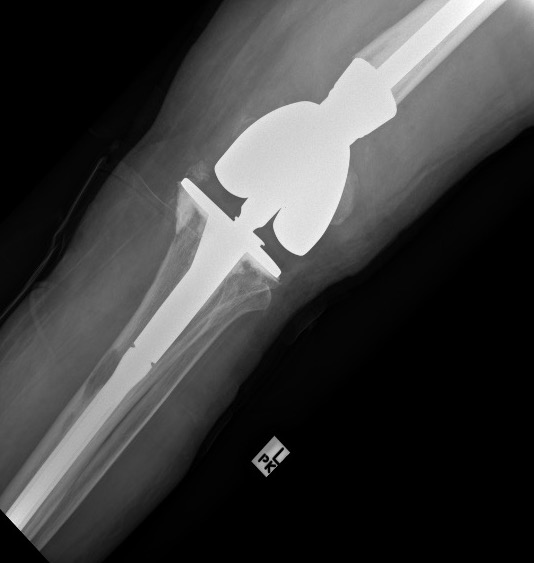
Orthopedic Management
1. To confirm diagnosis - biopsy isolated lesions
2. To treat impending or actual pathological fracture
3. Rarely to excise solitary lesions

Prognosis
Survival has doubled recently in younger patients
- new medications / immunotherapy + stem cell transplantation
Almost all patients eventually relapse
- meta-analysis of minimal residual disease after chemotherapy
- associated with increased long term survival
- mean disease free survival 54 months with minimal residual disease versus 26 months
- mean overall survival 98 months with minimal residual disease versus 82 months
Plasmacytoma
Definition
Single mass of plasma cells
- no plasmacytosis
- no other symptoms
Solitary bone lesion or Extra-medullary / soft tissue
50% with solitary bone lesion develop multiple myeloma within 10 years
Diagnosis
Exclude multiple myeloma
- bone marrow biopsy
- whole body PET / CT / MRI
Clinical
Tend to be younger and have better prognosis
- usually long bone or vertebrae
- in spine commonly present with rapidly progressive paraplegia
- this is more common in plasmacytoma then multiple myeloma
Management
Highly sensitive to radiotherapy
Chemotherapy iindicated for persistent disease after radiotherapy
Surgery
- pathological fractures
- stabilization of spinal lesions
Monitor for progression to multiple myeloma
Prognosis
Ozsahin et al Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006
- 206 solitary bone plasmacytoma
- treated with radiotherapy
- 5 year overall survival 74%
- 5 year probability of progression to multiple myeloma 45% at mean of 21 months
- bone marrow evaluation for plasma cell infiltration
- 70% of plasmacytoma progressed to multiple myeloma if bone marrow biopsy positive
- 8% progressed to multiple myeloma if bone marrow biopsy negative