Definition
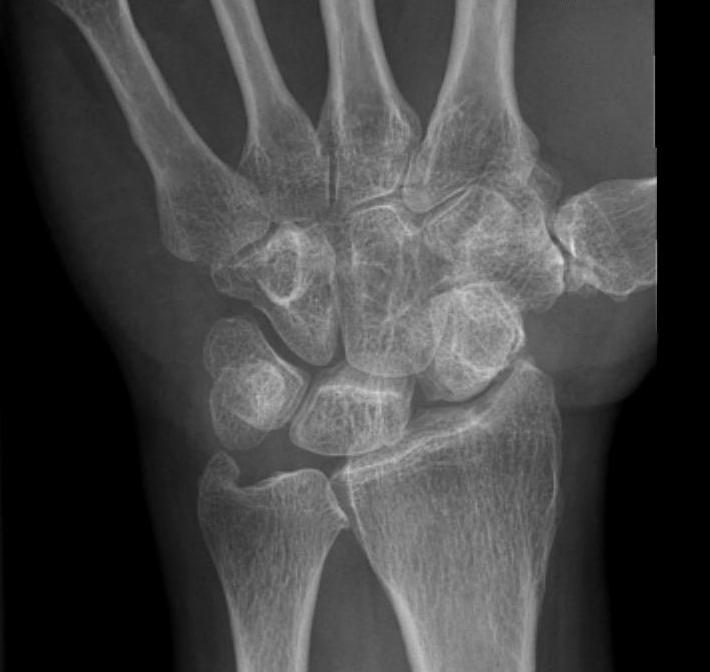
Scapho-lunate advanced collapse
- caused by malalignment of scaphoid on radius
- due to scapholunate disruption
Most common cause of wrist OA
Pathology
1. Radio-scaphoid degenerative changes
- from abnormal flexion of scaphoid
- scaphoid fossa is elliptical causing incongruence with flexion of proximal scaphoid
- loads scaphoid fossa of radius peripherally
2. Radiolunate joint preserved
- lunate fossa and proximal lunate spherical and congruent
3. Capitate under increasing load descends into gap
- increasing loads on capitolunate joint
- separation of scaphoid and lunate
- capitate shears off radial edge of lunate
- get destruction on both lunate and proximal capitate
X-ray
OA radio-scaphoid joint
Preservation of radiolunate joint
Staging
1. Styloid OA

2. Scaphoid Fossa OA
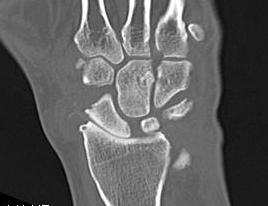
3. Lunato-capitate OA
- capitate descends in SL gap
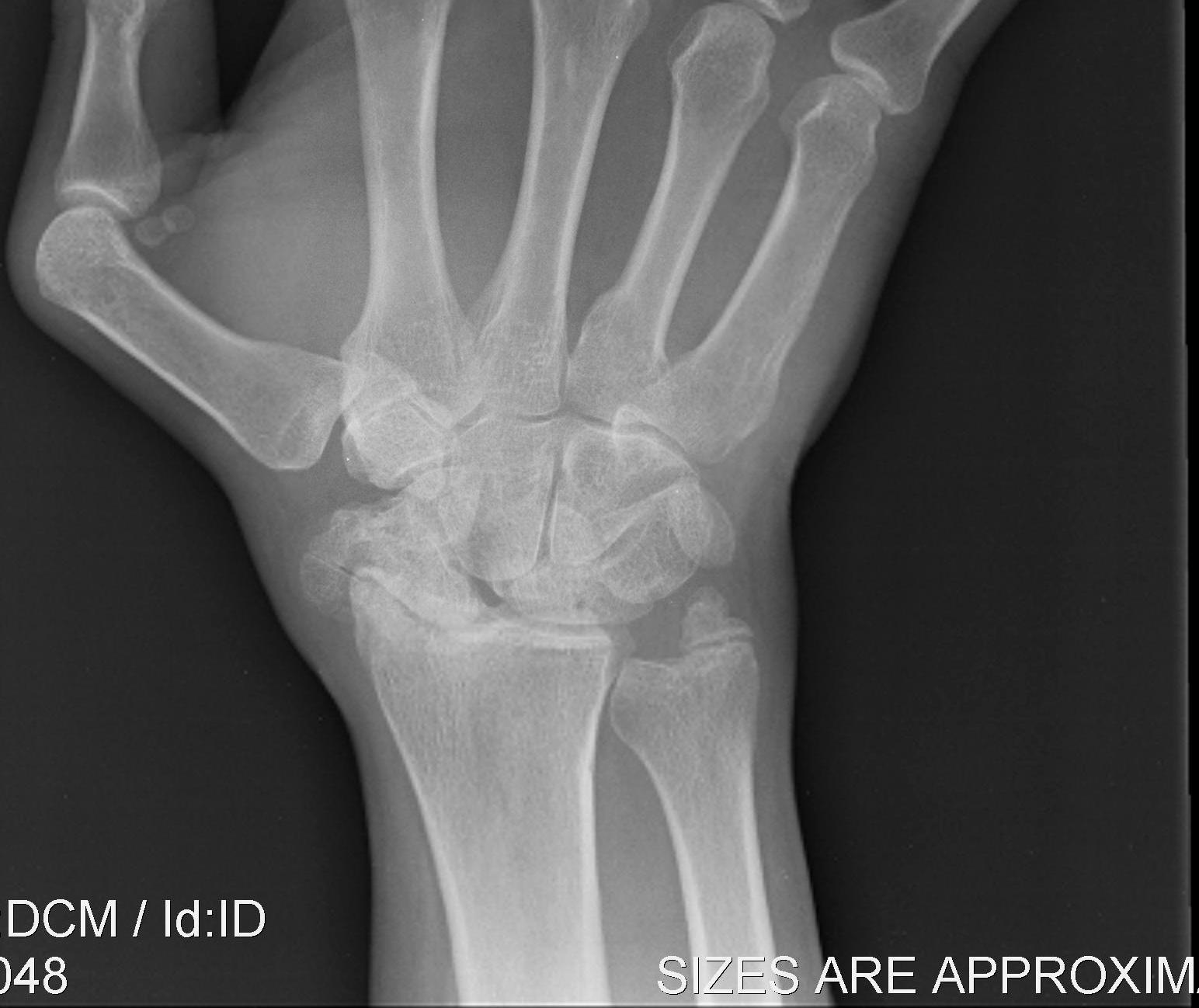
4. Pancarpal OA
DDx
SNAC
- preservation of scaphoid fossa and proximal scaphoid congruence
- arthritis at scapho-capitate joint
Management
Stage 1
Definition
- styloid OA
- degeneration between the radial styloid and distal pole scaphoid
Options
1. Styloidectomy
- early disease can respond well to styloidectomy
- remove at level A / no removal of scaphoid fossa
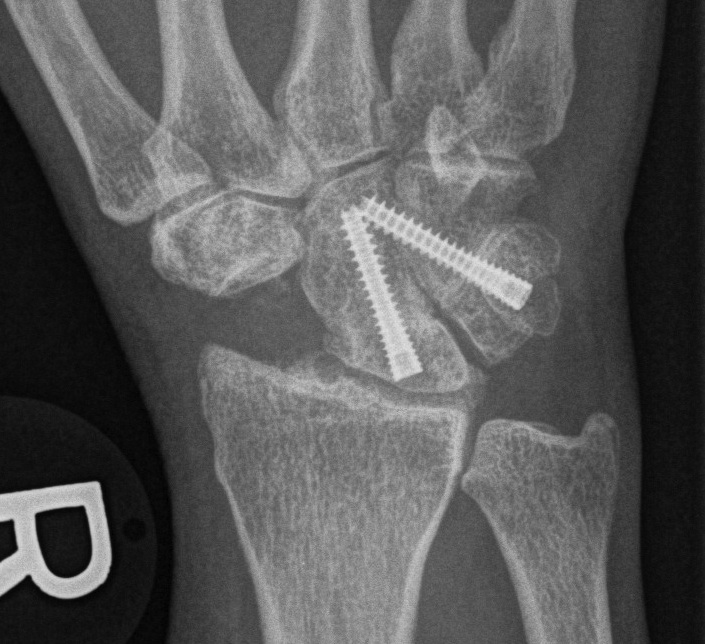
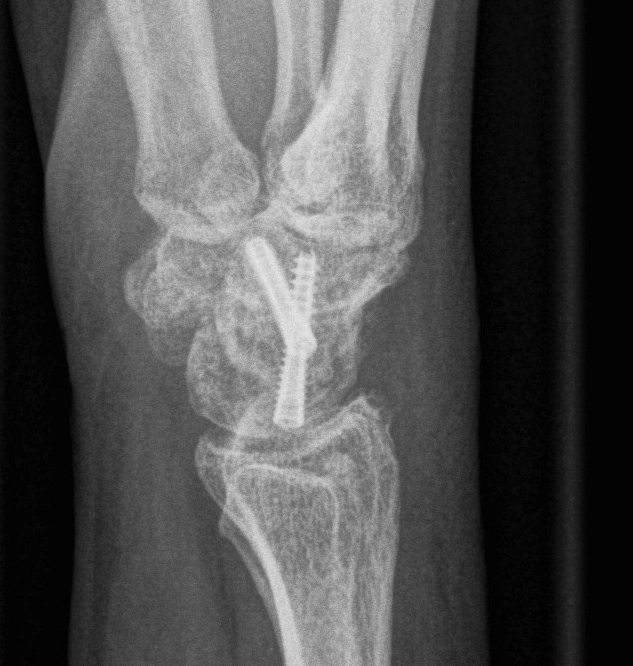
2. Scapholunate Reconstruction
A. Excise fibrous tissue and insert SL screw
- fibrous ankylosis
- remove screw at 12/12
B. Bone blocks with ligament
Stage 2
Definition
- scaphoid fossa OA
- OA extends to involve scaphoid fossa and proximal pole scaphoid
Options
A. Scaphoidectomy & four corner fusion
B. Proximal Row Carpectomy
Scaphoidectomy & Four Corner Fusion
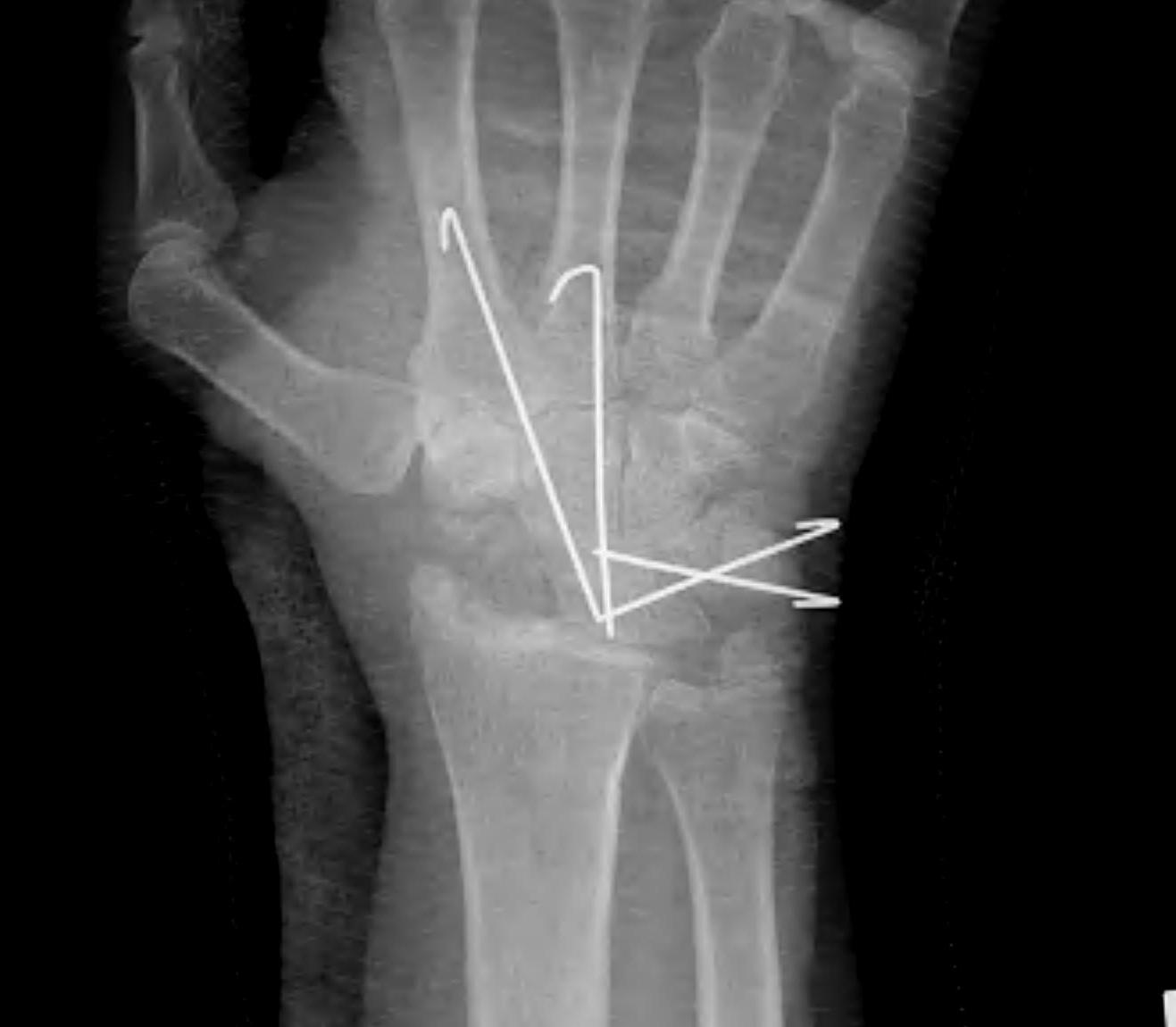
Theory
- fusion of lunate to capitate
- loading is through normal lunate fossa
- fusion of lunate-capitate can be difficult
- add hamate and triquetrum in so called 4 corner fusion
- greatly increases fusion rates
- seemingly no deleterious effects
- if leave out scaphoid replacement tends to drift into radial deviation
- can use scaphoid for bone graft (but may not be high quality)
Advantage
- increased stability comared with PRC
- increased ROM compared with total wrist arthrodesis
Approach
- universal posterior approach
- base of EPL (3/4 interval)
- can use Lister's tubercle for BG
- make window on radial side so as not to get late rupture of EPL
- denervate wrist / remove terminal branch PIN
- ligament sparing exposure / open capsule between dorsal intercarpal and radiocarpal
- closure ER under EPL at end of case
Technique
- resect scaphoid
- denude surfaces of lunate / capitate / hamate / triquetrum
- use good quality BG from distal radius
- must reduce the lunate out of extension or will impinge dorsally
Fixation
- headless compression screws
- dorsal circular plate
- K wires
Results
- strength 75-80% normal
- ROM 40 - 60% of normal
B. Proximal row carpectomy
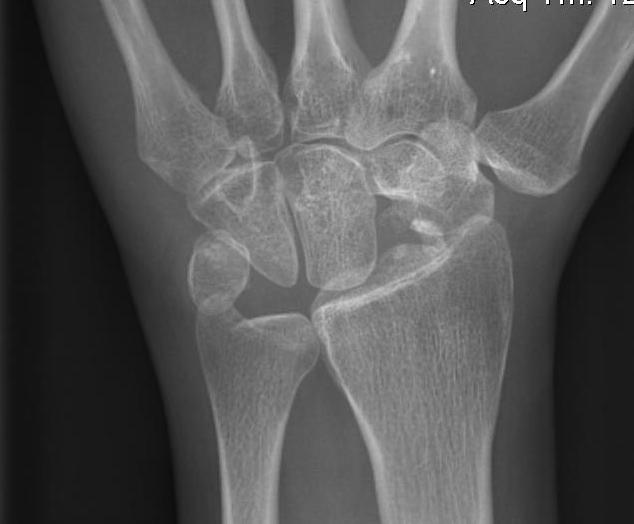
Aim
- for capitate to articulate with distal radius
Disadvantages
- proximal capitate often devoid of good cartilage
- discard good lunate cartilage
- weakness ensues due to lengthening of tendons
- reported pain / instability / degeneration
Indications
- probably best in low demand patients
- not in stage 3 SLAC
Technique
- perform through standard dorsal approach
Results
- RCT of 4 corner fusion v PRC are comparable
Stage 3
Definition
Capito-lunate OA
- capitate migrates proximally between the scaphoid and the lunate
Options
A. Scaphoid excision & 4 corner fusion
B. Proximal Row Carpectomy
C. Wrist Arthrodesis
Note
- PRC may be bad options in stage 3
- they depend on the capitate and by definition the capitate is arthritic
Stage 4
Definition
Collapse / pancarpal OA
Options
Wrist arthrodesis
