indications
Background
Indications
RA
OA
AVN
Platelet Rich Plasma
Definition
Platelet rich plasma
Concept
2 main components
1. Platelets
- contain PDGF, TGF, VEGF
2. Growth factors
- ILGF
- FGF
Formed from the separation of whole blood into plasma and RBC
- separation usually achieved with centrifugation
Platelet concentration
Distal Femur Fractures
AO Classification
Types
1. Supracondylar
2. Unicondylar
3. Intracondylar
Xrays
Supracondylar / Extra-condylar
Arthroplasty
Indications
Patient > 70
Gjertsen et al JBJS Am 2010
- 4335 patients > 70 with displaced subcapital fractures
- minimum 1 year follow up
- 1 year mortality same in each group / 25%
- 22% reoperation in ORIF v 3% in hemiarthroplasty
- more pain / higher dissatisfaction / lower quality life in ORIF group
Options
Hemiarthroplasty
- unipolar monoblock
- unipolar modular
Surgery
Indications
1. Significant functional impairment
2. PIPJ contracture
- originally thought to intervene early
- Macfarlane showed residual FFD always about 30o
- may need to release check rein ligaments / accessory collateral ligaments
3. MCPJ contracture >30o
4. Trigger fingers
- must do limited fasciectomy
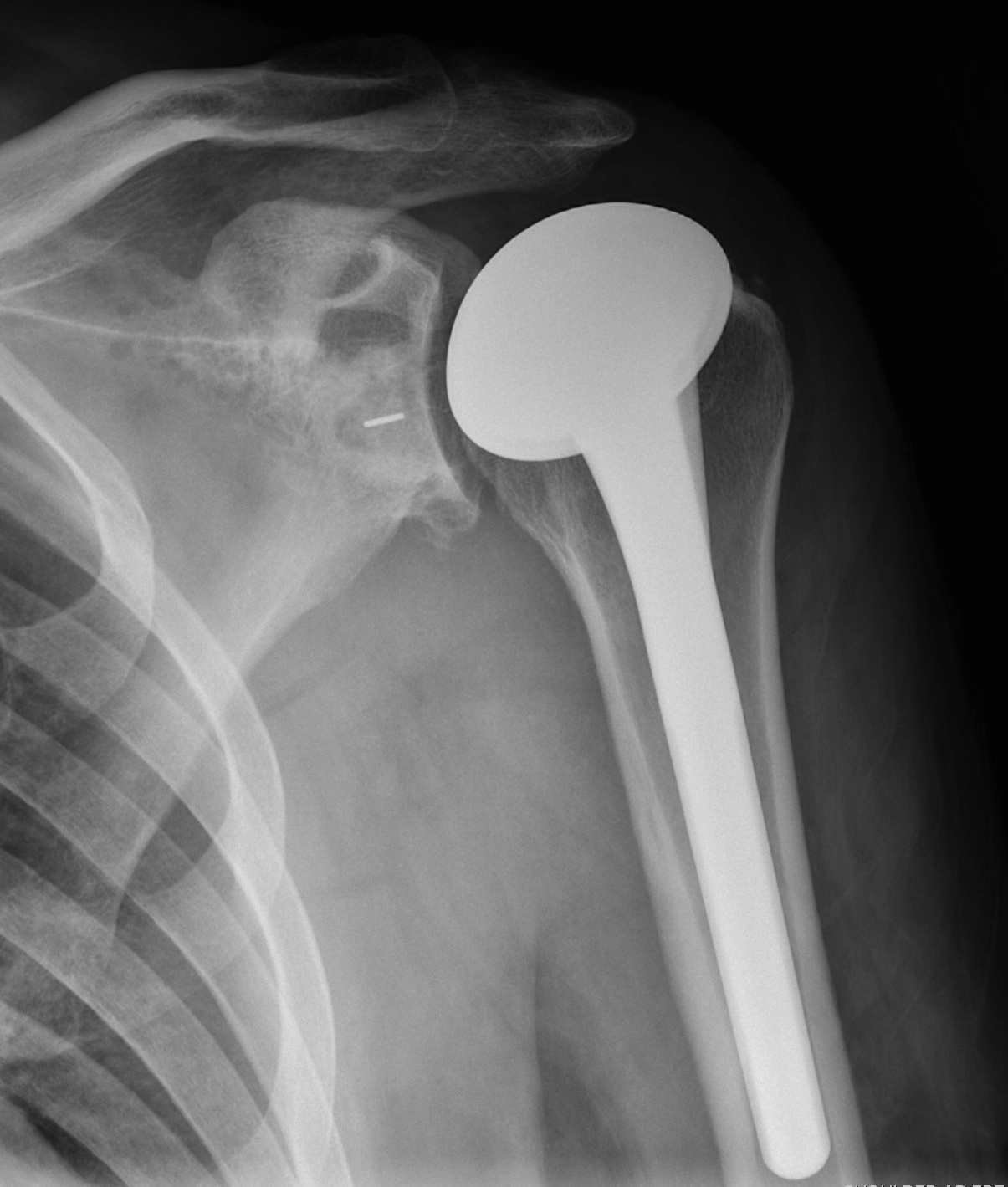
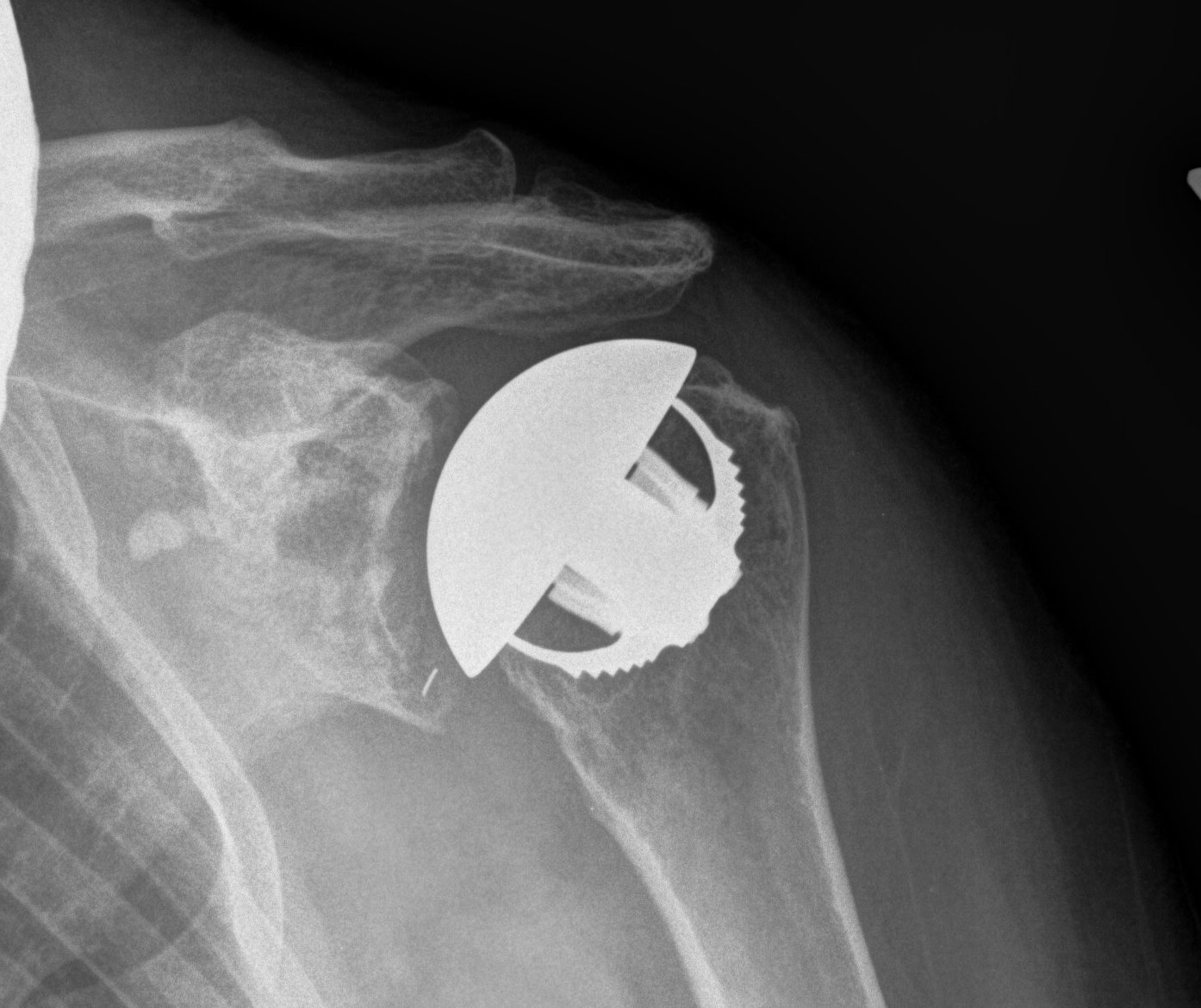
Ankle Arthroplasty
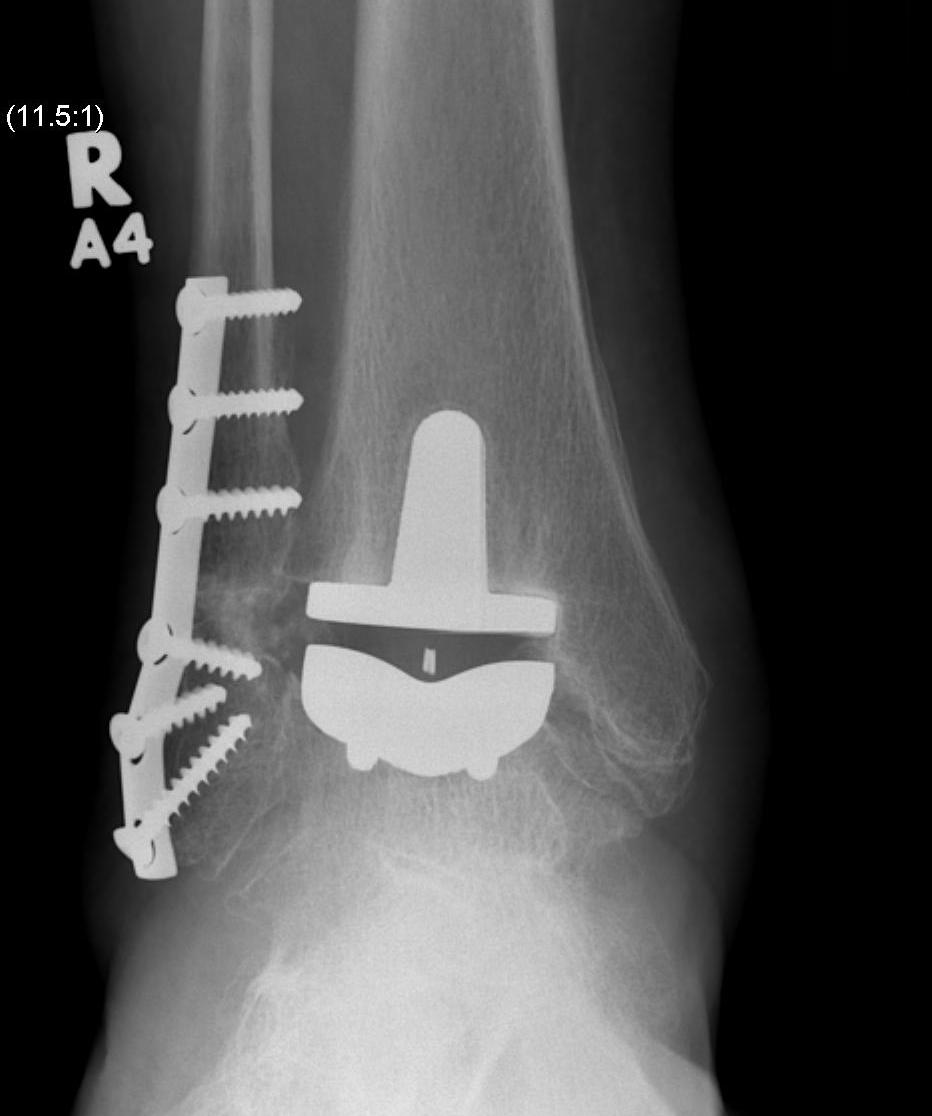
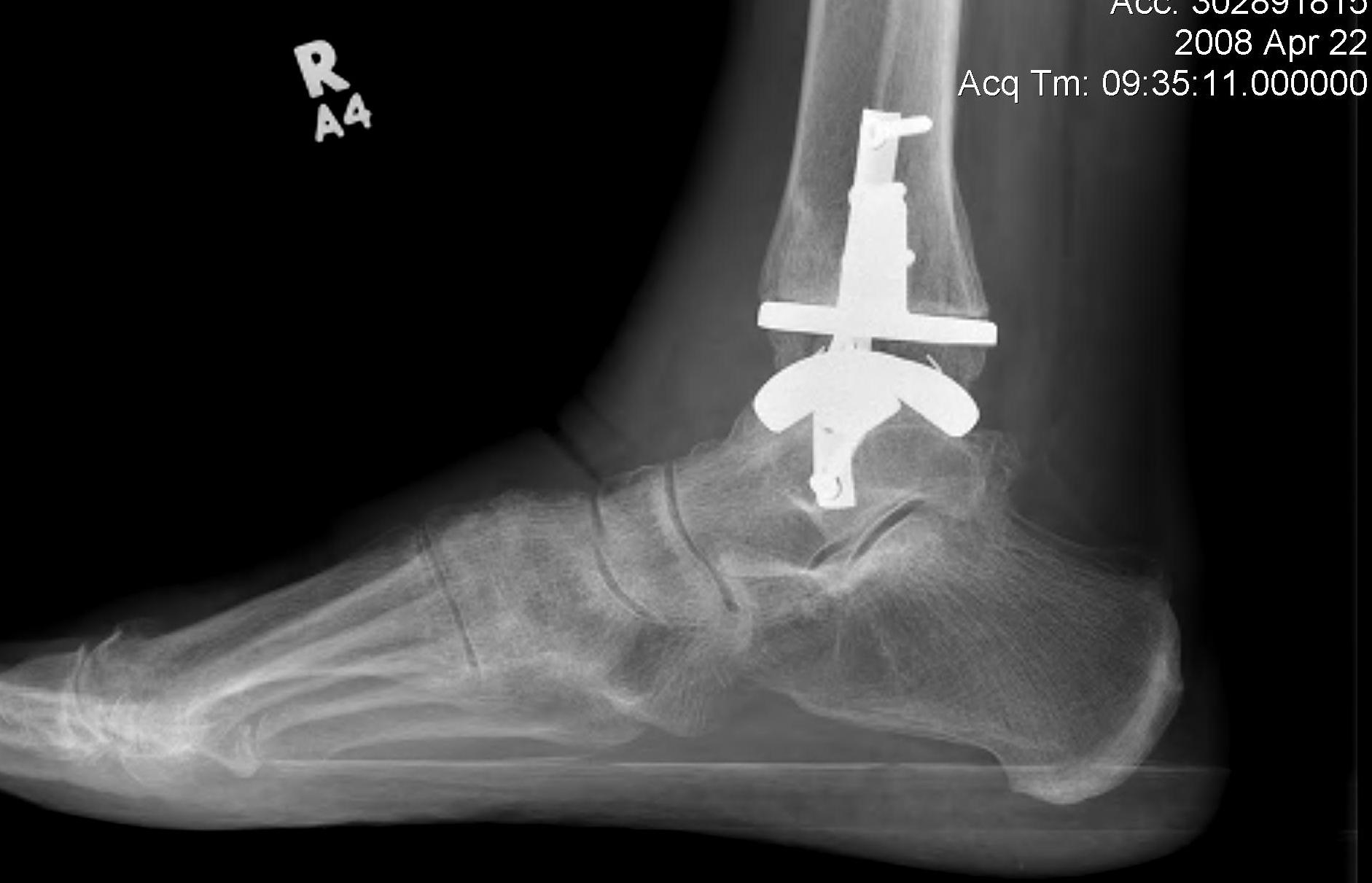
History
First generation (late 70s early 80s)
Results
Stems
Advantage
1. Reduce implant loosening
- offset load sharing to diaphysis
- 30% if > 70 mm
2. Restore optimal alignment
Indications
1. Using augments or bone grafting
2. Increased constraint
- VVS / hinge
Planning
Indications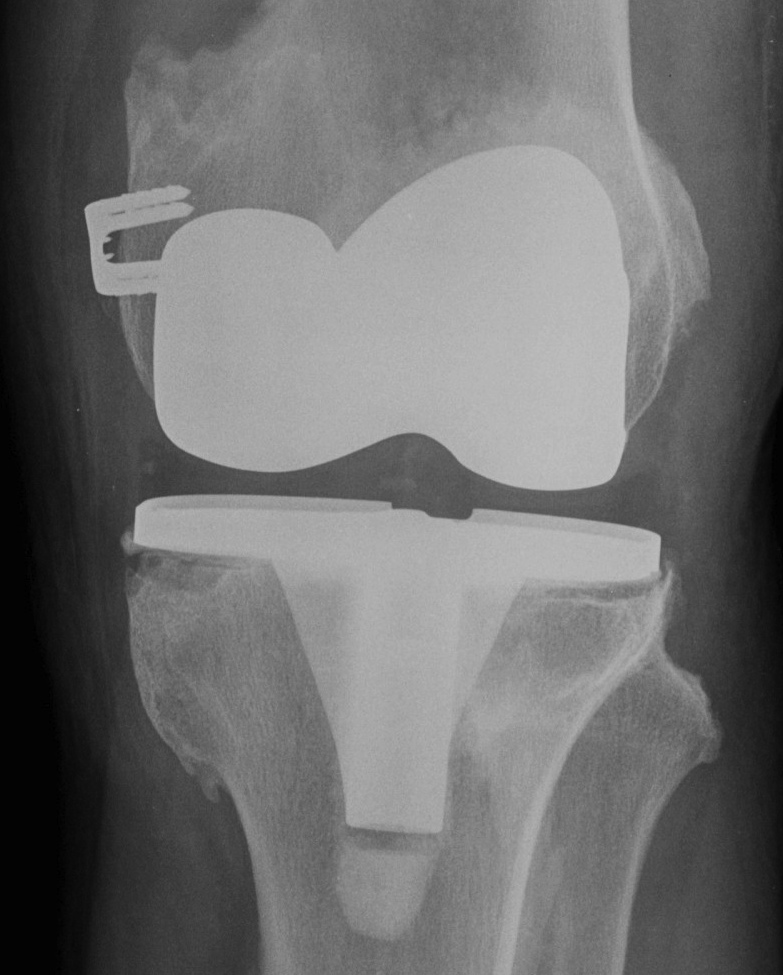
Aseptic loosening
Infection
Instability
Wear & breakage components
Fracture
Stiffness
Pain
Aims
Restoration of anatomical alignment
Restoration of joint line
Restoration of bone stock
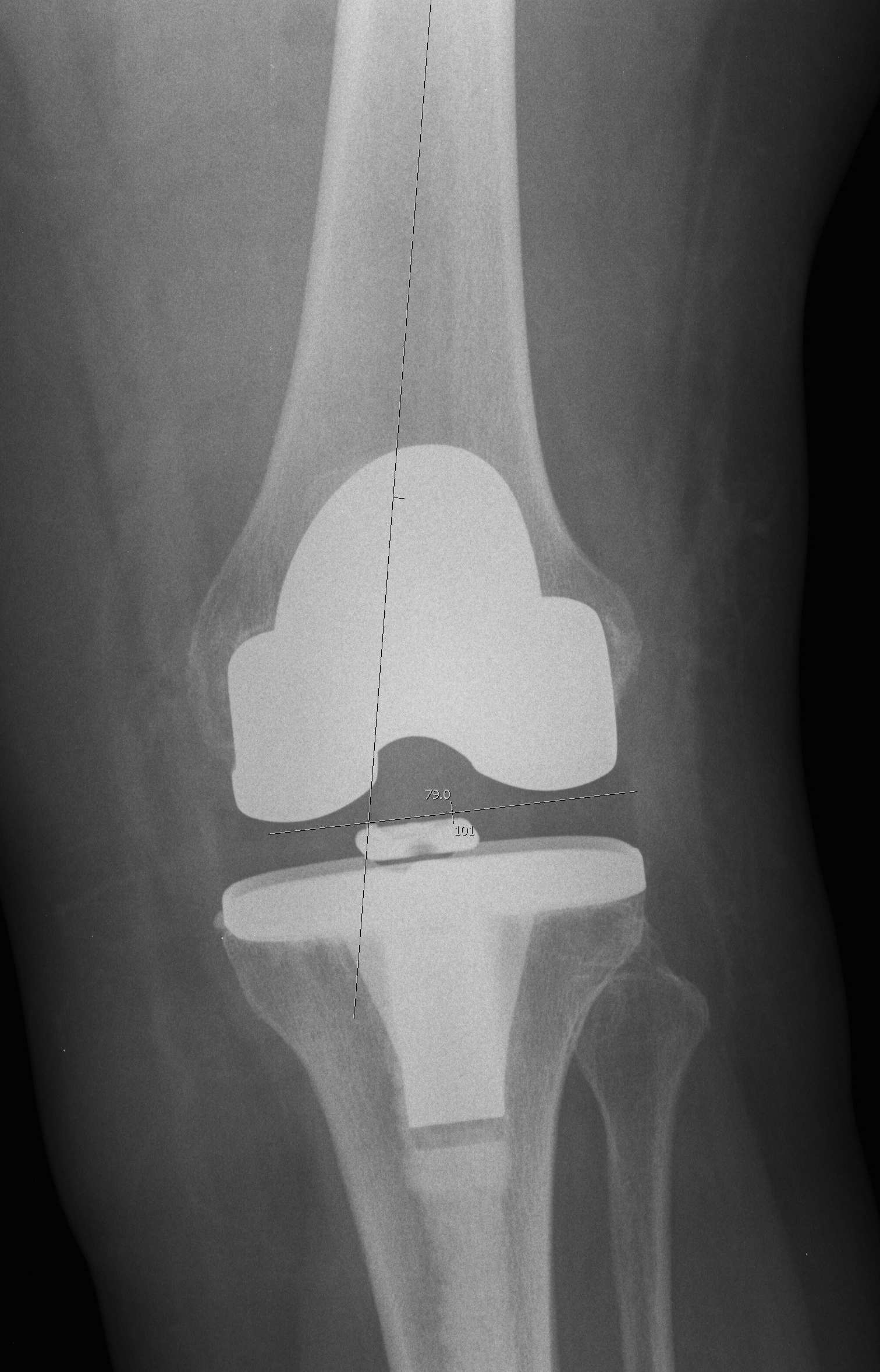
Navigation
Aim
Attempt to reduce outliers in all 3 planes of the knee
- improve alignment
- theoretically improve survival and outcomes
Types
Image based
Pre-op CT
- uncommon
- resource heavy
