Epidemiology
Relatively rare
Average age 50
Men 4:1 Women
Usually dominant arm
Aetiology
Primary
- rare
- 2% of all cases
- associated with heavy manual labour
Secondary
- trauma - intra-articular distal humerus fractures
- capitella OCD
- synovial chondromatosis
- repetitive athletic overuse
Pathology
Begins radiocapitellar joint and progresses to ulnohumeral joint
Forces across joint about 1/2 body weight
- increased in strenuous work
- small cross sectional area
- increases contact stresses
Symptoms
Stiffness
End range pain
- minimal in mid range
- pain when olecranon and coronoid osteophytes impinge
Progress to pain throughout entire range in end stage of disease
Functional range
- 100 degrees flexion extension arc (30 - 130)
- 100 degrees forearm rotation (50 degrees supination and 50 degrees pronation)
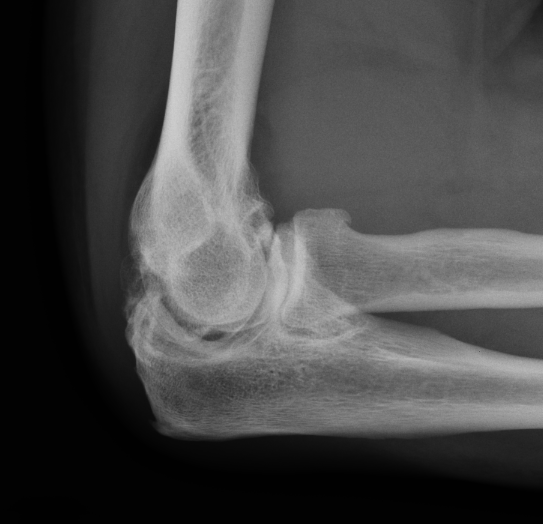
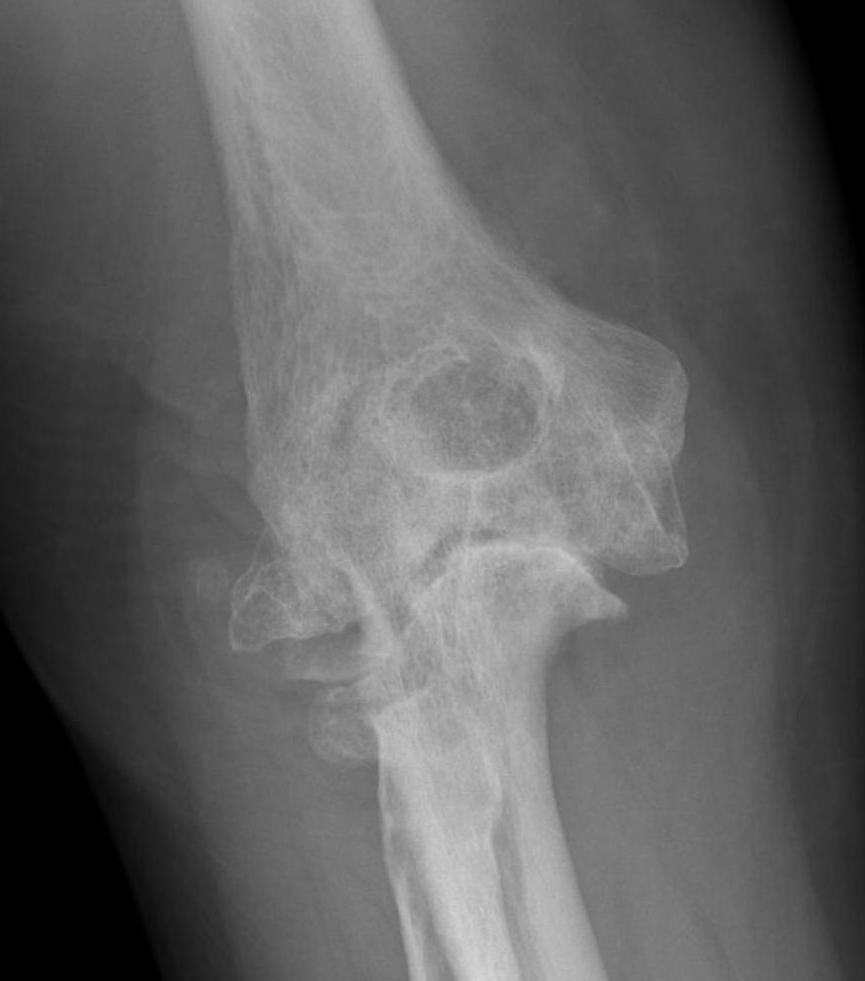
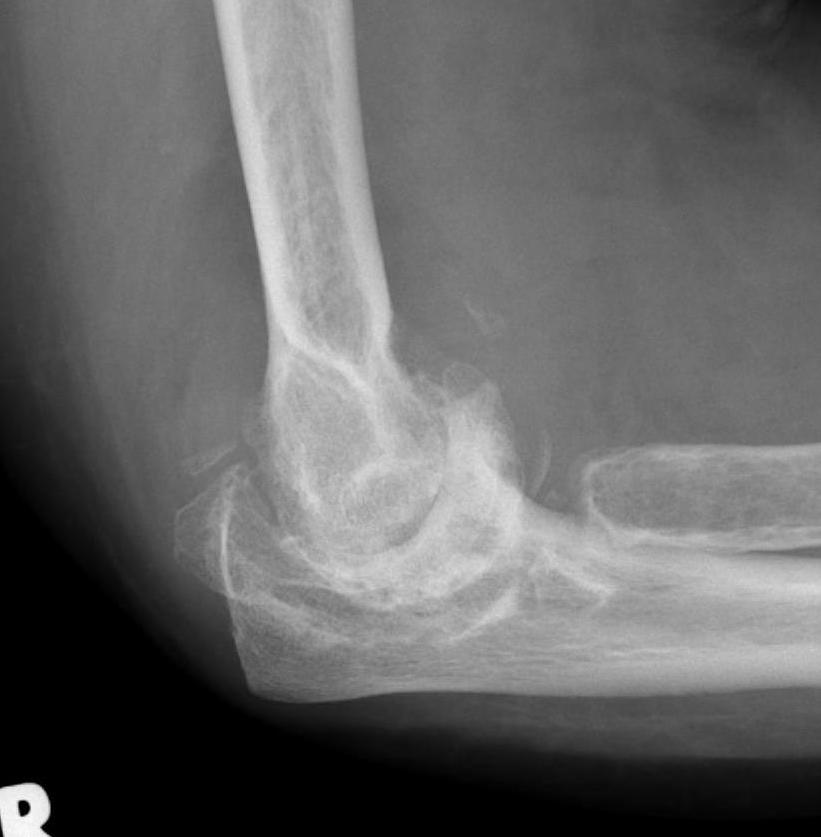
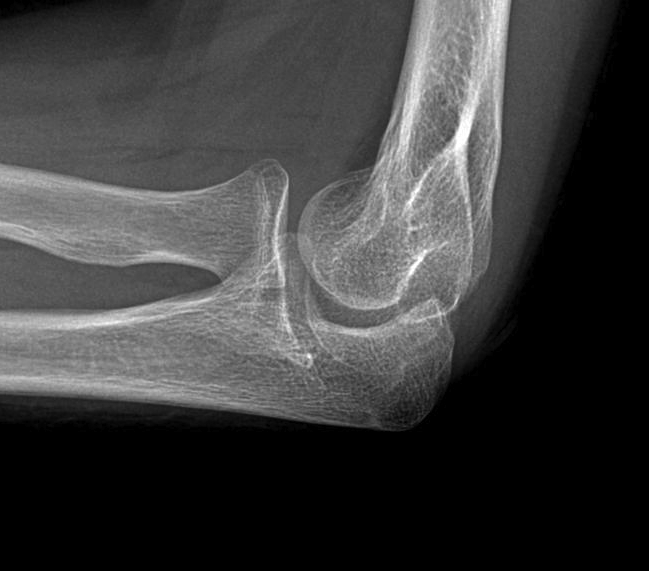
X-ray
Early stage
- preserved radiocapitellar and ulnohumeral joints
- osteophytes of the olecranon and coronoid
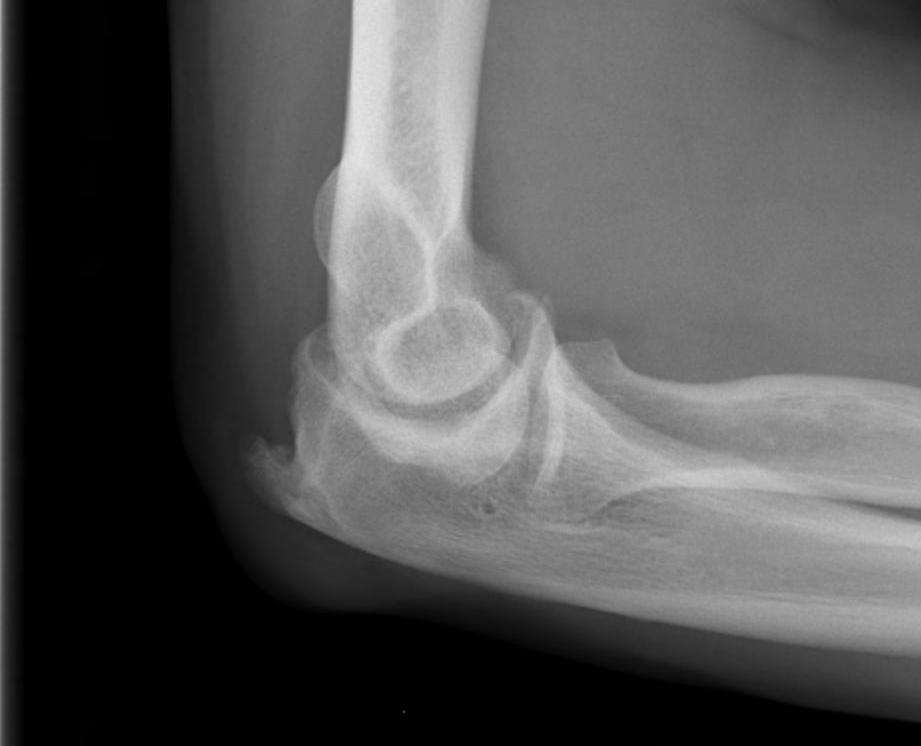
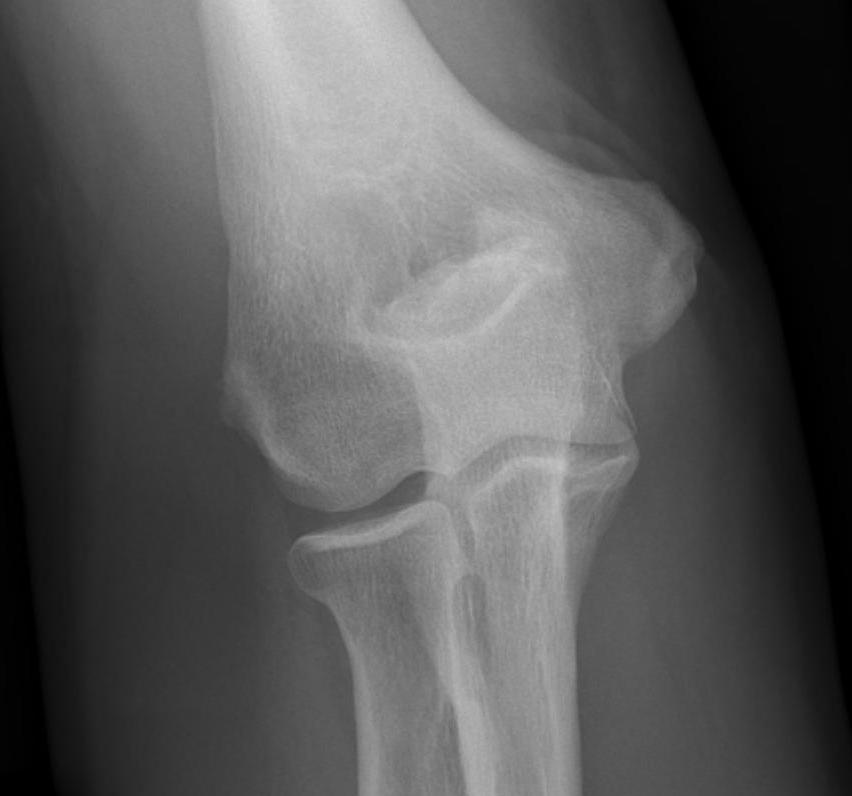
Lateral xray demonstrating olecranon and coranoid osteophytes
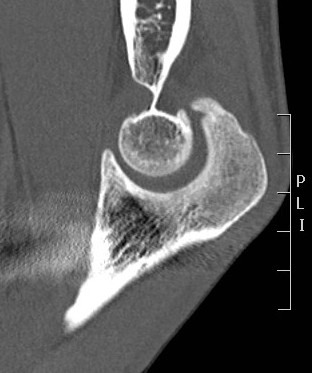
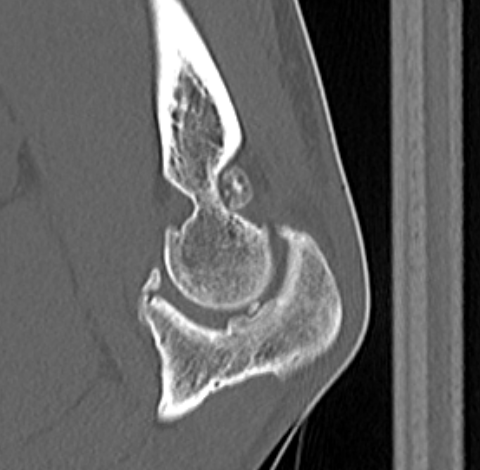
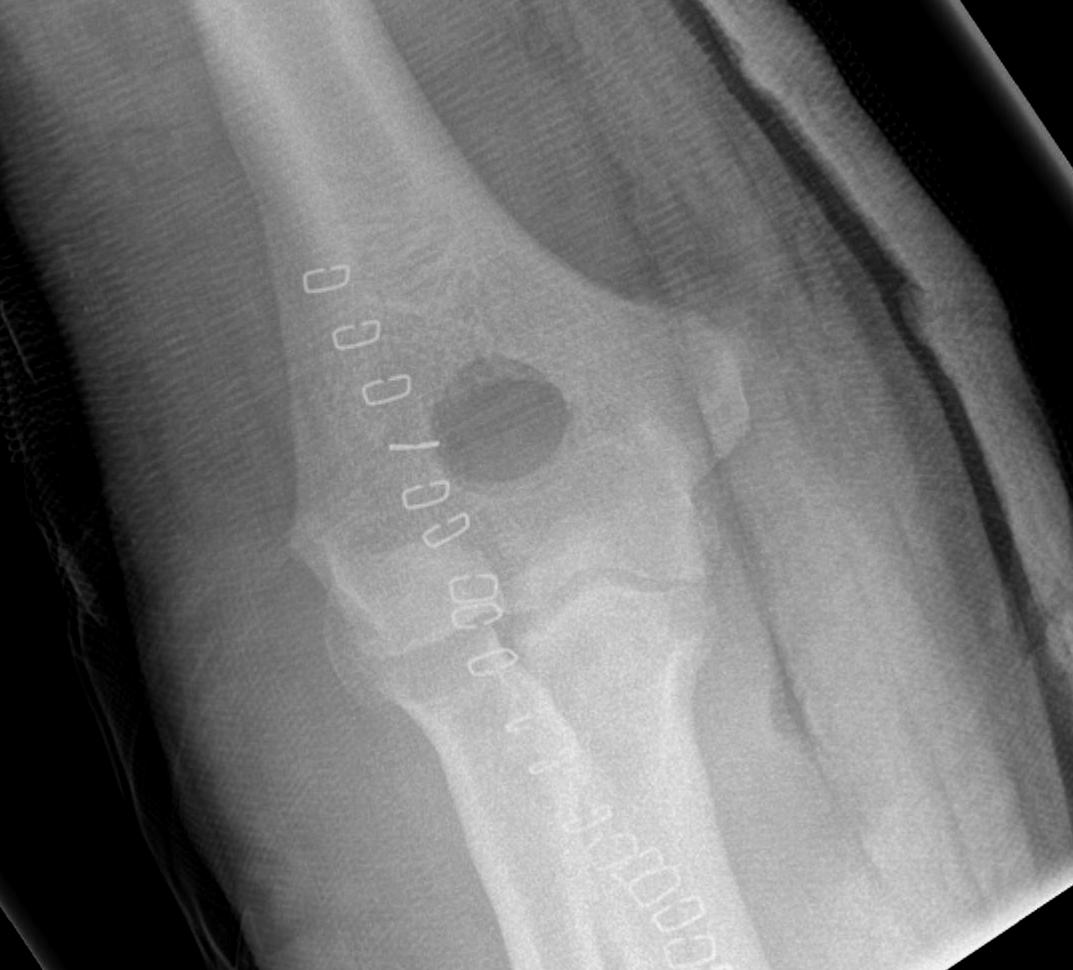
CT
Define antomy pre operation
Identification loose bodies
Osteophyte of the olecranon likely impinging in extension
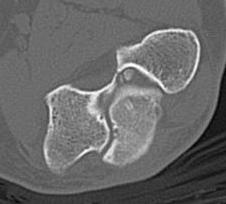
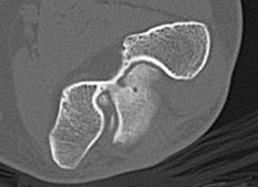
CT demonstrating loose bodies in the ulnohumeral joint
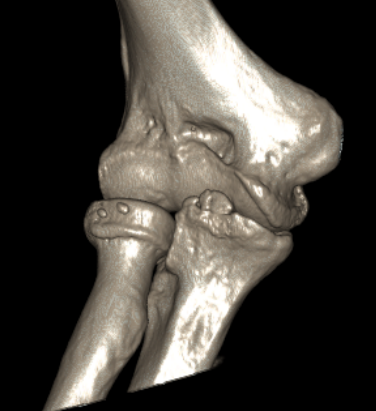
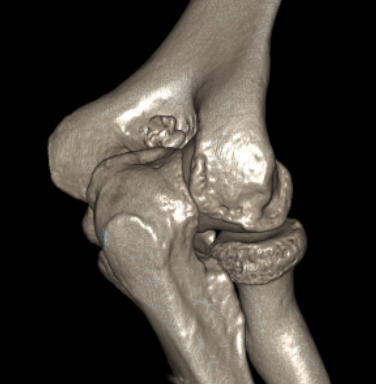
Multiple loose bodies in anterior and posterior elbow joint
MRI
Useful in detecting early chondral damage
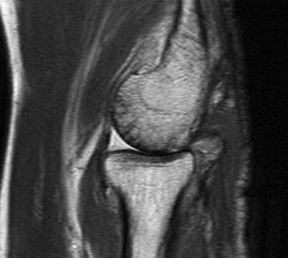
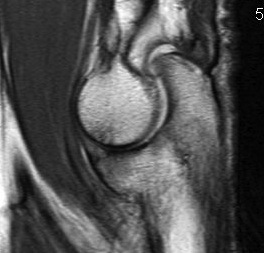
MRI chondral damage radiocapitella joint Chondral thinning ulnohumeral joint
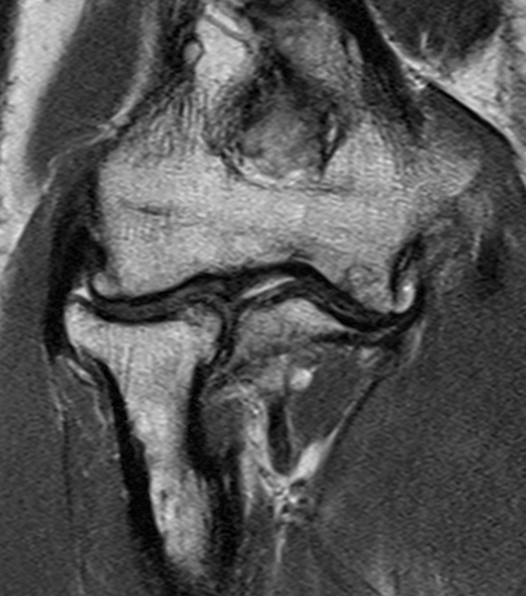
Chondral changes in the radiocapitellar and ulnohumeral joint
Arthroscopy
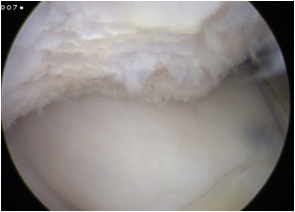
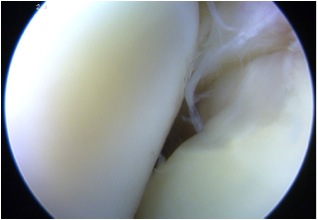
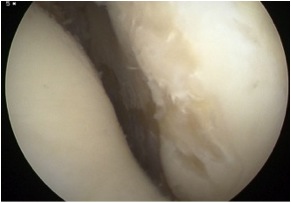
Chondral damage capitellum Chondral damage radial head Chondral damage ulnohumeral joint
DDx
Inflammatory arthritis / Rheumatoid arthritis
- minimal osteophytes
- severely arthritic joint spaces
- have pain throughout range of motion
Management
Non operative
Analgesia
Injections
Injections
Limited evidence
Technique
Soft spot
- lateral approach
- triangle of lateral epicondyle / lateral olecranon / radial head
Kim et al J Clin Ultrasound 2013
- 40/40 injections intra-articular with ultrasound guidance
- 31/40 injections intra-articular with palpation guidance
Results
Van Brackel et al Arthroscopy 2006
- 18 patients treated with 3 injections of hyaluronic acid
- some pain relief at 3 months, none at 6 months
Operative
Options
Open debridement
Outerbridge-Kashiwagi (OK) procedure
Arthroscopic debridement
Interposition arthroplasty
Total elbow arthroplasty
Open Debridement
Goals
Remove coracoid and olecranon osteophytes
Capsular releases
Approach
Universal posterior approach
Lateral interval
- distal humeral: elevating BR and ECRL
- distal: between ECRB and EDC
Medial interval
- find and protect ulna nerve
- proximal: between triceps and brachialis
- distal: detach pronator teres
Technique Morrey
A. Muscle releases
- brachialis released from humerus
- triceps released from humerus
B. Capsulotomy / capsulectomy
- anteriorly elevate brachialis off capsule
C. Excision of HO
D. Removal of osteophytes
- coronoid / olecranon
E. Debridement of osteochondral flaps / loose bodies
F. +/- Release of collateral ligaments
- preserve anterior band of MCL
- ligament reconstruction & hinged elbow fixator if becomes unstable
G. +/- Radial head debridement / excision
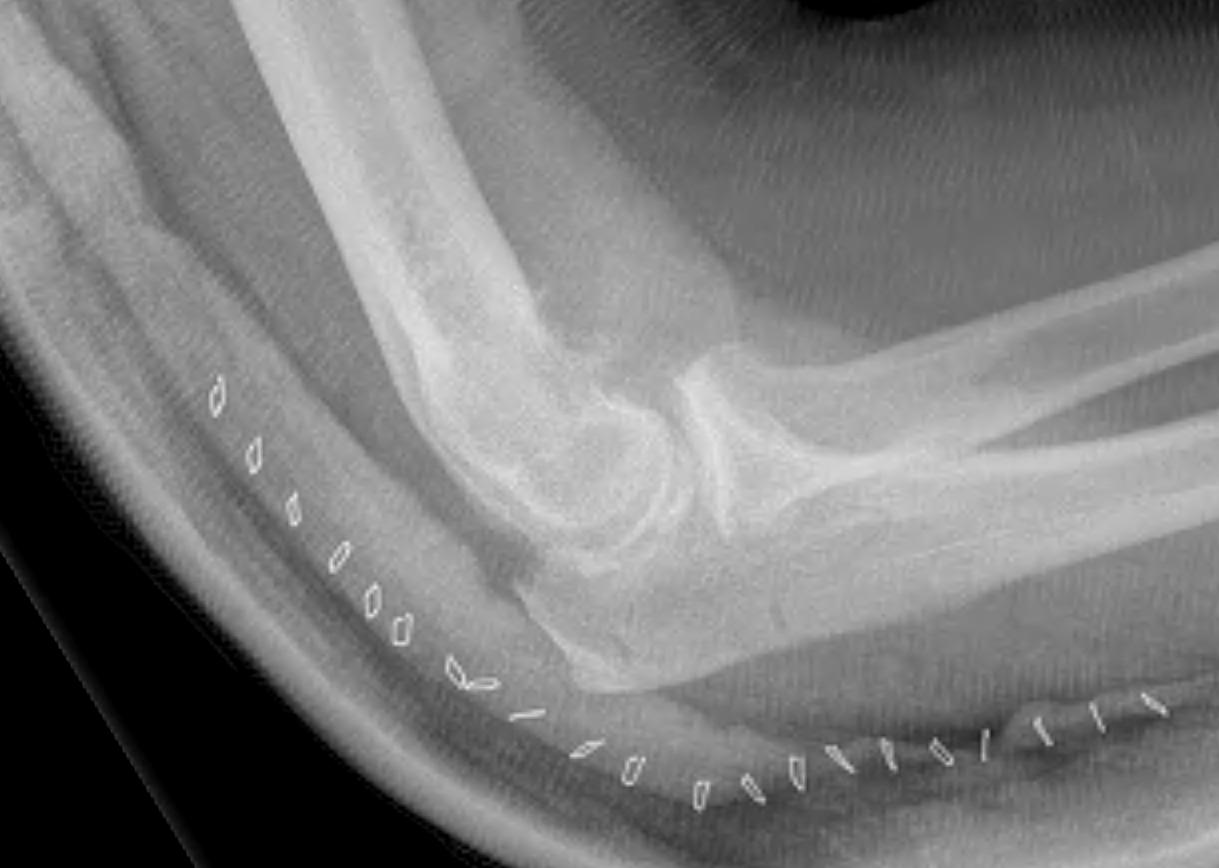
Outerbridge-Kashiwagi (OK) procedure
Concept
Posterior approach
- drill hole in distal humerus
- allows access to coranoid process for debridement
Technique
Vumedi Outerbridge Kashiwagi (OK) procedure surgical technique
Posterior approach and triceps split
- excision of posterior capsule
- excision of tip of olecranon
Access to anterior compartment via olecranon fossa
- 1 cm diameter hole
- debridement of coranoid +/- radial head
- removal of loose bodies
Results
- 178 OK procedures
- survivorship with total elbow arthroplasty as end point
- 100.0% at 1 year
- 98.8% at 5 years
- 98.0% at 10 years
Arthroscopic Debridement
Relative Contra-indications
- previous ulna nerve transposition
- severe soft tissue contractures
- bridging HO
Technique
Elbow osteoarthritis arthroscopic debridement surgical technique PDF
Vumedi arthroscopic debridement elbow arthroscopy
Anterior joint
- remove loose bodies
- resect coronoid osteophytes
- anterior capsular release to improve extension
- +/- radial head resection
Posterior joint
- remove loose bodies
- resect olecranon osteophytes
Results
- systematic review of open versus arthroscopic debridement elbow OA
- no difference in ROM improvement / outcome measures / complications
Sochacki et al Arthroscopy 2017
- systematic review of arthroscopic debridement for elbow OA
- 9 articles and 213 elbows
- evidence of improved ROM and outcome scores with low complication
Carlier et al Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 2019
- prospective study of 87 patients
- significant improvements in pain, ROM and strength
- radial head resection did not improve outcomes
Case
Post elbow fracture malunion / posterior impingement / FFD 40o
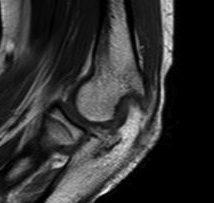
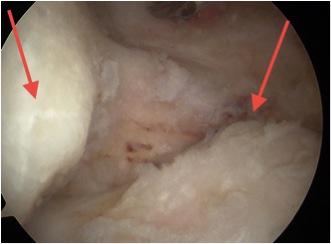
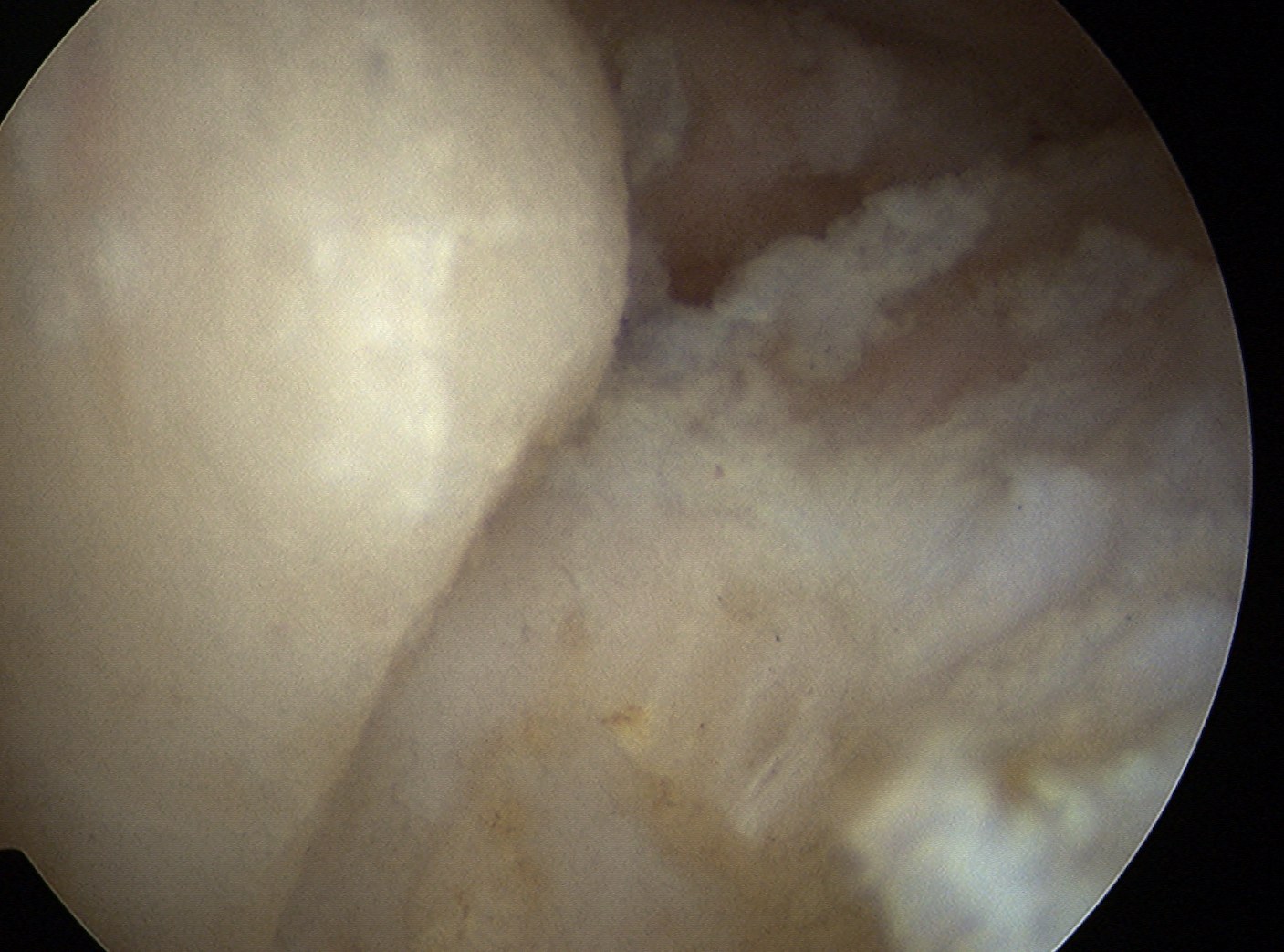
Posterior elbow arthroscopy, with arrows pointing to olecronon tip on the right in the flexed and extended position
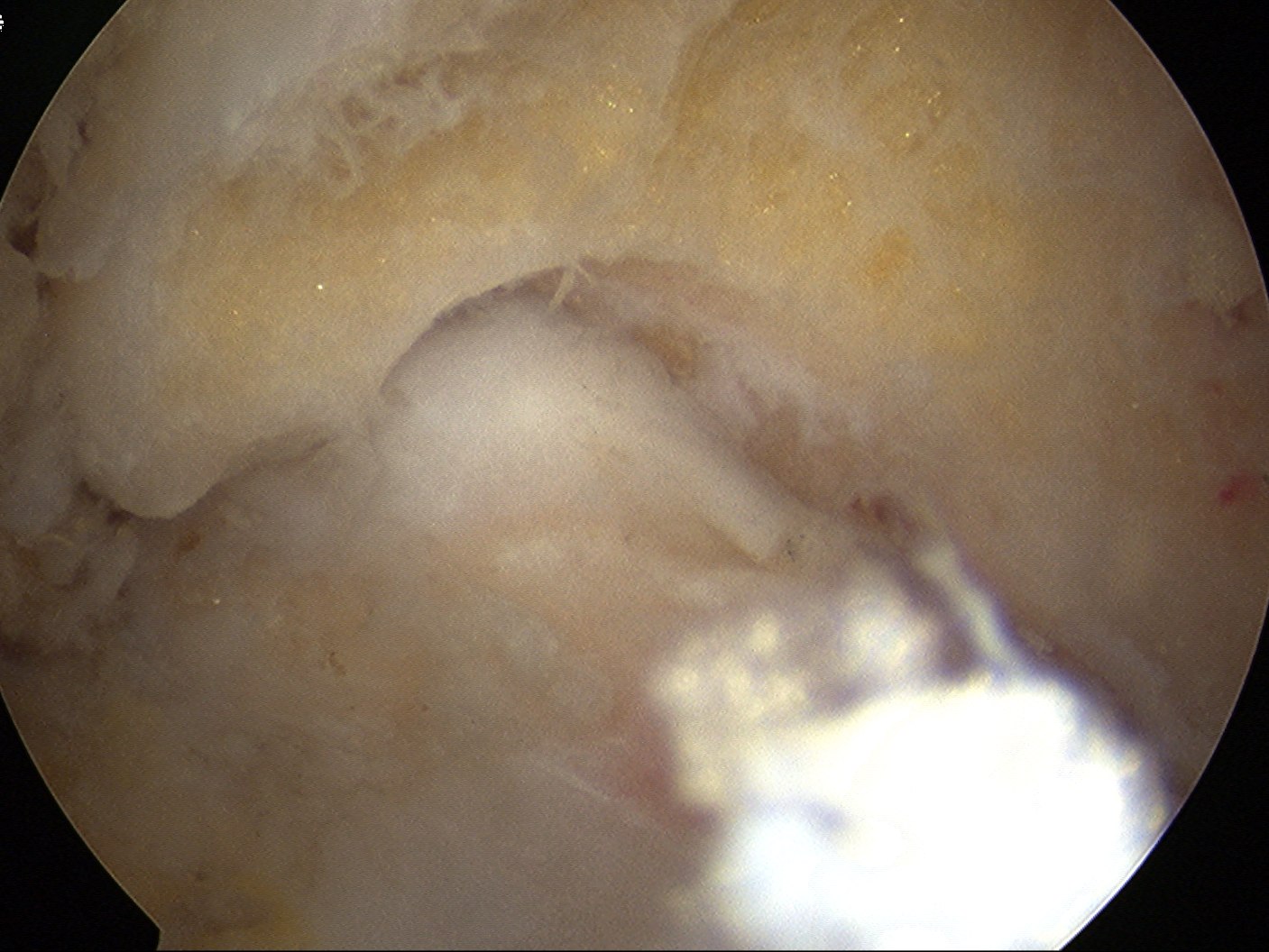
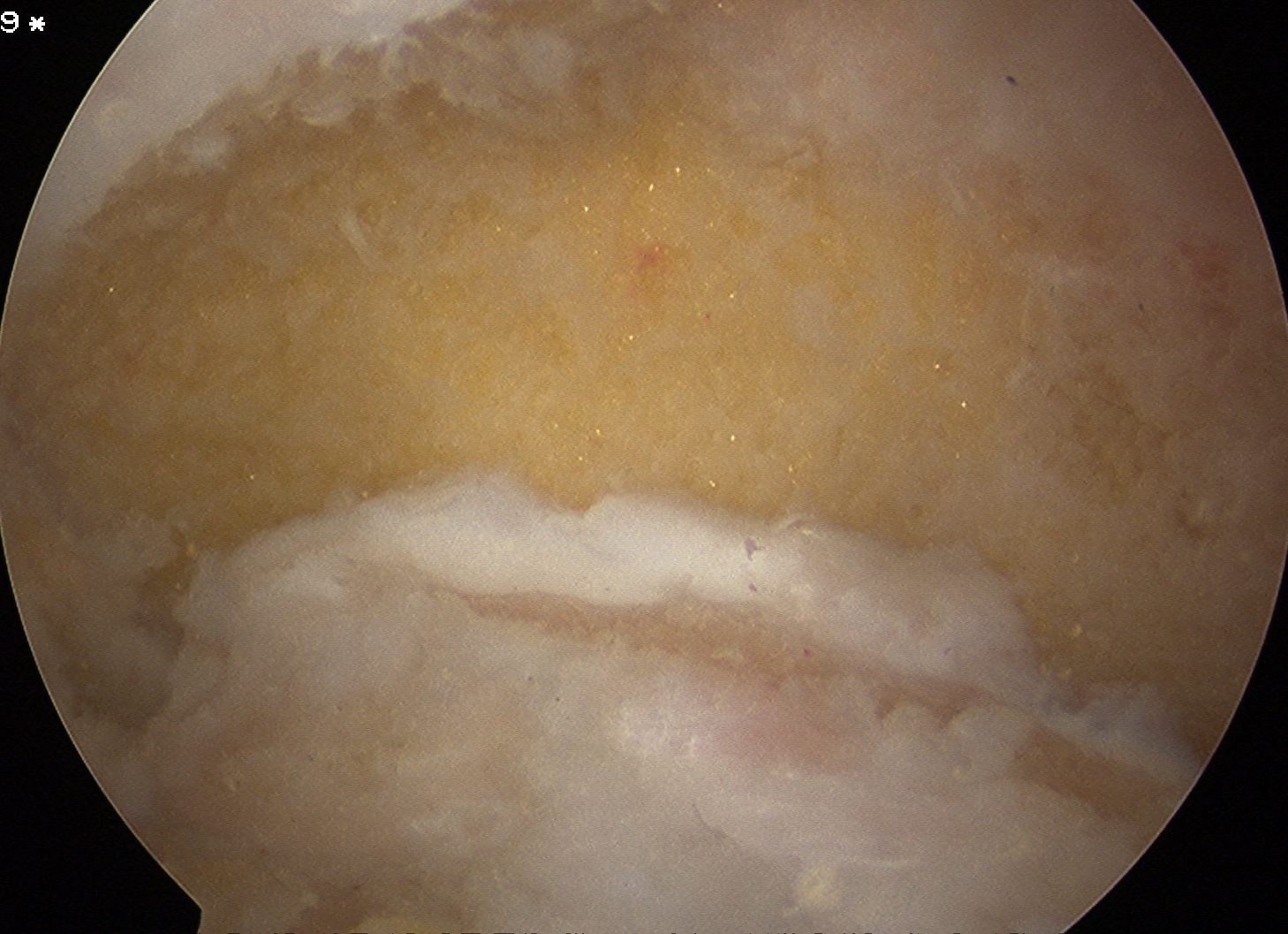
Post debridement of the tip of the olecranon, in the flexed and extended elbow position
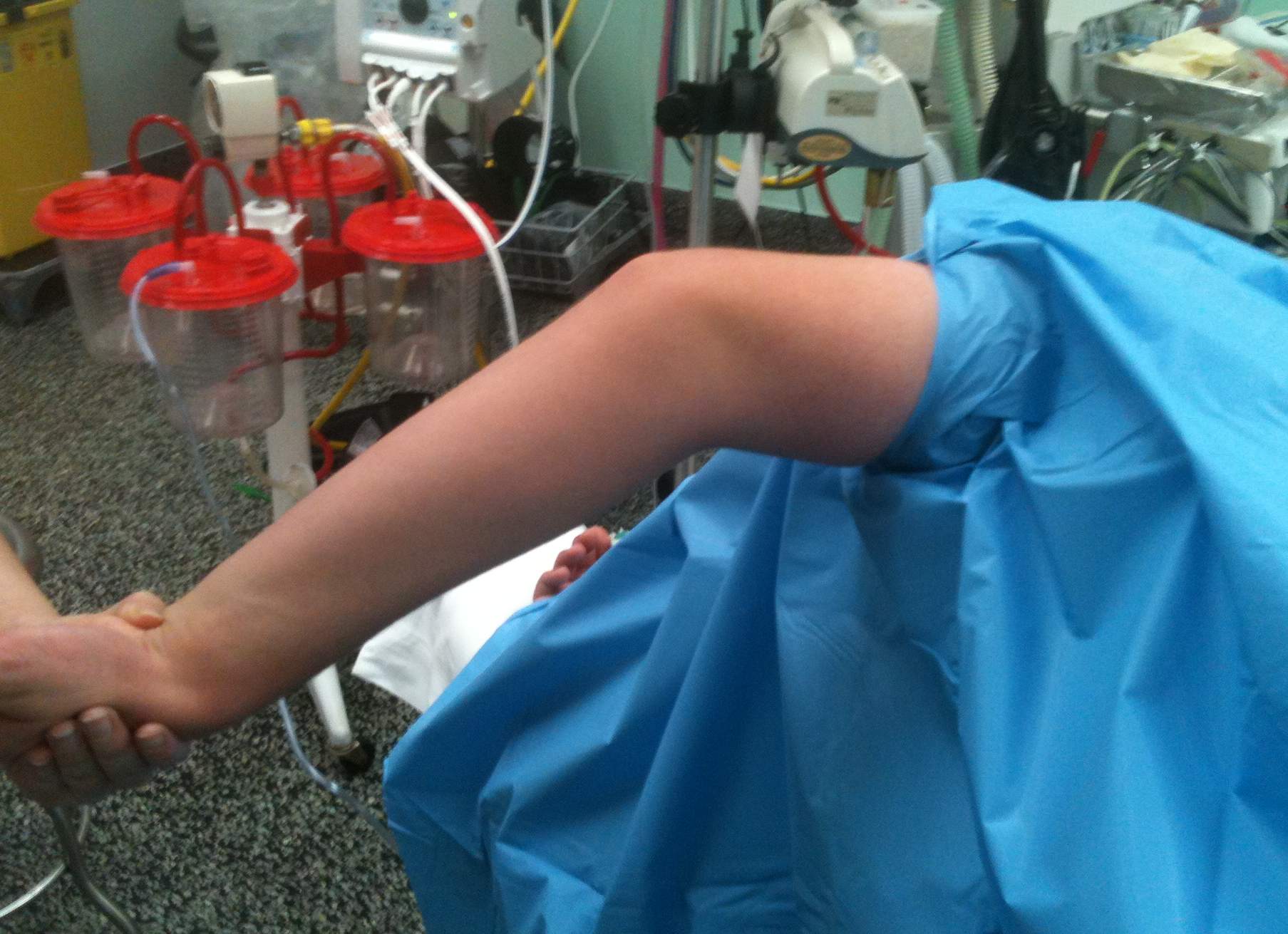
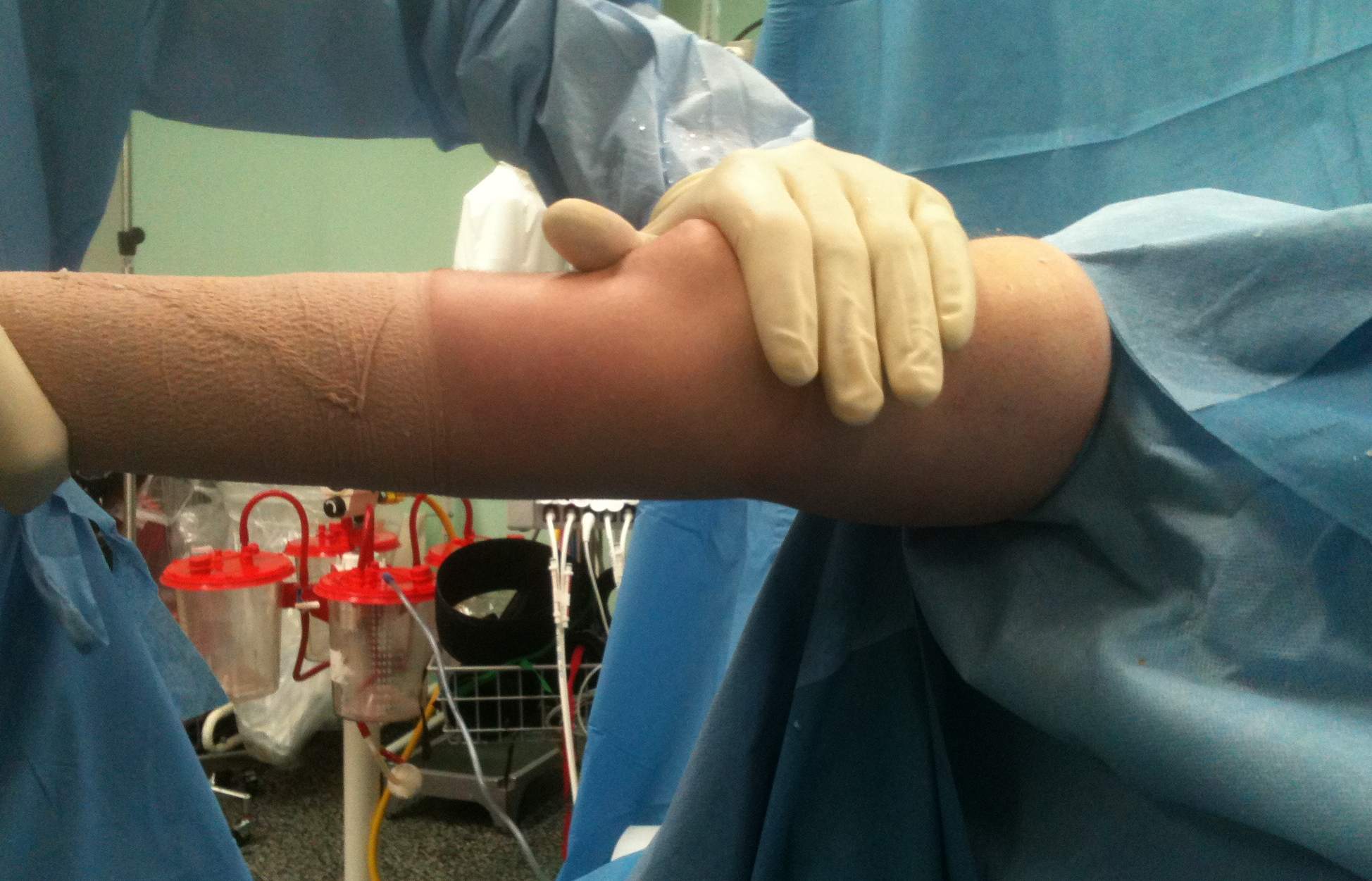
Elbow extension pre and post arthroscopic debridement
Interpositional arthroplasty
Technique
Vumedi elbow interpositional arthroplasty video
Elbow interposition arthroplasty surgical technique PDF
Strip of fascia lata / achilles tendon allograft
- graft passed around end of humerus to cloth front and back
+/- hinged external fixation with distraction
Results
Lanzerath et al Int Orthop 2022
- systematic review of 5 studies and 67 patients
- 21% revision rate
Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA)
Indications
- > 65
- sedentary
Results
TEA uncommonly required for primary OA
? reduced long term survival compared to RA
- 1220 TEA from Australian Joint Registry
- percentage revision was 10%, 15%, and 19% at 3, 6, and 9 years
- revision rate for OA > trauma and RA
- 20 TEA for primary elbow OA with mean 9 years follow up
- 3 mechanical failures
- no improvement in extension