Defect
Abnormality of type 1 collagen
- amino acid substitution of glycine with another amino acid
- prevents triple helix formation
Many many deformities described
- some 286 mutations of Type 1 collagen described
Sillence Classification
There are actually now 7
Type I
- mild
- AD
- blue sclera
Type II
- lethal in utero
- AR
- blue sclera
Type III
- severe
- AR
- white sclera
- multiple deformities without intervention
- wheelchair bound and non ambulatory
Type IV
- moderate to severe
- white sclera
- AD
- very rare
DDx
NAI
Rickets
Diagnosis
Skin biopsy
- assessment of type 1 collagen
- fibroblast cell culture
DNA study
Skeletal Manifestations
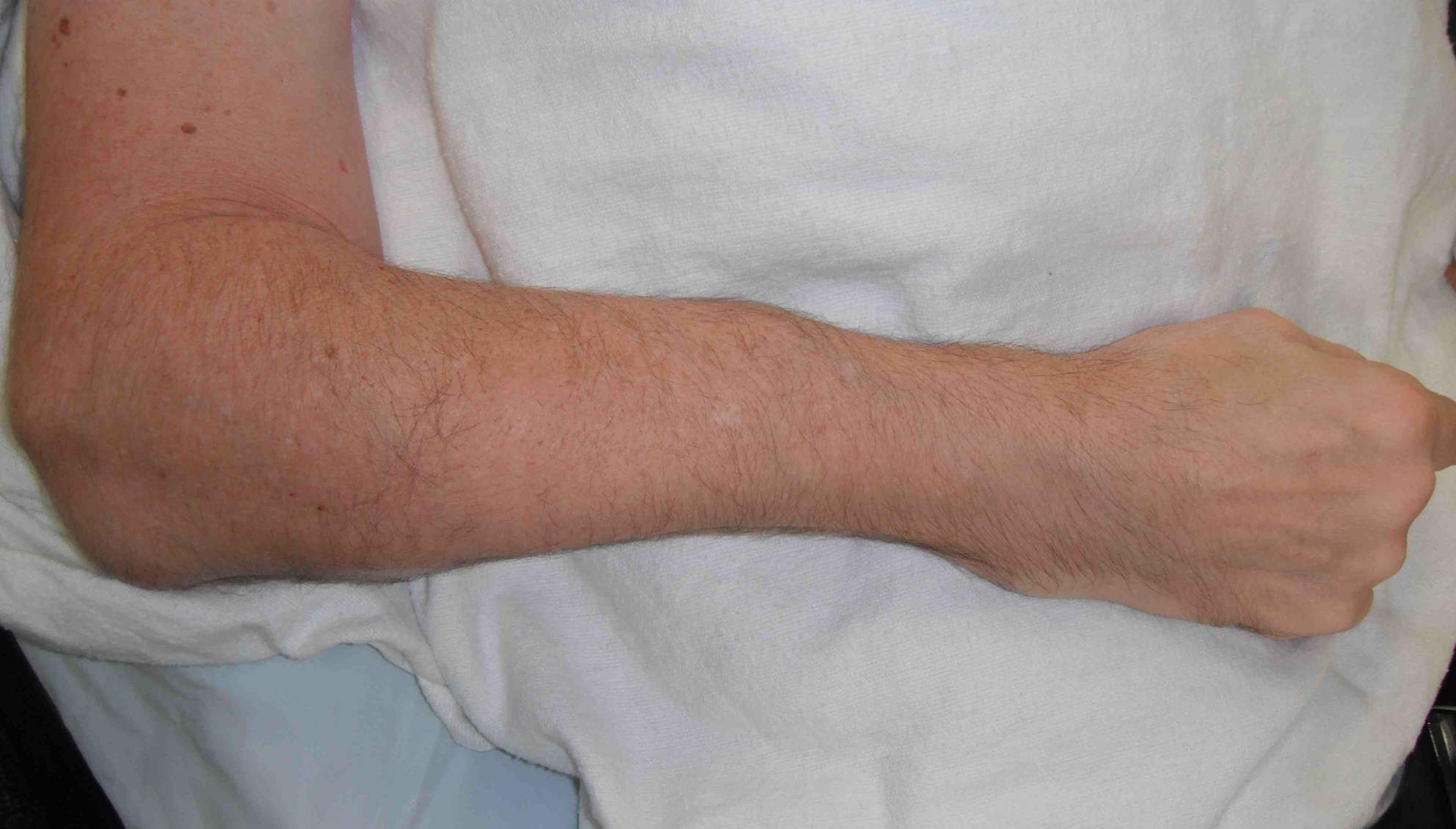
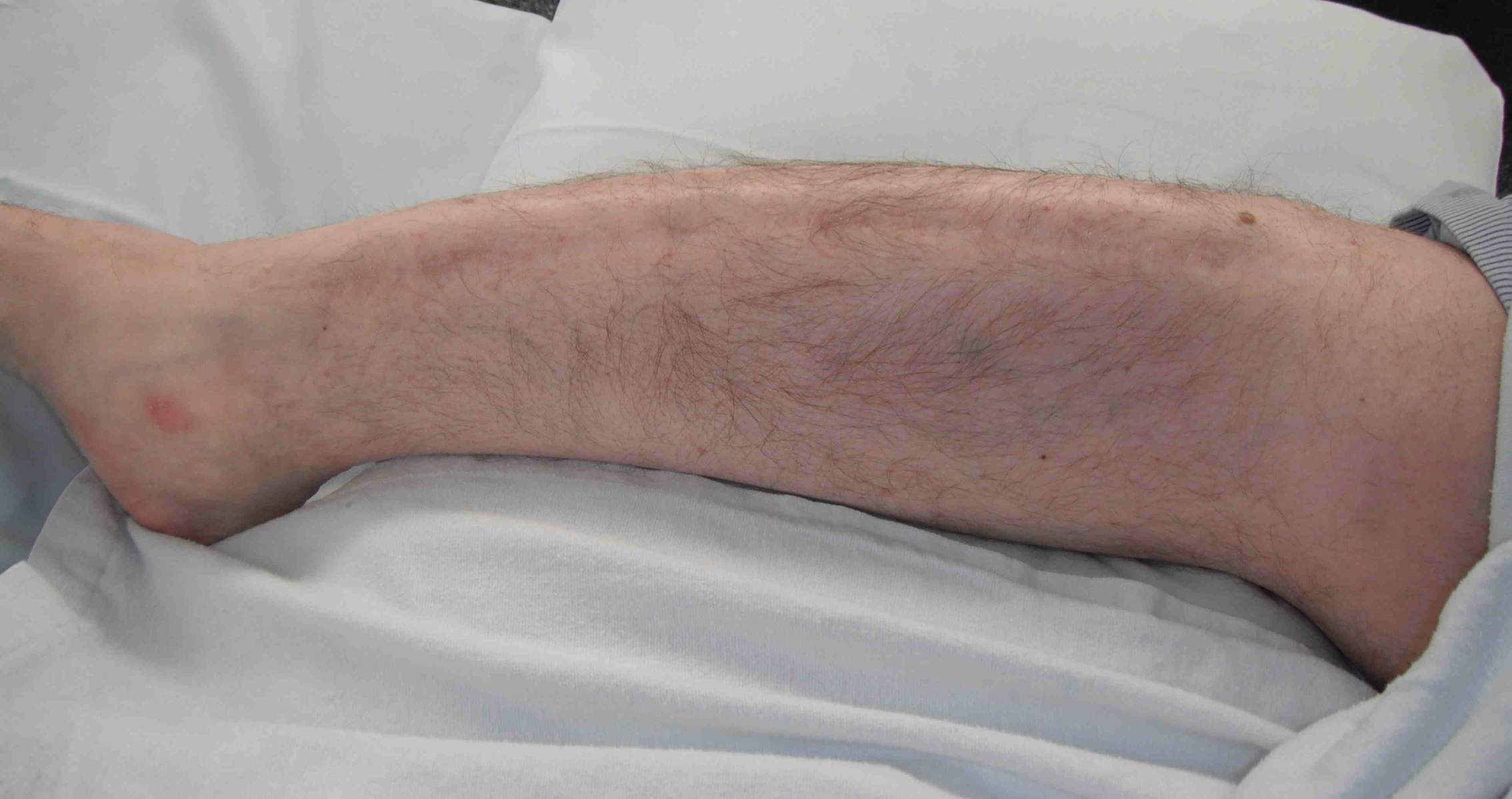
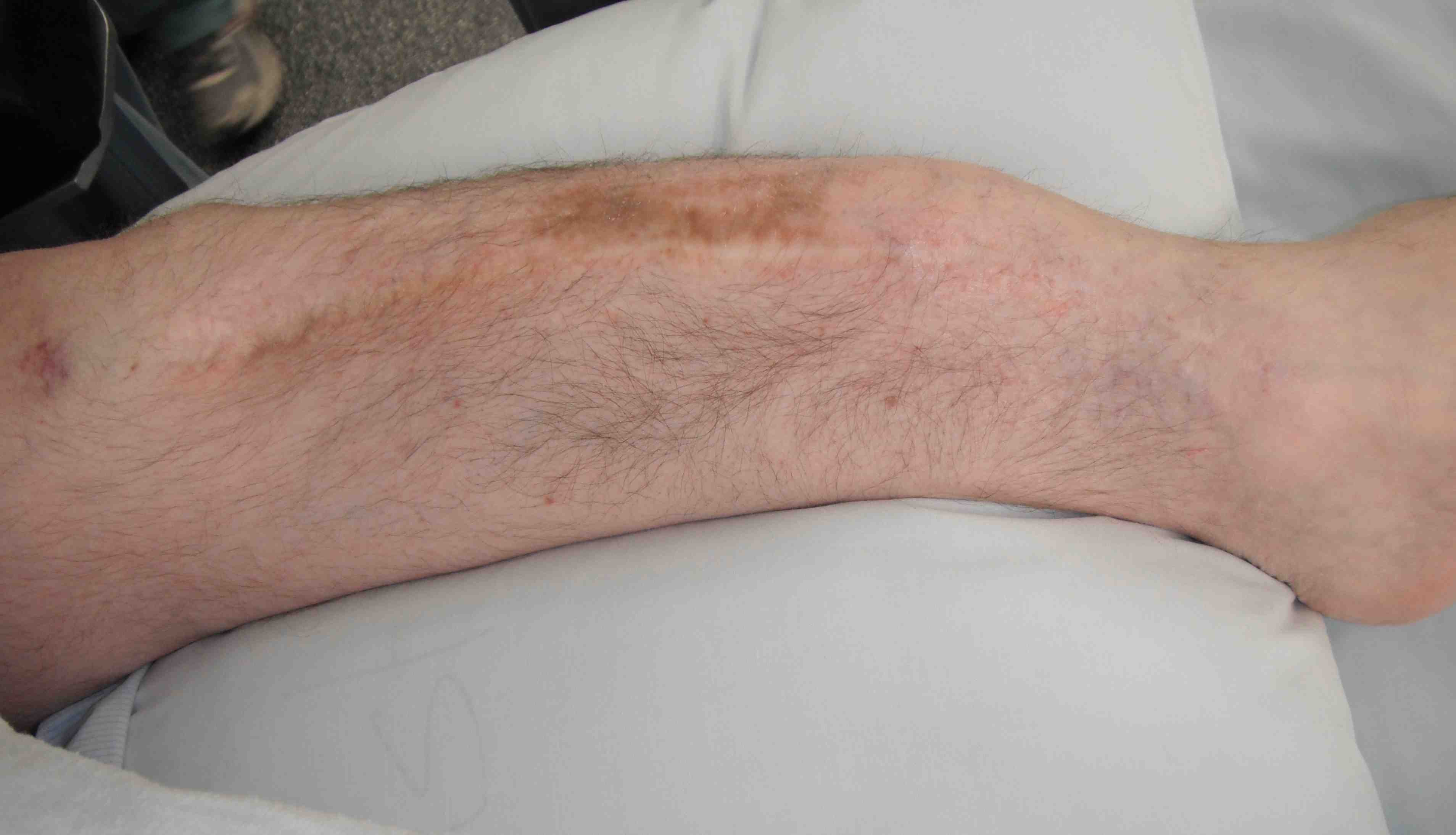
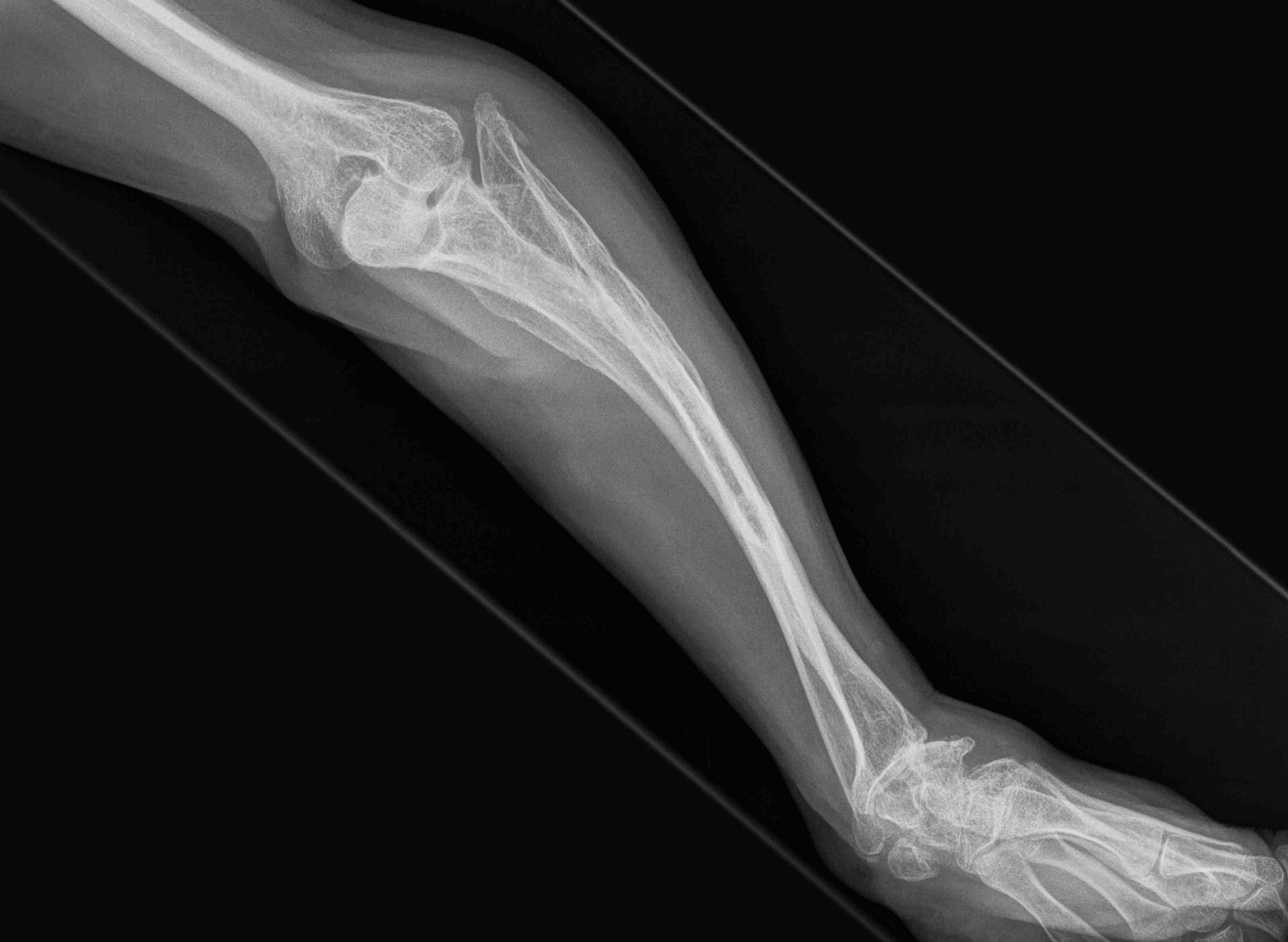
Frequent multilevel fractures with limb deformity
- tibia
- femur
- forearm

Coxa vara
- femoral neck shaft < 110o
- correct with multiple osteotomies
Kyphoscoliosis
Surgery
- indicated for curve reaching 40o as will be progressive and non flexible
- > 60o impairs respiratory function
Problems
- bony fragility
- increased use of pedicle and TP hooks and sublaminar wires
Basilar impression / invagination
Very serious problem
- the foramen magnum invaginating into the posterior fossa
- leads to stenosis with resultant hydrocephalus
- compression of the cerebellum, brain stem, and cervical cord
Lateral cervical spine radiograph
- upward migration of the cervical spine into the base of the skull
- deformity may be subtle and requires careful scrutiny of the radiographs
Various descriptions of the characteristic skull shape
- Darth Vader
Extraskeletal Manifestations
Blue sclera
- due to translucent sclera can see underlying choroid and blood vessels
- due to defect type 1 collagen
Dentinogenesia imperfecta
- teeth appear brownish or bluish
- are soft, translucent and prone to cavities
- defect type 1 collagen
Hearing problems
- defect hearing bones
Fragile skin and fragile capillaries
Valvular Disease
Mitral prolapse and Aortic Regurgitation
Management
Nonoperative Management
Bisphosphonates
Increase BMD and cortical thickness and cancellous trabeculation
- reduces bone pain
- decrease fracture rate
- maintains shape of long bones and vertebrae
Mechanism of action
- inhibits osteoclasts
Pharmocokinetics
- very poor bioavailability (.6 - 7)
- incorporated into skeleton
- long half life there (1.5 - 10 years)
Problems
- need period off medications
- doesn't decrease fracture healing but probably does decrease osteotomy healing (i.e. avoid around time of IM rodding)
- osteonecrosis of the jaw: a rare side effect in adults, not seen in children
Results
Glorieux et al NEJM 1998
- increased BMD by 40%
- reduced fracture rate by 1.7 per year
- evidence new bone formation in vertebrae
- did not alter rate fracture healing
Bone marrow transplant
Increased mesenchymal stem cells
Operative Management
Goals
Prevent fractures
Treat or prevent deformity
Technique
Multilevel osteotomy with IMN
- must be expandable or get fracture and deformity below level
Expandable telescopic IM rods
Concept
- lengthen as the bone grows
- male and female portions
- lock in epiphysis top and bottom
Sheffield Rods
- T piece
- 20% revision at 5 years
Fassier-Duval Rods
- epiphyseal portion is threaded
