Definition
Joint inflammation secondary pyogenic organism
Epidemiology
All age groups
Usually children
- 50% < age 3
M= F
Any joint
- Infants = Hip
- Children = Knee
- Adults = Large Joints
IVDU - SCJ & SIJ
Pathogenesis
Two Routes
1. Haematogenous
- distant focus
- seeds synovial membrane
2. Direct Extension
A. Osteomyelitis
- neonates & children
- from adjacent focus of OM
(i) Via Trans-physeal vessels in neonates
- Haversian & Volkmann's canals in children
(ii) Intra-articular metaphysis
- proximal & distal femur
- humerus
- proximal tibia
- ? distal fibula
B. Overlying Soft tissue Infection
C. Inoculation
- penetrating injury
- iatrogenic
Predisposition
Host
- immunodeficiencies
Joint
- previous joint trauma
- RA
- previous HCLA
Bacteraemia
Aetiology
Microbes vary with age
Neonates < 1/12
60% hospital acquired
- premature or unwell
- group B streptococci most common
- E coli & other Gram negative bacilli
- S aureus
Infants & Children <3 years
S Aureus
S. pneumoniae / pyogenes
H Influenzae
- reduced by immunisation
Children > 3 years
As above
Adults
S Aureus > Strep > G -ve
N. gonorrhoeae
- most common in young healthy adult / 70%
- may be polyarticular / associated with rash
- urethral swab / joint fluid PCR
- can treat with antibiotics alone
- usually no need for drainage unless fail to respond
IVDU - Gram negative
Community-Acquired
- S Aureus / MRSA
- Group B Strep
Kingella kingae
- Gram negative coccobacillus
- previously unrecognised
- because is slow and difficult to grow
- colonises nasopharynx, spread through blood stream
- take 14 days to culture
- put in specific BACTEC culture bottle
- sensitive to penicillin
Pathology
Synovium oedematous & hyperaemic
- cloudy synovial fluid
> 2/7 frank pus
- cartilage destruction
- starts at areas of joint contact
Synovial membrane replaced by granulation tissue
- adhesions wall off pockets of pus
- fibrous ankylosis
Physis destroyed if intracapsular i.e. hip
- joint dislocation
- AVN femoral head
- Tom Smith OA
Cartilage Destruction
1. Proteolytic Enzymes
- Lysosomal - Collagenase / protease
- from neutrophils / microbes / synovium
2. Inflammatory cascade
3. Pressure
- degrades cartilage
- AVN / dislocation
Clinical Features
Infant
History prior infection
- Eg umbilical sepsis
Irritability / failure to thrive
Low fever ~ Beware
Joint warm & swollen
Decreased active ROM
- pseudoparalysis
Intra-articular pressure high
- joints held in position to maximise joint volume
- hip abducted / flexed / ER
- knee flexed
Painful and decreased ROM
Child
As above
- easier to localise
Psoas sign
- pain on extension and IR
Bloods
ESR
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- stickiness of RBC
- reflects fibrinogen concentration
- centrifuge blood tube and measure time to settle
- > 30
Not reliable in first 48/24 / Neonate / Steroids
Takes weeks to drop (3/12)
- lags behind resolution
CRP
Acute phase protein synthesised by liver
- > 10
WCC + differential
Elevate in 40 - 60%
- PMN leukocytosis
- left shift
Blood Culture
Positive 40 - 60%
Aspiration
Indications
- knee / ankle
- shoulder / elbow
- ASAP
Contra-indications
- neonate hip
- aspiration difficult & need GA
- drain ASAP
MCS & Cell count
WCC > 50 000 per ml
Neutrophils > 75%
Gram stain Positve 30%
Culture positive 60%
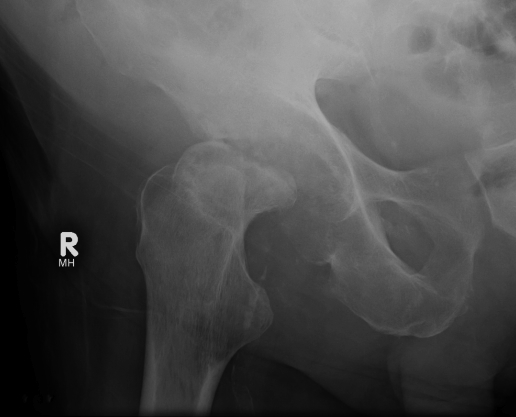
X-ray
Neonate Hip
- wide joint space
- subluxed
- 1° OM in metaphysis
Sequelae of hip septic arthritis
- Tom Smith's arthritis of infancy
- 6mth old with dislocated hip & normal acetabulum
- indicating recent onset injury to hip
- complete AVN of head
Te Scan
DDx focal metaphyseal OM
Identify AVN femoral head
US
100% sensitive at detecting fluid in joint
- useful to diagnose hip effusion
MRI
DDx
- OM
- psoas abscess
Diagnosis
Transient synovitis v Septic Arthritis
Kocher criteria (for child with painful hip)
- fever
- Inability to weight bear on affected side
- ESR > 40
- WCC > 12000
4/4 criteria
- 99% chance that the child has septic arthritis
3/4 criteria
- 93% chance of septic arthritis
2/4 criteria
- 40% chance of septic arthritis
1/4 criteria
- 3% chance of septic arthritis
DDX
Infants & Child
1. Acute OM - Can get symptomatic effusion
2. Cellulitis
3. Transient Synovitis - Afebrile / ESR normal
4. Psoas abscess
5. JRA
6. Trauma
7. Perthes / SUFE in hip
8. Haemophilia
Adults
1. Gout
2. Pseudogout
3. RA / other inflammatory arthritis
Management
1. Surgical Drainage
Surgical emergency
- arthrotomy or arthroscopy
- Washout pus +++
- ± Synovectomy
- closure over drain
Hip
- anterior approach / Smith Petersen approach
- preserves blood supply to femoral head
- allows inspection of femoral metaphysis for OM
- between TFL and sartorius / G. med and RF
- 1 cm capsulotomy
- +/- drill neck (MRI useful to detect OM)
- leave capsule open
- close over drain
- assess hip stability
- may need brace or POP
2. Antibiotics
Start after MCS
- start broad spectrum bacteriocidal
- gram stain as guide
Choice
- Flucloxacillin & Gentamicin adults
- Flucloxacillin & Ceftriaxone paeds
Timing
- IV AB until systemic toxicity & local swelling subside & CRP normal
- ~ 2/52
- usually continue oral antibiotics for further 4/52
Complications
Joint destruction - ankylosis / OA
Neonate Hips
- dislocation / subluxation
- destroyed epiphysis - Growth disturbance / LLD / coxa vara / breva
- absence of head / AVN
- pseudoarthrosis of femoral neck