Management
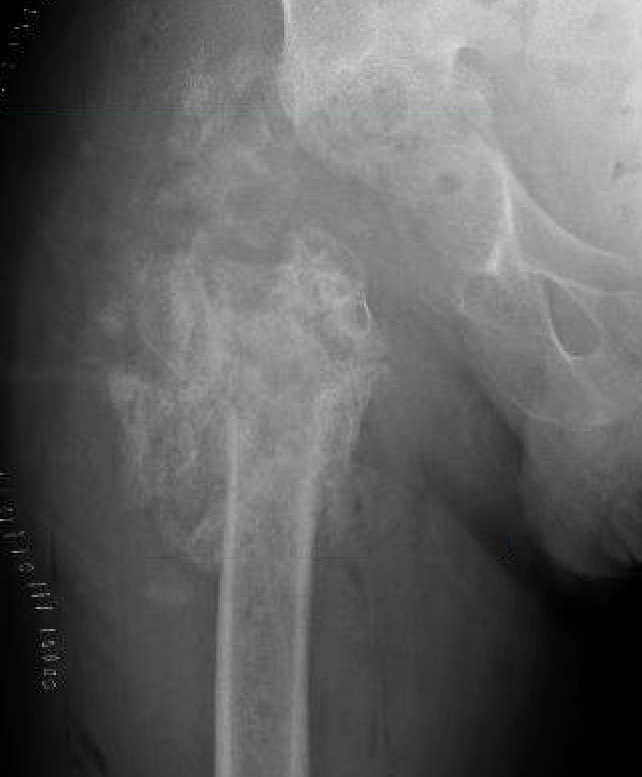
Tsukayama Classification


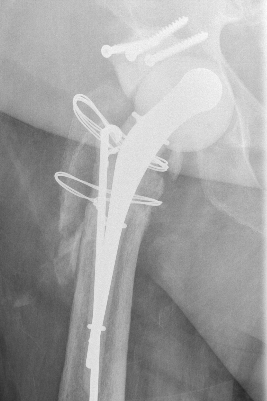
1. Standard trochanteric osteotomy
2. Sliding trochanteric osteotomy
3. Extended trochanteric osteotomy

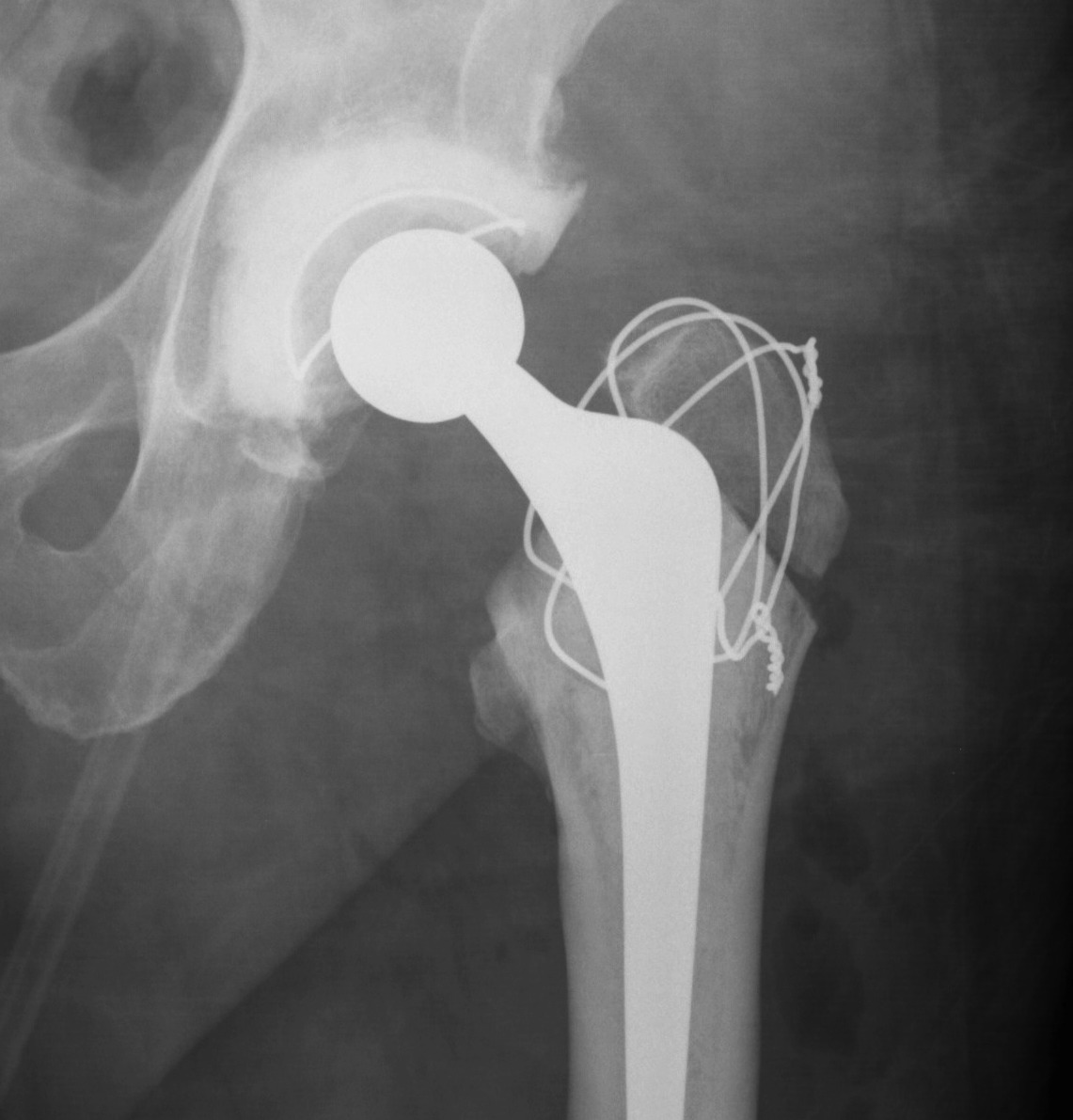
Ranges
- up to 4%
Focal pain
- typically anterolateral thigh
- often tender
- corresponds to tip of stem
1. Instability
Types
- early
- late / failed bony ingrowth
Cause
- micromotion at distal stem
Patient > 70
Gjertsen et al JBJS Am 2010
- 4335 patients > 70 with displaced subcapital fractures
- minimum 1 year follow up
- 1 year mortality same in each group / 25%
- 22% reoperation in ORIF v 3% in hemiarthroplasty
- more pain / higher dissatisfaction / lower quality life in ORIF group
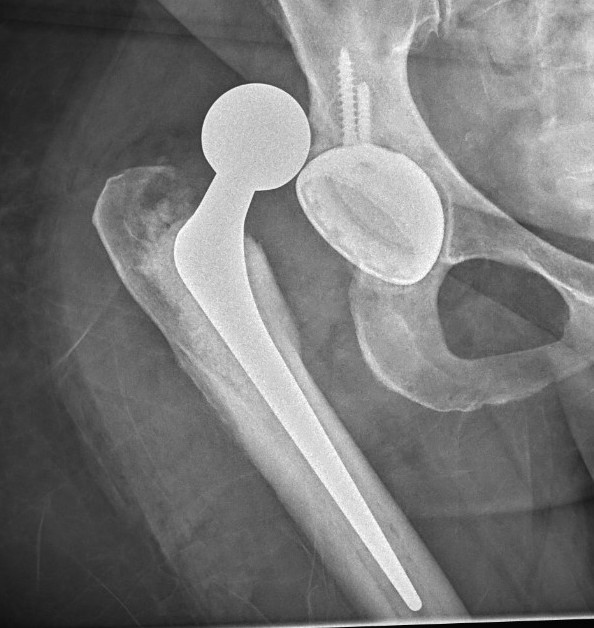
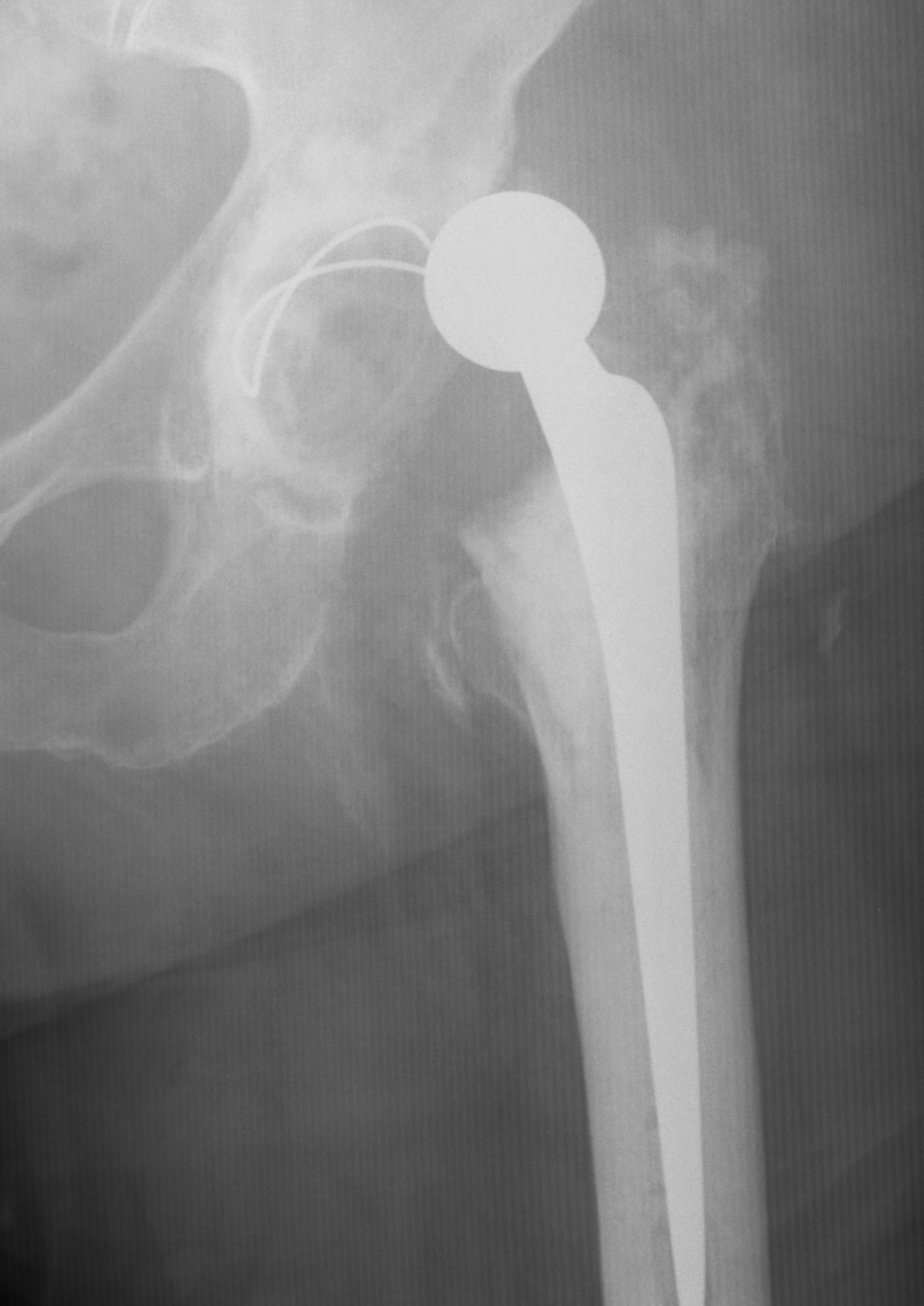
Hemiarthroplasty
- unipolar monoblock
- unipolar modular
Femur
Multiplanar deformity
- worsend by previous surgery
- may require osteotomy
Acetabulum
Dysplasia often present
- not as severe as in DDH
LLD
Can be significant
Abductors
Have been short for long time
- difficult to restore length
Extra-pelvic blood vessels
Femoral Artery
MCFA
LCFA
Profunda Femoris
Obturator artery
Intrapelvic vessels
External iliac artery and vein
Obturator artery
Superior and inferior gluteal
Anatomy
- anterior division of common iliacs / L5-S1
Set up
- on side
- charnley supports posterior on sacrum
- anteriorly on ASIS
- patient slightly tilted backwards
- avoids cup retroversion
Posterior Approach
- identify short ER
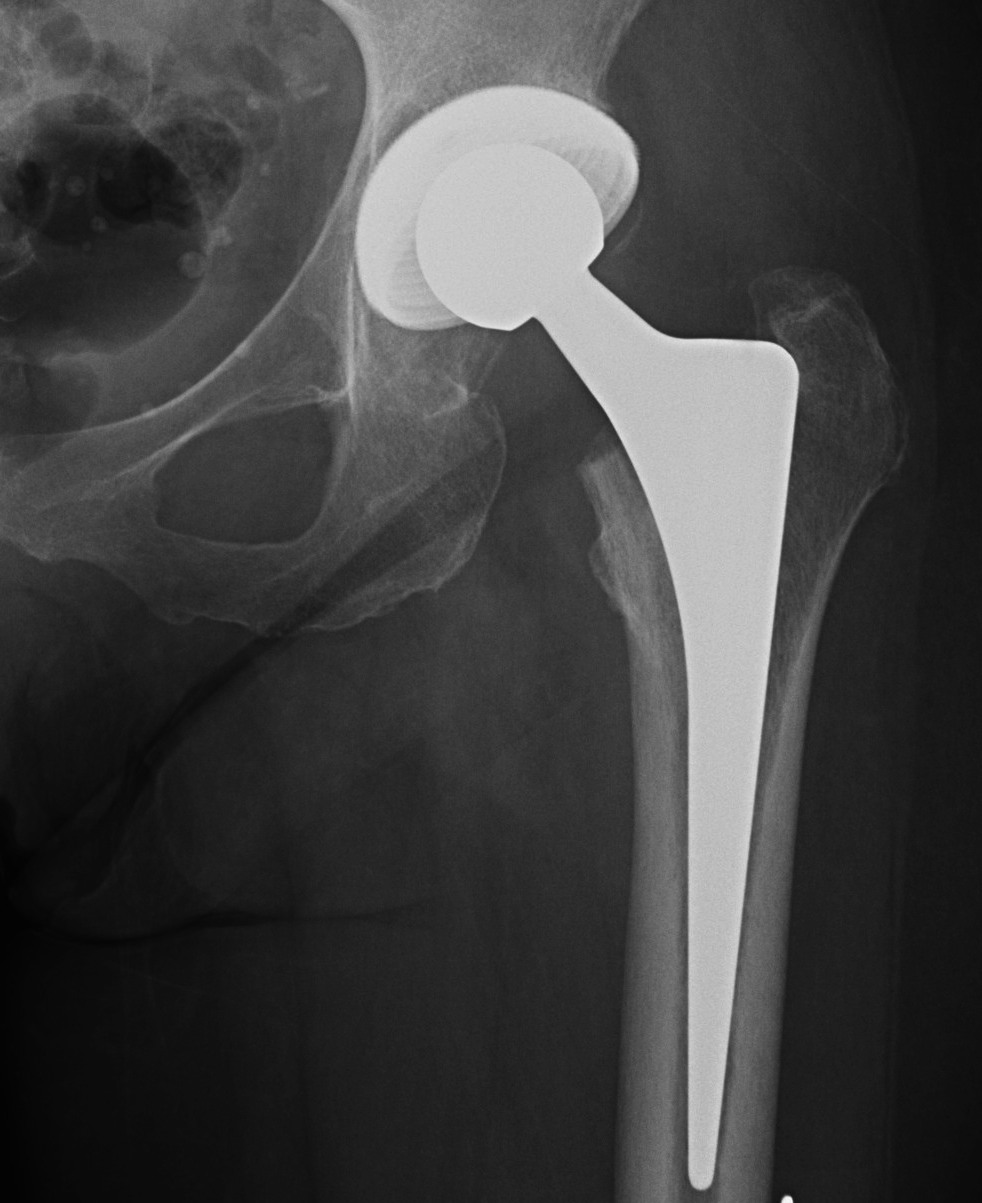
Initial press fit
- implant geometry fits the cortical bone in the proximal femur
- good initial mechanical stability
Biological fixation for success
- good press fit
- minimal micromotion
- bony or fibrous tissue ingrowth or ongrowth
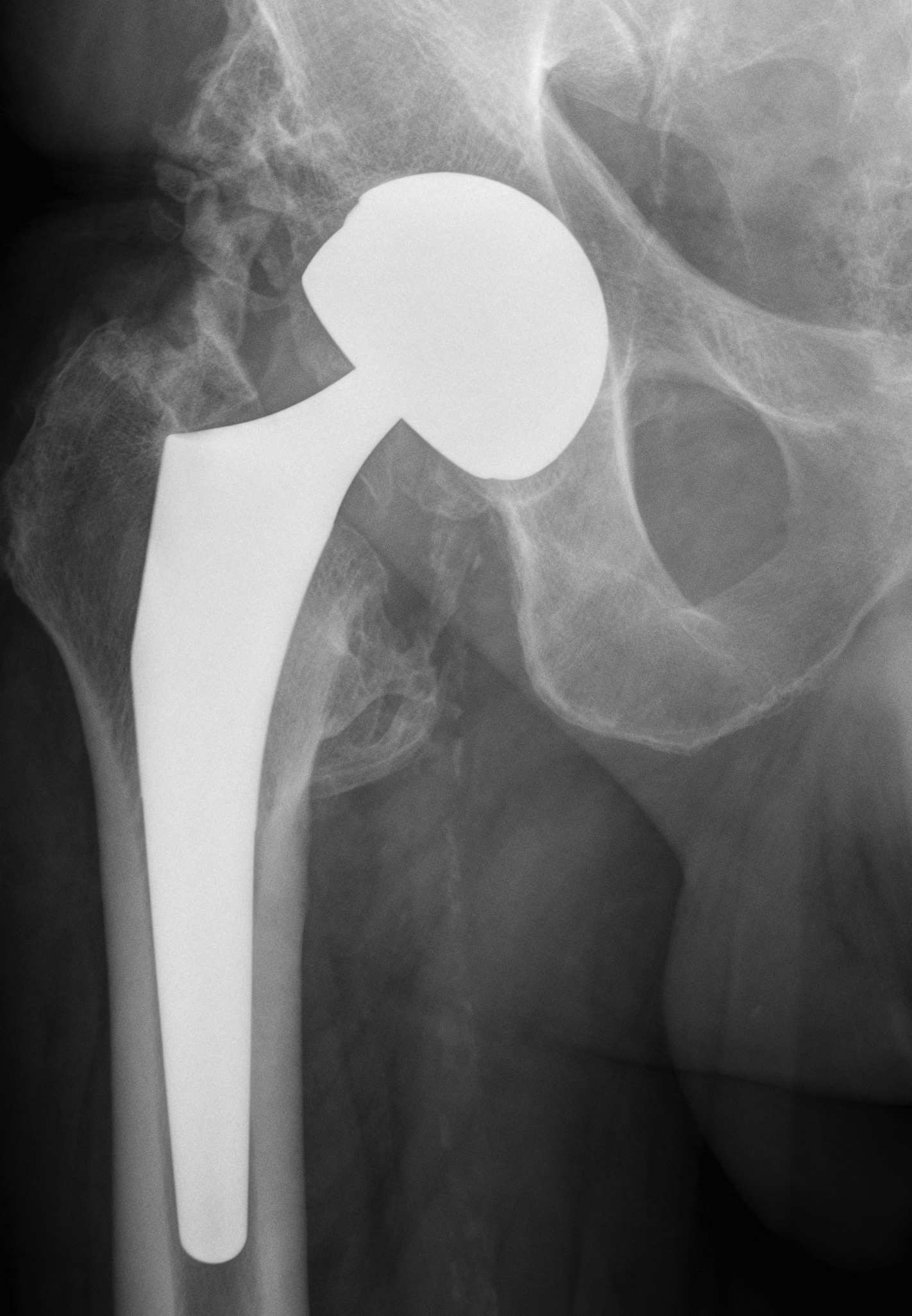
Wear
Stability
Normal feel of hip
Increased ROM
Large head
- increase volumetric wear
- less penetrative / linear wear
Small head
- increased linear wear
- decreased volumetric wear