High risk patients
Total hip and total knee arthroplasty
Hip fractures
Major trauma
Elective spinal patients
Options
Mechanical prophylaxis
Chemoprophylaxis
Mechanical prophylaxis
Graduated Compression Stockings
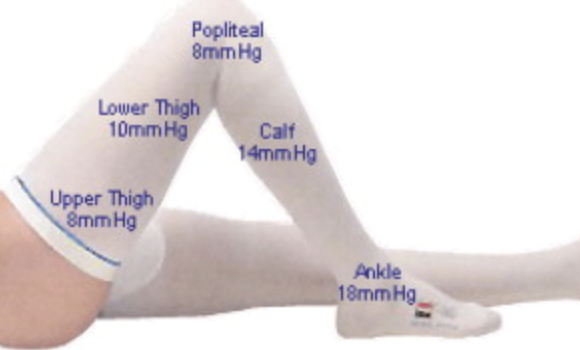
Mechanism - graded compression highest at ankle and lowest above knee
Precautions - peripheral vascular disease / recent skin graft / severe leg edema
Results
Sachdeva et al Cochrane Database Review 2018
- 20 RCTs and 1700 patients
- GCS reduces incidence of DVT and PE compared to control groups
Pneumatic Compression Devices (PCD)
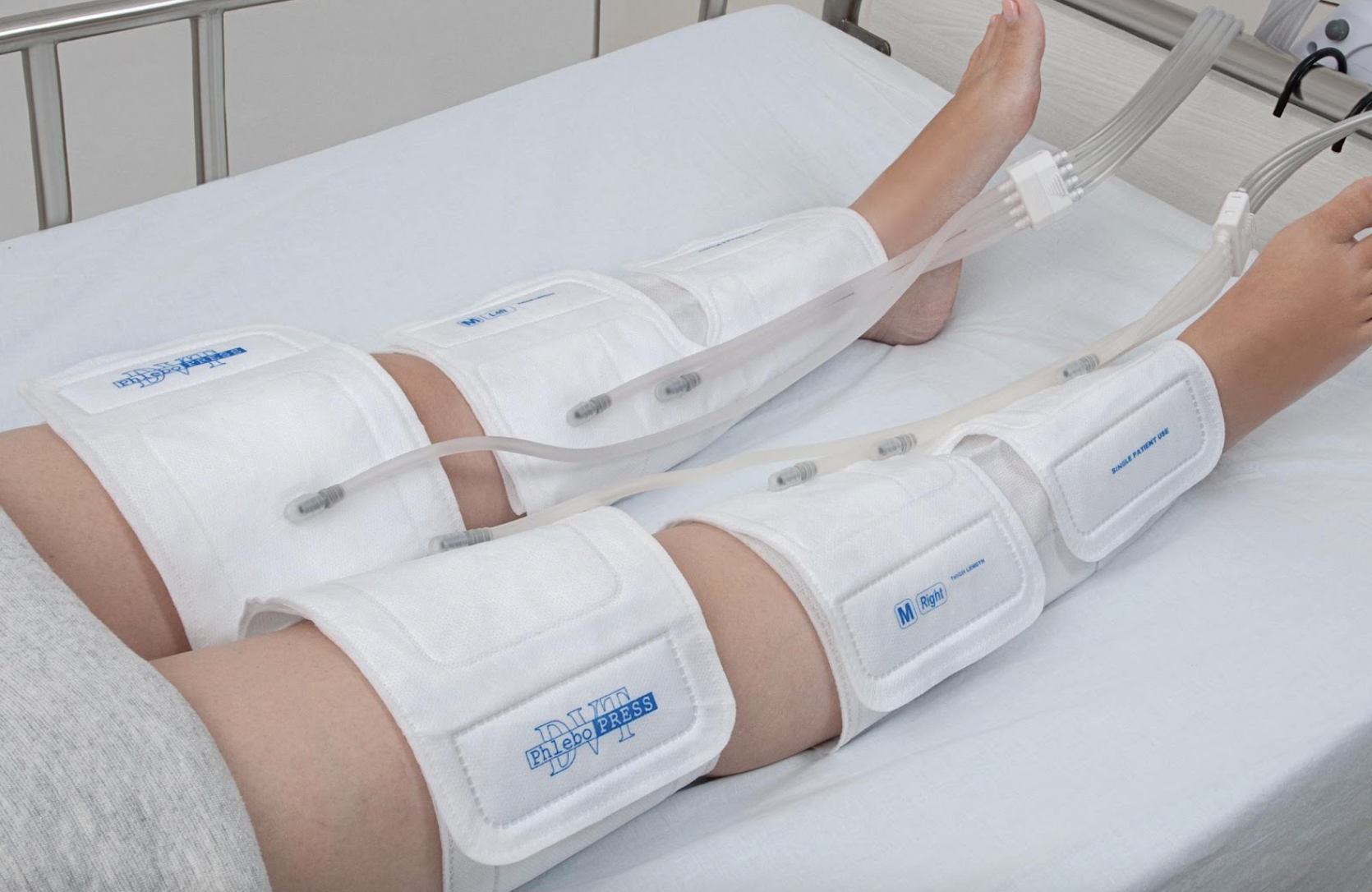
Results
Kakkos et al Cochrane Database Review 2022
- 34 RCTs and 15,000 orthopedic patients
- PCD alone: DVT 4%, symptomatic PE 1%, major bleeding 0.3%
- PCD + pharmocology: DVT 2%, symptomatic PE 0.7%, major bleeding 2%
- 540 THA treated only with graduated stockings and pneumatic compression
- routine ultrasound day 4 and 7
- incidence proximal DVT 1%
Chemoprophylaxis
Contraindications to chemoprophylaxis
Active bleeding
High risk bleeding
- hemophilia
- thrombocytopenia - platelets < 50
- history GI bleeding
Severe hepatic disease (INR < 1.3)
Renal impairment
- must adjust LMWH and oral factor Xa inhibitor doses
History of HITT (heparin induced thrombocytopenia)
Recent neurosurgery or eye surgery
Spinal anesthesia
Queensland Health Guidelines for Prevention of DVT
LMWH
- prophylaxis 12 hours after insertion
- typically withhold for 4 - 6 hours after removal
Oral Factor Xa inhibitors
- 24 hours minimum after insertion
- 6 hours after withdrawal
Timing
Queensland Health Guidelines for Prevention of DVT
Onset
Hemostasis obtained
Heparin / LMWH - 12 hours post op
Oral factor Xa inhibitors
- Rivaroxaban 6 - 10 hours post op
- Dabigatran 4 hours postop
- Apixaban 12 - 24 hours post op
Duration
TKA - 10 - 14 days
THA - 4 - 5 weeks
Options
Aspirin
Heparin
Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH)
Oral factor Xa inhibitors - Rivaroxaban, Apixaban
Warfarin - usually used for treatment
Heparin
| Definition | Dose | Mechanism | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Naturally occurring anticoagulant Mixture of sulphated mucopolysaccharide chains Heterogenous molecular weights ~ 15 000 daltons |
Bolus 5000 units IV Maintenance 1000 u /hr Check APTT 6 hours after change Check APTT daily Maintain APTT 70-120 |
Binds to Anti-thrombin III |
Short half life 2 hours Good for bridging anticoagulation Antidote: protamine |
Infusion Requires monitoring Inhibits platelets Affected by renal function HITT
|
Action
Binds to Anti-Thrombin III
- causes conformational change causing increased affinity for thrombin (x 1000) & Xa
- also inhibits aggregation of platelets
Indication in orthopedics
Patient requires surgery and on maintenance warfarin
Used to bridge anticoagulation
Heparin Induced Thrombocytopenias / HITT
Paradoxical thrombosis
- due to drug-antibody binding to platelets
- causes arterial and venous thrombosis, and skin necrosis
- resolves promptly with ceasing heparin
- 80% cross-reactivity with LMWHs
- patients should have regular platelet checks in first week of heparin / LMWH
Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH)
| Definition | Types | Mechanism | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Fractionated heparin Molecular weight < 5000 |
Enoxeparin / Clexane - 0.5 mg/kg od - 40 mg od
Dalteparin / Fragmin - 5000IU od |
Antifactor Xa |
Longer half life than heparin Decreased bleeding due to reduced platelet effect No monitoring required Antidote: Protamine sulfate |
Given by injection Reduce dose with low GFR Increase dose BMI > 40 Difficult to reverse HITT |
Action
Pure Anti Xa
- to inactivate thrombin the chain has to attach to antithrombin III & heparin simultaneously
- because LMWH are too short to do this
- only inhibit Xa
- less platelet interaction
Decreased bleeding because no anti-thrombin action / platelet interaction
Results
- RCT of 1000 THA of warfarin v dalteparin
- warfarin: DVT 24%, proximal DVT 1%, symptomatic DVT 4.5%
- dalteparin: DVT 13%, proximal DVT 1%, symptomatic DVT 1.5%
Direct oral Factor Xa inhibitors
| Definition | Types | Mechanism | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Act directly on Factor X |
Rivaroxaban 10 mg od Apixaban 2.5 mg bid Dabigatran 220 mg od |
Factor Xa inhibitor |
Oral dosing No monitoring required Antidotes available for each |
Interact with statins |
Mechanism
Act directly on Factor X - do not use ATIII as an intermediate
Aspirin
| Definition | Types | Mechanism | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetylsalicyclic acid |
Aspirin 80 - 300mg |
COX inhibitor | Oral form |
GI bleeding Stomach upset Not indicated in high risk patients |
Mechanism
- irreversibly inhibits cyclo-oxygenase in platelets
- blocks thromboxane A2 formation
Results
- 17,000 hip fracture and arthroplasty patients
- aspirin v placebo
- aspirin: DVT/PE 1.6%
- placebo: DVT/PE 2.5%
Warfarin
| Definition | Types | Mechanism | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin K antagonist |
|
Structural analog of Vitamin K Limit factors II,VII,IX,X |
Oral form Antidote - FFP / Vitamin K |
Delayed effect for first 3 days Requires monitoring Multiple interactions |
Mechanism
Structural analogue of vitamin K
- blocks the activation of vitamin K
- factors II, VII, IX, X & Protein C + S are vitamin K dependent
Disadvantage
1. Paradoxical procoagulant effect in initial period
- needs cover with another anticoagulant
2. Delayed Effect
- half-life of factors ranges between 6 and 60 hours
- there is a window period of 3 days with increased PT but no true anticoagulation exists
3. Teratogenic - contraindicated in pregnancy
4. Requires monitoring - goal is INR 2.0
Metabolism
Oral warfarin is readily absorbed & almost entirely albumin-bound
Metabolised in liver
Potentiators
- Cimetidine
- Phenytoin
- Trimethoprim
- Cephalosporins
- Tramadol
Inhibitors
- Rifampicin
- Phenobarbitone
Reversed with parenteral Vit K or FFP
Dosing
Starts simultaneously
- 5 mg nocte for 2 days
- then daily dose as per INR
- usually 3 - 5 mg
Treatment INR
- 1.5-2.5 DVT
- 2.5-4.0 PE
Prophylaxis INR
- 1.5 - 2
Results
Mismetti et al J Thromb Hemost 2004
- meta-analysis
- vitamin K antagonists less effective than LMWH in preventing total or proximal DVT
- no significant difference in rates of major bleeding or haematoma
Results
Oral Factor Xa inhibitors v LMWH
- RCT of 2500 THA patients
- 30 days of rivaroxaban v 14 days enoxeparin
- rivaroxaban: DVT 2%, PE 0.1%, bleeding 7%
- enoxeparin: DVT 8%, PE 0.5%, bleeding 6%
- RCT of 3100 TKA patients
- rivaroxaban v enoxeparin 10 - 14 days
- enoxeparin: DVT/PE 10%, symptomatic DVT/PE 1.2, PE 0.5%
- rivaroxaban: DVT/PE 7%, symptomatic DVT/PE 0.7%, PE 0.3%
IVC Filter
Indications
- complications of anticoagulation therapy
- recurrence of PE whist fully anticoagulation
- high rate of death if subsequent event / further embolic load on right ventricle
Disadvantage
Surgical procedure
- inserted through groin
- need to be removed
Results
Bicalo et al J Arthroplasty
- filter vs IV heparin
- 3 of 28 complications for heparin
- 1 of 26 for filter
