Epidemiology
11-18 years
Aetiology
Usually severe trauma
Ossification
Head 5-6 months (1)
GT 2-5 years (5)
LT 9-13 years (9)
Delbert Classification
Type 1
- transepiphyseal separation / fracture
- rarest
- associated with hip dislocation
- AVN 100%
Type 2
- transcervical fracture
- commonest 50%
- AVN 50%
Type 3
- basicervical
- second most common 30%
- AVN 30%
Type 4
- intertrochanteric fracture
- AVN 10%
Management
Type I
Undisplaced
Rare situation
- spica
- watch carefully for displacement
Issue
- would like to stabilise
- any fixation must cross physis
Displaced
Emergency
Anatomical reduction
- single closed attempt
- open / Watson Jones approach
Fixation
- < 3 years K wires
- > 3 years cannulated screws crossing physis
Spica post op < 10 years old
Type II
Undisplaced
Hip spica
- need to watch carefull
Displaced
Anatomical reduction
- closed + capsulotomy
- open
Fixation
- < 3 years K wires crossing physis
- > 3 cannulated screws crossing physis
Spica post op < 10 years
Type III
Undisplaced
Hip spica v ORIF
- displacement a risk
- can leave fixation short of physis
Displaced
Closed reduction
- < 3 years K wires
- > 3 cannulated screws / pediatic hip screw
Spica post op < 10 years
Type IV
Undisplaced
Hip spica v ORIF
- displacement a risk
- can leave fixation short of physis
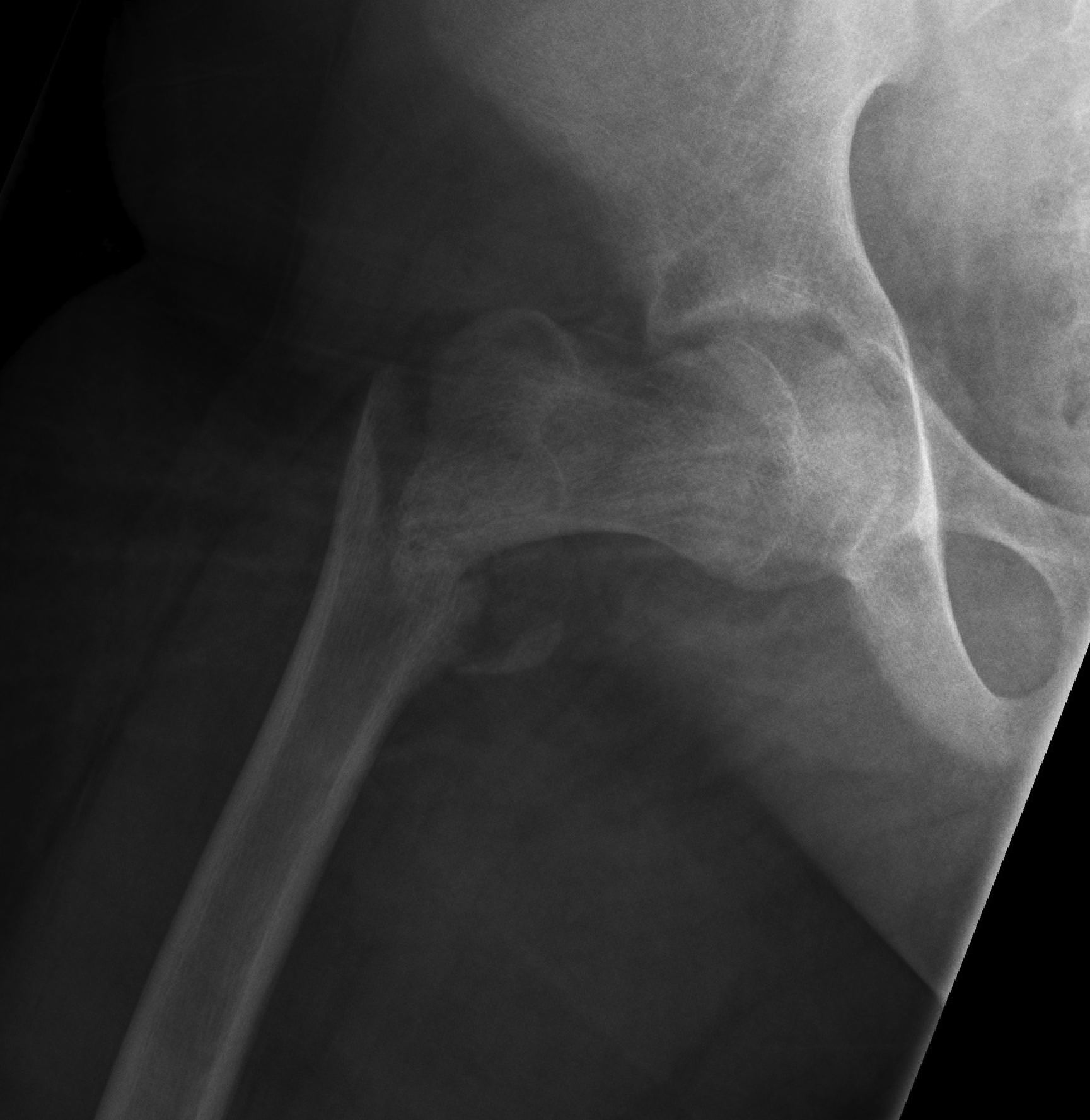
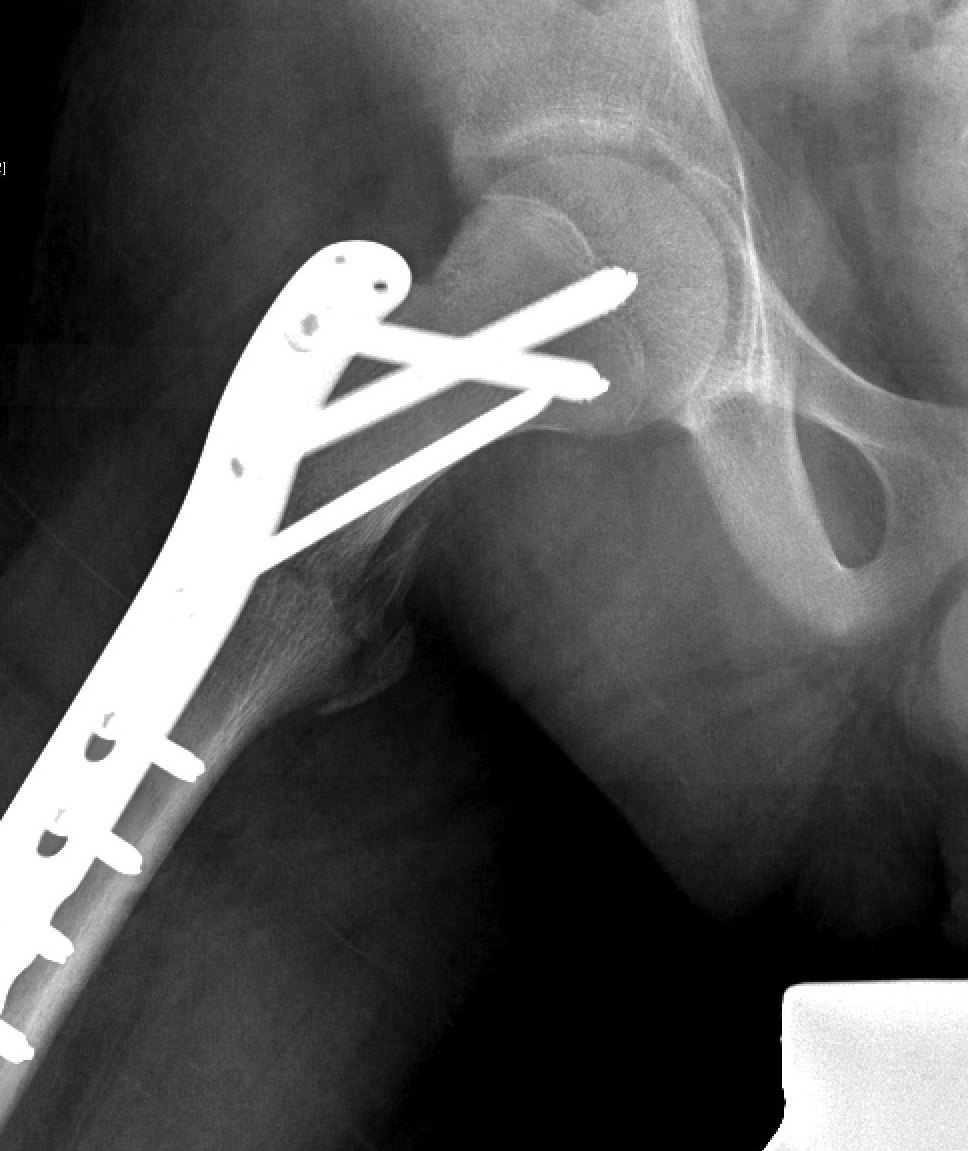
Displaced
Closed reduction
- < 3 K wires
- > 3 pediatric hip screw
Spica post op < 10 years
Complications
AVN
Urgent decompression of hematoma
- no real evidence
Options
- NWB
- bisphosphonates
- hinged articulated distracting external fixators
Non-union ~13%
Increased with non operative management
Treat with valgising osteotomy +/- BG
Growth Arrest / LLD
Contra-lateral distal femoral epiphysiodesis
Coxa Vara
Valgising subtrochanteric osteotomy
