Definition
Dysproportionate dwarfism
- short limbs and normal trunk
- rhizomelic
DDx
- physeal dysplasia (SED, MED)
Aetiology
FGF Receptor 3
- point mutation
- decreases endochondral ossification
- normal intramembraneous ossification
- FGFR3 is found in all pre-bone cartilage & in CNS
- FGFR3 inhibits chondrocyte proliferation in the proliferative zone
- appears that in achondroplasia the receptor is overactive & inhibits the proliferative zone
Inheritance
AD
- 85% from spontaneous mutation
Pathology
Defect in enchondral bone formation / Proliferative zone
- dalteration in normal chondrocyte maturation, hypertrophy & degeneration
- abnormal clustering of chondrocytes
Hypertrophic Zone
- narrow & irregular cells of differing sizes
Clinical Presentation
At birth
- short limbs & normal trunk
Lower Limbs
Tibia
- bowing
Knees
Genu varum
- long fibula
- may need fibula epiphysiodesis
Inverted V shaped distal femoral epiphysis
- flared metaphysis with ball in socket epiphyseal/metaphyseal junction
Hips
FFD hips + increased lumbar lordosis
Coxa vara
- short femoral necks
- horizontal acetabular roof
Pelvis
Square iliac bones
- " elephant ears"
- narrow siatic notch
Champagne-glass pelvic cavity
- the pelvis is wider than it is deep
Spine
Thoraco-lumbar
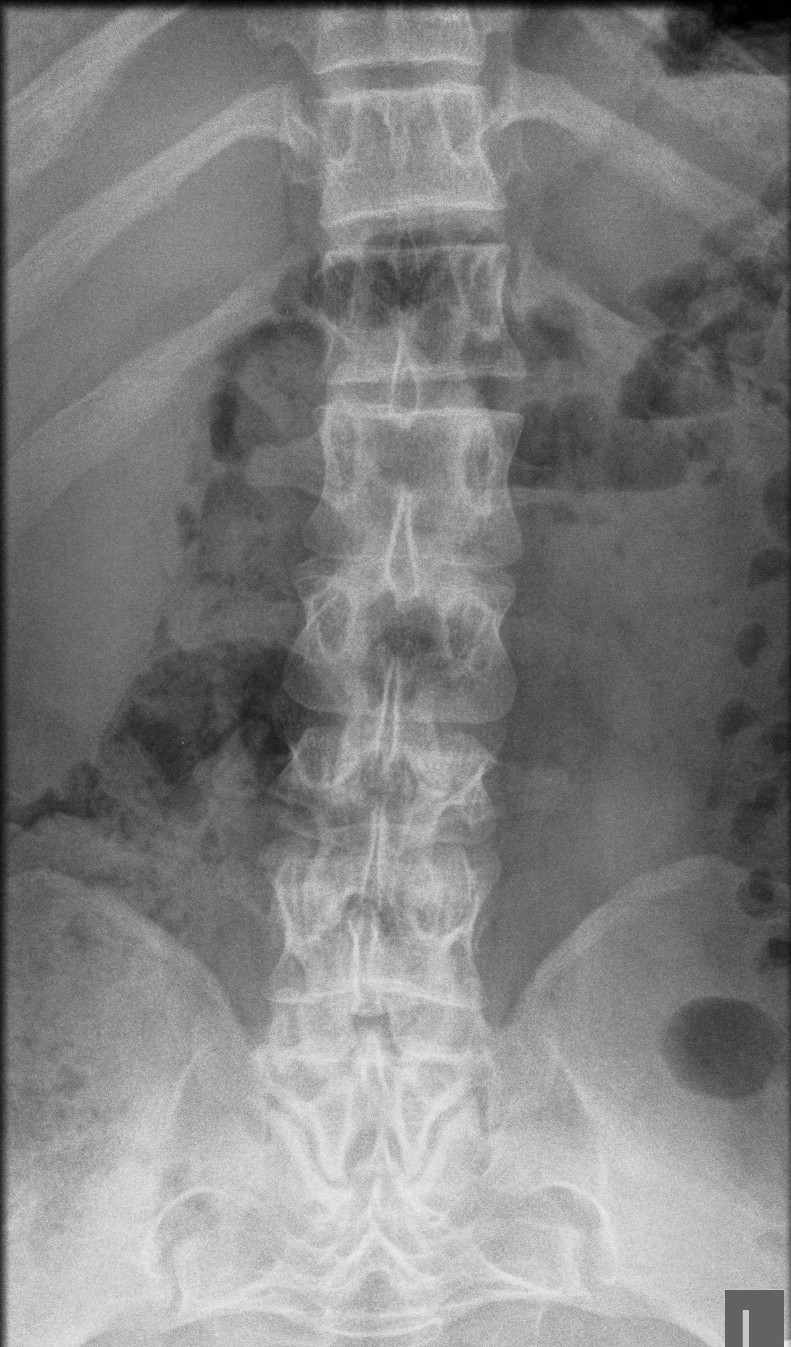
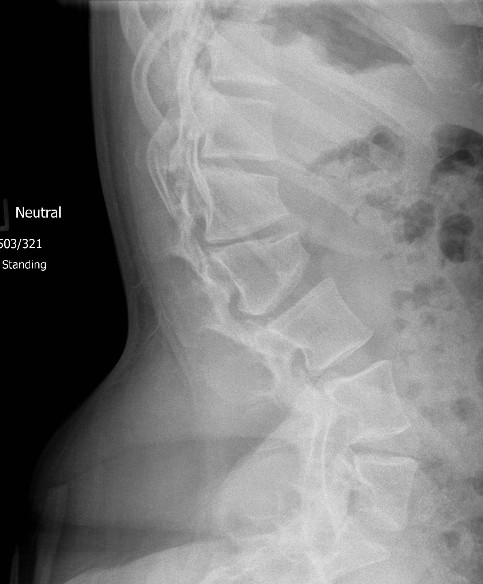
Increased lumbar lordosis
Non-rigid TL kyphosis
- usually resolves with ambulation
- due to hypotonia
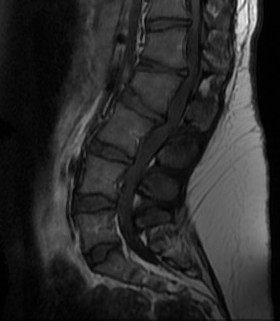
Spinal canal stenosis
- decreased inter-pedicular distance
- narrows from L1 down (normally increases)
- short pedicles
Platyspondyly
- bullet shape vertebrae
- anterior inferior body beak T12- L2
- posterior scalloping of vertebral bodies
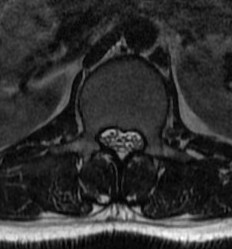
Cervical
Foramen magnum stenosis
- responsible for higher mortality in infants
- may have symptoms myelopathy
- often presents with apnea / snoring
- can cause sudden death
- MRI / sleep studies
Upper Limbs
Hand
Trident hand in 50%
- persistant space between middle & ring in extension
Stubby tubular bones
- normal bone girth
Fingertips only reach to hips
- difficulty with hygiene
Humerus
- posterior bowing / limitation of extension
Elbow
- cubitus varus
Forearm
- bowed ulna
- radial head dislocation
Head
Large skull with frontal bossing
Operative Management
Spinal Stenosis
Present later in life
- 50% or more of patients
- require multilevel laminectomy +/- fusion
