Definition
Circulation of tissues within a closed osteofascial space are compromised by increased pressure within that space
Most common
- anterior leg compartment
- flexor compartment forearm
- deep posterior leg compartment
Aetiology
Prerequisite is volume restricting envelope
- fascia & skin
- POP
- dressings
1. Increased contents
Bleeding / edema
- fracture
- osteotomies
- crush injuries
- post - ischaemic swelling
2. Decreased size
Tight casts & dressings
Tight closure of fascial defects
Fracture reduction
Pathogenesis
Increased local tissue pressure increases pressure within intracompartmental veins
- local AV gradient is reduced
- causes decreased local perfusion secondary to Starling Forces
Metabolic tissues demands not met
- loss of tissue function & viability
- distal pulses remain as ICP < SBP
- digit capillary refill remains as venous return extracompartmental
Symptoms
1. Pain
- most important sign
- much great than expected
- masked by coma / neural injury
- unrelieved by opiates
2. Paraesthesia
- often early
- pins & needles or decreased sensation to light touch
- distribution important
- nerve of that compartment will be affected
Signs
3. Palpation
- swollen, tense compartment
4. Passive Stretch
- pain on passive stretch
- subjective
- complicated by underlying trauma
5. Paresis
- may be due to proximal nerve injury or guarding 2° to pain
6. Pulses
- pulse & capillary refill are normally present
Diagnosis
Clinical Diagnosis
Tense compartment with pain +++
Pain on passive stretch
Intramuscular Pressure Measurement
Pressure Measurement
Indications
1. Unresponsive
- head injury
- ventilated
2. Uncooperative
- children, drug abusers
3. Underlying peripheral nerve deficit
- tibial fracture with CPN nerve deficit
Techniques
1. Needle - Manometer Method (Whitesides)
- 18G needle is connected via a 3 way stop cock to an air filled 20 ml syringe
- air filled tubing which is connected to a Hg Manometer
- a small amount of saline sits in tube connected to needle
- compression of the syringe raises the pressure till saline flows into the compartment
- this is indicated by the meniscus moving
2. Arterial Pressure Transducer
- i.e. devices used in ICU to measure arterial blood pressure and CVP
- no need to inject fluid
- pressure in saline tube equalizes with compartment
- connect to Wick or Slit catheter
- slits have many longitudinal slits to equalize pressure in tube with compartment
3. Stryker Device
- Variation on 2
Interpretation
Matsen > 45 mmHg
Mubarek & Rorabeck > 30 mmHg
Whitesides - within 30mmHg of DBP
Management
Prevention
Remove all tight dressings
- splitting POP decreases pressure by 30%
- bivalving & cutting padding reduces pressure by another 55%
- elevate limb
Avoid hypotension
Ream without tourniquet
Early fasciotomy
Full-length skin incision
Complete fasciotomy of all compartments
Assessment of muscle (colour / consistancy / contraction / bleeding)
Debridement dead muscle
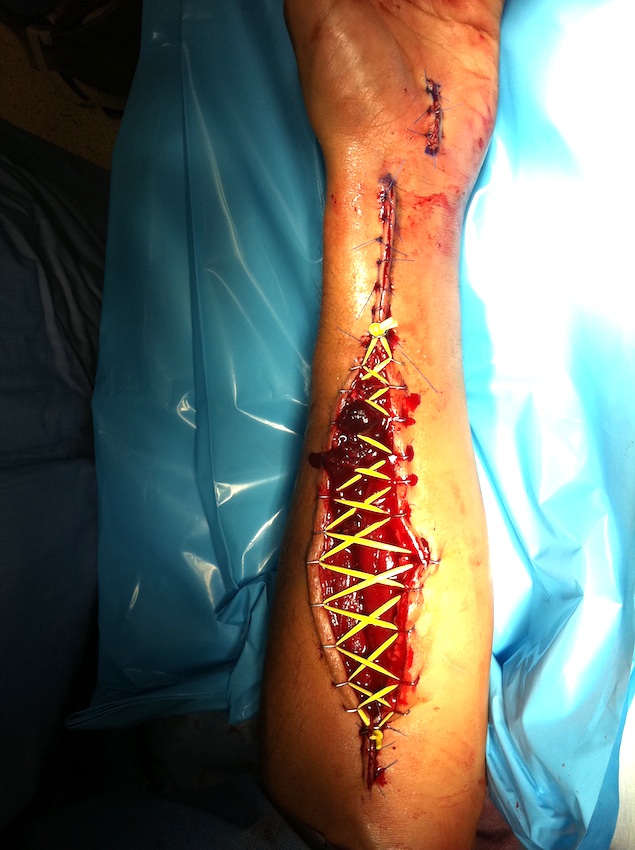
Delayed DPC / graft
2 Incision Technique Leg
Anterolateral compartments
- incision halfway between crest of tibia & fibula
- identify and protect SPN
- expose lateral intermuscular septum (transverse cut)
- release Anterior & Lateral compartments
Posterior compartments
- incision 2 cm posterior to posterior margin of tibia
- identify and protect saphenous vein / nerve anteriorly
- identify septum between superficial & deep compartments
- release fascia over Gastro-Soleus (superficial posterior compartment)
- release deep posterior compartment which is located behind the tibia / FDL
Perifibular Approach / Single incision Technique
Lateral incision beginning just posterior to fibula
- expose & protect CPN
- posteriorly release superficial posterior compartment
- release FHL (deep posterior compartment
- anteriorly expose and release anterolateral compartments after identifying SPN
Compartment Release Forearm
4 interconnected compartments
- volar superficial
- volar deep (FDP / FPL / pronator quadratus)
- mobile wad (BR, ECRL, ECRB)
- extensor
Volar
- incision from medial elbow to carpal tunnel
- must release lacertus fibrosis and carpal tunnel
- divide fascia
- this will release superficial flexor muscles
- ensure release mobile wad
- ensure release FDP
Dorsal
- often volar release wil decompress dorsal compartment
- usually ulnar sided incision
- proximal over muscle belly
- distally is mostly tendons
Compartment Release Hand
Two dorsal incisions
- over MT 2 and MT 4
- release interossei compartments
Carpal tunnel incision
- release thenar / hypothenar / adductor
- release carpal tunnel
Compartment Release Foot
2 dorsal incisions
- over MT 2 and MT 4
- release 4 interossei compartments
Medial incision
- release medial / central and lateral compartments
Complication
Volkmann's contracture
- ischaemic muscles fibrose & contract
- causes deformity & stiffness
- nerves damaged with variable numbness
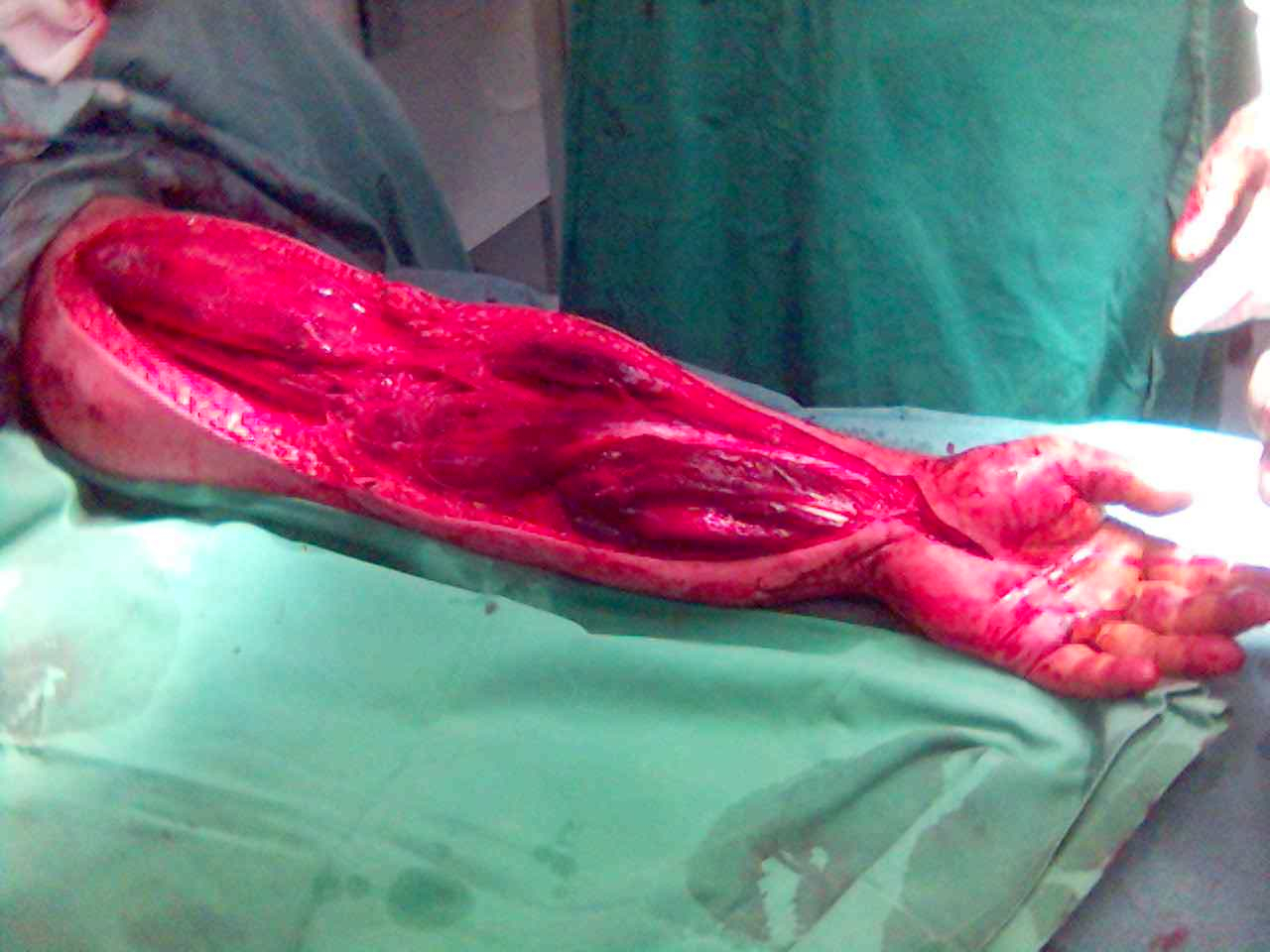
1. Antebrachial Compartment Syndrome
Aetiology
Supracondylar fracture of humerus
Both bone forearm fractures
Examination
Tense compartments
Pain +++
Passive extension of the digits or wrist increases pain
Paresthesias in median nerve distribution
Forearm Fasciotomy
Decompression extending from elbow to wrist
Compartments (3)
- mobile wad
- volar
- dorsal
Incision
- medial arm
- across elbow
- continue as Henry approach into forearm
- can continue into palm as CTD incision
Release
- lacertus fibrosus (releases median nerve at elbow)
- fascia of forearm (releases superficial volar)
- deep fascial compartments (FCU / FDP / FPL)
- mobile wad
Remeasure dorsal compartment
- often decompression of volar compartment will reduce dorsal pressures
Consequences
Volkmann's ischemic contracture
- result of delayed diagnosis
- severe muscle fibrosis & neuropathy
- clawing of fingers
Muscles most commonly affected
- FDP
- FPL
Transfers
- BR to FPL
- ECRL to FDP
Compartment Syndrome of Hand
Aetiology
Iatrogenic injuries
- arterial line or infiltration of IV medications
Crushing trauma
IV drug abuse
High pressure injections
- i.e. paint guns
Clinically
Hand compartment syndromes lack abnormalities in sensory nerves
- no nerves are found within compartment
- non specific aching of the hand
Increased pain, loss of digital motion, continued swelling
- tight swollen hand in a intrinsic minus position
- MP extension and PIP flexion
- intrinsic tightness (increased PIPJ motion with MCPJ flexion v extension)
Pressure measurement
Should have a lower threshold than in leg compartments
- pressures greater than 15-20 mmHg is a relative indication for release
Compartments
10 separate osteofascial compartments
- dorsal interossei (4)
- palmar interossei (3)
- adductor pollicis (1)
- thenar and hypothenar (2)
Decompression
CTD
- release thenar / hypothenar / adductor pollicis
- 2 x dorsal incisions over MC 2 and 4
