Definition
Pseudogout
- Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate (CPPD) crystals
- inflammatory arthritis of older individuals
Chondrocalcinosis
- refers to any calcium in cartilage / menisci
Epidemiology
M:F 2:1
Patient > 50
Sometimes familial
Association
DM
Hypothyroidism
Gout
Hyperparathyroidism
Haemochromatosis
Pernicious Anaemia
Onchronosis
Pathology
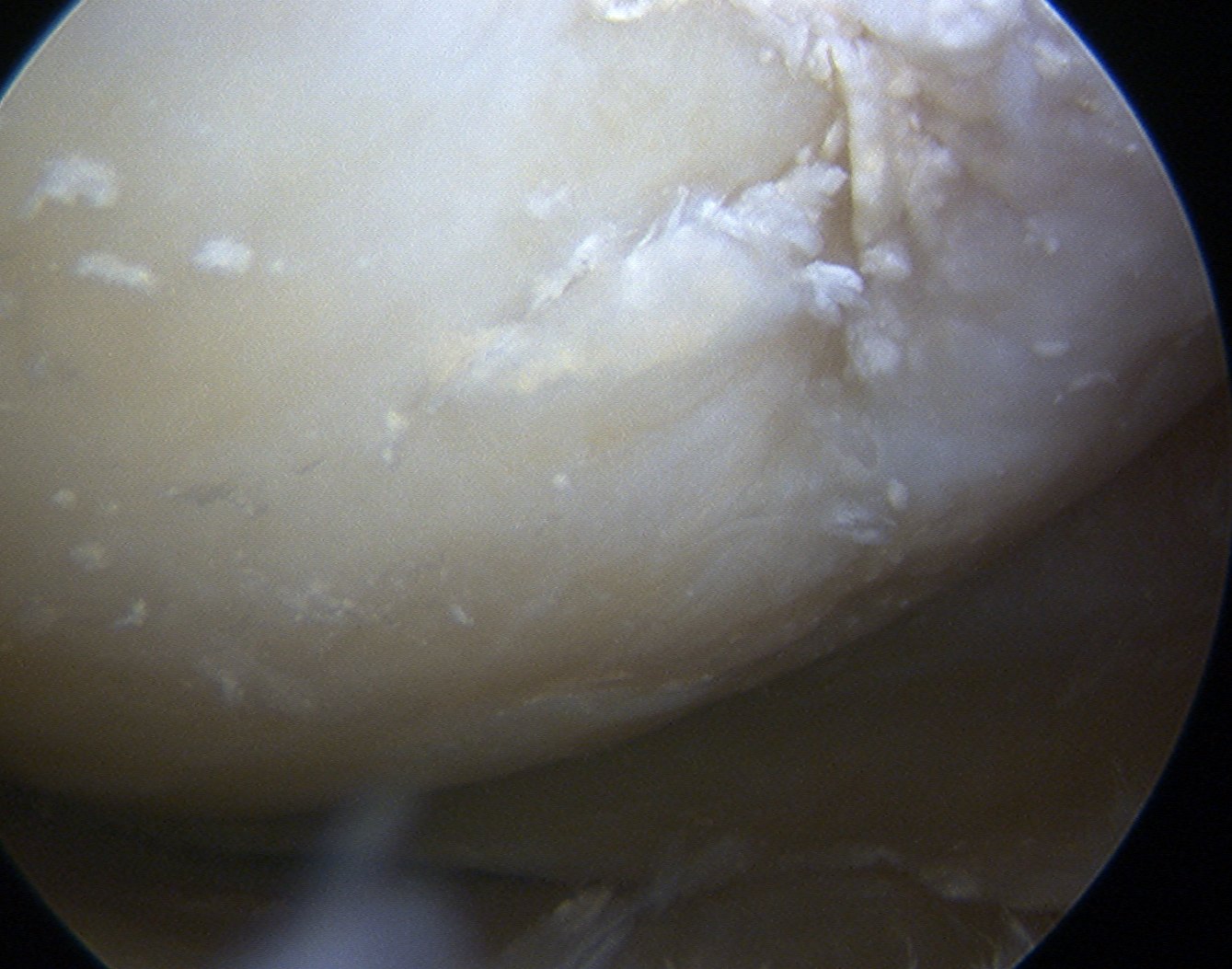
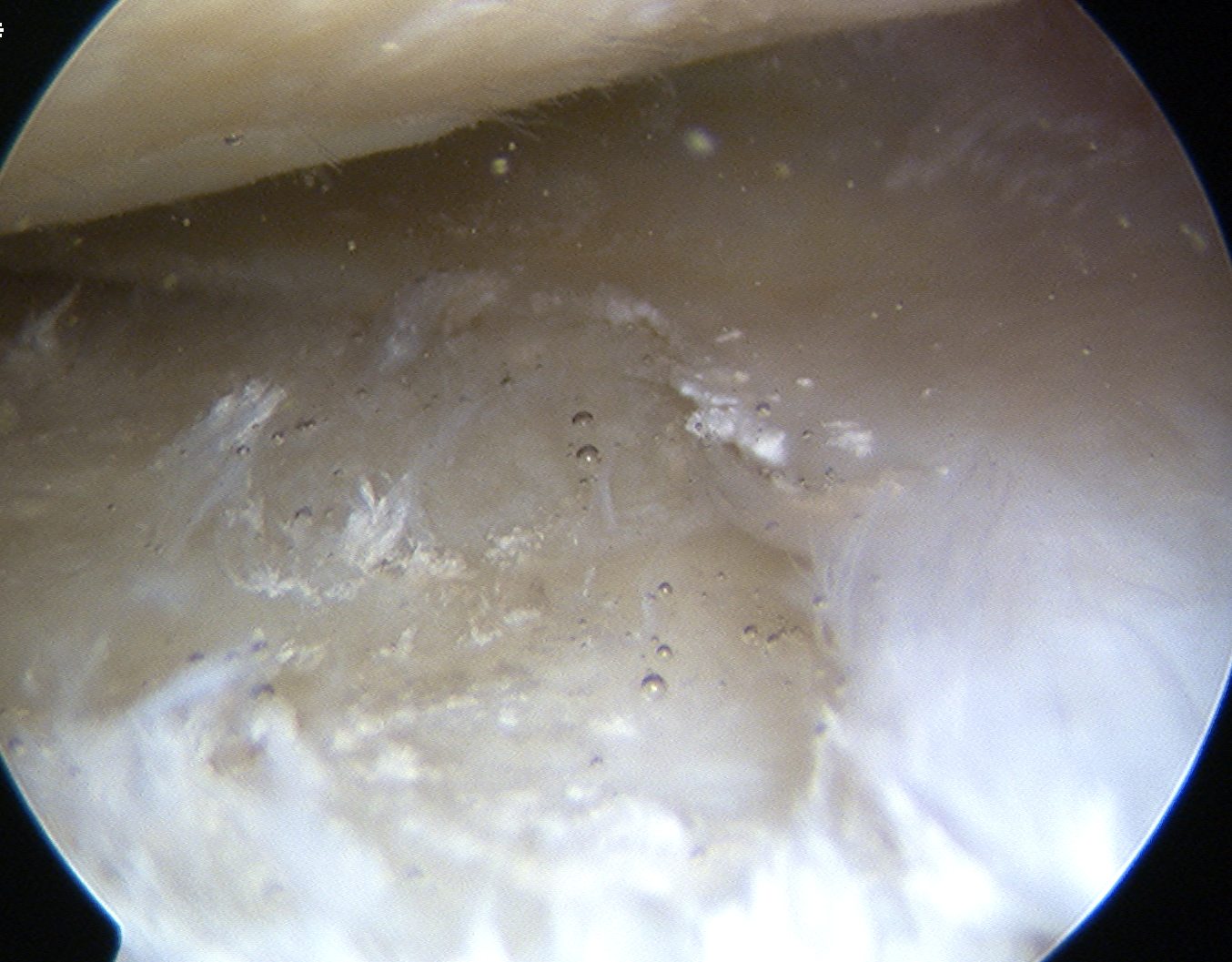
CPPD deposited in
- joint capsule
- articular cartilage
- fibrocartilage / meniscus
Crystals seen at margin of degenerating cartilage
- pyrophosphate generated at chondrocyte surface in abnormal cartilage
- combine with calcium to form crystals
Occasionally the crystals are released into the joint & an acute arthritis results
- activation of vasoactive & chemotactic factors
- neutrophils attracted & phagocytose crystals
- release of lysosomal enzymes into joint fluid
Chronic chondrocalcinosis predisposes to development of 2° OA
- crystals embedded in articular cartilage have desiccating effect
Clinical presentations
1. Asymptomatic Chondrocalcinosis
Majority of people
- incidental finding
- calcium of menisci
- usually involved with degenerative changes
2. Pseudogout
Rapid onset inflammatory arthritis
- peak in 24/24
- subsides in 1/52
May be provoked by
- trauma
- surgery
- illness
Usually affects large joints
- Knee > Shoulder > Wrist
- typically monoarticular
- less pain than gout
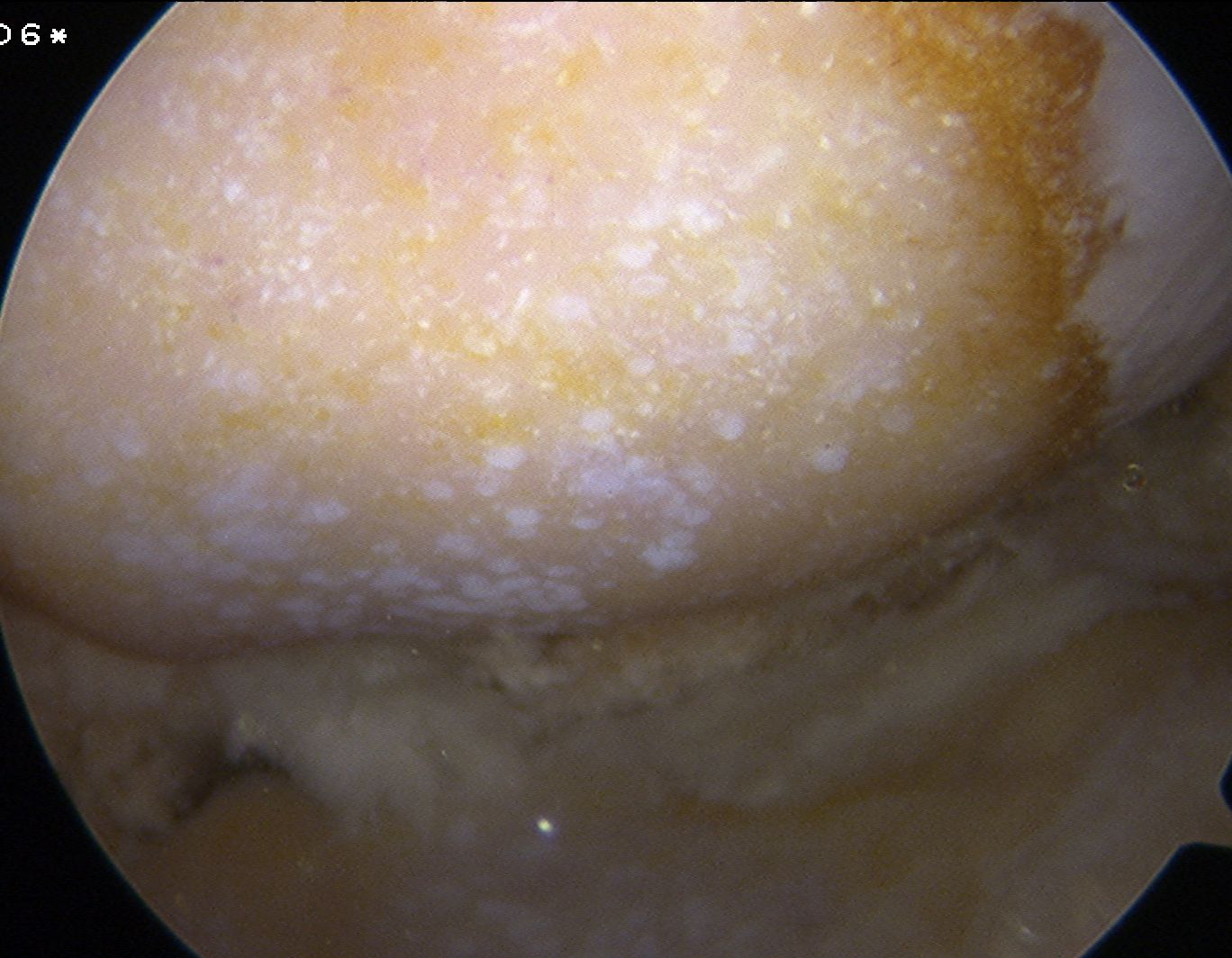
3. Chronic CPPD Arthropathy
OA 2° CPPD
Pseudo-Osteoarthritis
- polyarticular disease like OA
- in hips & knees
- due to CPPD in cartilage altering the biomechanics
In more unusual joints for OA
- ankles, shoulders, elbows
- very common in PFJ
- has radiodense crystals
4. Pseudo- Rheumatoid Arthritis
Acute synovitis & chronic arthritis
- rapidly progressive joint destruction
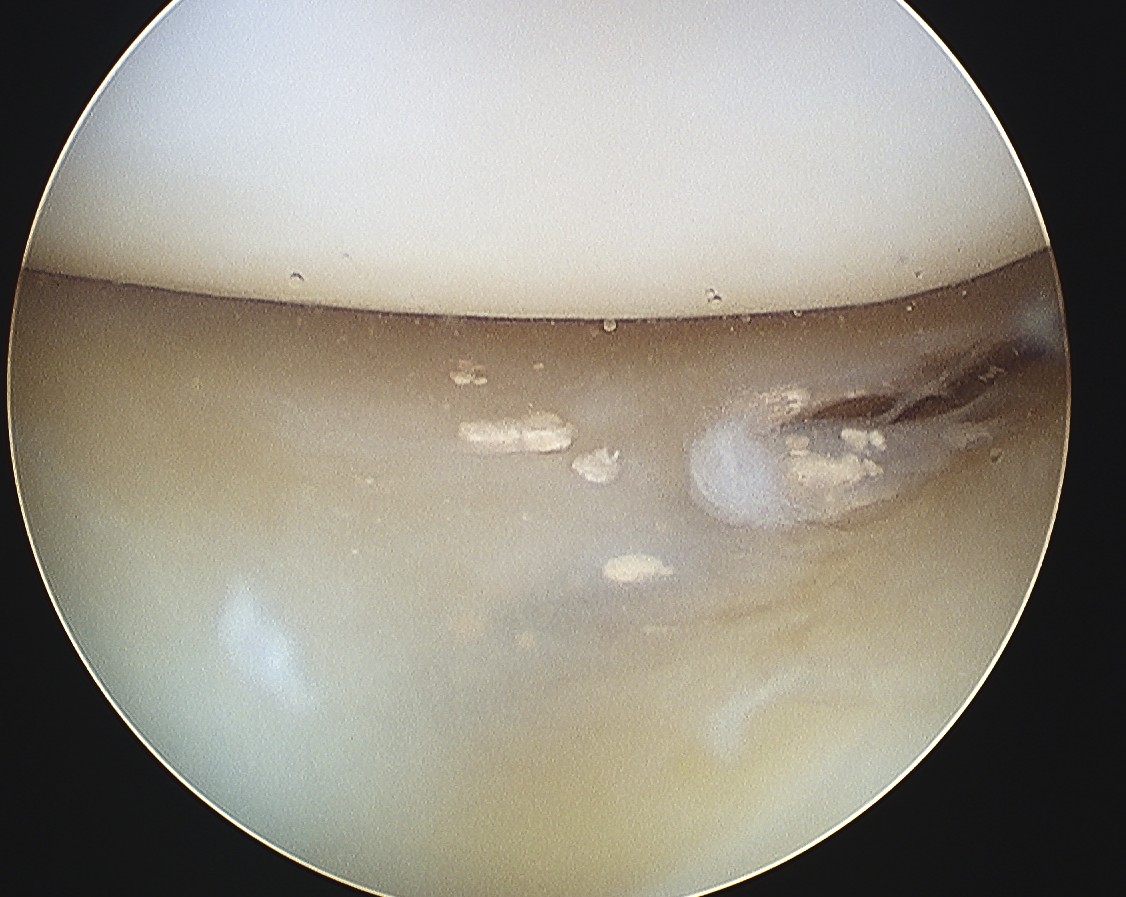
Synovial Fluid
CPPD crystals seen extracellular & in neutrophils
- rhomboidal
- weakly positively birefringent
- IE Blue parallel to 1° order red filter & 135° to polarizer
X-ray
Chondrocalcinosis
Calcium in fibrocartilage & CT
- punctate densities
- menisci / TFCC / pubis / annulus
Findings of OA usually present
Unusally joints
- PFJ
Screening Bloods
Ca / PTH
U&E
Serum Fe / Fe studies
TFT
Serum Alk Phos
Differential Diagnoses
Hyperparathyroidism
X-rays show subperiosteal erosions
Blood tests show hypercalcemia / increased PTH
Ochronosis
Often severely affects spine / shoulders / hips / knees
Hemochromatosis
Disorder where iron deposited in many tissues including articular cartilage
- concomitantly get cirrhosis of the liver / CCF /diabetes / bronze skin
- chondrocalcinosis often prominent feature
- calcification of multiple joints and discs
- serum Fe and IBC raised
Management
Options
1. NSAIDS
2. HCLA
3. Colchicine
- 80% response
4. Joint washout
Joint washout
Don't debride / perform synovectomy
Worsens symptoms