Definition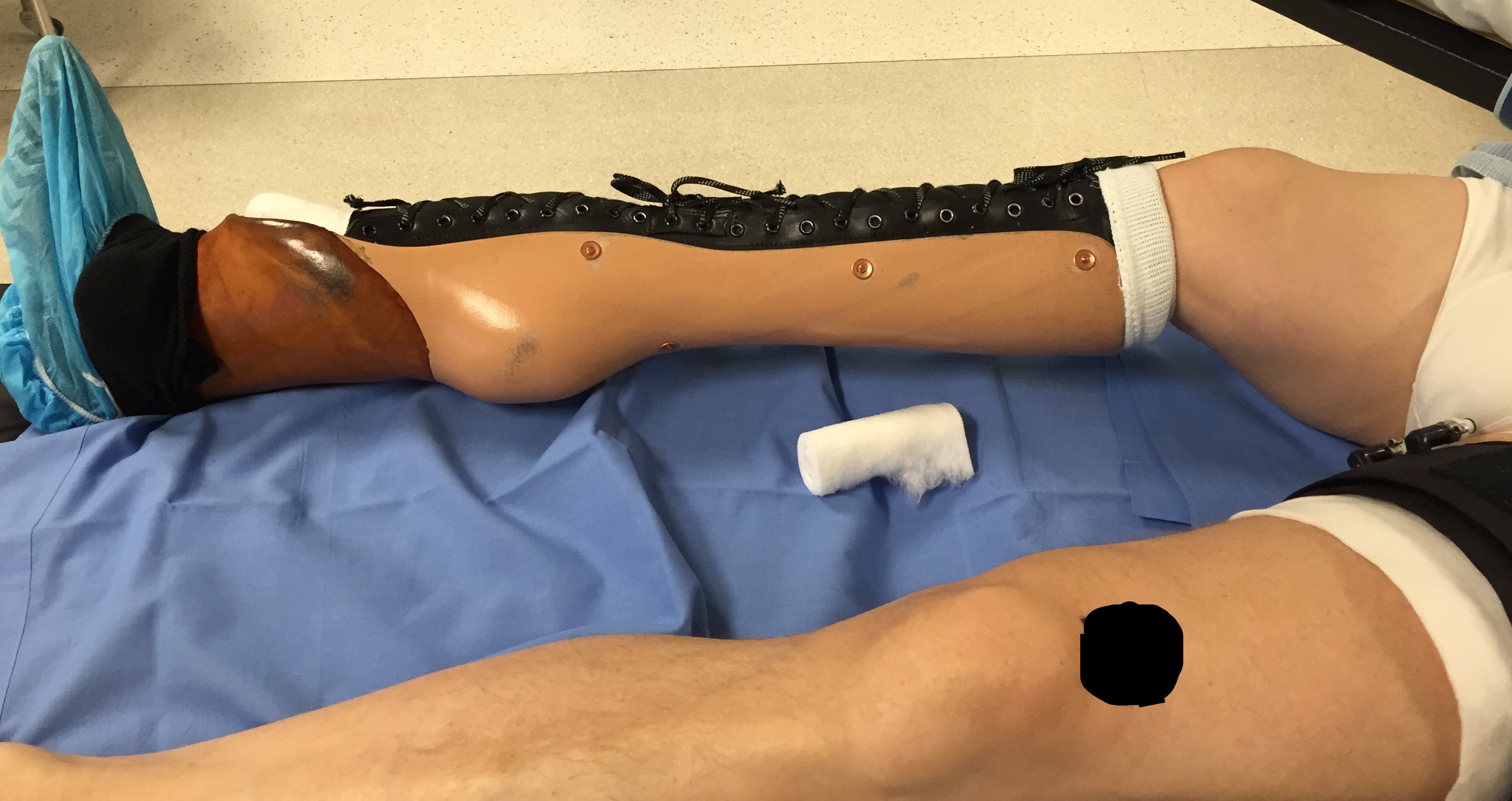
Proximal Focal Femoral Deficiency
- congenital malformation
- characterised by failure of normal development of the proximal femur
Epidemiology
Rare
- 1 in 50 000
Bilateral in 15%
- usually more severe
Association
Fibular hemimelia in 2/3
ACL deficient
May also be associated with
- CTEV
- Cleft palate
- CDH
- Congenital spinal deformity
- Dysraphism
Aitken's Classification
Class A
- short femoral shaft with coxa vara
- head of femur present, neck may be absent early
- adequate acetabulum
- bony connection between head & neck present at maturity
- may be pseudarthrosis at point of connection
Class B
- pseudoarthrosis between head and shaft
- shorter femoral shaft with small bony tuft on proximal end
- head of femur present
- adequate acetabulum
Class C
- no femoral head
- acetabulum severe dysplastic
- very short femoral shaft with bony tuft proximally
Class D
- femoral head & acetabulum completely absent
- femur consists of condyles only
Signs
Child with very short leg
- large shoe raise
- LLD above GT
DDx of shortening above GT
- DDH
- PFFD
- Tom Smith arthritis / post septic arthritis
- Tumour
Also
- short involved thigh segment
- characteristic posture (Flex / Abducted / ER hip)
- Ship's Funnel Sign
Bulky upper thigh segment
- sharply tapering to knee
Issues
1. Pseudoarthrosis
2. Instability of the hips
3. Coxa vara
4. LLD
5. Inadequate lateral femoral condyle
6. Inadequate proximal musculature
7. Malrotation
Management
Class A & B
Femoral heads present
1. Stabilize pseudarthrosis with IM Rod
2. Hip stabilisation
- pelvic osteotomy
- femoral osteotomy
3. Limb lengthening
Class A
1. Realign Coxa Vara
- subtrochanteric osteotomy
2. Equalise LLD
- lengthen femur or
- shorten / epiphysiodesis other femur
Note:
- if lengthen femur need to watch knee doesn't dislocate
- ACL deficient
- may have to bridge knee with external fixator
Class B
1. Fuse pseudarthrosis
2. Limb lengthen or amputate as required
Class C & D
No femoral heads
Stabilise hip
- pelvic support osteotomy
- osteotomy proximal femur
- supported by ischium
- distal osteotomy for mechanical axis
- need lengthening as well
Foot above contralateral knee
- knee fusion + symes
- essentially AKA
Foot below contralateral knee
- rotate then fuse knee / Van Ness Rotational Osteotomy
- ankle acts as knee joint / essentially BKA
- BV become anterior
- require good functioning foot
Bilateral
Usually Class C or D
- can usually walk well without prosthesis
- surgical procedures usually detract from mobility
- should not be treated surgically unless such severe foot deformity that cannot ambulate without prosthesis / Symes
