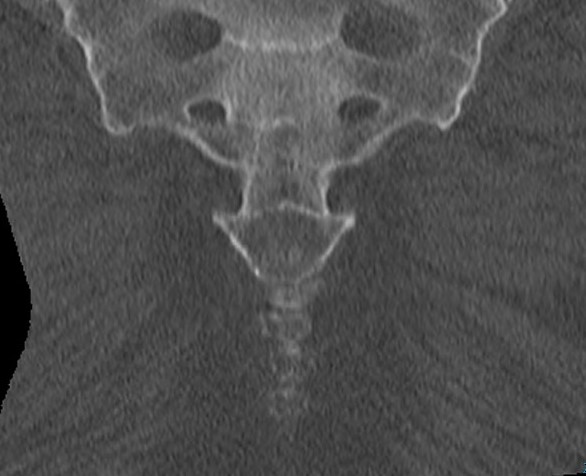
Definition
Pain in region of coccyx
Epidemiology
Women
- often obese
- mean age 40 years
Aetiology
Fracture
Difficult vaginal delivery
Subluxation / hypermobile coccyx
Anatomy
3 or 4 fused coccygeal vertebrae
Triangular structure
Usually a joint with sacrum
- can be fused
Pathology
Symptomatic patients
- no evidence increased number of segments
- often more angular
- increased rate of sacral - coccygeal fusion
Symptoms
Pain in coccyx
Difficulty sitting
Signs
Painful to touch
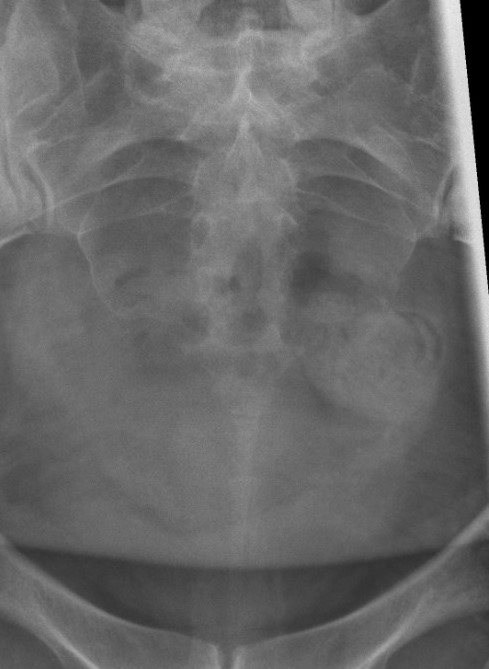
Xray
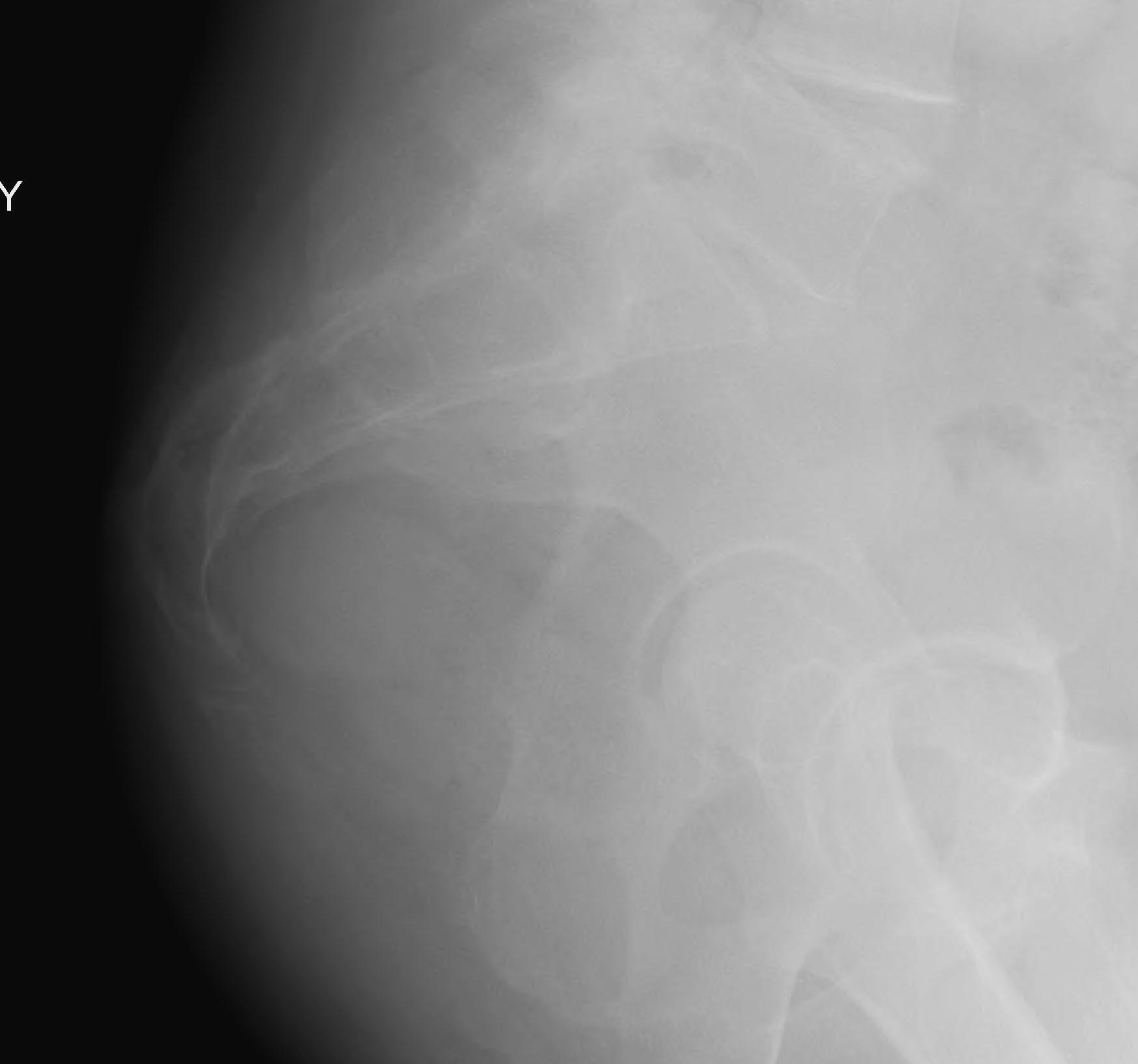
Dynamic radiographs
- standing and sitting radiographs
- looking for hypermobility
- > 25o
Note: Not all coccygodynia is from hypermobile coccyx
Spicule on coccyx
- may be seen in immobile coccygodynia
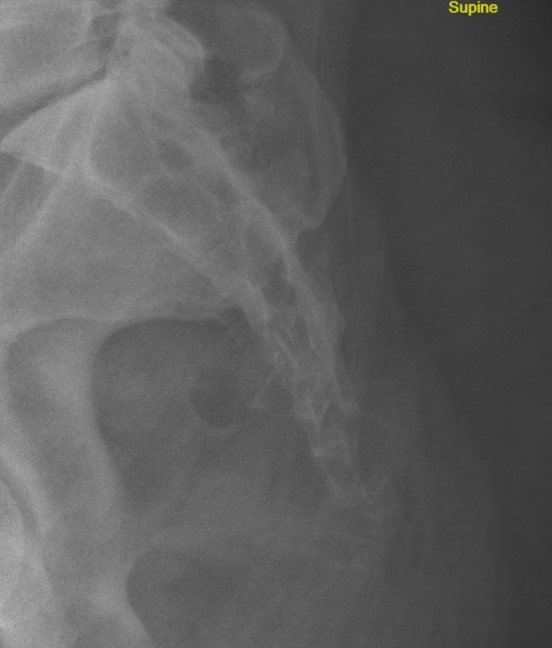
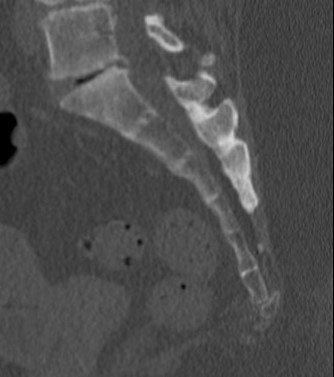
Posterior displaced coccyx fracture
CT
MRI
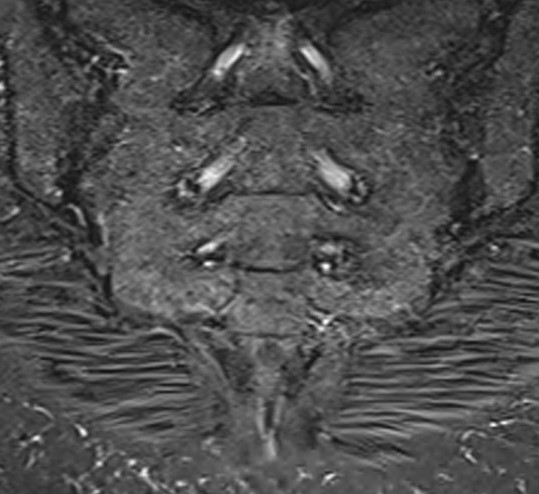
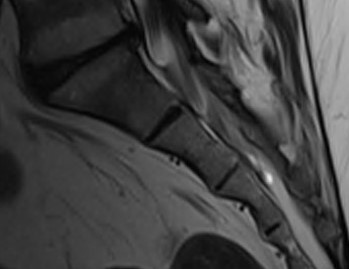
Show inflammation
Management
Non Operative
Options
Analgesia
Cushions
HCLA
HCLA
1. HCLA
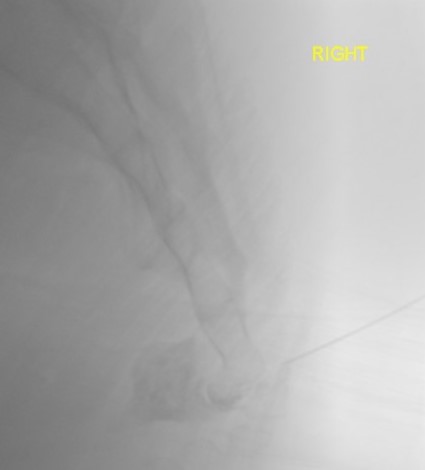
Mitra Pain Physician 2007
- injection HCLA under II in 14 patients
- patients with acute pain / < 6 months fared much better
2. Manipulation
Maigne et al Spine 2006
- randomised trial of intra-rectal manipulation (x3) v physiotherapy
- mild improvements in group with manipulation
- best results in patients with acute, traumatic coccydynia
Operative
Excision of Coccyx
Preparation
Bowel prep
Oral metronidazole
- 24 hour treatment
- day before surgery
Pre-op and post operative antibiotics
- Penicillin / Gentamicin / Metronidazole
Technique
- patient prone on 4 poster
- want to flex hips as much as possible
- vertical incision away from perianal skin
- through fascia
- G max reflected
- subperiosteally dissect coccyx
- ensure don't leave tip
Results
Trollegard et al JBJS Br 2010
- 41 patients with coccygectomy
- post trauma / childbirth / idiopathic onset
- 33/41 good or excellent results
- 5 superfical infections