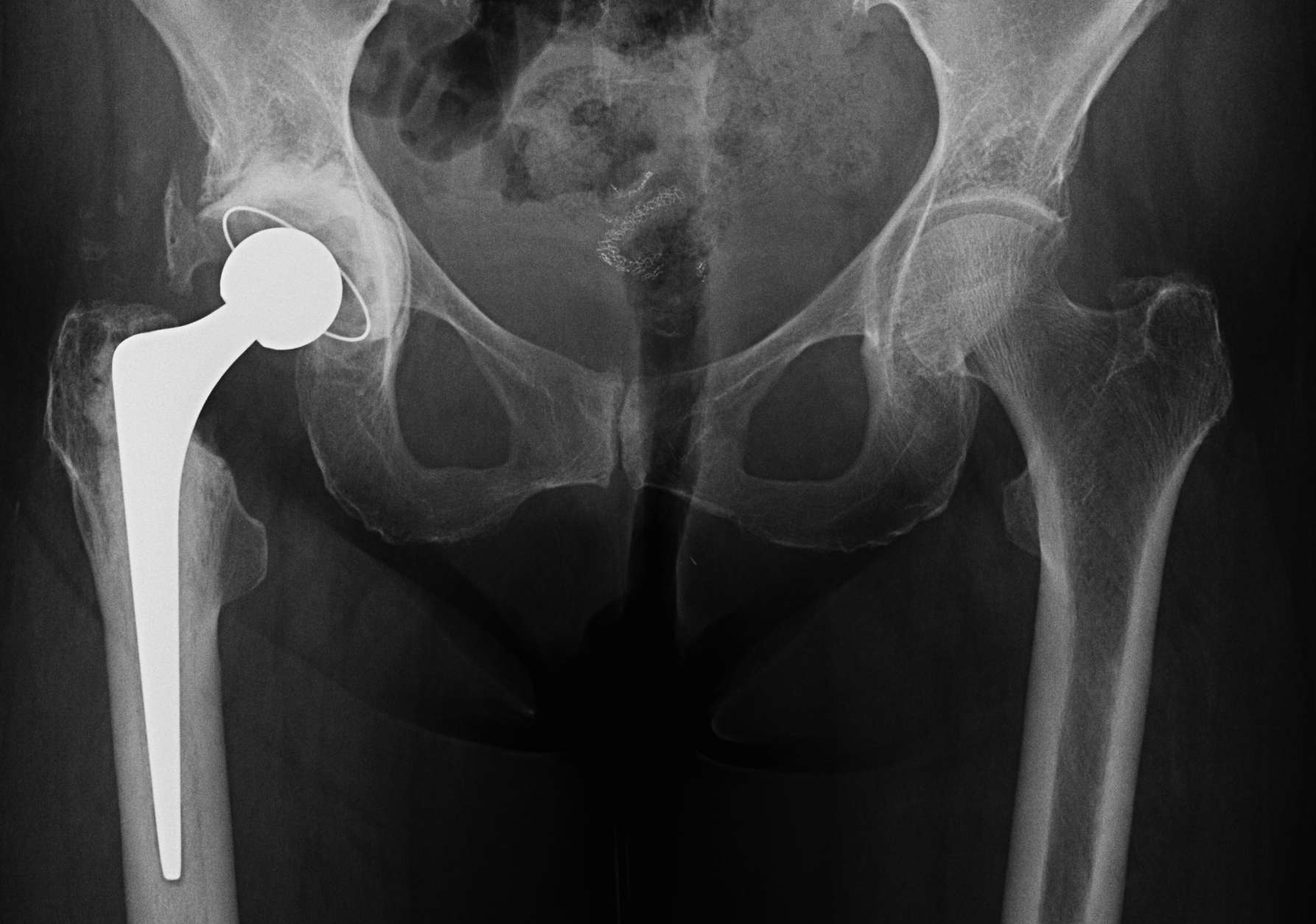
Complications of LLD
1. Abnormal gait / risk of falls
2. Lower back pain / scoliosis
3. Nerve palsy
- sciatic nerve - tolerate average 4.4cm lengthening
- common peroneal nerve - tolerate average 2.7 cm lengthening
4. Instability / dislocation
Pre-operative assessment
Examination
True LLD
- anatomical discrepancy in leg lengths
- ASIS to medial malleolus
Apparent / Perceived LLD
- altered mechanics
- scoliosis and pelvic obliquity
- hip fixed flexion deformity (FFD) & adduction - apparent shortening
- abduction contracture - apparent lengthening
- umbilicus to medial malleolus
- can measure with blocks
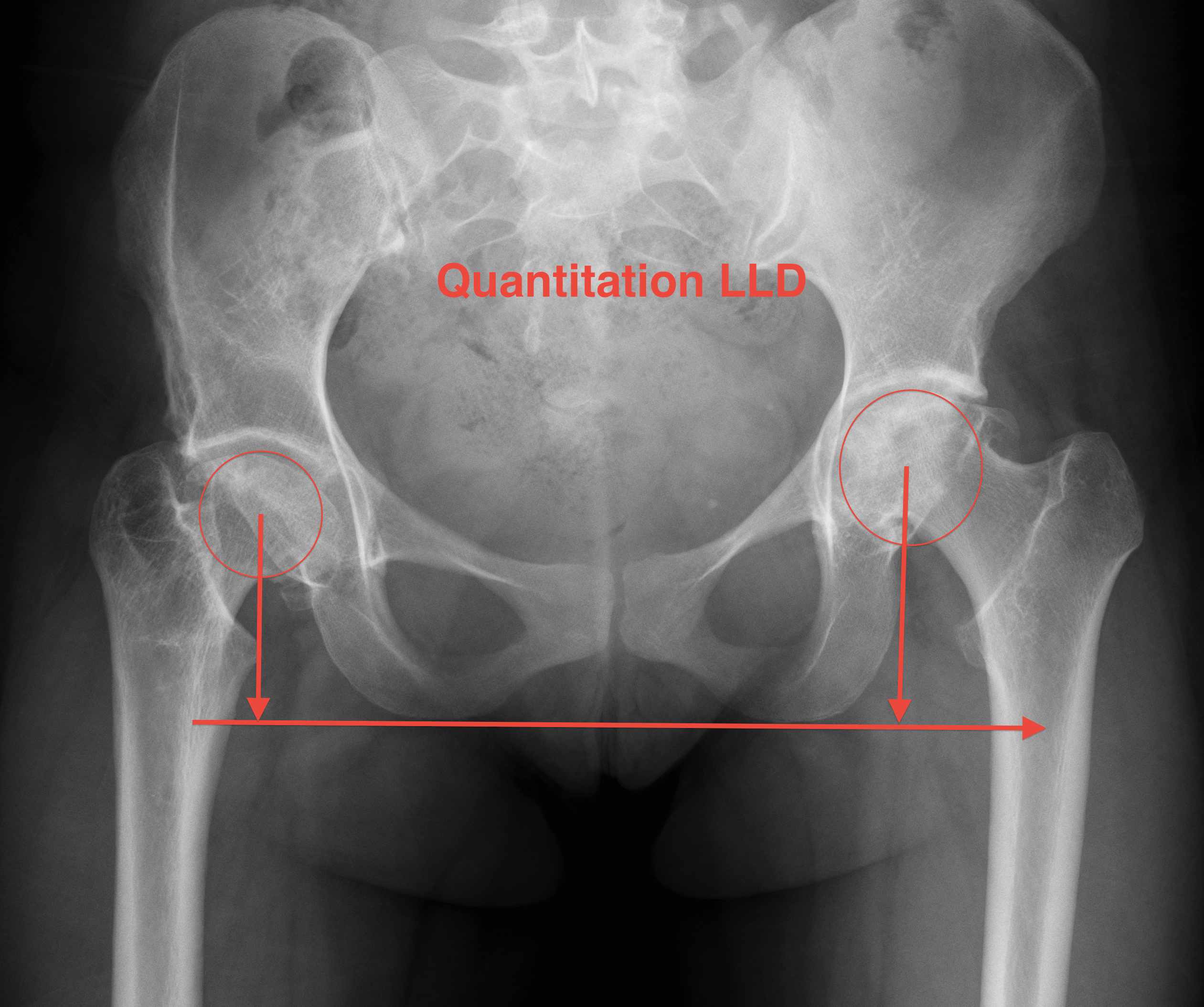
X-ray templating
AP pelvis
- both femurs IR 15o / compensate for anteversion
- symmetrical abduction / adduction of femurs
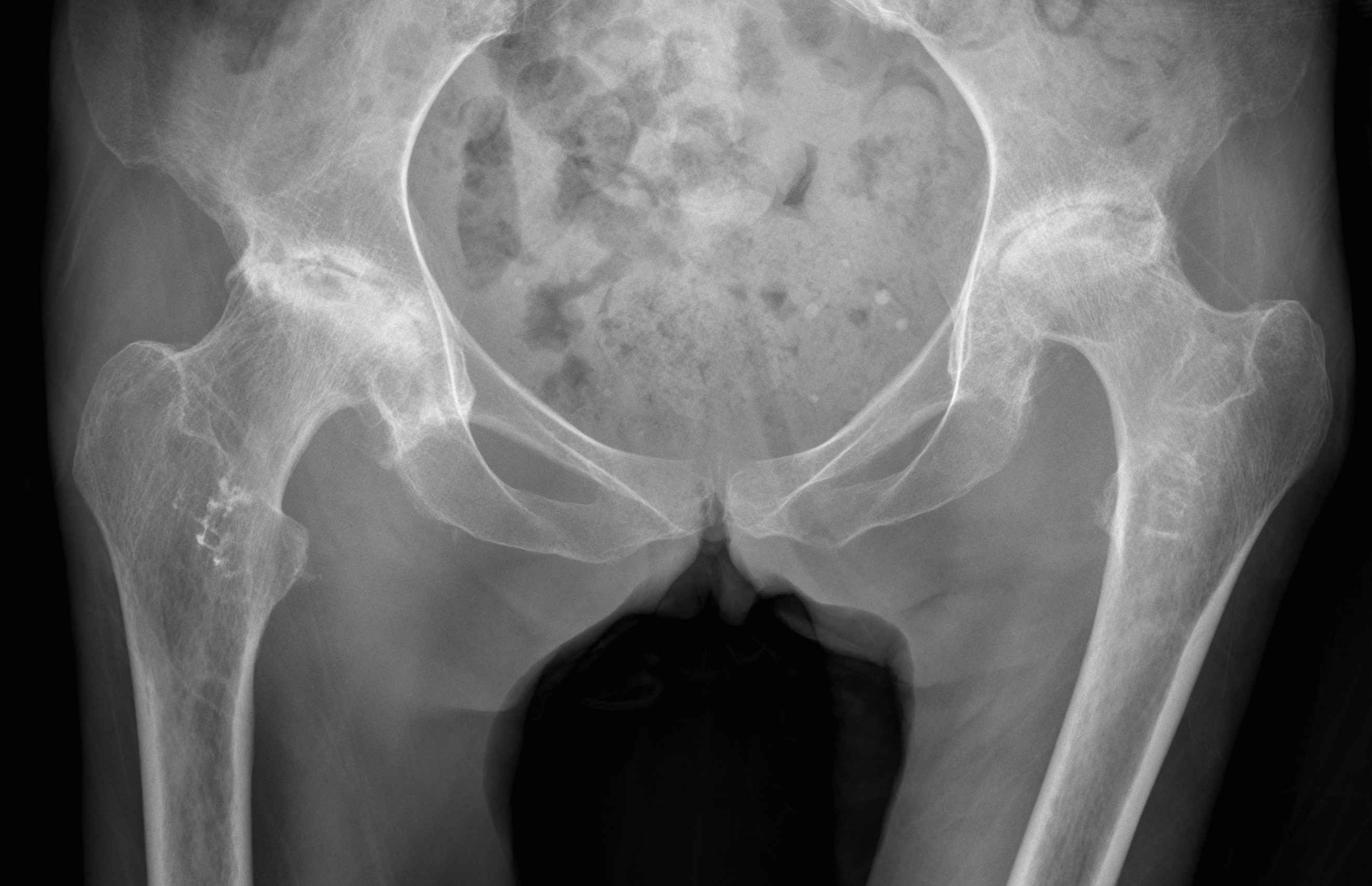
Abnormal femur position
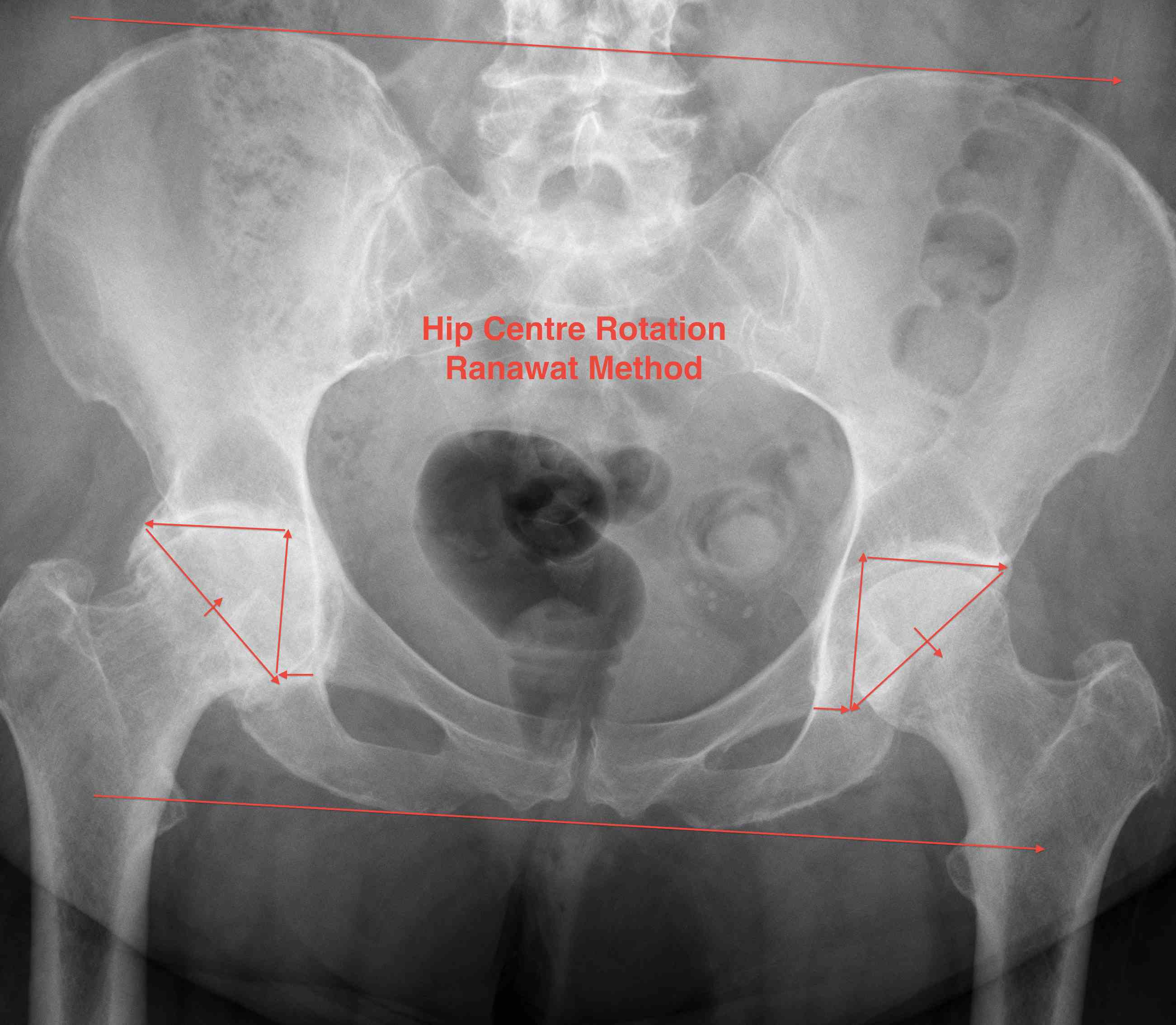
Pelvic landmarks
- inferior aspect of ischial tuberosities
- tear drop
- center of rotation
Femoral landmarks
- lesser tuberosity
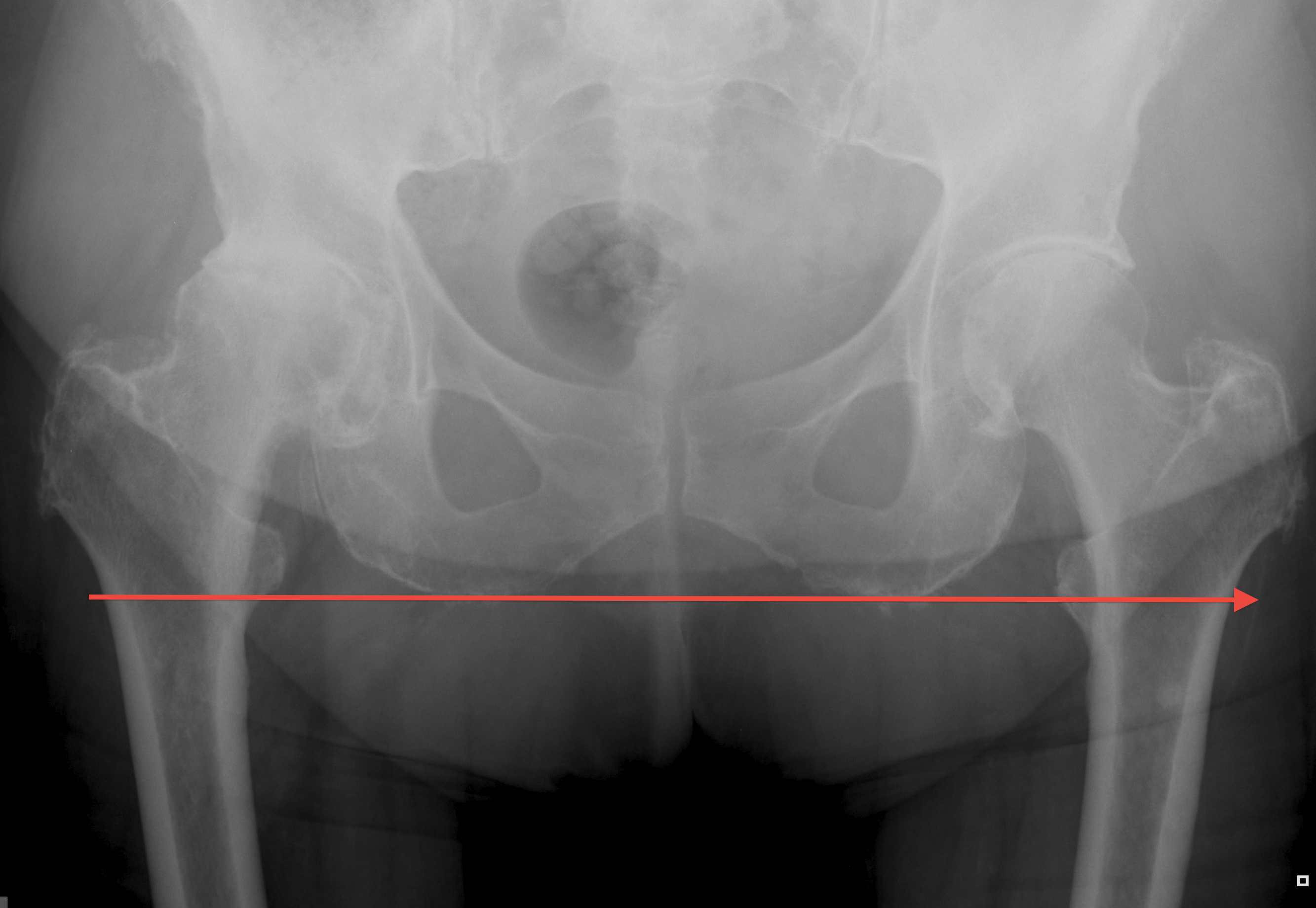
Intra-operative assessment
1. Leg to leg comparison
Careful patient positioning
- ASIS perpendicular to floor and patient stable
- place both legs in same position i.e. flexion / adduction
- supine - palpate medial malleolus
- lateral - palpate heels
2. Tests
Shuck test
- distract femoral head from acetabulum
Drop Kick Test
- with thigh extended, knee should be able to flex past 90 degrees
- if tension too tight, knee will extend
ROM
- if hip tension too tight, ROM especially IR / ER / extension is limited
3. Intra-operative measurement
Mechanical referencing / Pins
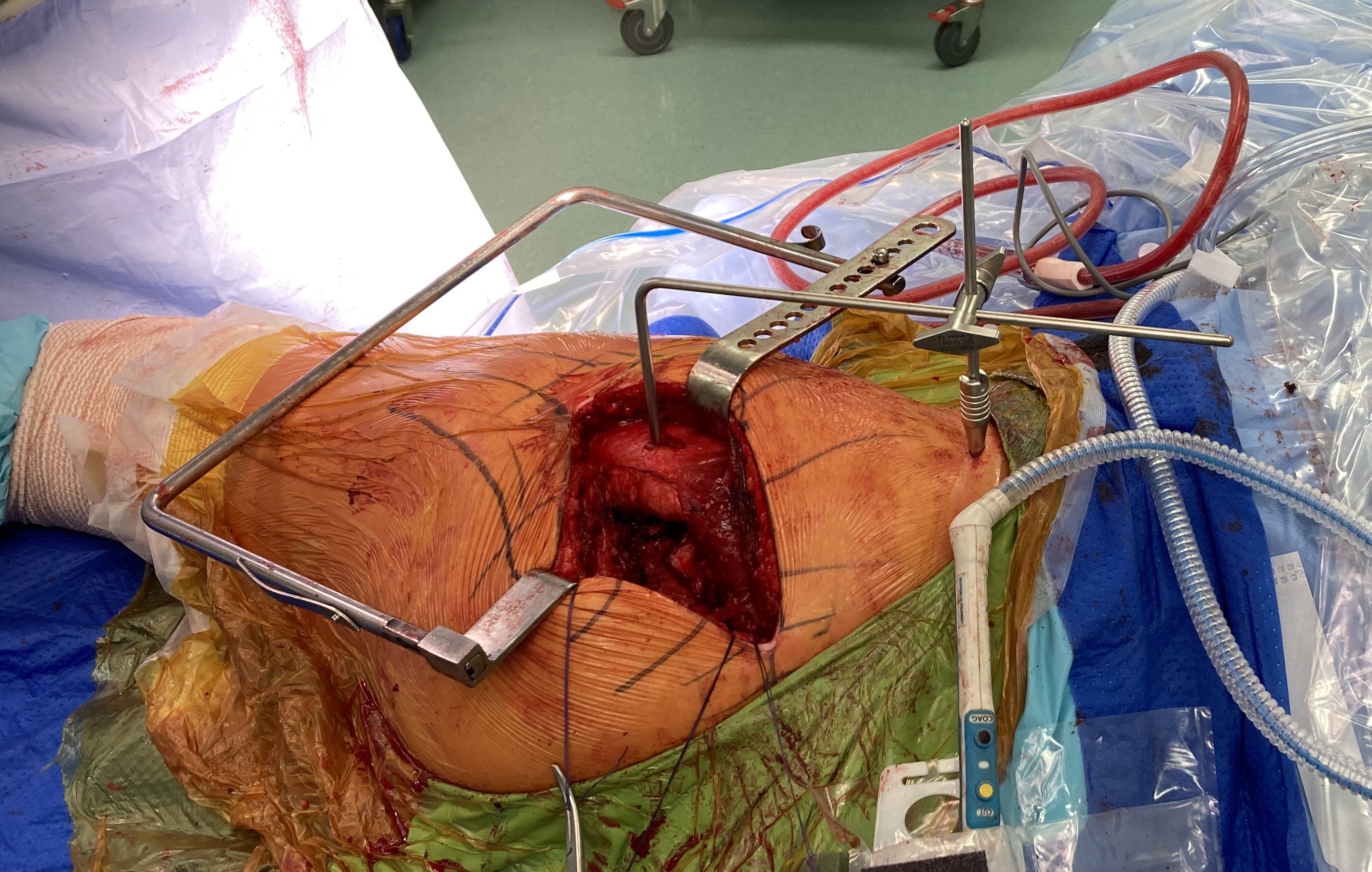
Technique
- pin in pelvis / pin in femur
- must place leg in similar position each time to measure leg distance
- measure horizontal distance (LLD) and vertical distance (offset)
- comparison study of mechanical vs freehand
- mechanical reduces incidence of LLD
Fluoroscopy
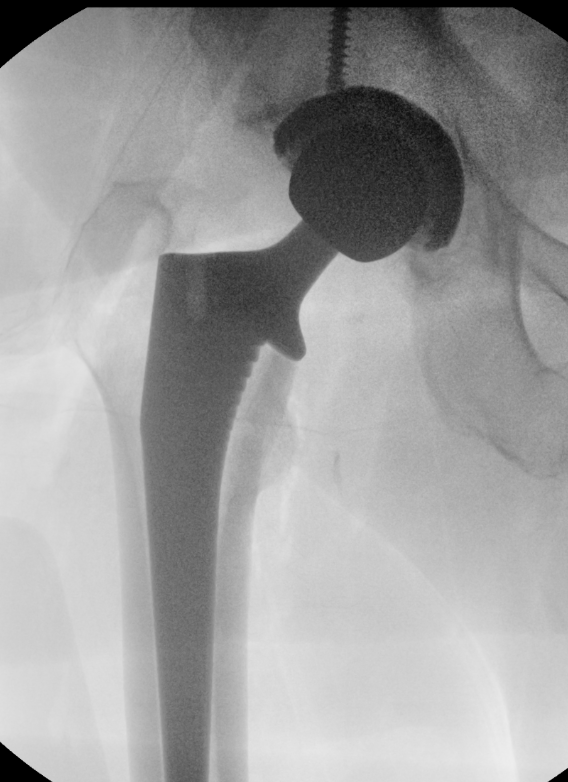
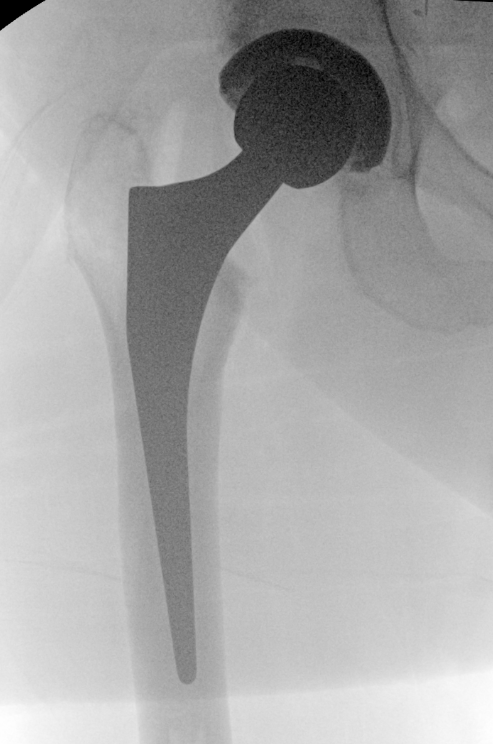
Sun et al Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2024
- meta-analysis of use of intra-operative fluoroscopy versus conventional navigation in THA
- fluoroscopy reduces incidence of LLD
Image-less Navigation
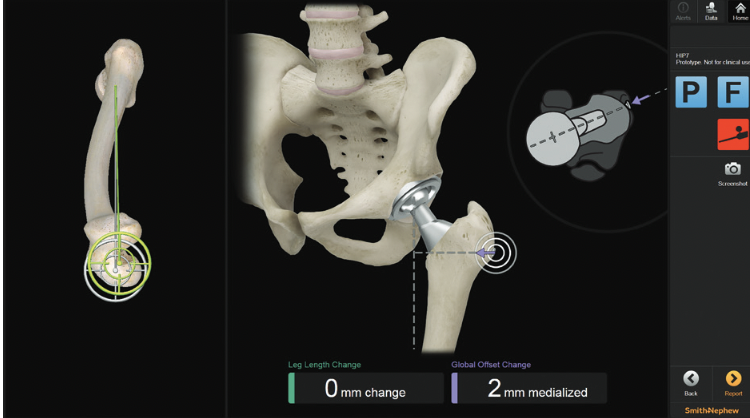
Smith&Nephew RI Hip Navigation
Migliorini et al J Orthop Traumatol 2022
- meta-analysis of image-less versus conventional THA
- image-less reduces LLD
CT navigation
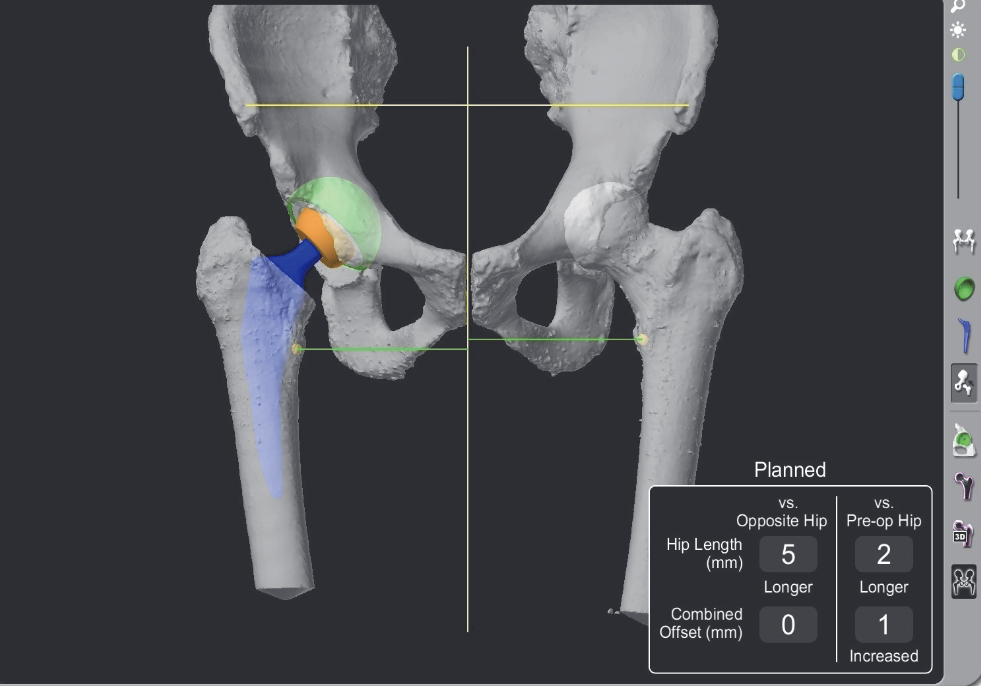
Migliorini et al Eur J Med Res 2023
- meta-analysis of CT navigation versus conventional in THA
- CT navigation reduces LLD
Postoperative LLD
Incidence
Transient perception of LLD common
- usually apparent leg lengthening
Cause
- leg was slightly short, now normal length
- contracture releases
Typically resolves over 6 months
Management
Nonoperative
Delay using shoe lift for 6/12
- allows apparent LLD to resolve
Shoe insert for opposite leg
Operative
- 21 cases of LLD mean 4 cm following THA
- treated with revision
- LLD restored to within 1 cm in all cases
