Definition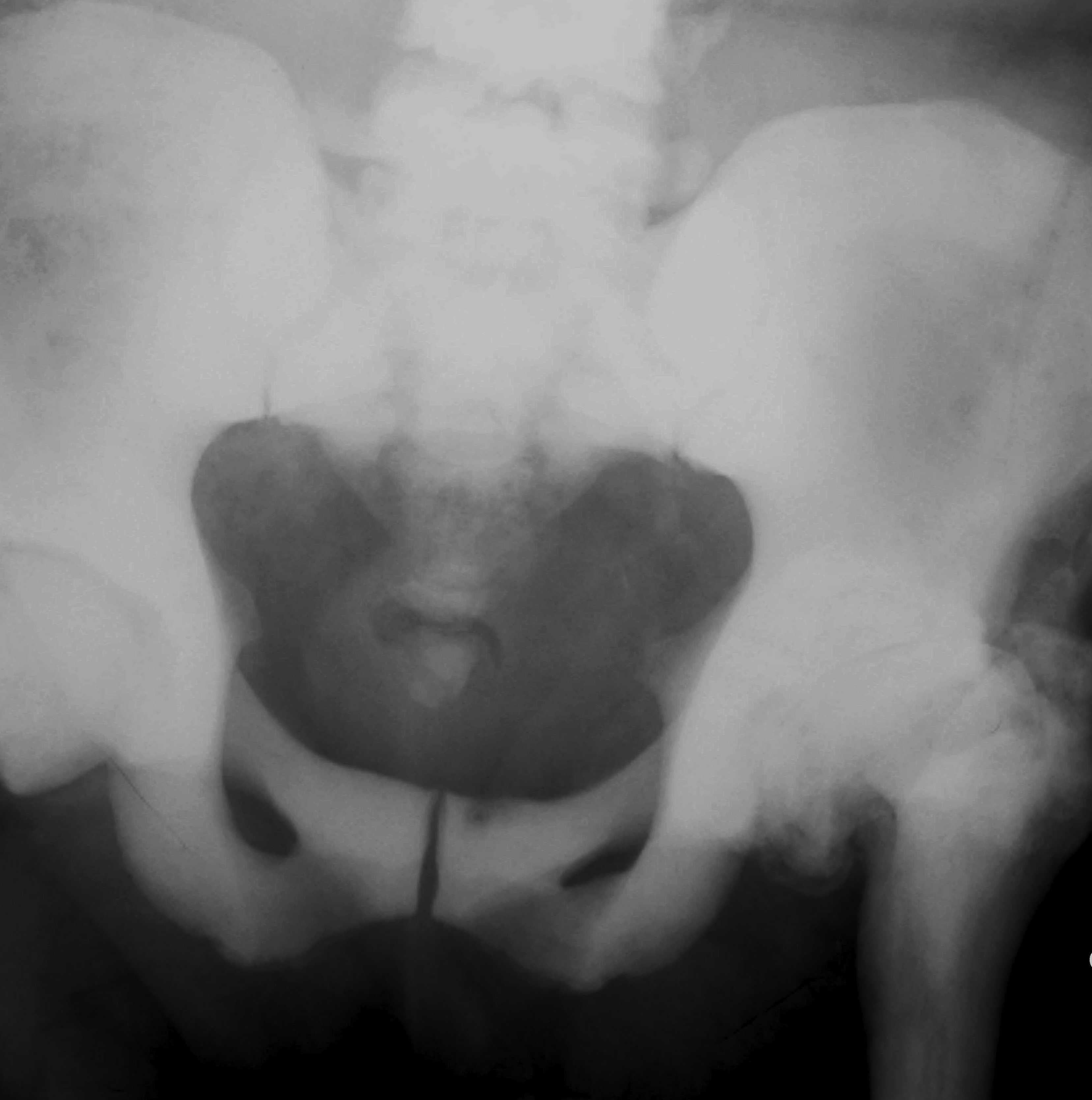
Inheritable bone disorder characterised by defective osteoclasts
- resulting in hard and brittle bone
Pathophysiology
Defect of osteoclasts
- unable to acidfy Howship's lacunae
- unable to resorb bone
- missing ruffled border
Heterogenous group
- 60% defect of proton pump
- 5% carbonic anhydrase defect
Inability to remodel bone with thickened sclerotic cortex
- impinges on medulla
- woven bone architecture
- thickened cancellous trabeculae
Unresorbed calcified cartilage
- prone to fracture
Forms
1. Malignant AR
Few survive first decade
- bony overgrowth of medulla
- blocks hematopoiesis
- anaemia/neutropenia/thrombocytopenia
- need bone marrow transplant to survive
Cranial nerve compression
- overgrowth foramina
- optic, auditory, facial n
Fracture
2. Intermediate AR
Moderate anaemia
Some nerve compression symptoms
Frequent fractures in first decade
3. Benign AD
Most common
- diagnosed after fracture
- 40% asymptomatic
- due to variable penetrance
Clinical Features
1. Frequent long bone fractures
- femur and tibia
2. Long bone deformity
- callus slow to organise
- lateral bowing of femur
3. Hip
- coxa vara
4. OA
- common in hip
- compression of cartilage on hard bone
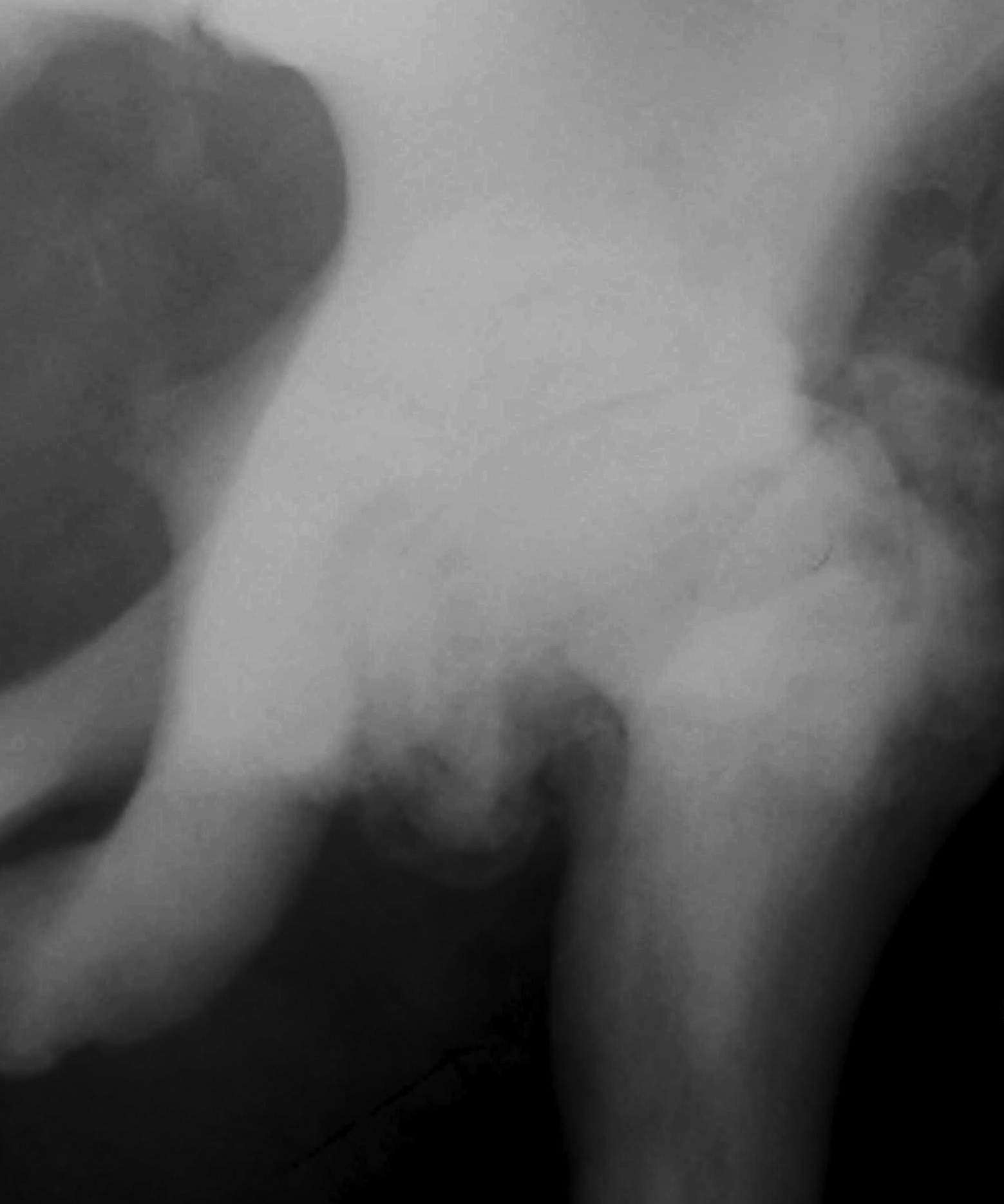
5. Spondylosis
6. Osteomylelitis
- 10 % patients
- most often in mandible
- lack of marrow vascularity
- impairment of white cell function
7. Cranial nerve compression
- 20-25%
- optic, auditory, trigeminal, facial
X-ray
Generalised sclerosis
- subchondral sclerosis in pelvis
Endobone
- bone within bone
- failed resorption of primary spongiosa
Vertebral end plate thickening
- rugger jersey vertebrae
Erlenmeyer flask deformity
- widened club like metaphysis
- in children
Transverse banding of metaphyses
Management
Non operative
1. Interferon gamma
Mechanism
- increases bone resorption
- improves hematopoiesis and leucocyte function
2. High dose vitamin D / diet low in calcium
Mechanism
- stimulates osteoclasts
3. Bone marrow transplant
Indication
- children with malignant form
Operative Management
Fractures
Attempt to treat non operatively if possible
- ORIF difficult
- nil medullary canal
- break drill bits
ORIF
Plates often fail
- IM load sharing devices best
Increased time to union
Difficulty drilling, inserting screws and pins
- drills over heat and break
- advance 1cm at a time
- frequent cleaning and cooling
- alternate drill bits
Longer surgical time
Arthroplasty
Technical difficulties
Unable to use hand reamers
- recreate medullary canal
- burrs needed
- use II to check
- short narrow stems
- can consider resurfacing
Complications
Increased risk intra-operative fracture
Increased risk infection
