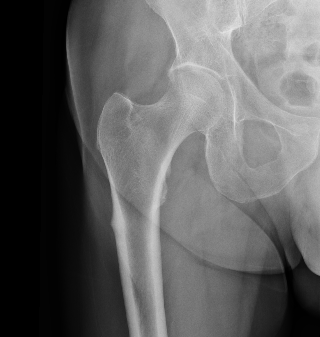
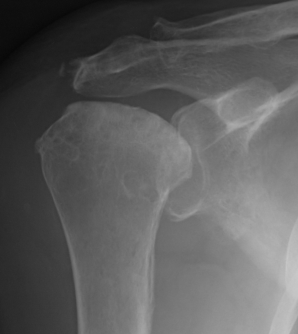
Osteoporosis
Epidemiology
1/3 caucasian women > 64
Risk Factors
Insufficient bone mass at time of skeletal maturity
- peak bone mass is achieved at age 25
Rapid loss of bone after menopause
Low body weight / weight loss / history of smoking / steroids
Primary
Type 1
- postmenopausal
- high turnover / osteoclast mediated
- F x 6