Vancouver A Vancouver B Vancouver C
Incidence
- 32,000 THA
- 3.5% risk of peri-prosthetic fracture at 20 years
- greater trochanter fractures most common (35%)
Australian Joint Registry 2023
- 430,000 THA
- 20 year revision rate 8%
- infection / dislocation / fracture / loosening 90% of revision indications
- fracture 21% of revision indications
- registry data only captures revisions, not fixation with retained prosthesis (hence under-reports periprosthetic fracture)
Epidemiology
Femur 90%
Acetabulum 10%
- usually intra-operative
Etiology
1. Intra-operative fracture
2. Osteolysis
3. Trauma
4. Infection
5. Osteoporosis
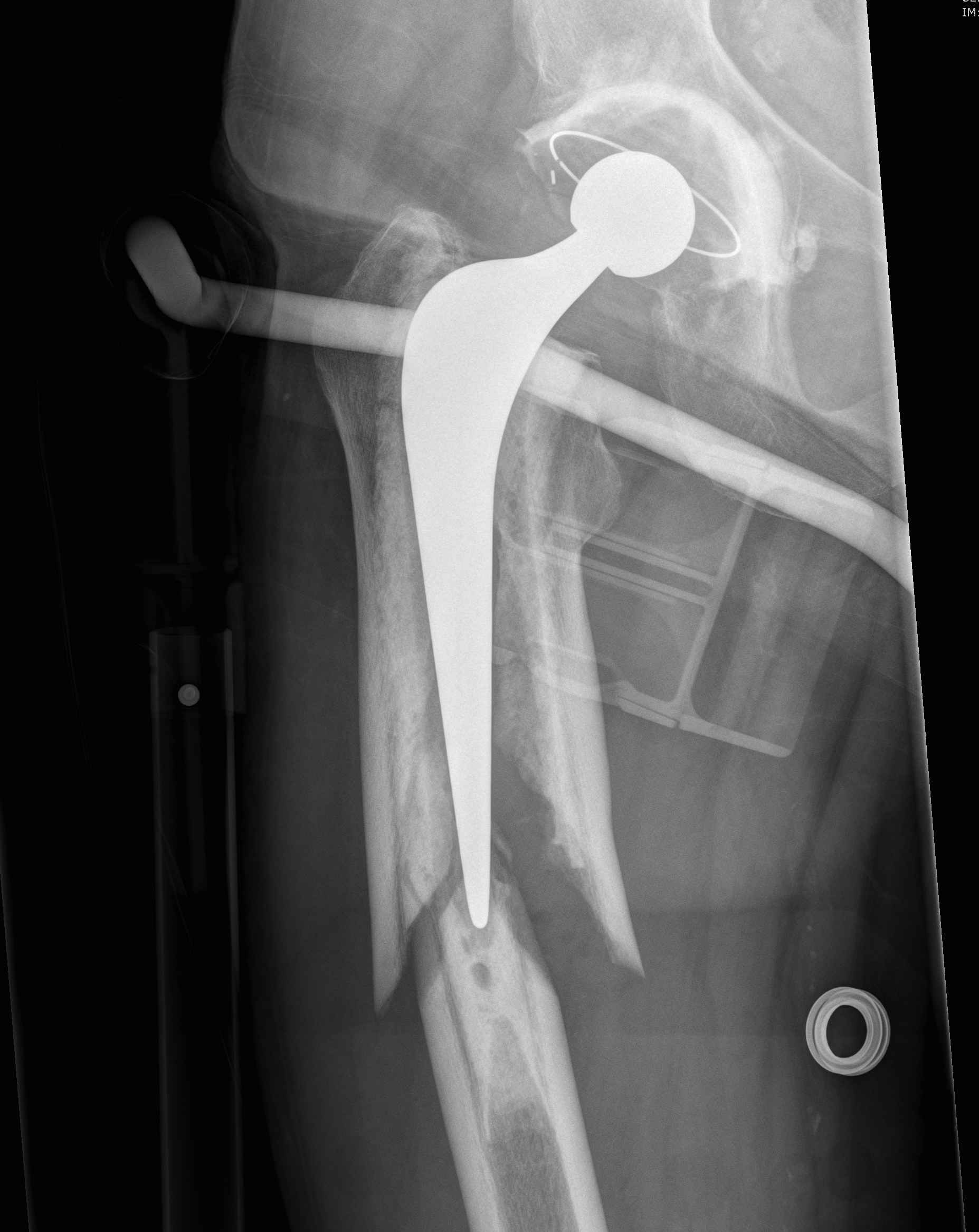
Vancouver Classification
Based on location, fixation, and bone quality
Helps guide surgical treatment
| Type A (trochanters) | Type B (around stem) | Type C (distal to tip of stem) |
|---|---|---|
| Greater trochanter | B1 Stem well fixed (ORIF) | ORIF |
| Lesser trochanter | B2 Stem loose (ORIF/Revision) | |
| B3 Stem loose with bone loss or severe comminution (Revision) |
Type A: Avulsion greater or lesser trochanter
Greater trochanter
Indication for surgery
- pain
- instability
- weakness / limp
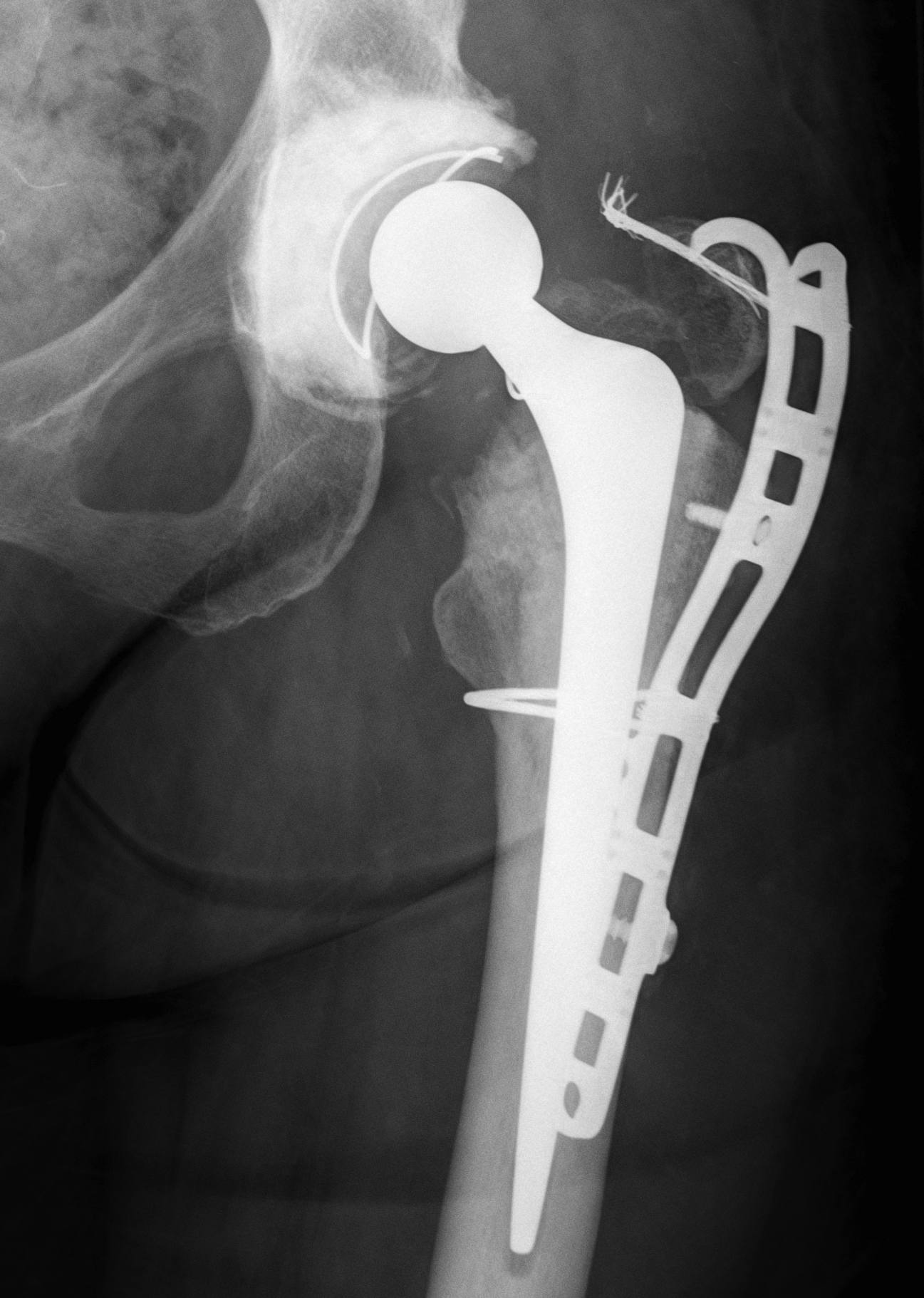
ORIF with plate

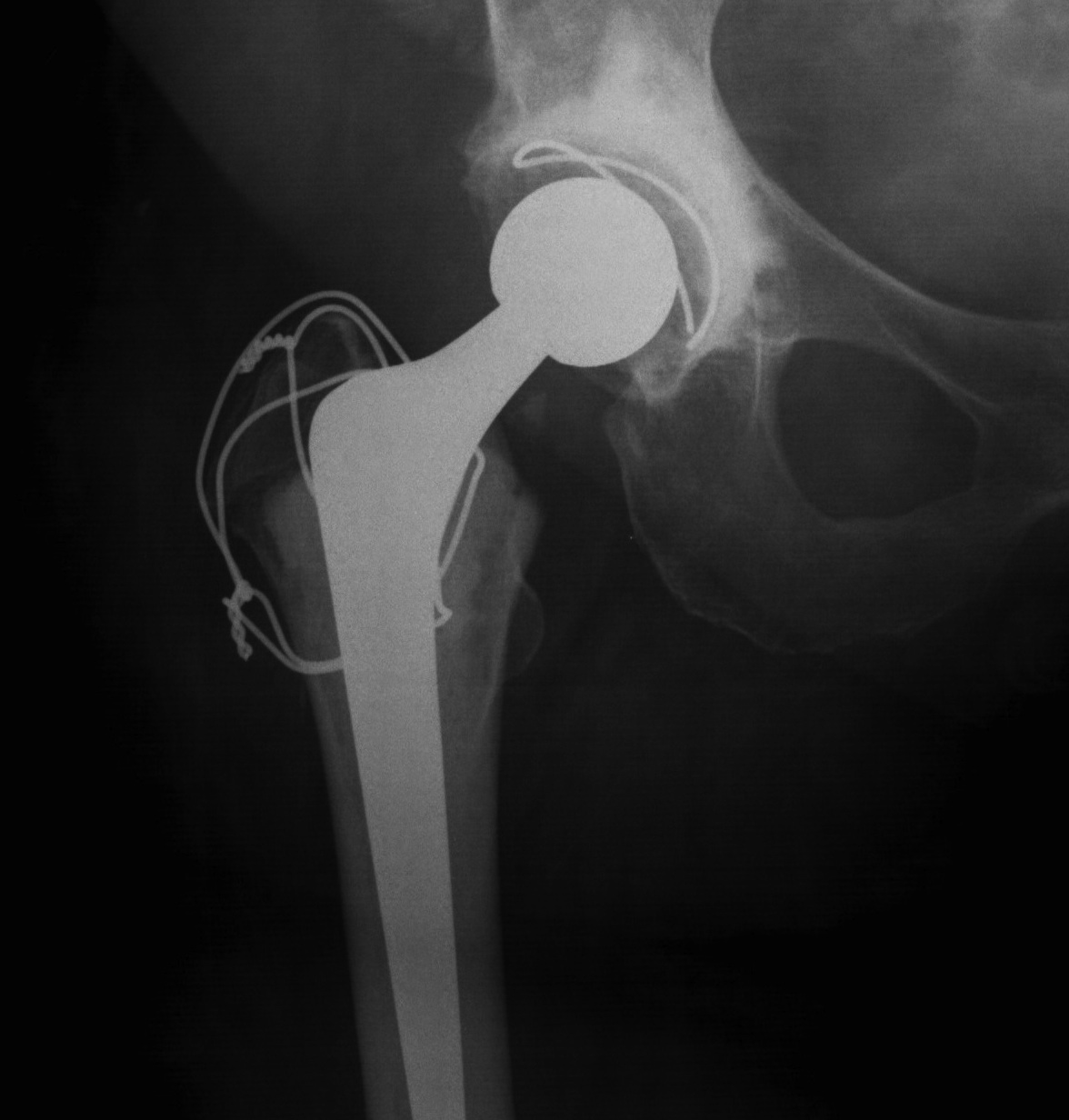
ORIF with wires
Lesser trochanter
Indication for surgery
- extend to implant
- indications of implant instability
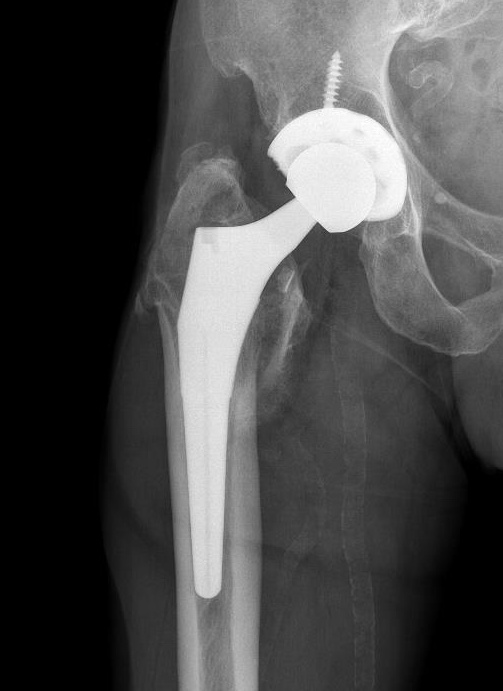
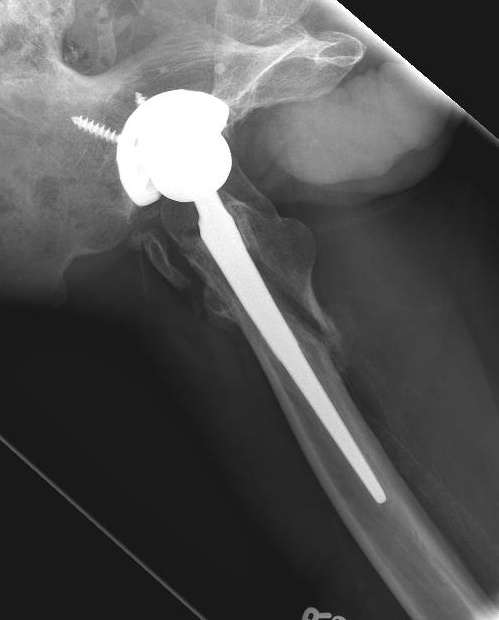
LT fracture around THA
Type B: Fracture around the stem
Epidemiology
Lindahl et al J Arthroplasty 2005
- Swedish hip registry of 1049 periprosthetic fractures
- B1: 29%
- B2: 53%
- B3: 4%
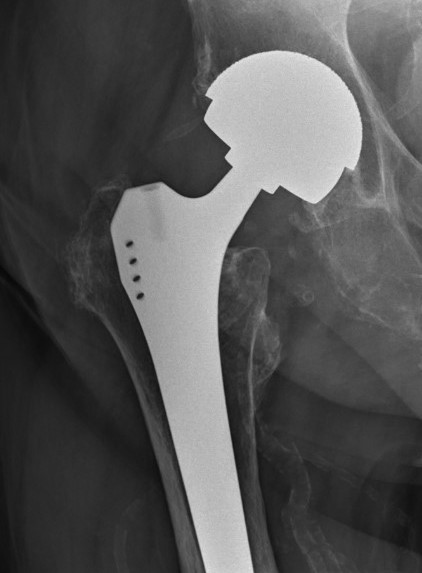
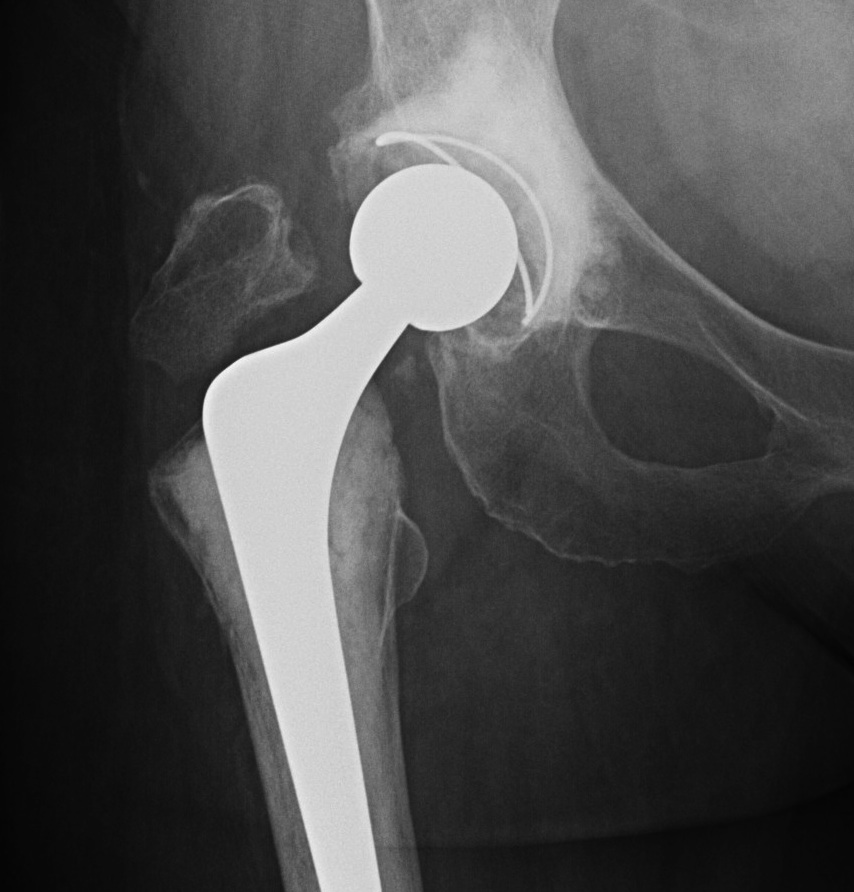
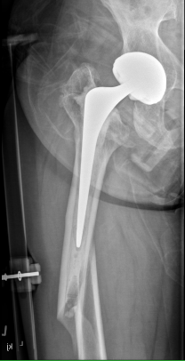
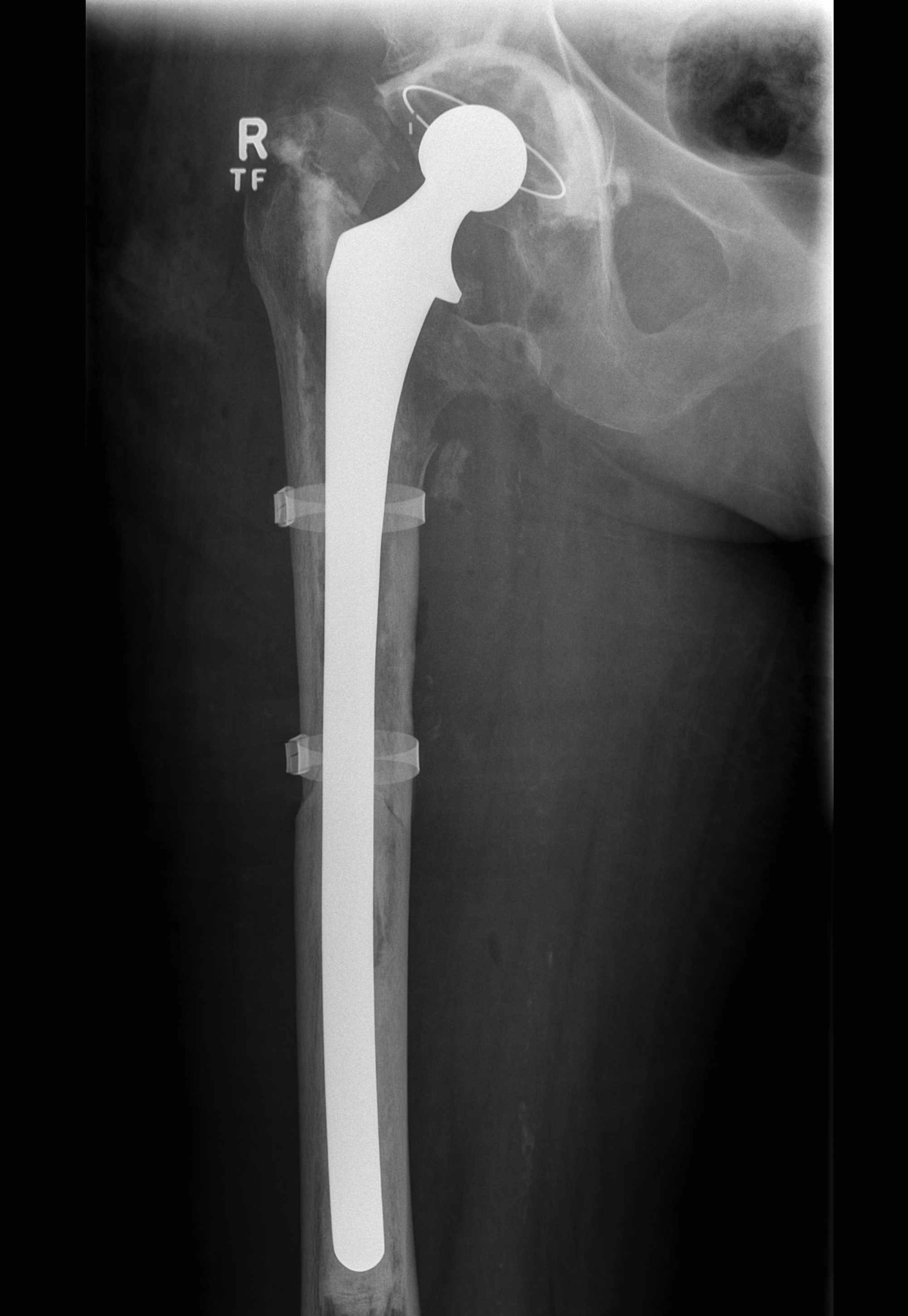
Type B1: Fracture around stem, likely well fixed
Stability
- 45 presumed type B1 periprosthetic fractures
- in 20% the femoral component was unstable
Management
ORIF with locking cable plate and +/- Cortical strut allograft
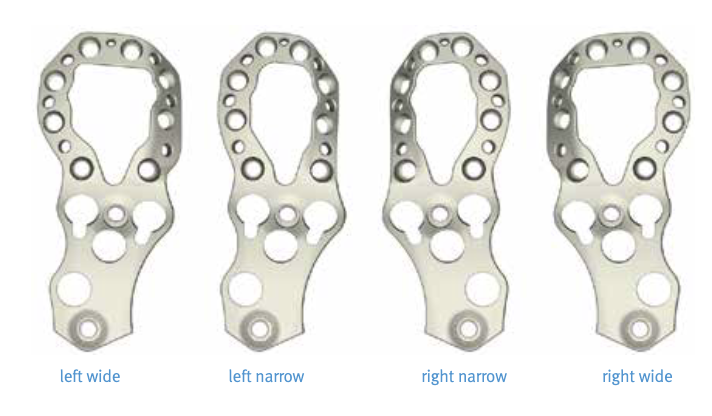
Plates
Contoured anatomical fit with trochanteric extension
Variable angle locking screws to go around implants
Cable options
Unicortical screw options


Results
Moore et al J Arthroplasty 2014
- systematic review of 37 papers and 682 cases
- B1 with strut: union rate 91%, infection rate 8%
- B1 without strut: union rate 92%, infection rate 4%
- longer union times with allograft strut
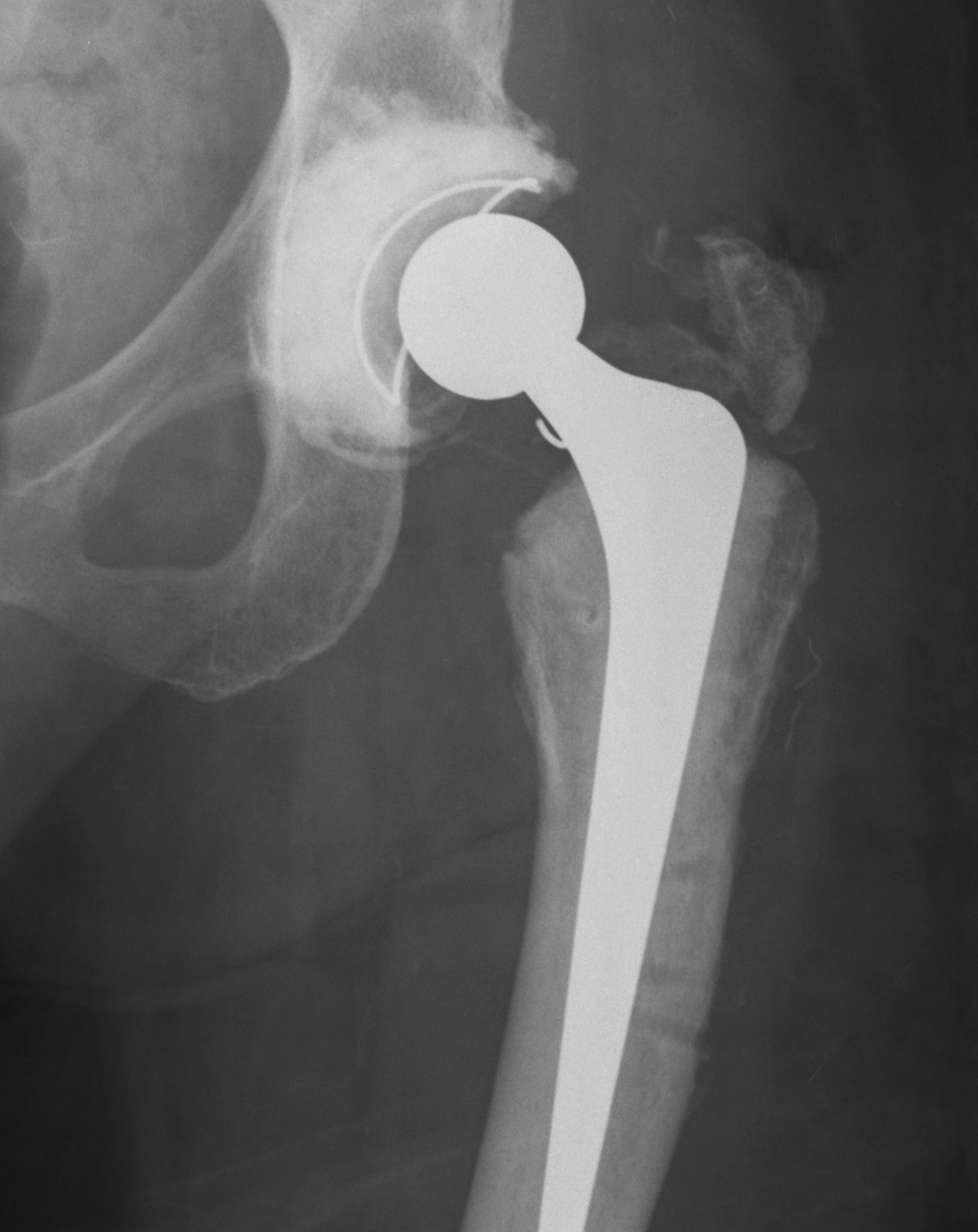
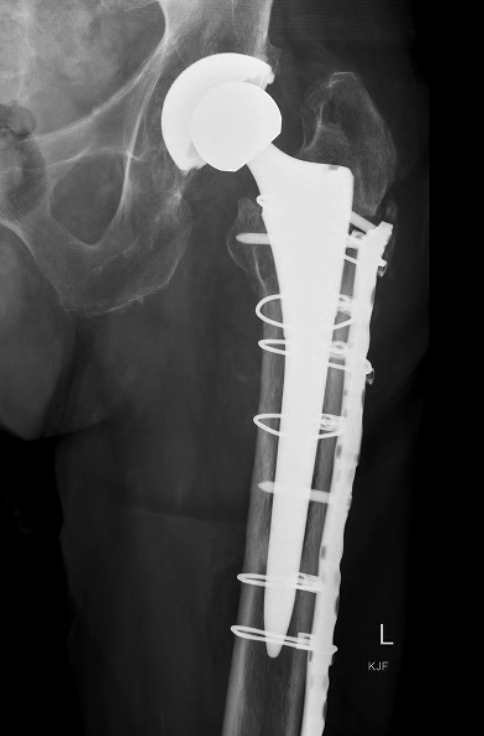
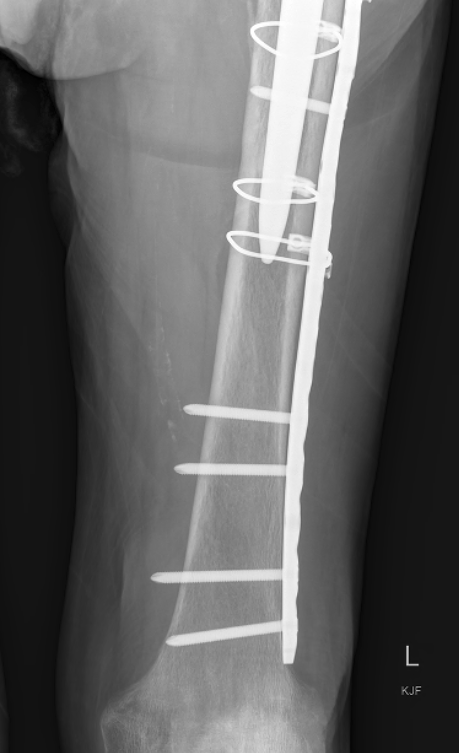
Type B2: Fracture around stem, femoral component loose
Management
A. Revision arthroplasty with long stem femoral implant +/- plate +/- cortical strut allograft
- distal fit (cemented / uncemented)
- must bypass distal extent of fracture by at least 2 cortical diameters
- requires cement removal
B. ORIF and prosthesis retention
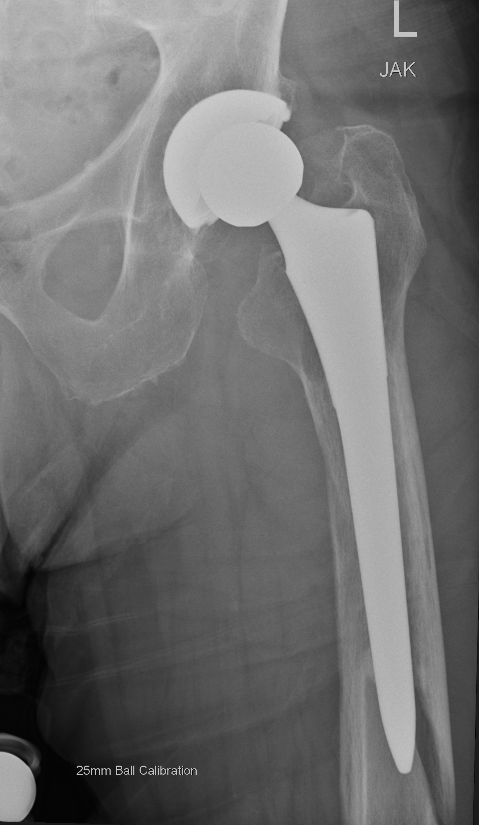
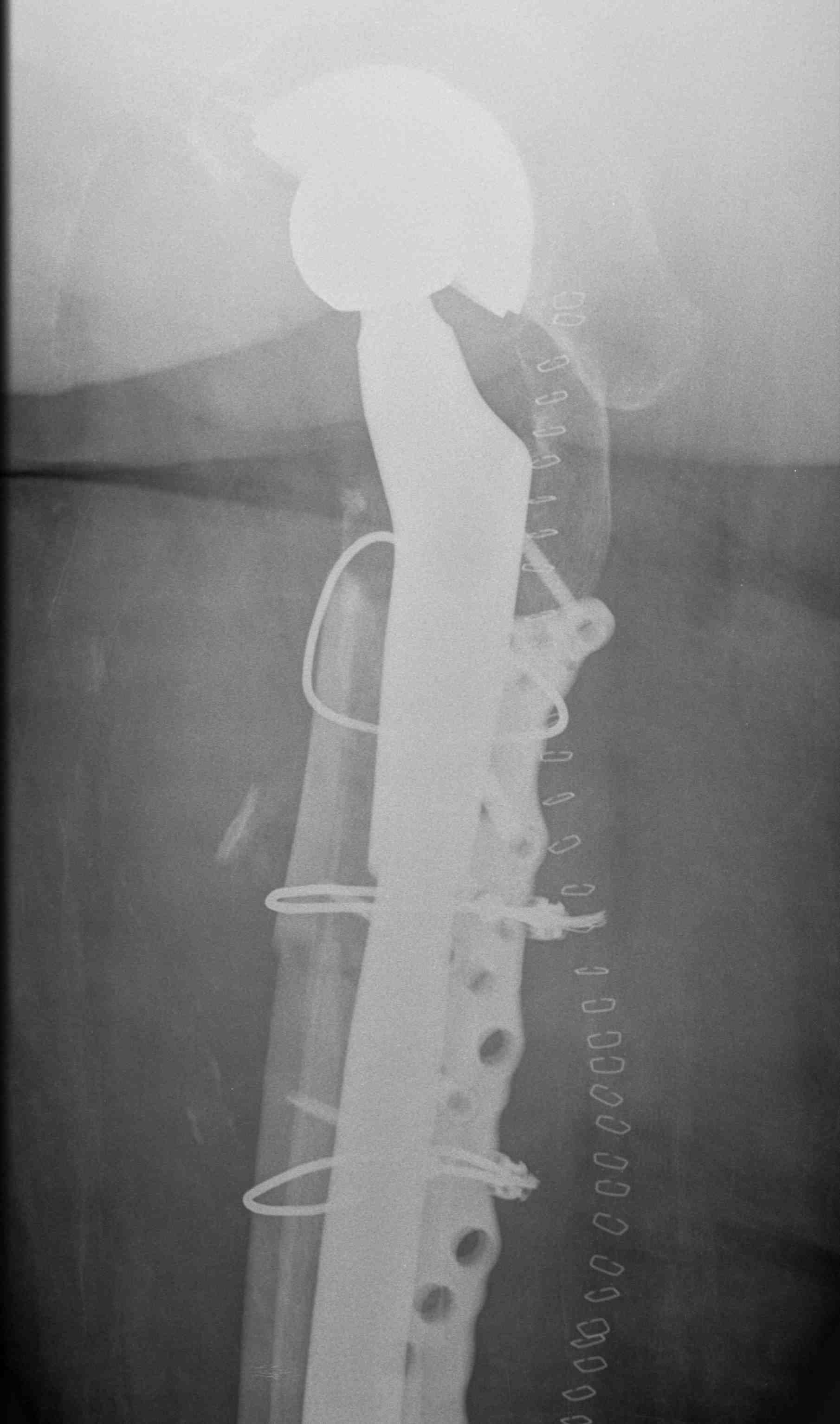
- cemented smooth polished taper-slip femoral stems
- bone-cement interface intact
- able to achieve anatomical reduction around stem
- indications may be relaxed in patient unable to tolerate full revision
C. ORIF with cement-in-cement revision
- requires polished taper-slip stem
- remove prosthesis and reconstruct bone/mantle
- downsize stem and cement within prior cement mantle
- requires implant details, and ability to downsize
D. ORIF with in-cement revision
- requires polished taper-slip stem
- remove prosthesis and reconstruct bone/mantle
- re-insert existing, or new same sized prosthesis into same mantle

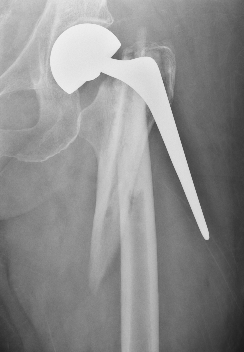
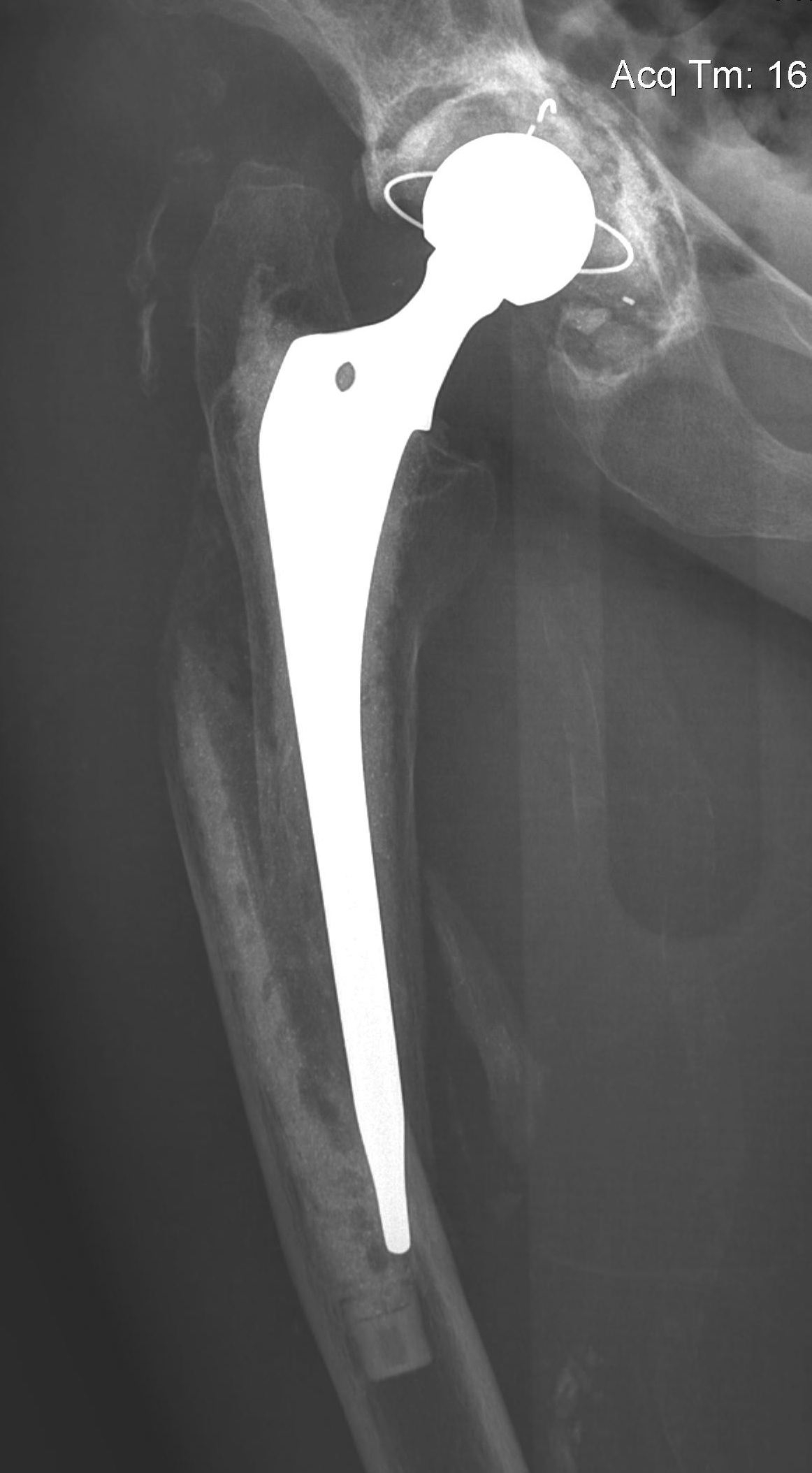
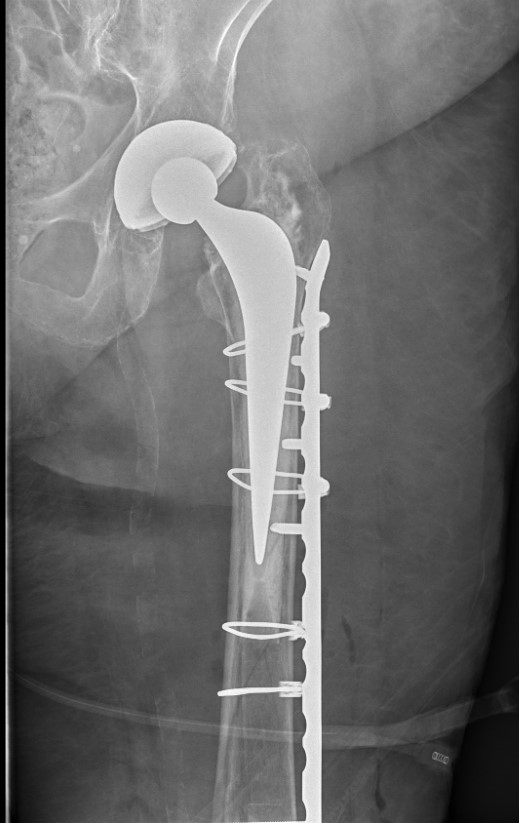
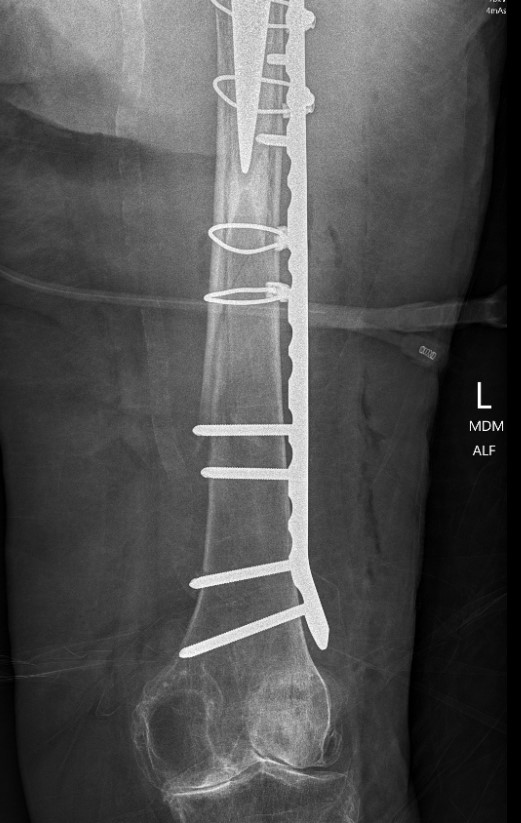
Long stem cemented revision
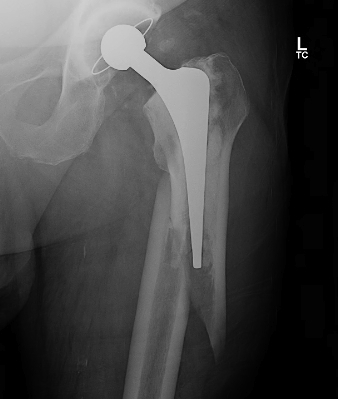
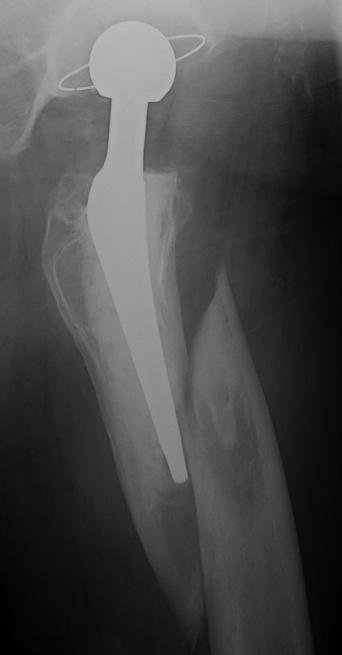
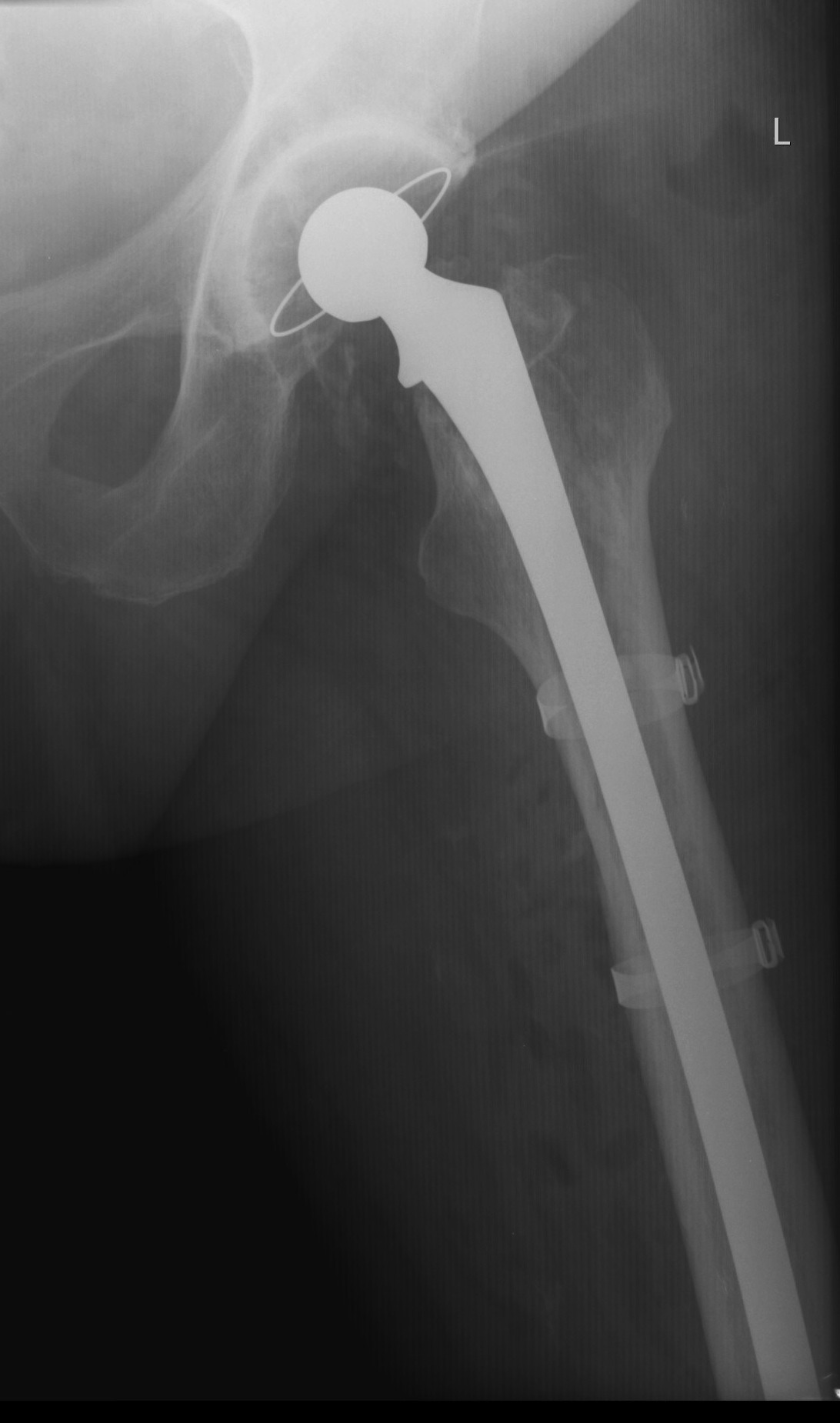
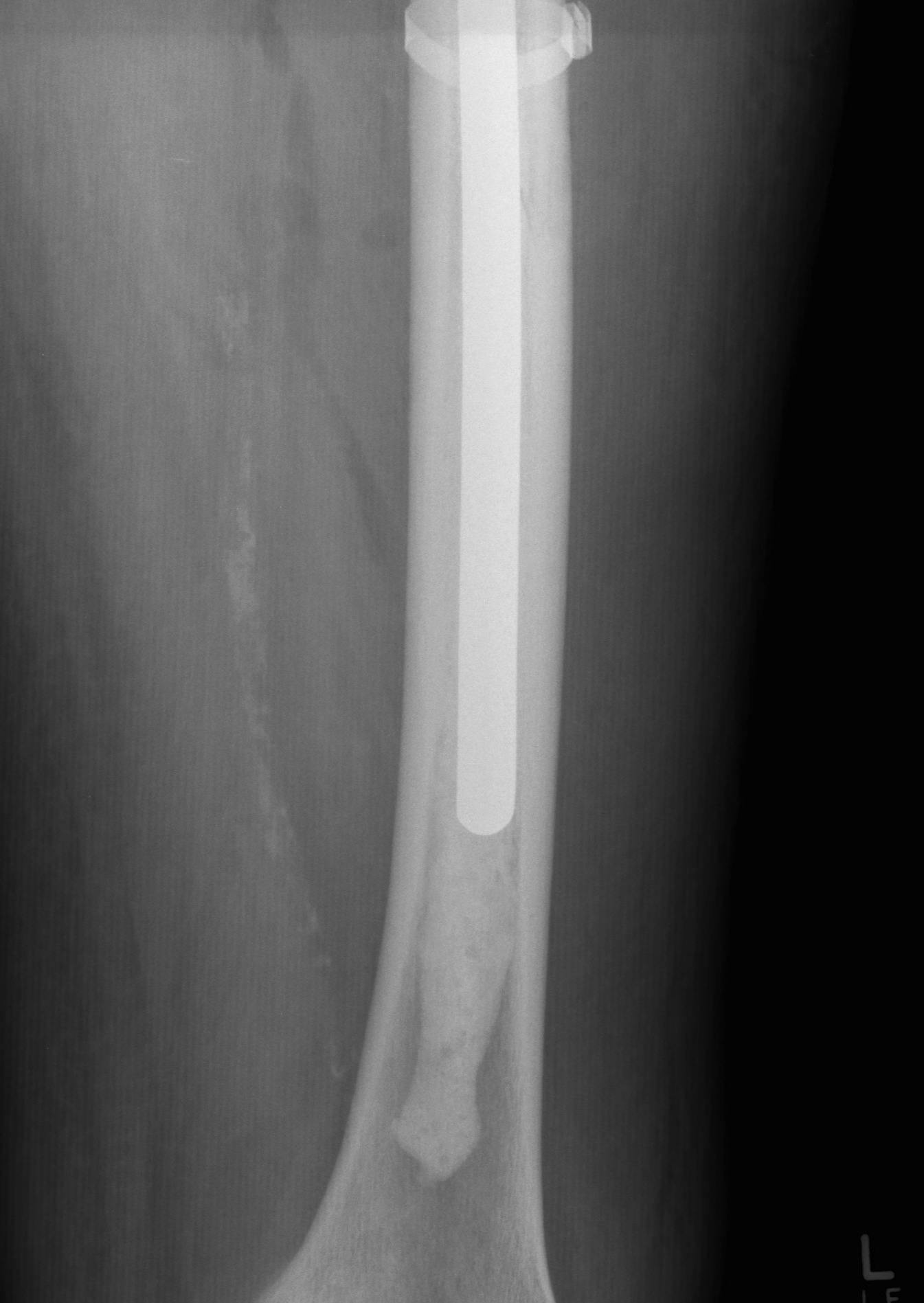
Long stem cemented revision
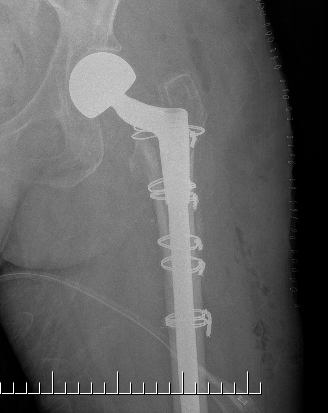
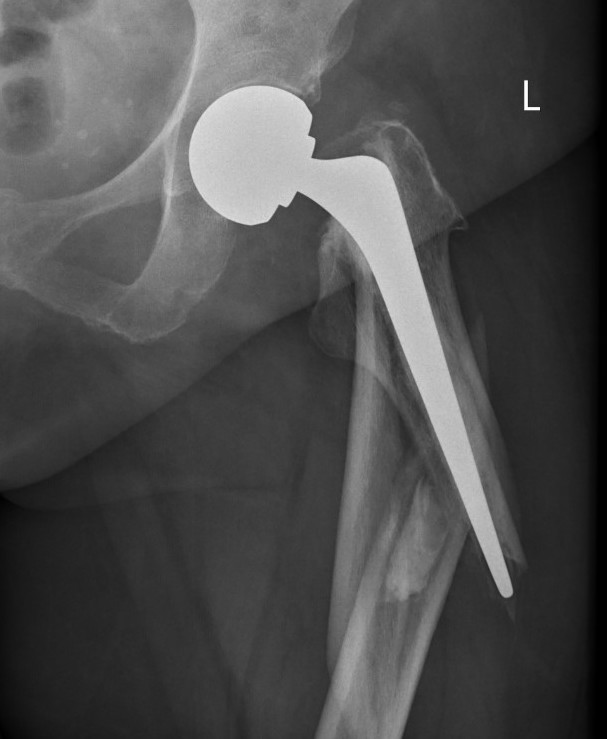
Long stem uncemented revision
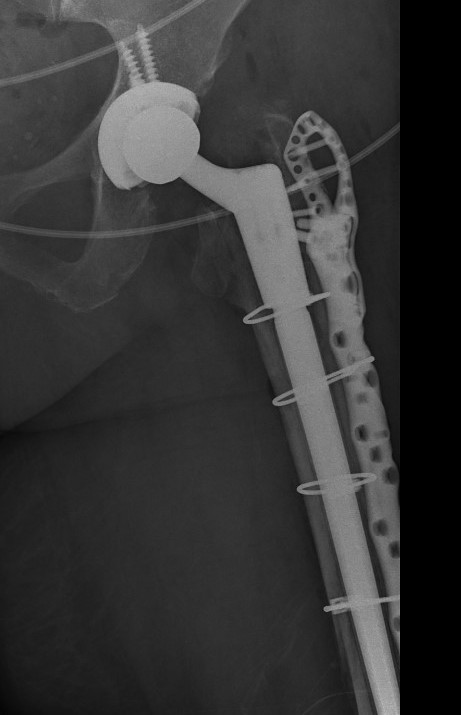
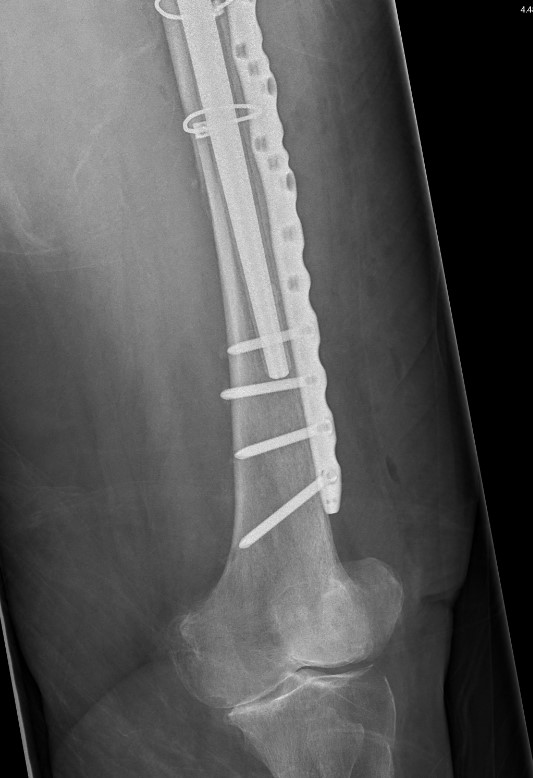
Revision uncemented arthroplasty with Zimmer cable plate
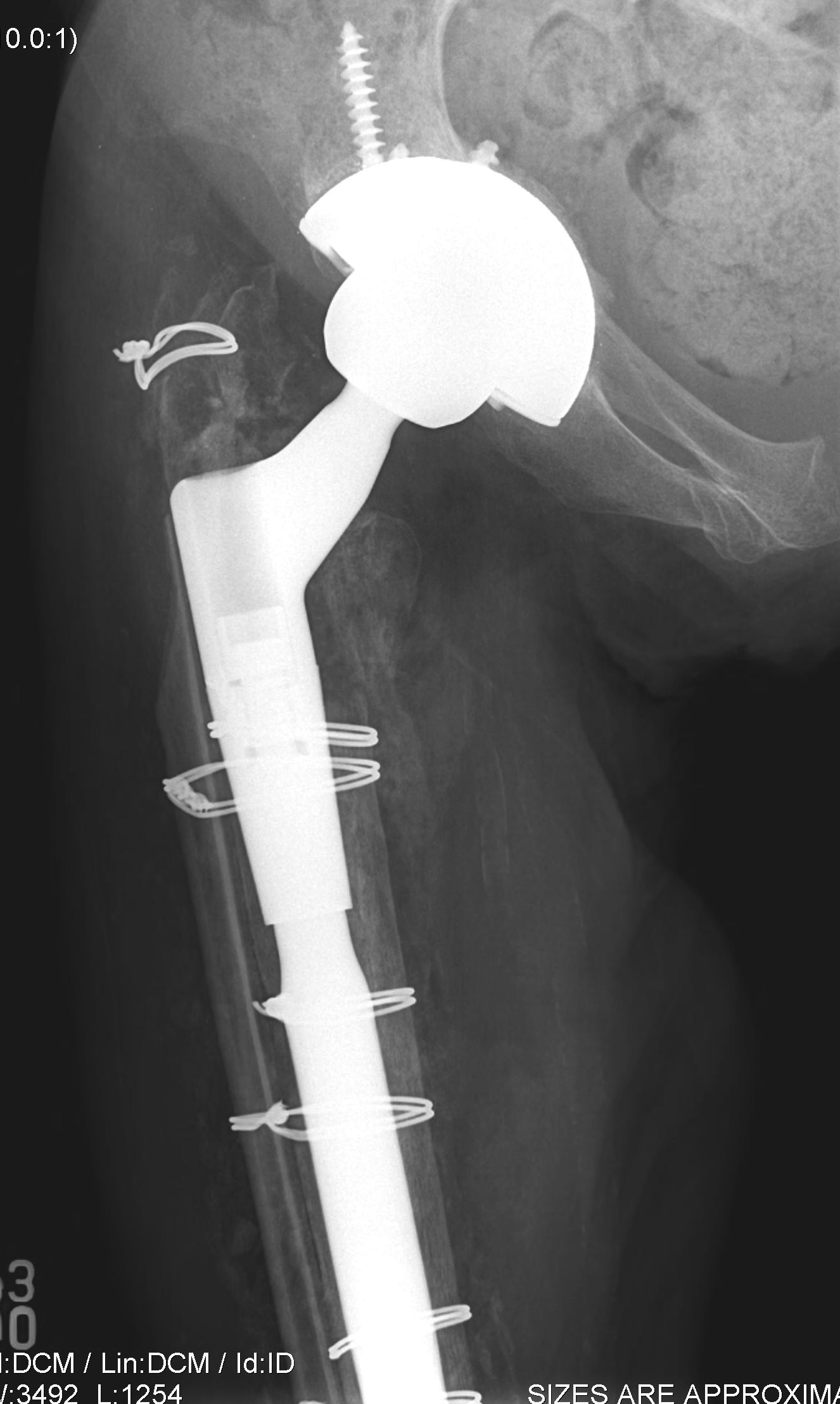
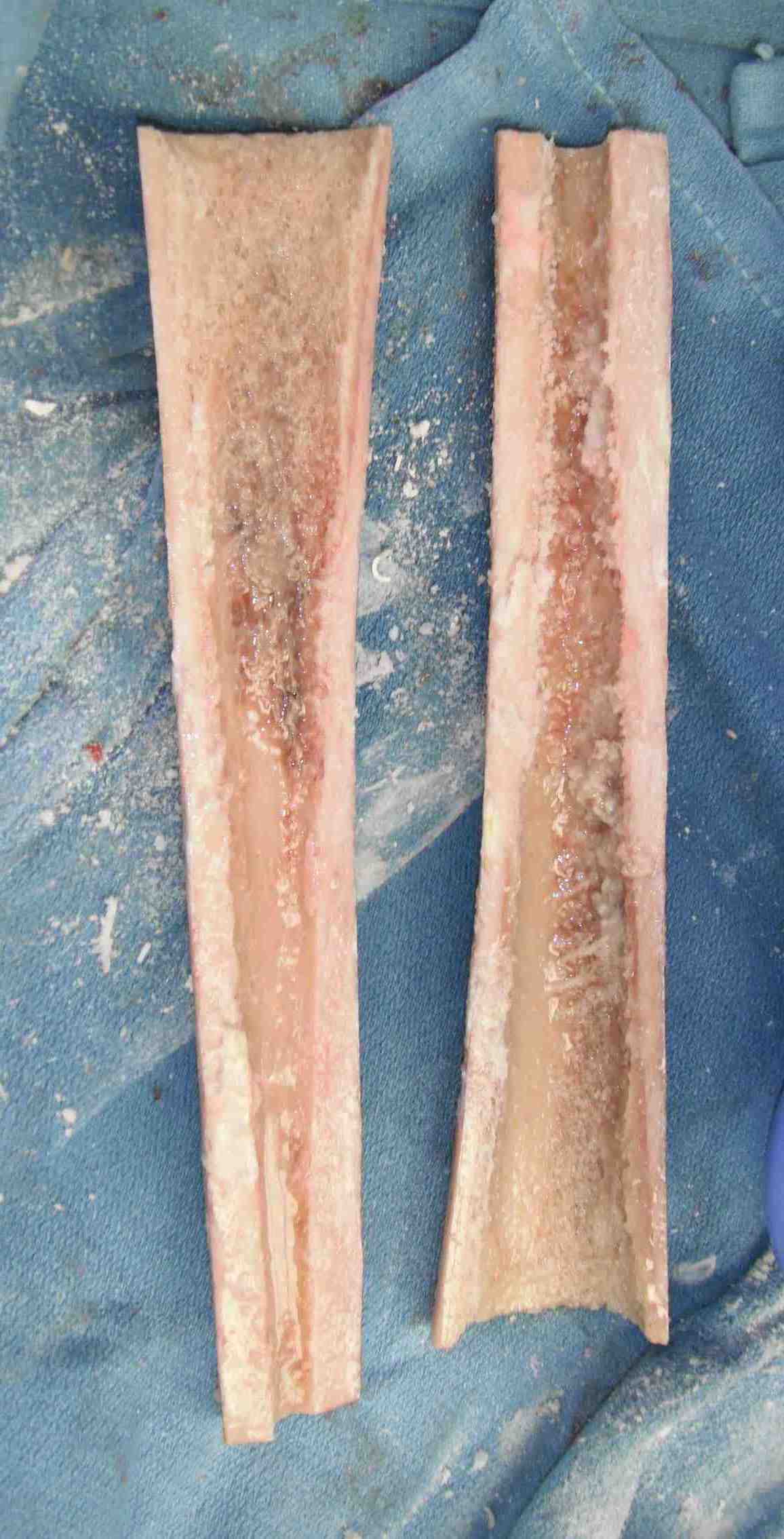
Long stem uncemented revision with cortical strut allograft
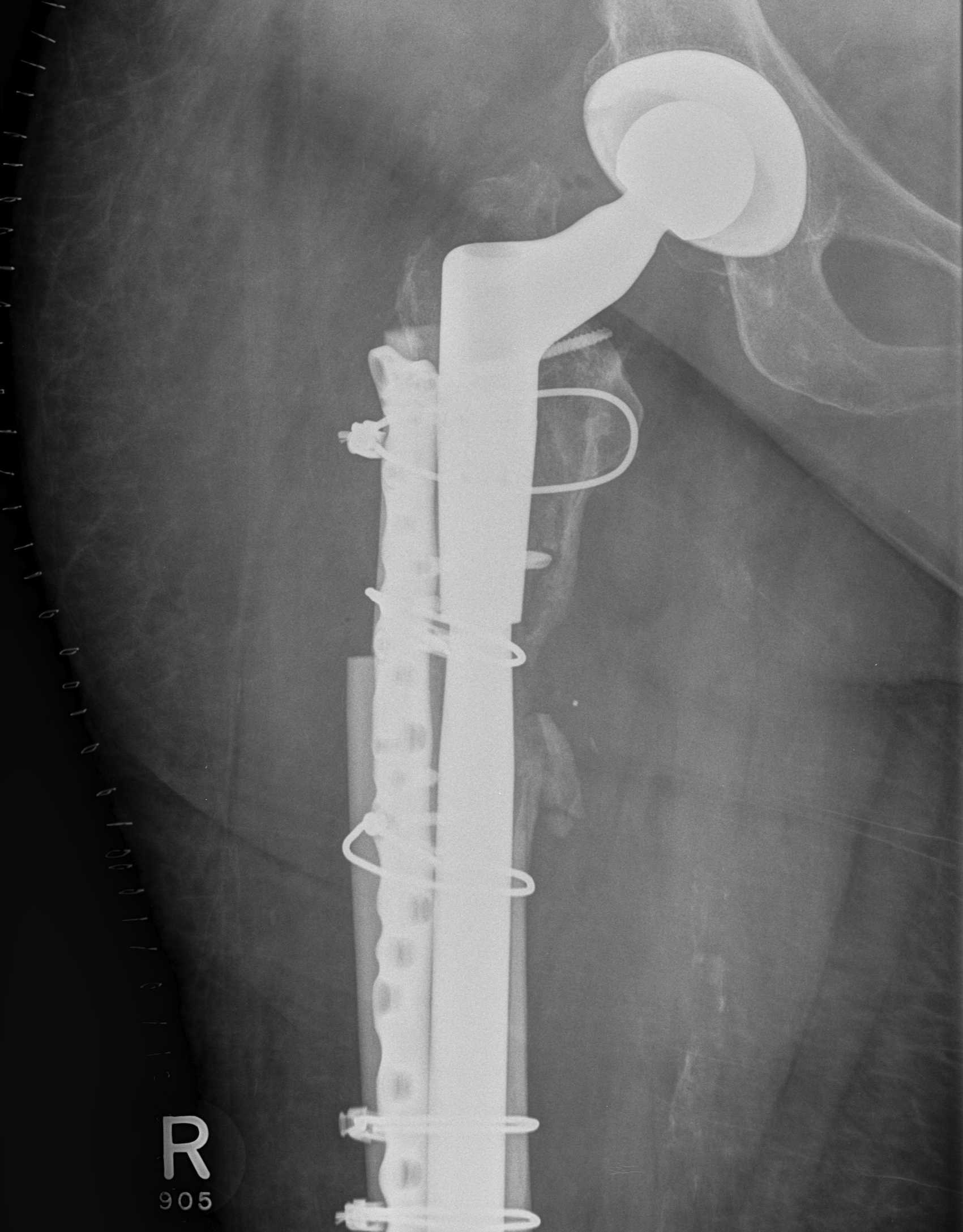
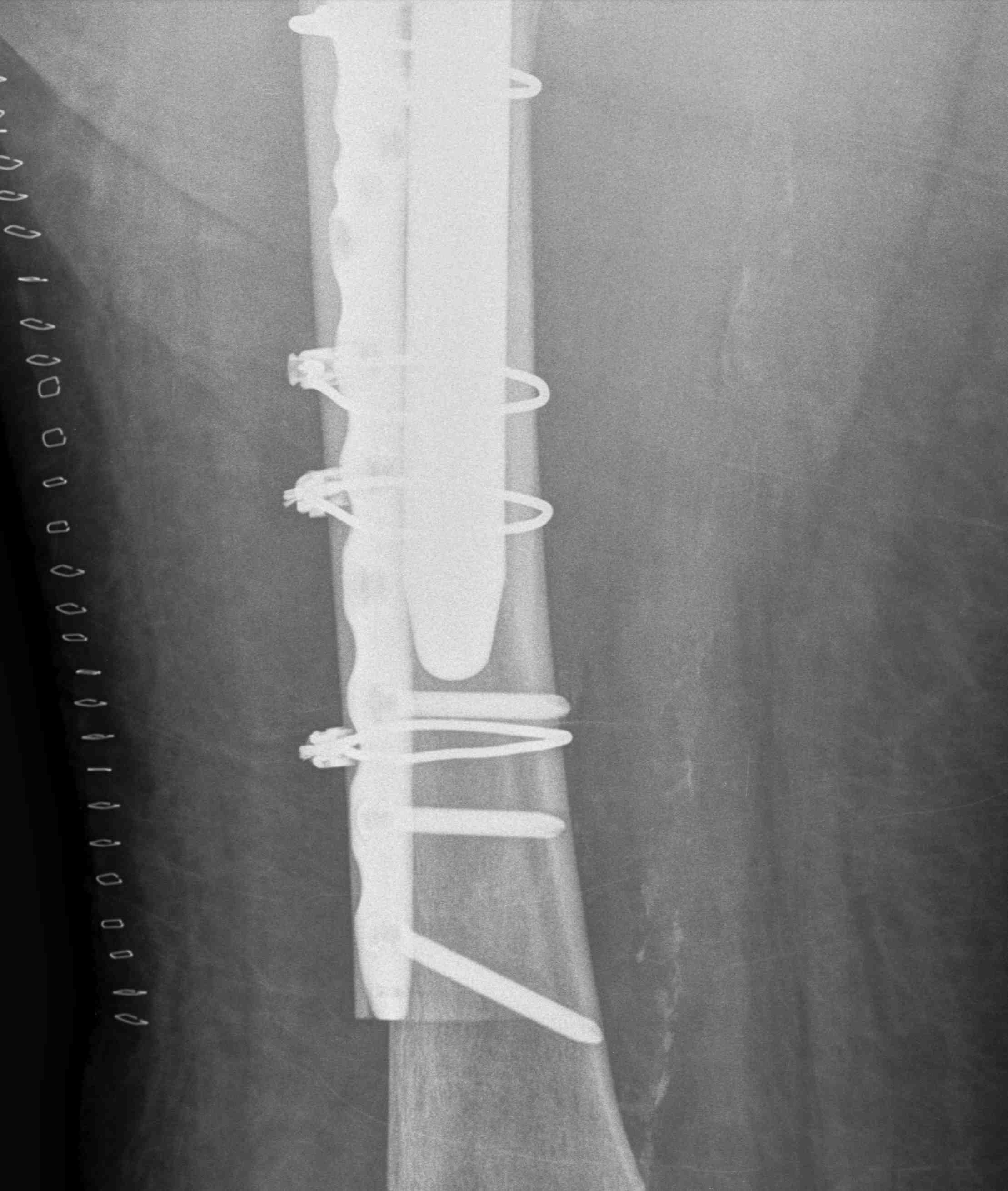
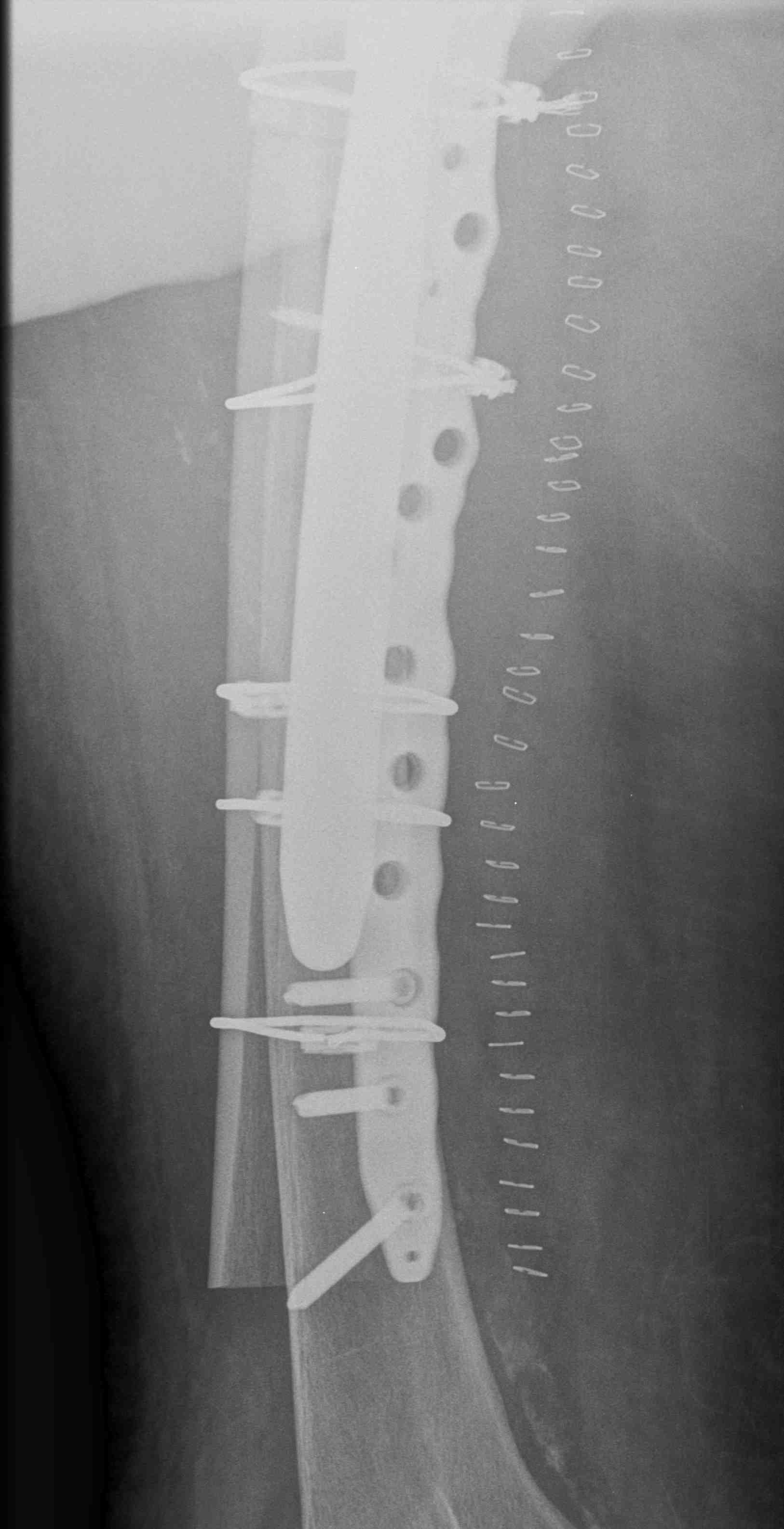
Long stem uncemented revision with plate + cortical struts
Results
Gonzalez-Martin et al, Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2023
- Metaanalysis of 17 studies (856 patients) comparing fixation and revision in vancouver B2
- Fixation has shorter surgery time, less transfusion, less complications, lower re-operation, and shorter LOS
- Same mortality
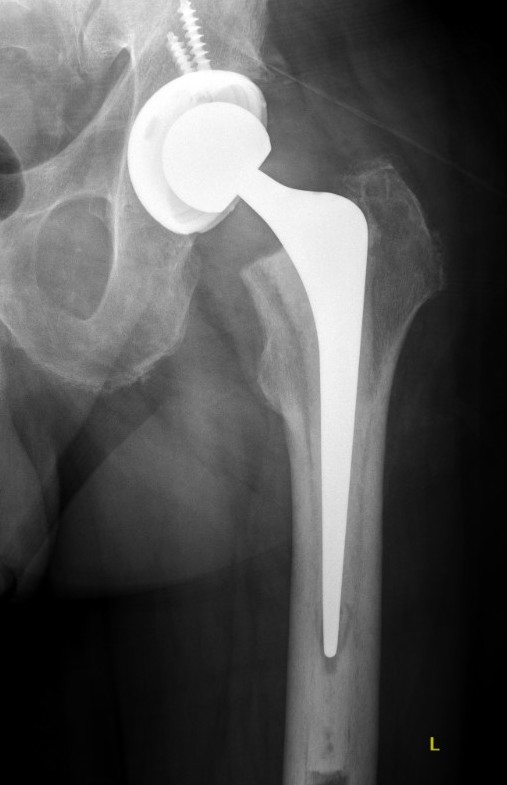
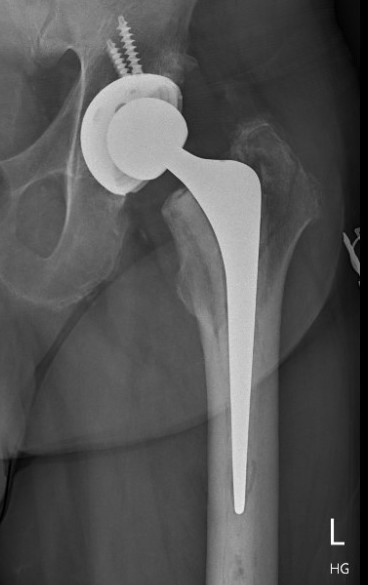
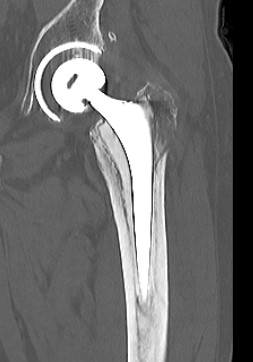
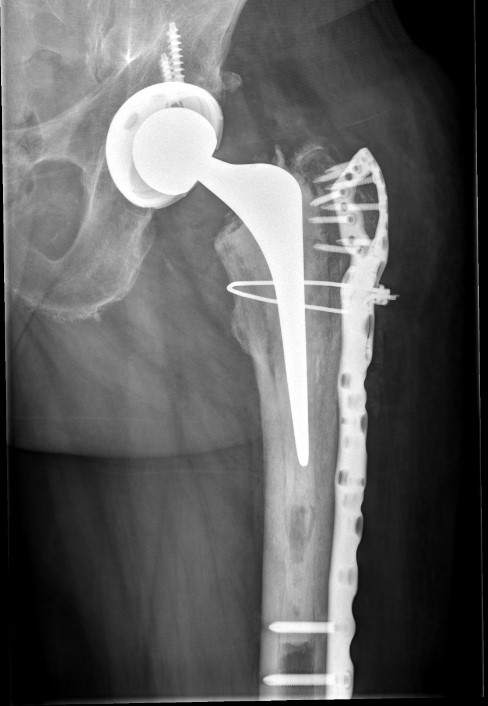
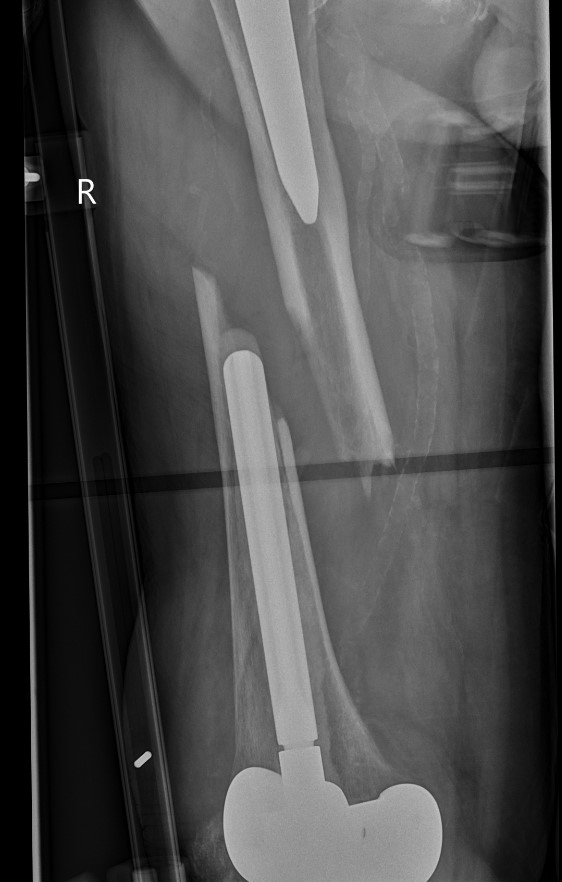
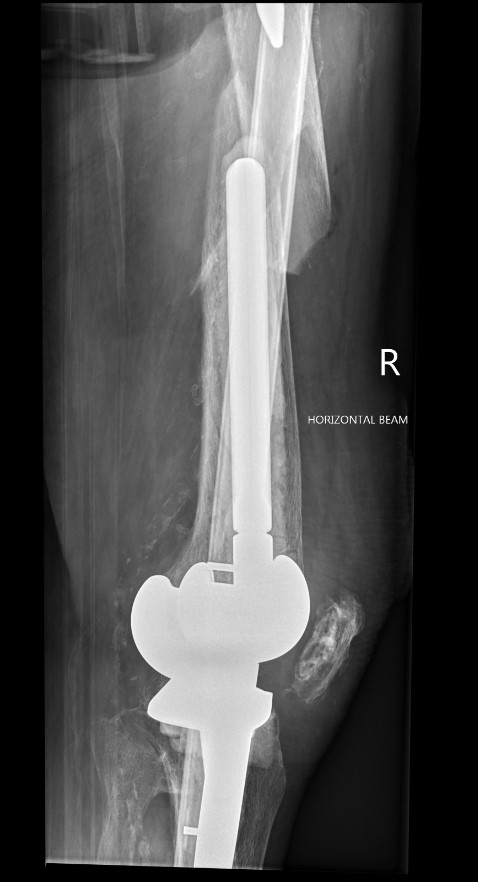
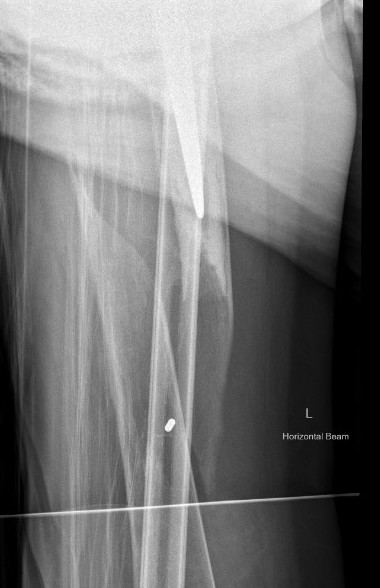
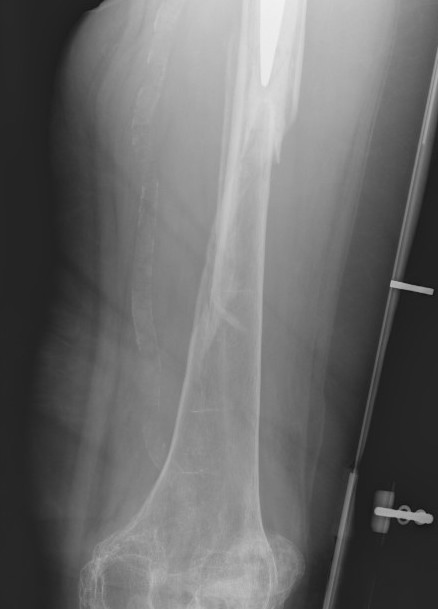
Fracture with stem subsidence around a polished tapered femoral stem treated with ORIF
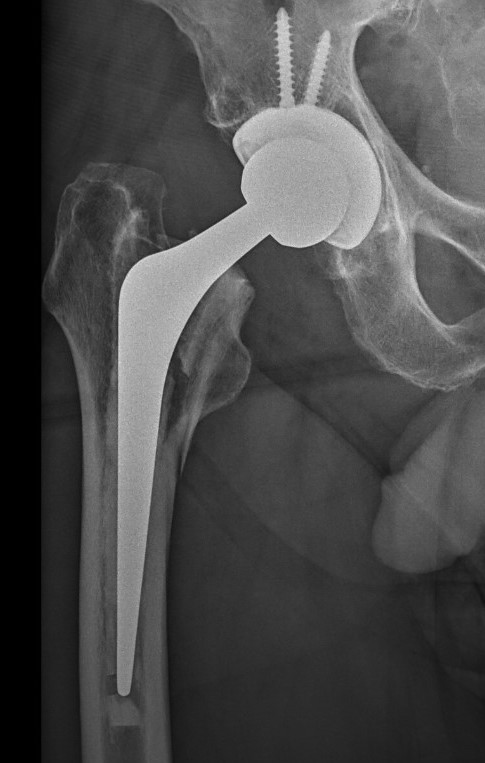
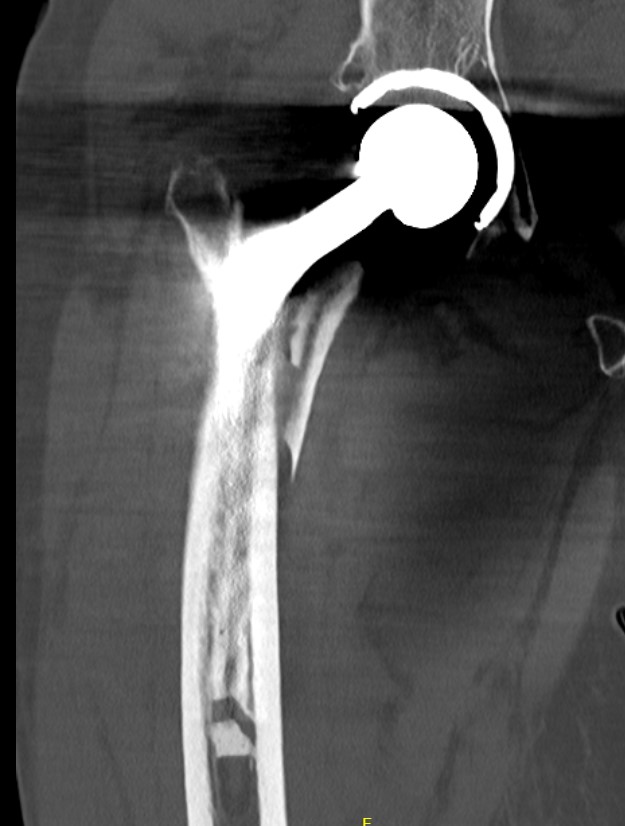
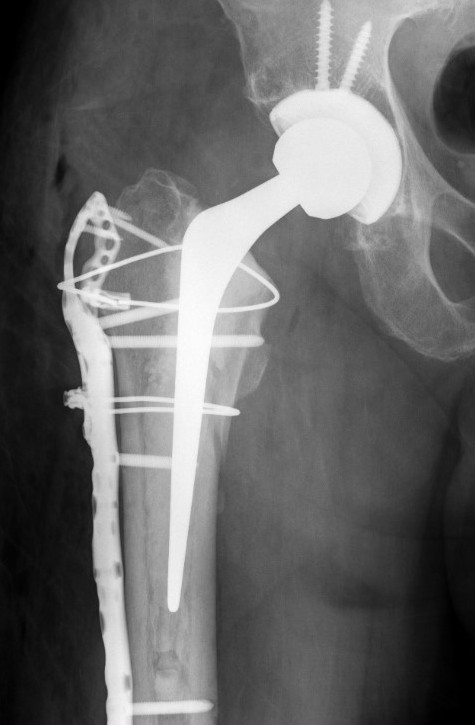
Fracture with stem subsidence around a polished tapered femoral stem treated with ORIF
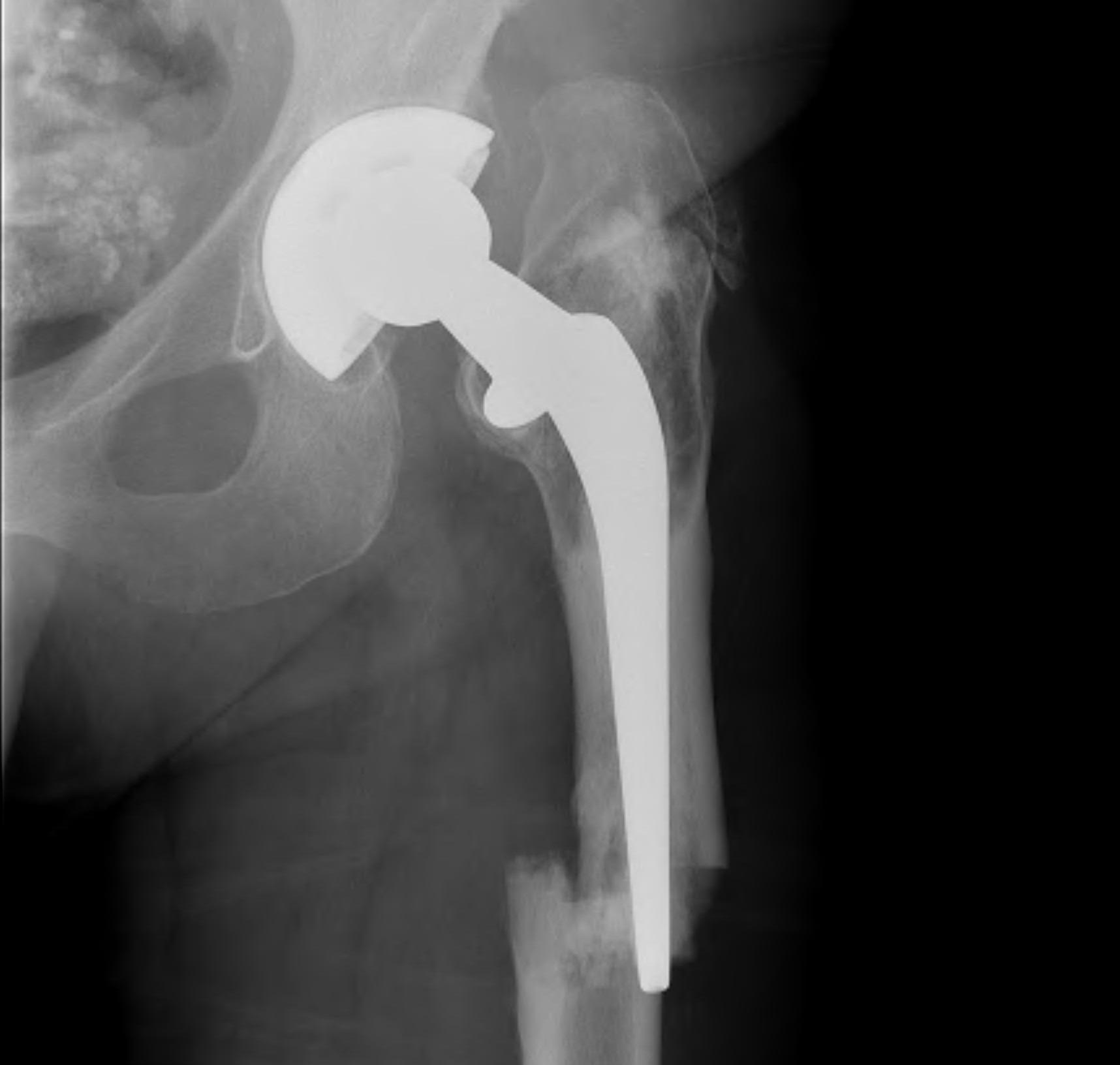
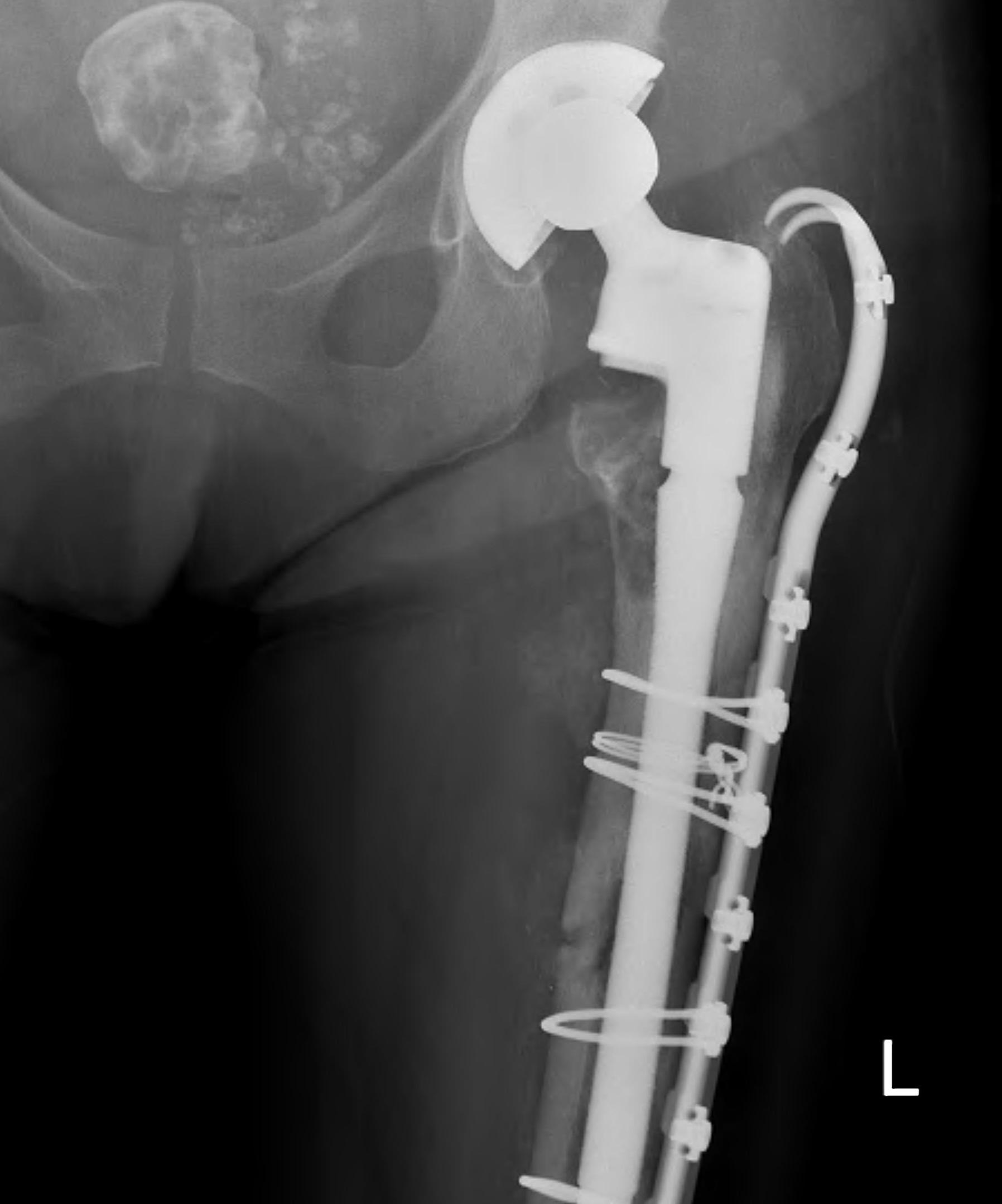
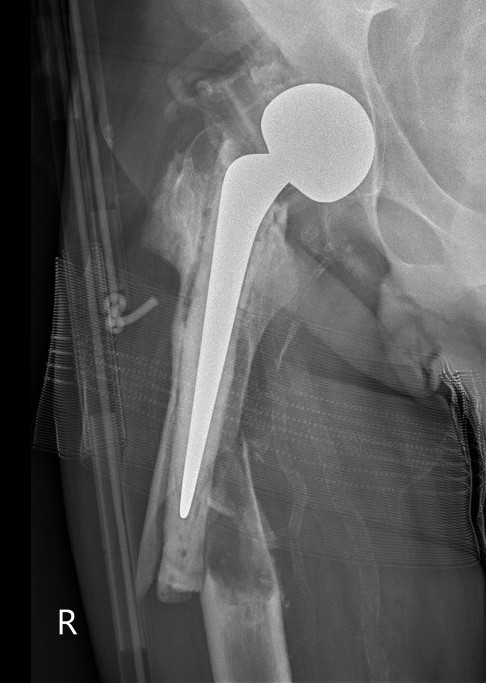
Type B3: Fracture around stem with poor bone quality (osteolysis of comminution)
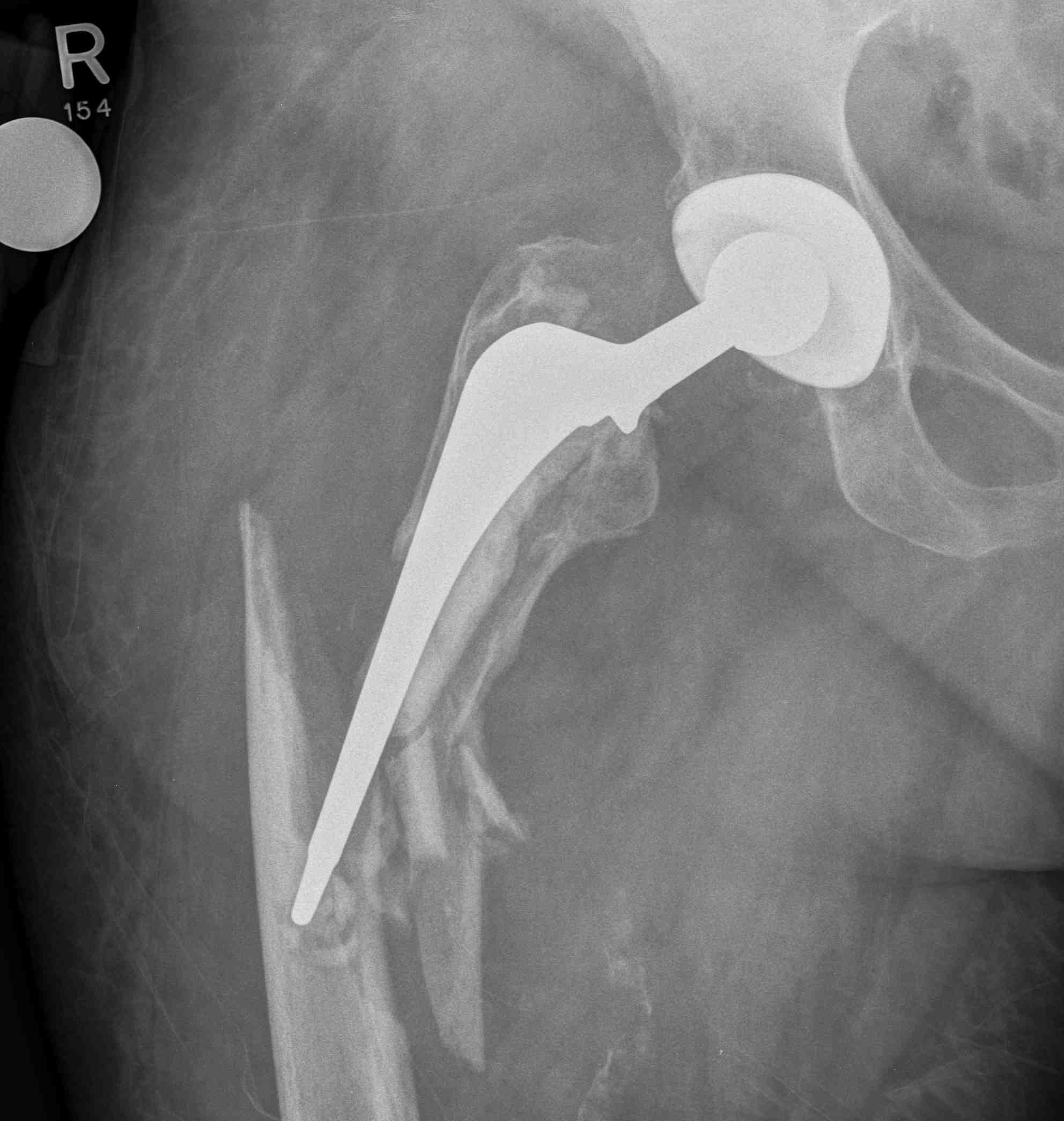
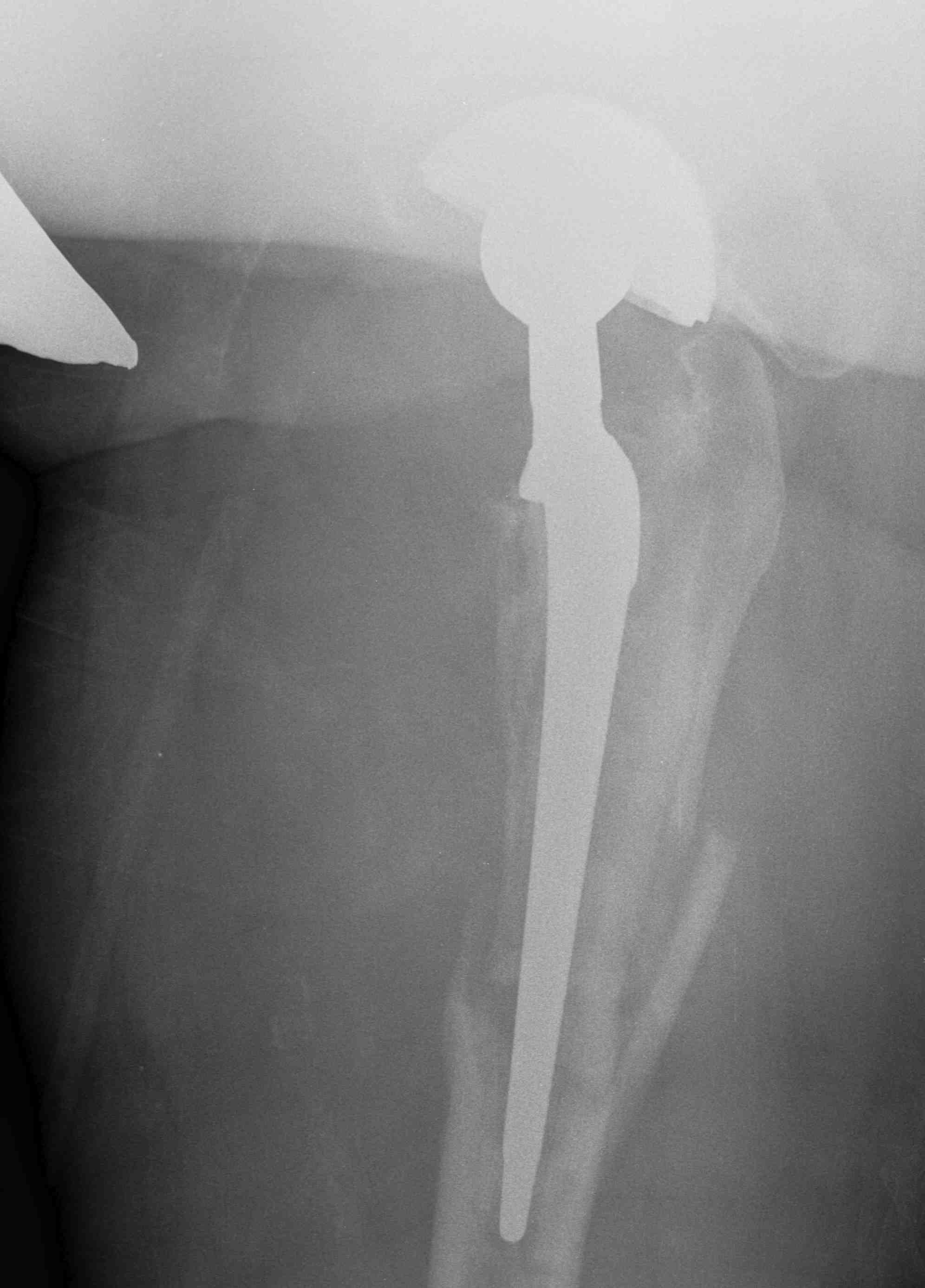
Options
- long stem modular revision implants +/- plate +/- cortical strut
- proximal femoral replacement
- impaction bone grafting
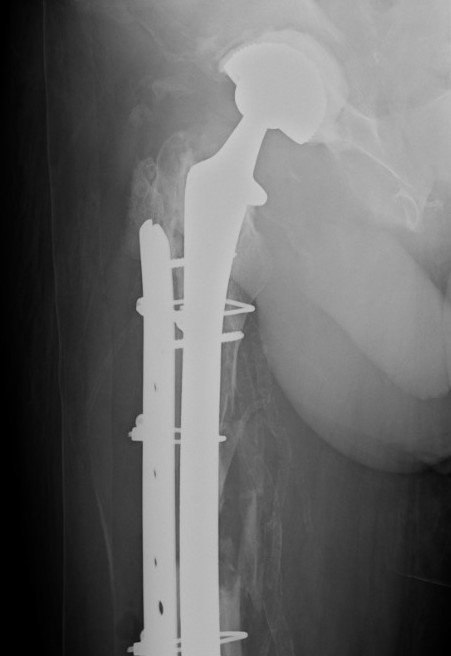
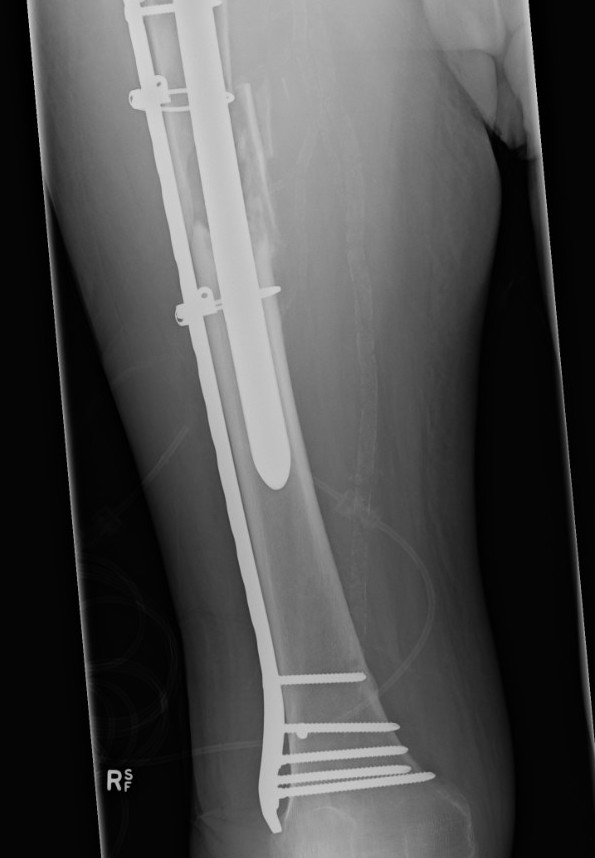
Results
- systematic review of 22 studies and 167 B3 periprosthetic fractures
- 160 treated with revision arthroplasty: 14% underwent reoperation
- 8 treated with ORIF: 29% underwent reoperation
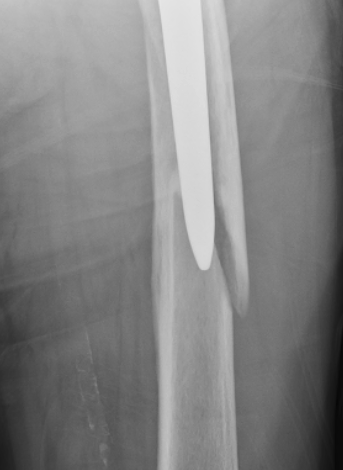
Type C: Fracture distal to tip of stem
Management
ORIF Locking cable plate +/- cortical strut allograft
- overlap femoral implant
- to distal femur
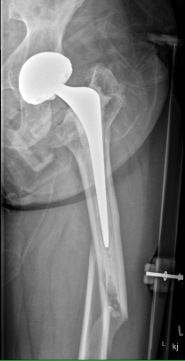
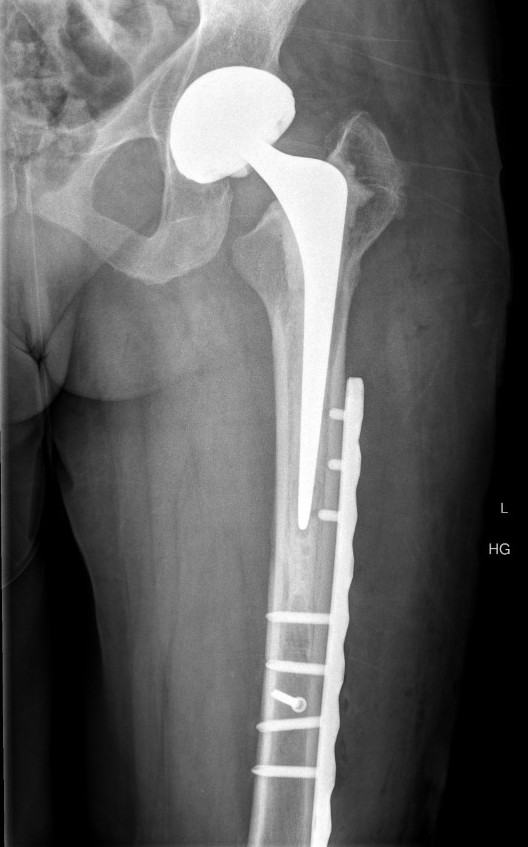
Inter-prosthetic femoral fractures