plate
Proximal Tibial Fractures
Definition
Metaphysical
Extra-articular
Treatment options
IMN
Plate
Results
Jindal et al. Indian J Orthop 2020
- systematic review
- no different in malunion
- infection more common in plate
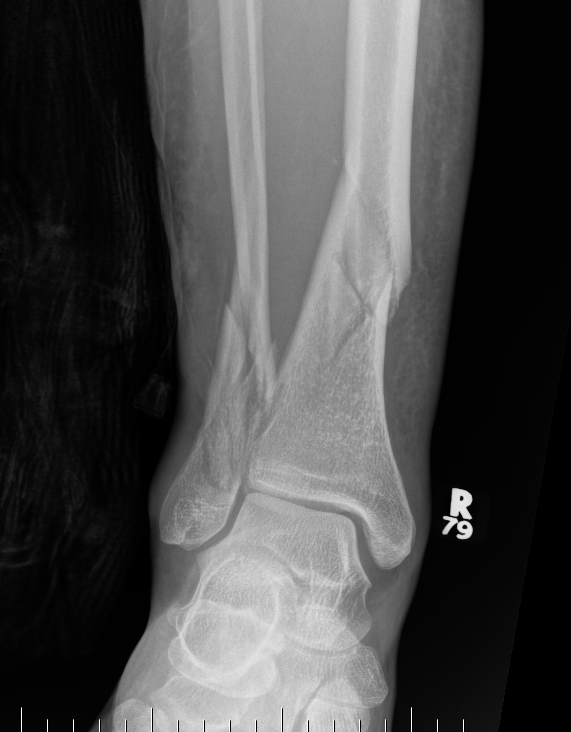
Distal Tibial Fractures
Distal Tibial Fractures
Definition
Metaphyseal
Extra-articular
Intra-articular Extension
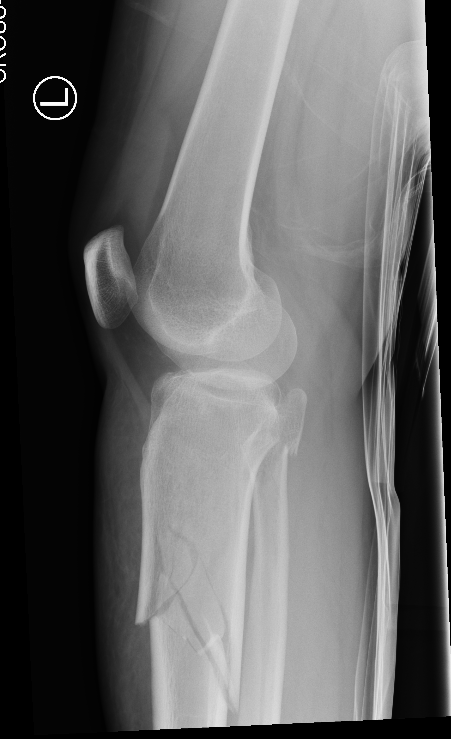
Distal Femur Fractures
AO Classification
Types
1. Supracondylar
2. Unicondylar
3. Intracondylar
Xrays
Supracondylar / Extra-condylar
Midshaft Tibial Fracture
Epidemiology
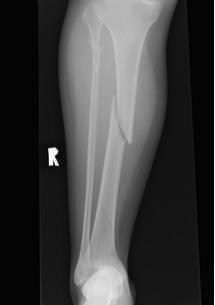
Most common long bone fracture
Aetiology
Young patients / sports
Elderly / simple falls
MVA - often compound
Tscherne Soft Tissue Classification
Grade 0
- nil ST injury
Grade 1
Distal Radius Fracture
Epidemiology
2 groups
1. Elderly
- low velocity injury
- osteoporotic
- need to start bisphosphonates
2. Young patients
- high velocity injury
Anatomy
Distal Radius Angles
- radial volar tilt 11°
- radial inclination 22°
- radius is 11 mm longer than ulna
- ulna variance 2mm positive on average
Proximal Humerus Fracture
Epidemiology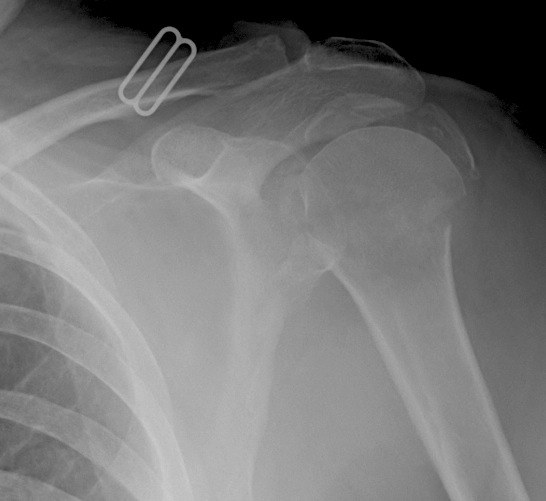
>65
Third most common fracture after hip and distal radius
Anatomy
Neck shaft angle 130o
Head retroverted 20o relative to shaft
Anatomical neck (junction of head and metaphysis)
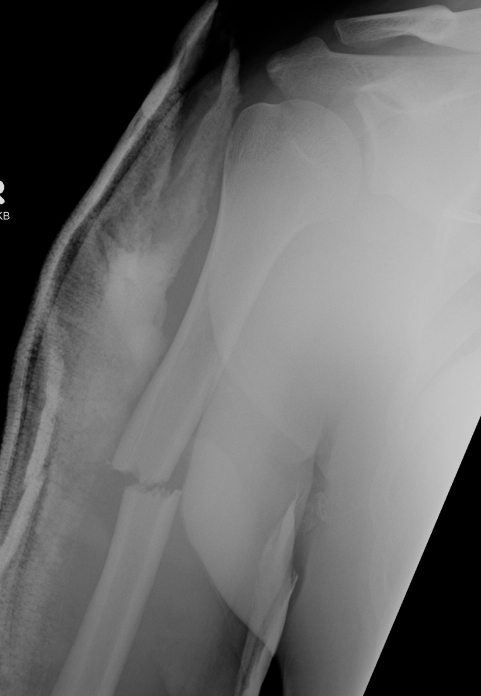
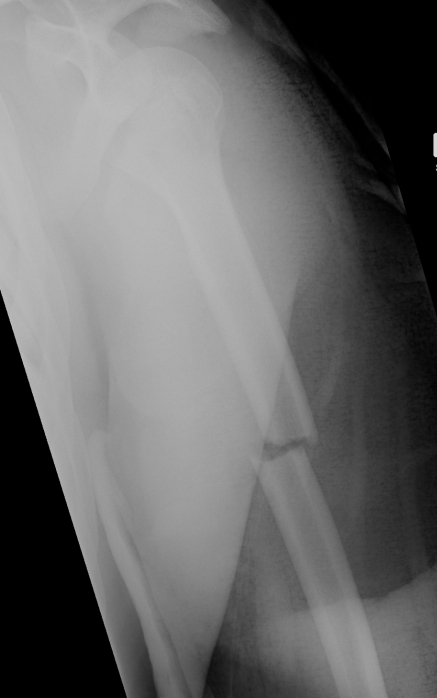
Humeral Shaft Fracture
Non operative Management
Indications
< 20o sagittal
< 30o coronal
< 3 cm of shortening
Options
Olecranon Fracture
Definition
Intra-articular proximal ulna fracture
Anatomy
Articulates with trochlea
- may have a central bare area
Triceps insertion
- via broad aponeurosis which blends with anconeus and CEO
Management
Non operative Management
Undisplaced fracture
- need to ensure triceps mechanism is intact
Forearm Fractures
Ossification
Primary
- 8 / 52 gestation radius & ulna
Secondary
- distal radius age 1
- distal ulna age 5
Non Operative Management
Unacceptable Position
< 10: > 15o malalignment
> 10: > 10o malalignment
Postreduction Positionin / Rule of Thirds