Technique
1. Templating
Xray
AP in plane of scapula
- template glenoid
- most inferior screw is in thick bone of scapular axillary border
AP humerus
- size and fit of diaphyseal and metaphyseal humeral components
CT
Xray

AP in plane of scapula
- template glenoid
- most inferior screw is in thick bone of scapular axillary border
AP humerus
- size and fit of diaphyseal and metaphyseal humeral components
CT
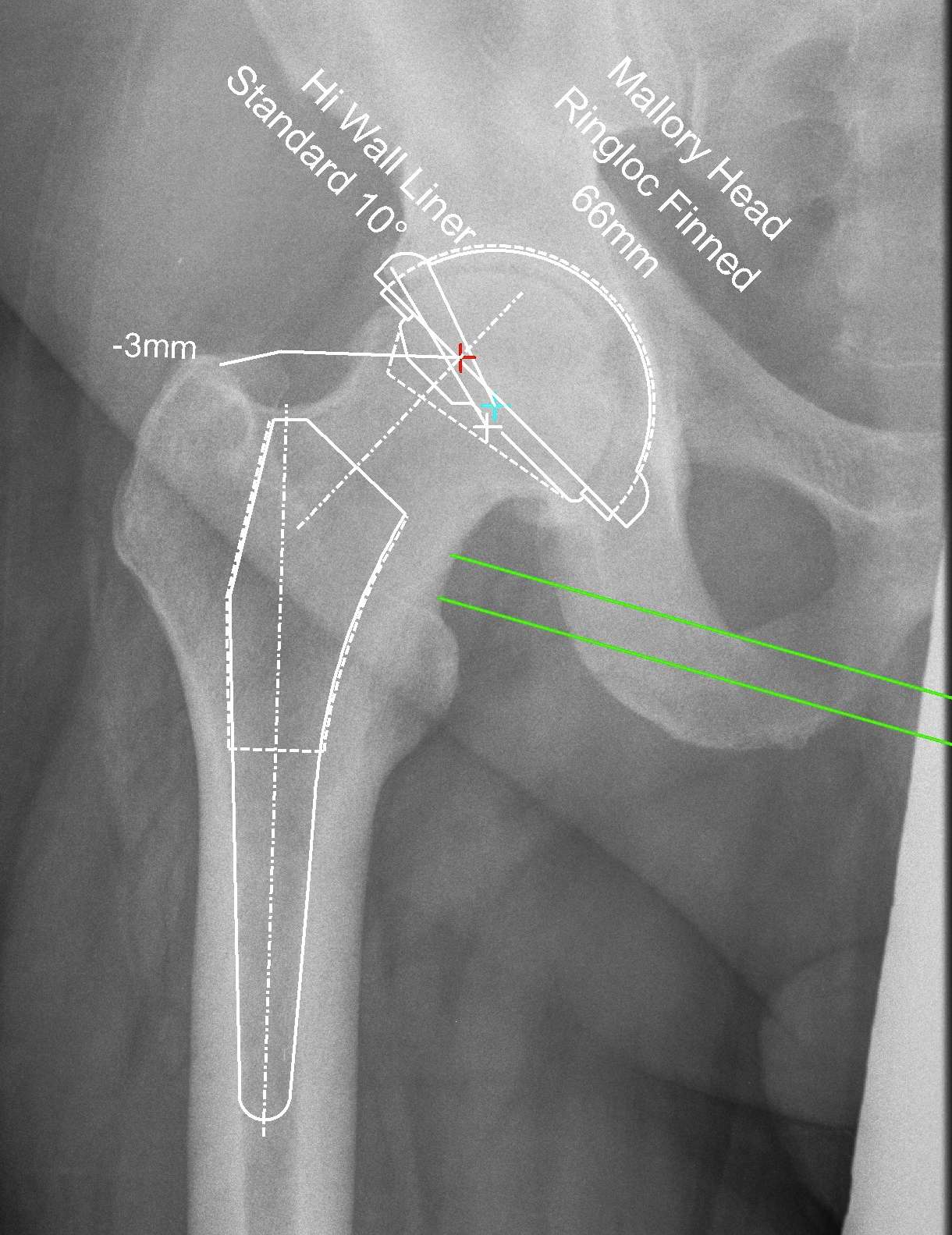
Reproduce the normal anatomical centre of rotation
Restore femoral offset
Maintain equal leg lengths
Usually template off normal hip
1. LLD
2. Offset
3. Femoral component
4. Acetabular component
5. Osteotomy / femoral seating
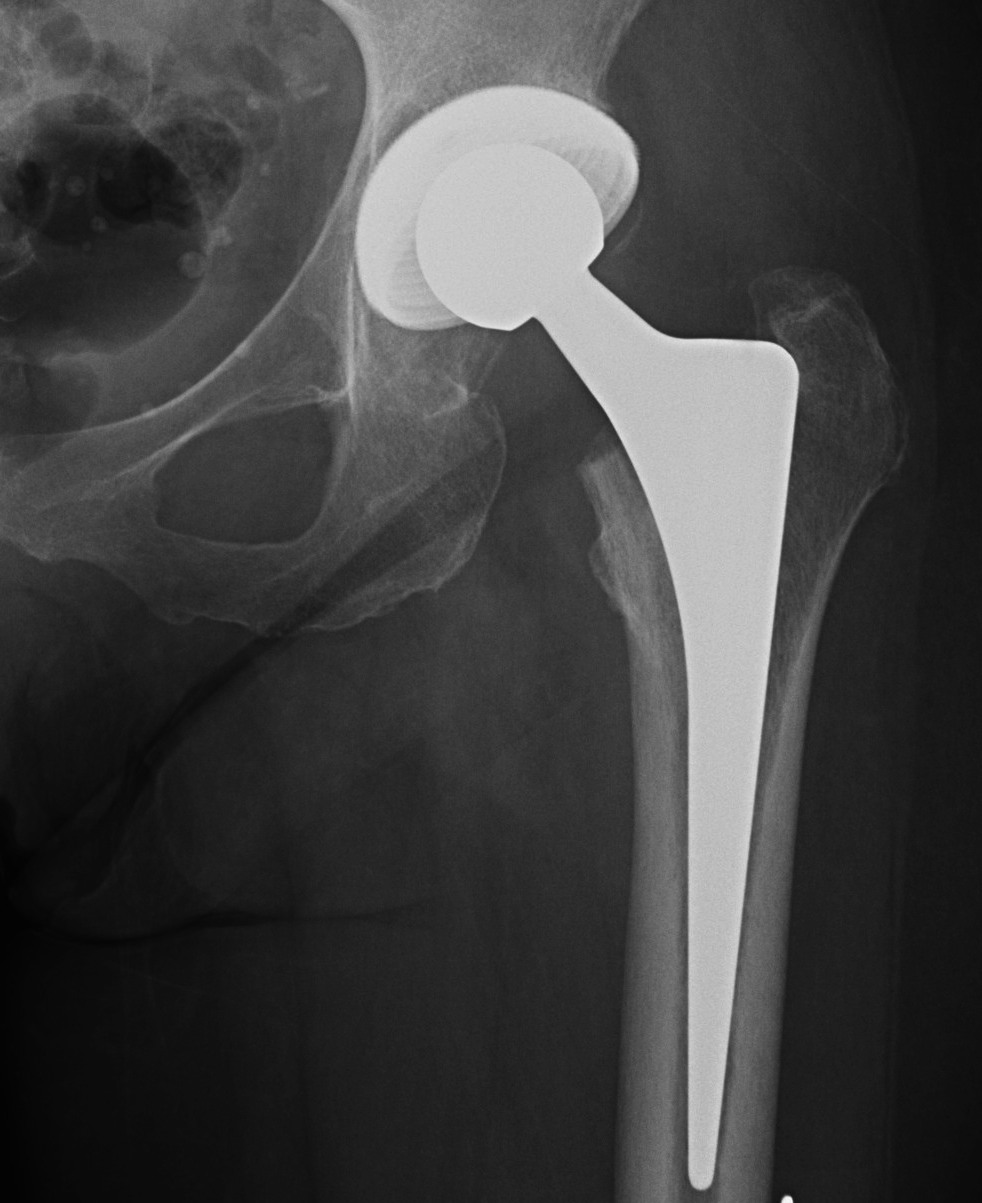
Templating
Approach
Fixation
Bearing Surface
Head Size
Offset
Disabling hip pain
Severe functional impairment
Failed non operative management
Painless deformity
Most common reason for litigation against orthopaedic surgeons in THR
Usually from lengthening
1. Nerve palsy
Sciatic nerve - tolerate average 4.4cm lengthening
Common peroneal nerve - tolerate average 2.7 cm lengthening
Lengthen by up to 15-20% of the resting nerve length
- but in reality is unknown and multifactorial