Normal development
1 year: Bow legs / 15° varus
2 year: Neutral
3 year: Knock knees / 10° valgus
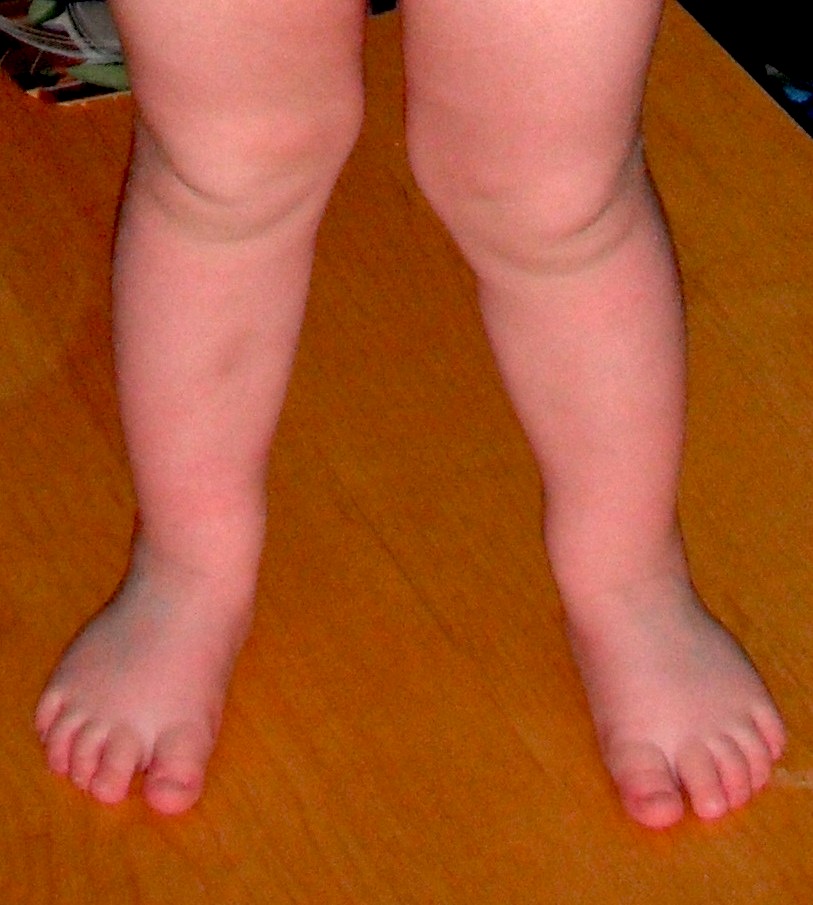
6 year: Physiological valgus / 6° valgus
Note range ~ 15° either way at each age
- persistence of physiologic variations may occur
- especially in some families & racial groups
Salenius and Vankka
- chart of normal tibio-femoral variations by age
History
FHx
Examination
Unilateral / bilateral
- angular profile
- femorotibial angle
- inter-malleolar / intercondylar distance (quantify)
LLD / rotational profile / joint laxity
Height vs Age
X-ray
Erect AP Standing Long Leg view
- patella directed forward
- femur & tibia on same Xray
Indications
- if pathological form suspected
- asymmetry
- < 5th percentile
- severe deformity
- positive FHx
- other musculoskeletal abnormality
Causes of both Varus and Valgus
Trauma: Malunion / Partial physeal arrest
Rickets / Renal disease
JRA
Osteopaenia
OI
NHx
Avoid dogmatic predictions
- clinical course variable
- not all cases resolve
Shoe wedges & other bracing ineffective
Prognosis
Uncertain
- genu valgum may cause CMP / PF Dislocations
- genu varum may cause OA Knee
Varus deformities
Physiologic Bow legs
1. Lateral tibial bowing
- occurs in first year of life
- nearly always resolves
2. Common Bowing
- involving the femur & tibia
- seen in second year
- prior to age 2 years, development of MFC lags behind lateral
- resolution occurs in most children
Management Physiological
Bracing doesn't affect the NHx
- exclude pathological causes of deformity & reassure parents
Surgery
- corrective osteotomy / epiphysiodesis / guided growth with 8 plates
- recommended for those children with persistence or worsening of physiologic varus
Pathological
Blount's
Rickets
Trauma - malunion / epiphyseal arrest
Infection - physeal damage
Skeletal dysplasia - achondroplasia / OI / enchondromatosis / metaphyseal chondrodysplasia
Anterolateral bowing - pseudoarthrosis
Fibrous dysplasia
JRA
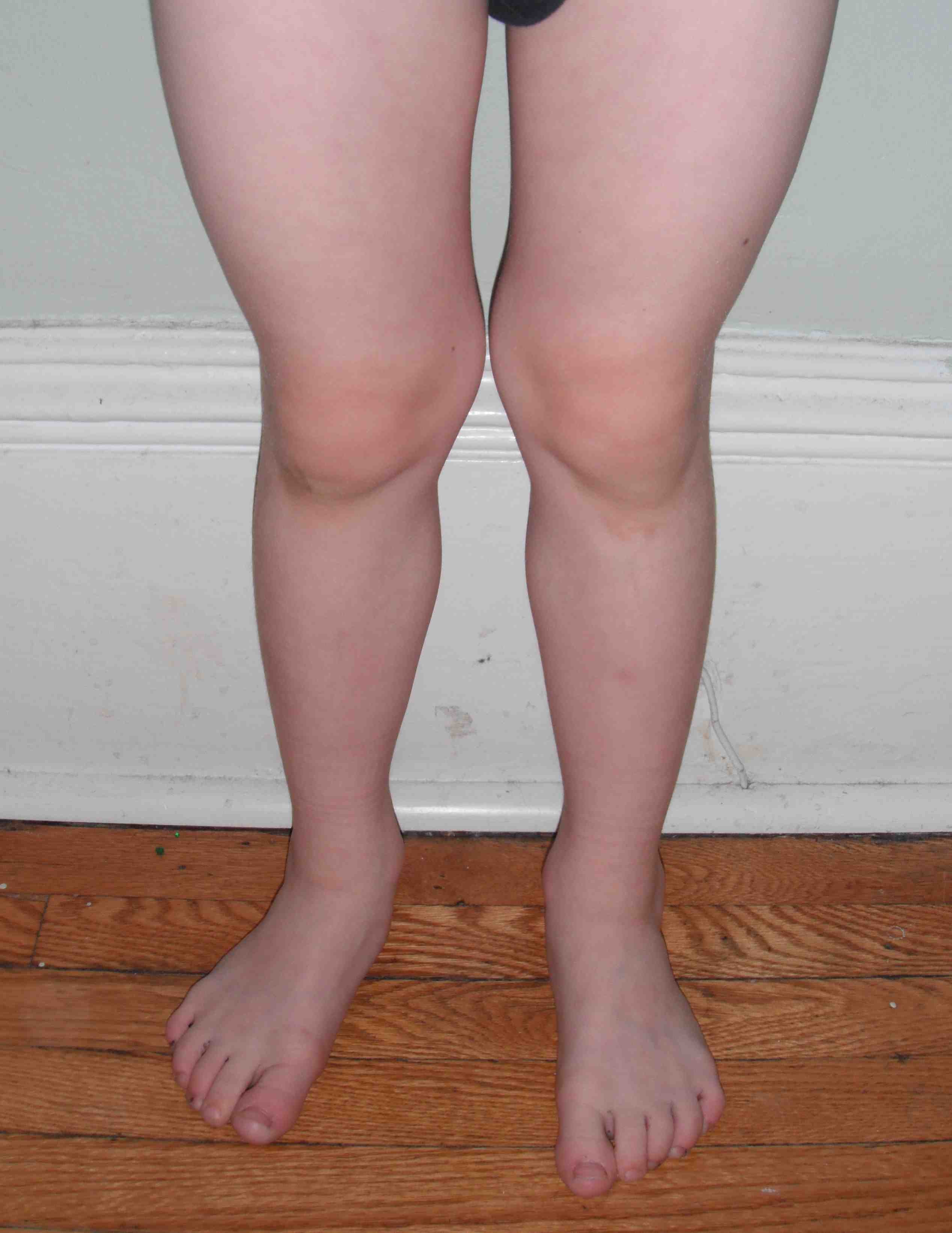
Valgus Deformities
Physiological Valgus
NHx
- knock knees very common age 2-6
- starts at 2 years
- maximum 3-4 years
- usually resolves by 7
- may not always resolve
- minimal correction occurs > 8 yo
X-ray if
- asymmetrical / Unilateral
- progressive
- LLD
- intermalleolar distance > 10 cm
- outside normal parameters i.e. 15° either side normal for age
Bracing
- no evidence of efficacy
Surgical Indications
- > 15° valgus
- cosmesis
- poor gait / function
- avoided < 12 years
Options
- osteotomy / hemiepiphyseodesis / Guided Growth with 8 plates
Pathological Valgus
Traumatic
1. Distal femoral physeal injury
- Usually SH I or II
2. Proximal tibial metaphyseal fracture / Cozen's
- tendency for valgus deformity
- reason why is uncertain
Theories
- rotation on xray hides valgus
- ST interposition
- overgrowth
Manage
- careful moulding cast into varus
- usually resolves over time
Infection - physeal injury
Congenital Posteromedial Bowing
Anteromedial Bowing - fibular hemimelia
Skeletal dysplasia - MED / pseudoachrondroplasia / Kneist
Multiple Osteochondromas
NMD - cerebral palsy / spina bifida
Lateral Condylar Hypoplasia
OI
Rickets
JRA
