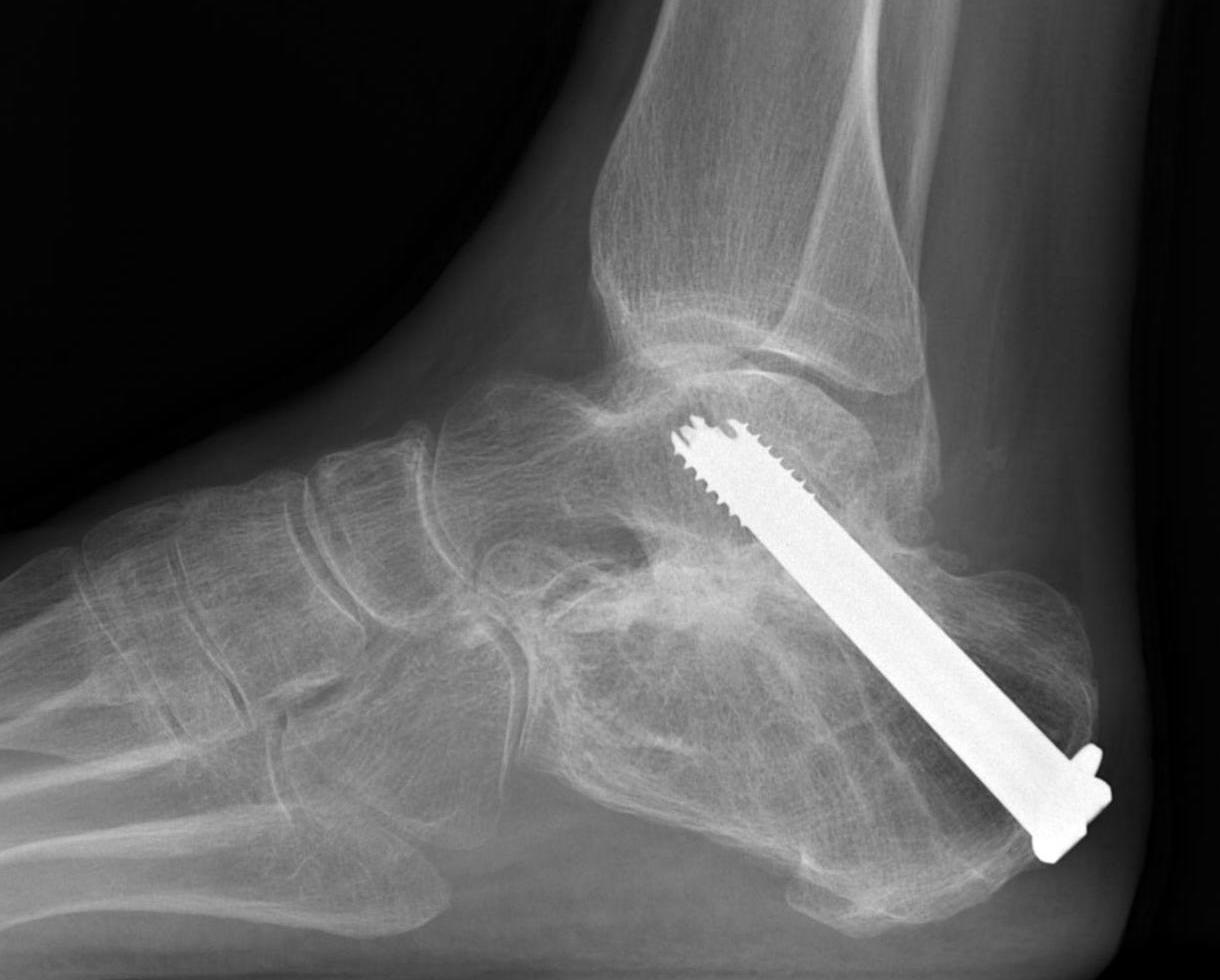
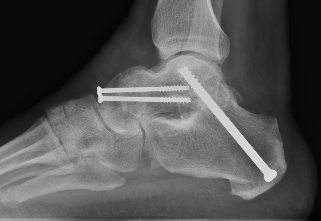
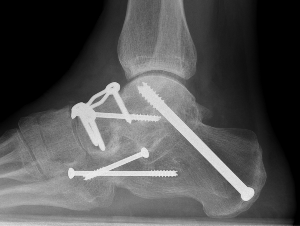
Definitions
Subtalar arthrodesis: Talocalcalcaneal joint
Double arthrodesis: Subtalar joint (STJ) + talonavicular joint (TNJ)
Triple arthrodesis: Subtalar + talonavicular + calcaneocuboid joint (CCJ)
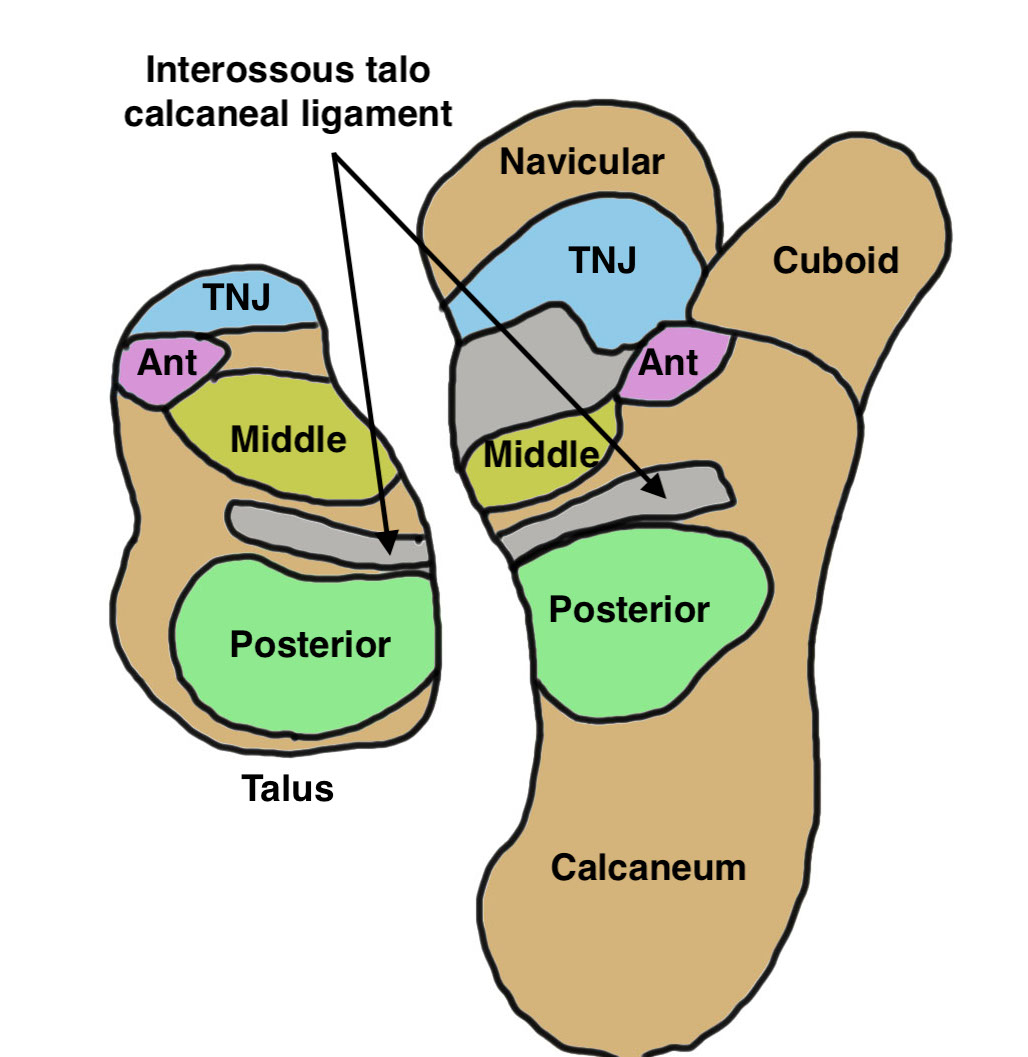
Anatomy
| Movement | Posterior facet | Middle facet | Anterior facet |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Inversion / eversion Pronation / supination |
Largest Saddle shaped |
Medial / sustentacular facet of talus Middle facet of the sustenaculum tali of the calcaneus |
Smallest Head of talus with anterior facet of the calcaneus |
| Walking on uneven terrain |
Indications
Concept
Cannot correct hindfoot deformity without correcting / reducing TNJ +/- CCJ
| Subtalar arthrodesis | Double / triple arthrodesis |
|---|---|
|
Isolated subtalar osteoarthritis Preserved TNJ and CCJ |
Arthritis of TNJ and CCJ as well as STJ |
| Post fracture with minimal deformity |
Deformity correction - fixed acquired planovalgus - calcaneal fracture with collapse and deformity - subluxed talus - rheumatoid arthritis - Charcot / Polio / Cerebral palsy |
Results
Outcomes
Variable due to high number of different indications for triple arthrodesis
Ebalard et al Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 2014
- 72 hind and midfoot fusions with minimum 10 year follow up
- 26% poor or bad outcomes
- 84% of patients had pain
- better outcomes with normal alignment
Double versus triple arthrodesis
DeVries et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2015
- 40 arthrodesis for valgus hindfoot deformity
- 20 double arthrodesis (STJ + TNJ), 20 triple arthrodesis (STJ + TNJ + CCJ)
- no difference in deformity correction between two groups
- suggest may not need CCJ fusion
CT
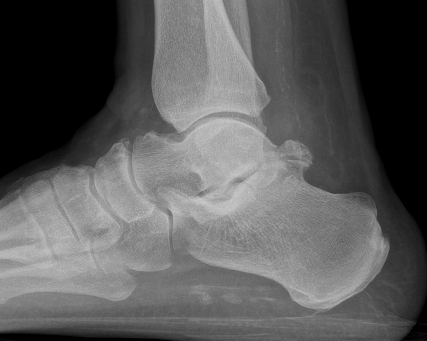
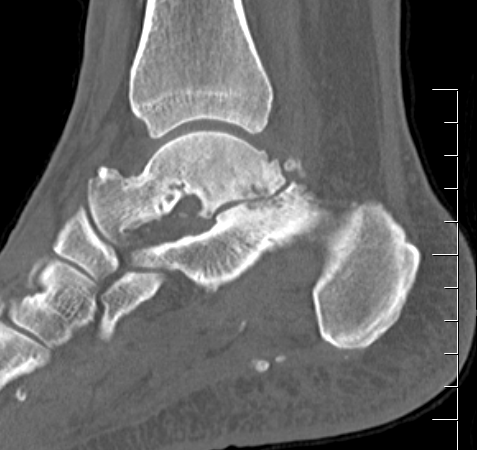
Subluxation of TNJ with advanced STJ OA
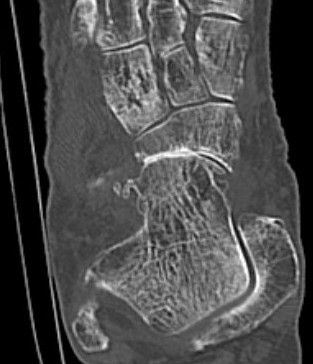
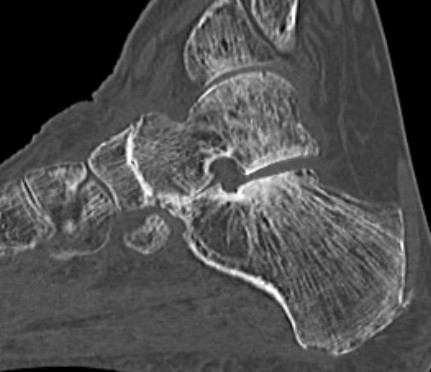
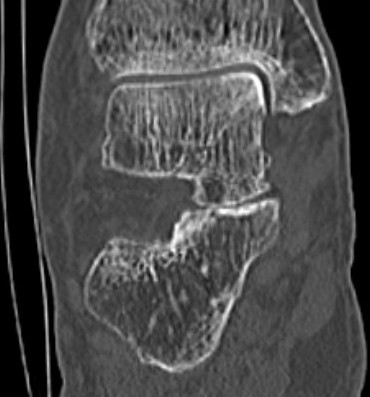
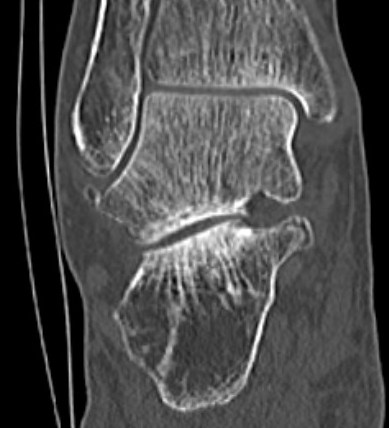
TNJ OA with posterior / medial / anterior facet OA of the subtalar joint
Injections
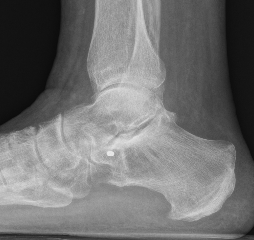
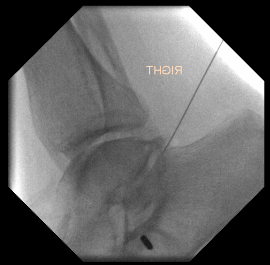
Injection to subtalar joint to see level of improvement
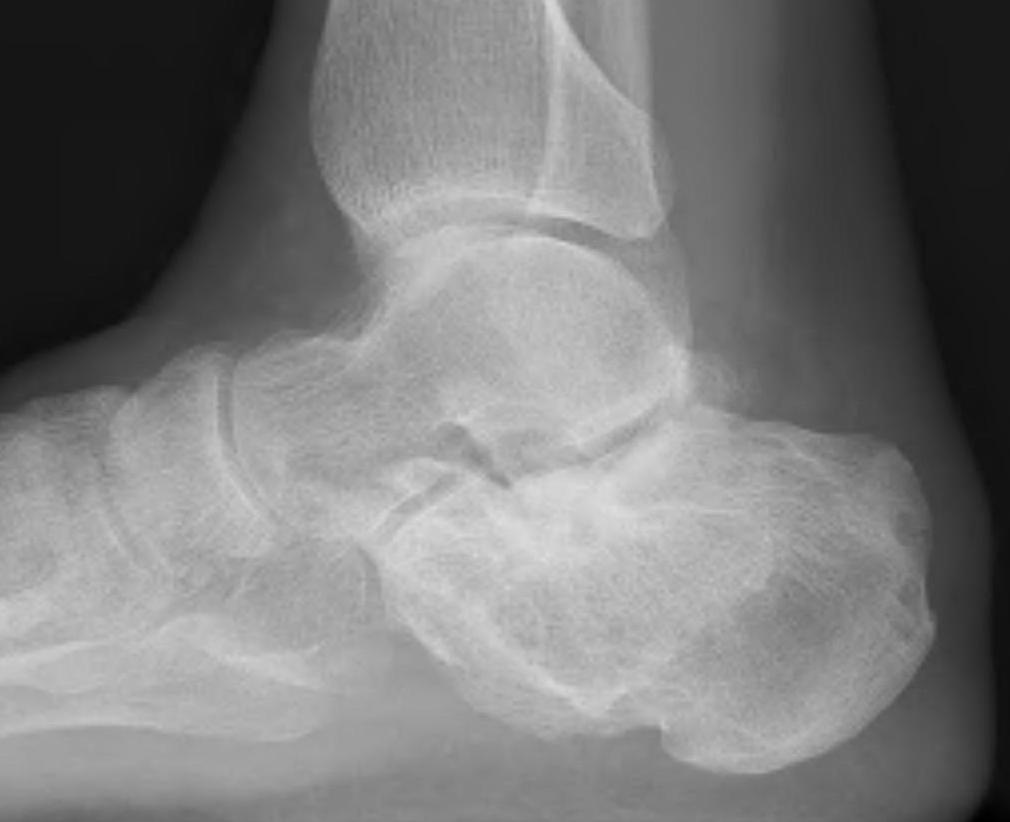
Subtalar Arthrodesis
Indication
Isolated STJ arthritis with minimal deformity
Options
Open
Arthroscopic
Silvampatti et al J ISAKOS 2023
- systematic review of open versus arthroscopic
- 22 studies with 1000 patients
- open: union rate 91% at average 16 weeks, complication rate 20%
- arthroscopic: union rate 96% at average 12 weeks, complication rate 13%
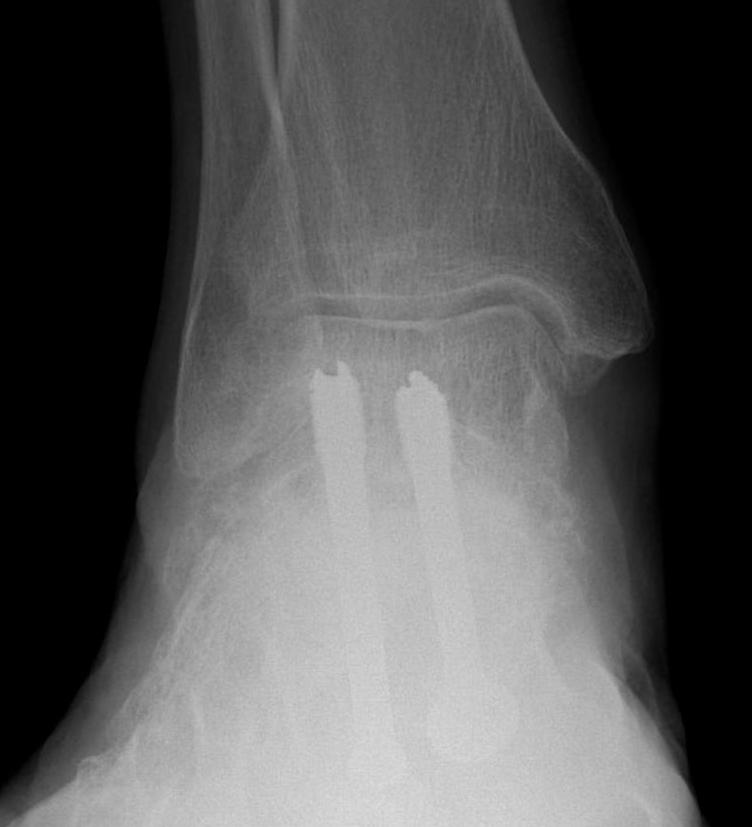
Open subtalar arthrodesis

Technique
Arthrex open subtalar arthrodesis video
JOMI open subtalar arthrodesis video
Patient supine with roll under hip to expose lateral aspect foot
Direct lateral approach
- tip of fibula toward base of 4th metatarsal
- internervous plane between SPN and sural nerve
Superficial dissection
- peroneal tendons lifted dorsally
- elevate EBD and fatty tissue over sinus tarsi
- expose STJ / CCJ / sinus tarsi
Deep dissection
- remove talocalcaneal interosseous ligament
- clear out sinus tarsi
- diathermy artery of tarsal sinus
- insert lamina spreader to expose posterior facet
- need to expose medial facet
Debridement of cartilage and bone
- recreate 2 flat surfaces that come together in 5o valgus
- drill holes to stimulate bleeding +/- bone graft
- if previous calcaneal fracture, decompress lateral wall (5 - 10mm removed)
Fixation
- 6.5 mm/ 8.0 mm cannulated screw
- inferior calcaneum into body and neck of talus / talus to calcaneum
Arthroscopic subtalar arthrodesis
Options
Lateral / supine position with lateral portals
Prone position with posterior +/- accessory lateral portals
Technique
Vumedi posterior arthroscopic subtalar arthrodesis video
Arthroscopic techniques lateral arthroscopic subtalar arthrodesis video
JBJS Essential Techniques Posterior Arthroscopic Subtalar PDF
Results
Banerjee et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2021
- systematic review of 10 studies and 240 feet
- union rate with arthroscopic subtalar fusion 95%
- time to union 10wks
- higher fusion rate with lateral approach
- lower complication rate with posterior approach
Shamrock et al Orthop JSM 2020
- systematic review of portals for arthroscopic subtalar fusion
- lateral portals nonunion rate: 1%
- 2 posterior portals nonunion rate: 8%
- posterior portals with accessory lateral portal nonunion rate: 6%
- no difference in complication rate
Triple arthrodesis
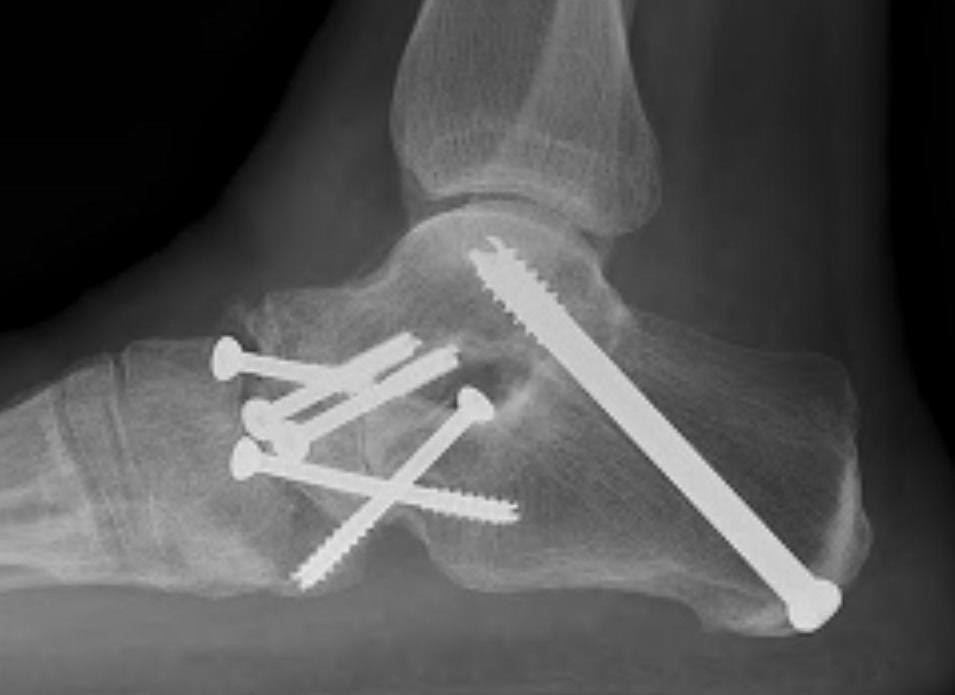
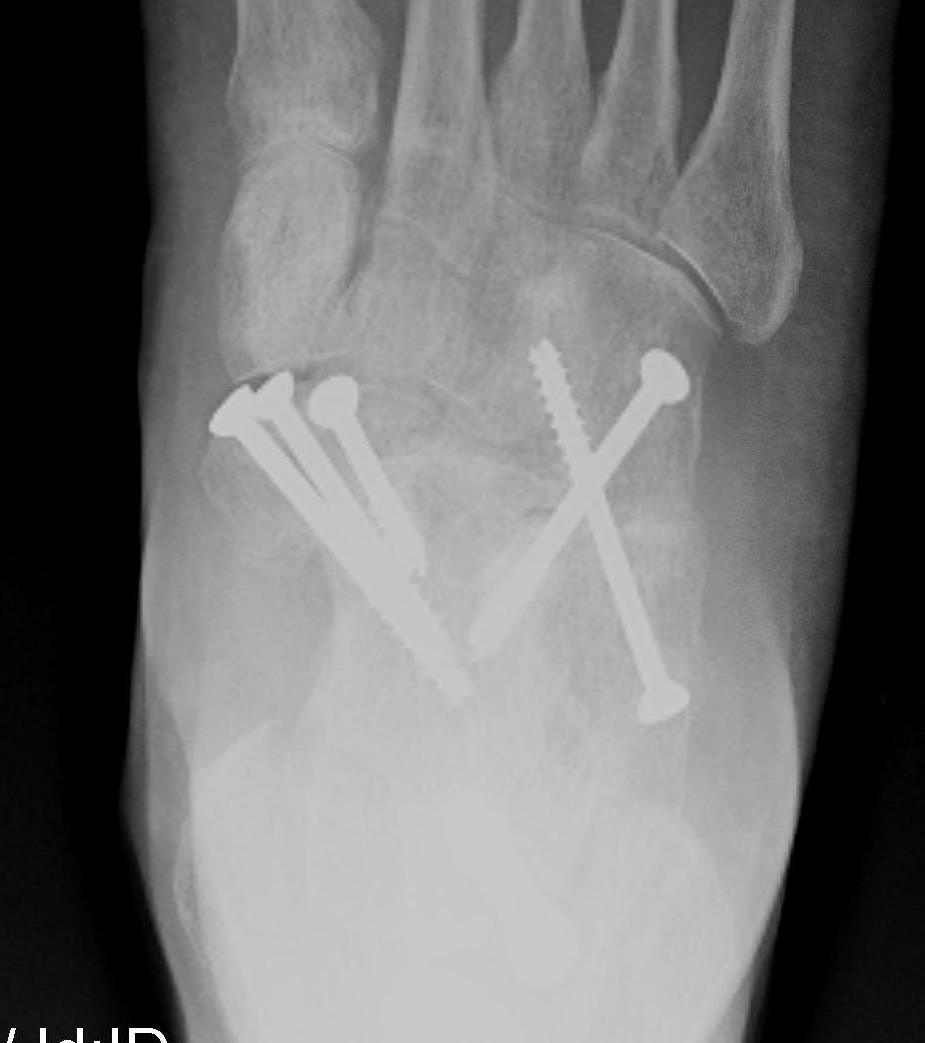
Valgus deformity
Goal
- correct position of the calcaneum under the talus - 5 degrees of valgus
Deformity
- talus internally rotated on calcaneum
- navicular abducted on talus
Issues
- TNJ / CCJ subluxed - need to open and reduce prior to reducing STJ
- may require tendoachilles lengthening
- may require allograft bone block
- may have deficient skin laterally
Technique
Acumed triple arthrodesis video
Acumed triple arthrodesis video 2
Lateral approach
- expose subtalar joint and CCJ
Medial approach to TNJ
- between Tibialis anterior and Tibialis posterior
- protect saphenous nerve and vein
- expose TNJ and debride joint
- reduce joint by adduction /plantar flexion / pronation
CCJ
- open and reduce joint
STJ
- reducing calcaneum back under talus difficult
- lamina spreader between lateral process talus and anterior aspect of calcaneum
- calcaneum internally rotates / talus externally rotates in screw like motion
- need to have all joints opened and exposed for this to occur
Tendoachilles lengthening
- formal Z lenthening
- Hoke lengthening - 2 half incisions laterally, 1 half incision medially between them
Fixation
- TJN screws
- CCJ screws +/- plate
- STJ screws
Complications
Infection / wound complications
Ebalard et al Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 2014
- 72 hind and midfoot fusions with minimum 10 year follow up
- 2 deep infections, 2 superficial infections
- 7 delayed wound healing
- 10 CRPS
Malunion / Deformity
Varus malunion
- relatively uncommon
- patients with cavovarus foot initially
- varus position of subtalar joint
- walk on lateral border of foot
- lateral column overload
Valgus malunion
- patient with planovalgus foot initially
- subfibular impingement / fibular stress fracture
- can lead to deltoid ligament failure and ankle OA
Nonunion
Cates et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2022
- systematic review of double versus triple arthrodesis
- union rate double: 92%
- union rate triple: 93%
- time to union 16 - 17 weeks
Allport et al Foot Ankle Int 2021
- 381 hind or midfoot arthrodesis
- 6X higher risk of nonunion in smokers
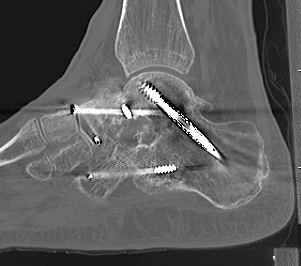
Union
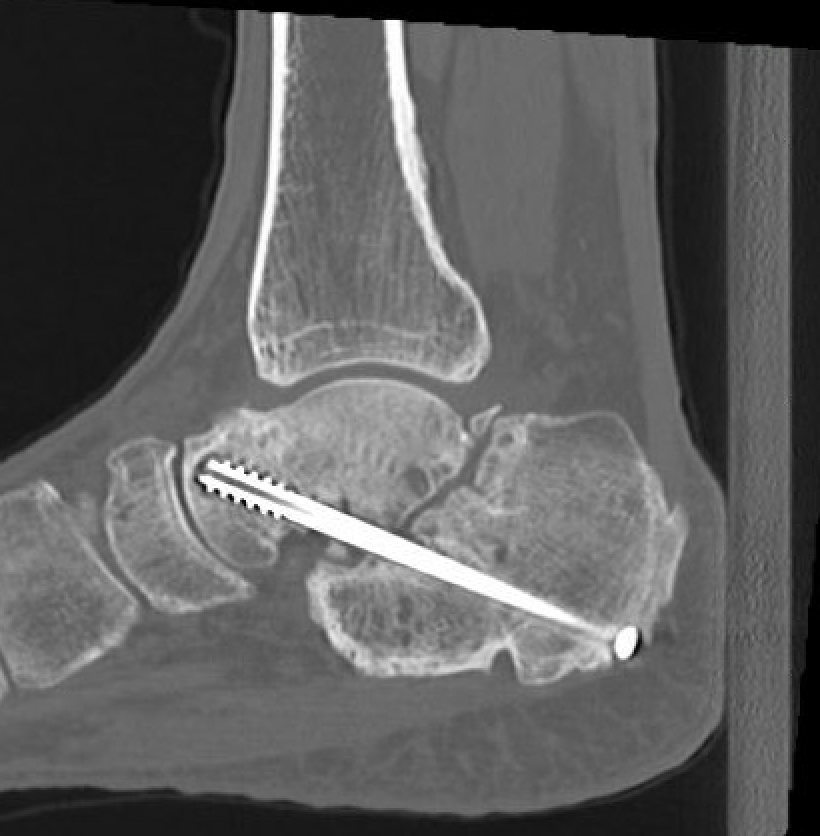
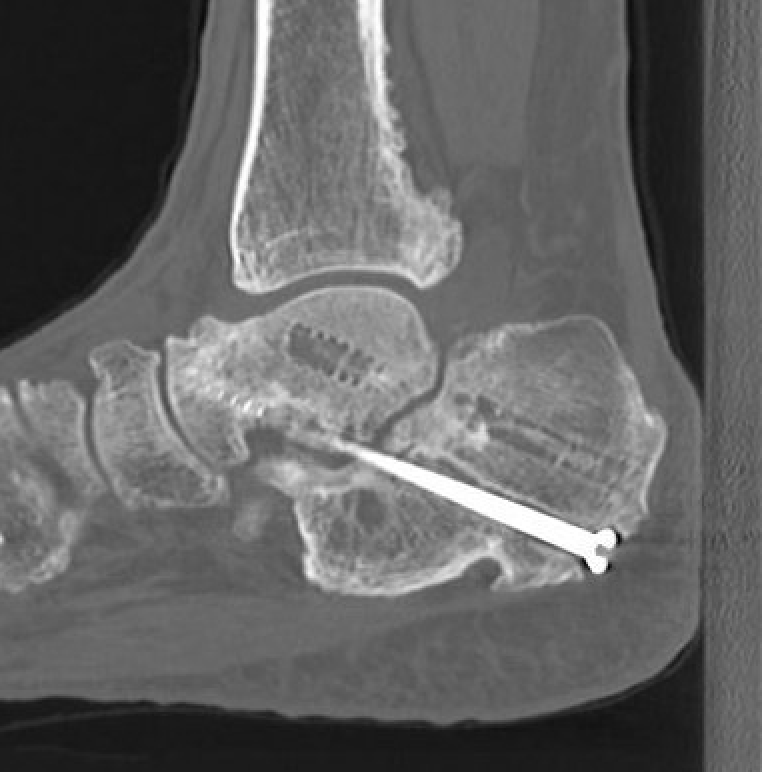
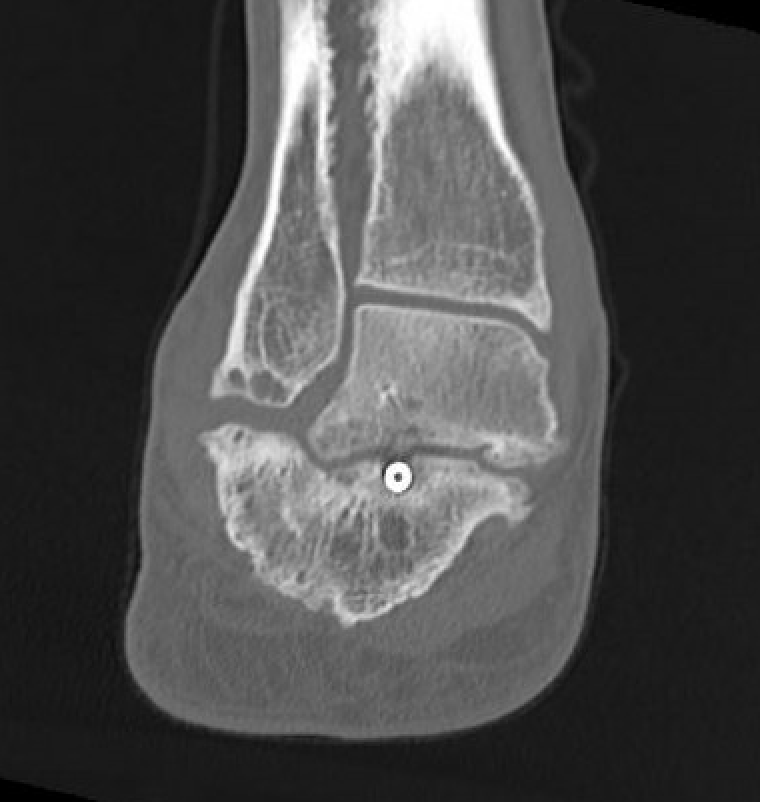
Nonunion
Ankle joint arthritis
Ebalard et al Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 2014
- 72 hind and midfoot fusions with minimum 10 year follow up
- 73% tibiotalar arthritis
