Definition
Cartilage capped bony projection on the external surface of bone
Epidemiology
Most common benign bone tumour / 9% of all bone tumours
85% solitary
15% multiple / multiple hereditary exostosis
Etiology
? secondary to injury of growth plate
- defect in Perichondral Ring of La Croix
- results from herniation & separation of fragments of physis through the periosteal bone cuff
More recent research suggests genetic mutation
Location
Any bone formed by endochondral ossification
Arises from cortex of long bone adjacent to physis
Most common location
- around knee (distal femur / proximal tibia / proximal fibula)
- proximal humerus
- hands and feet
More rarely scapula and spine
Natural History
Grows by endochondral ossification of enlarging cartilage cap
- no growth after skeletal maturity
Malignant Transformation
Low-grade chondrosarcoma
- isolated lesion < 1%
- more common with central lesions
Suspicious features
- growth after maturity
- increased thickness of cartilage cap on CT / MRI - > 2 cm
- increasing pain
- increased calcification / bony erosion / lytic areas on xray
- septal enhancement after MRI with gadolinium
- MRI / CT of 64 benign osteochondromas and 34 secondary chondrosarcomas
- cartilage cap 2 cm or more 100% sensitive and 98% specific for secondary chondrosarcoma
Malignant transformation of osteochondroma
Clinical
Often incidental finding
Bony lump - commonly noticed during adolescent growth spurt
Symptoms
- pain & tenderness - bursitis / tendon / neurovasular impingement
- decreased ROM
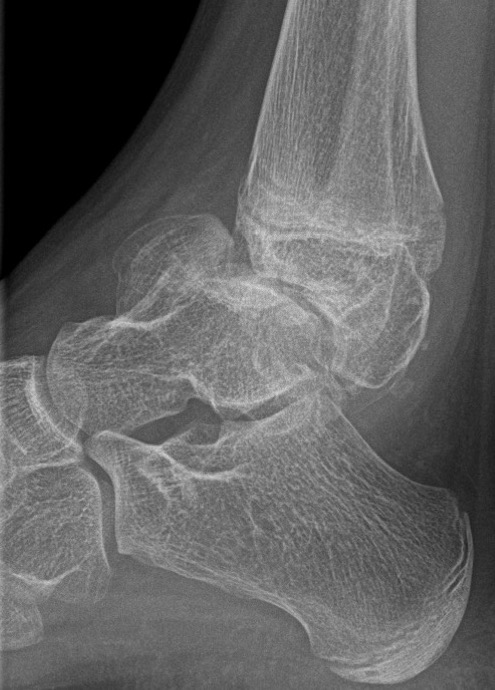
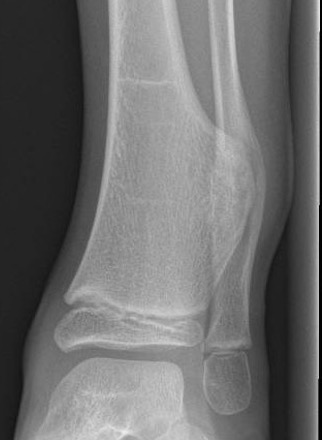
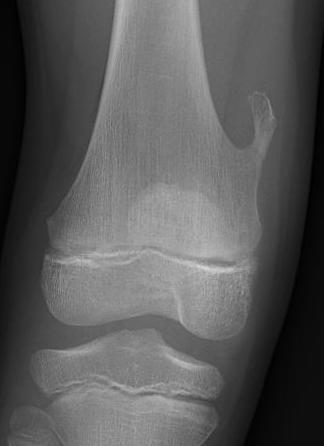
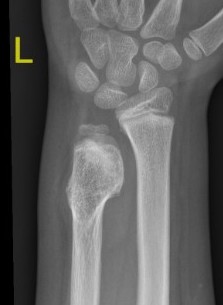
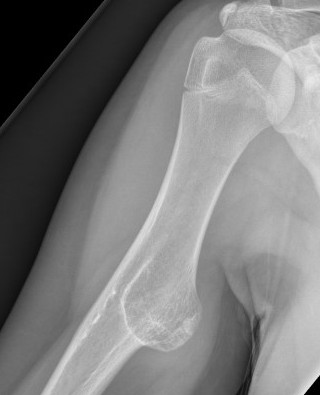
X-ray
Cortical and marrow continuity
Types
1. Pedunculated - has a stalk, points away from joint
2. Sessile - attaches to bone with a broad base
Pedunculated
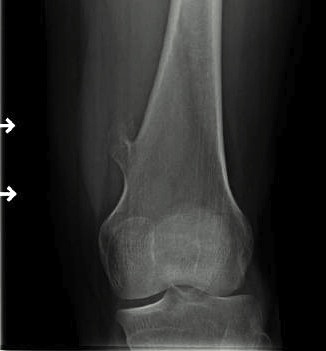
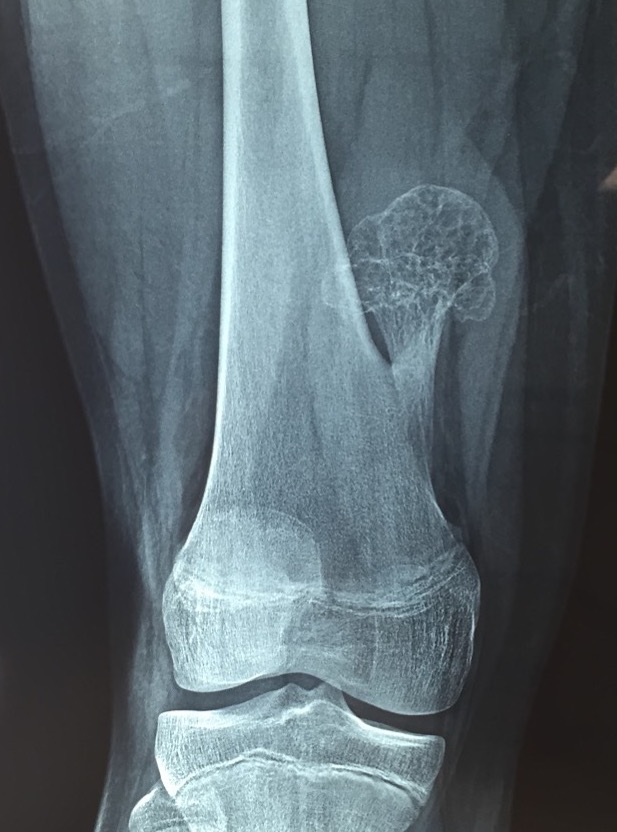
Protuberant bony lesion arising adjacent to physis
- directed away from joint
- cortical bone and marrow space continuous
Sessile
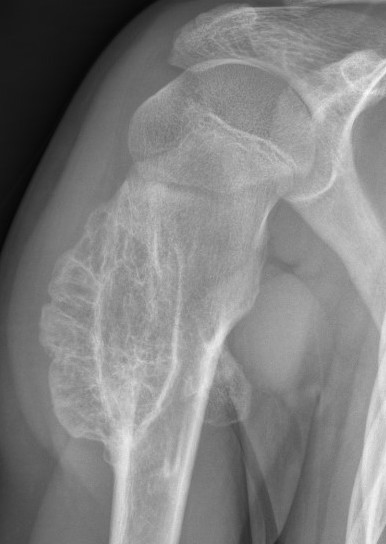
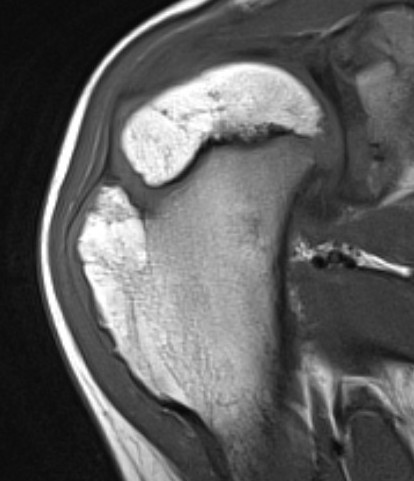
CT
Cortex and medullary cavity of normal bone contiguous with osteochondroma
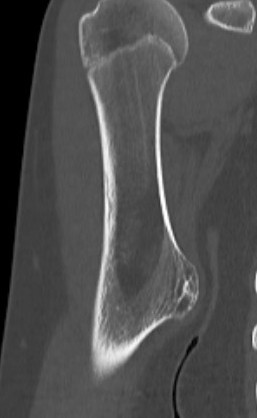
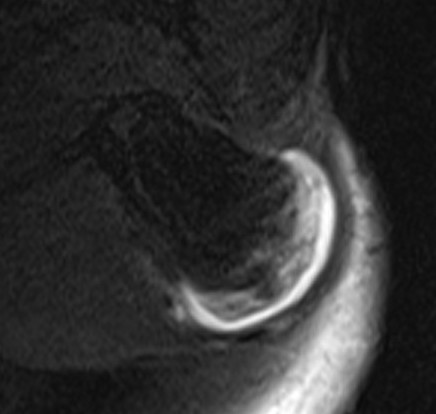
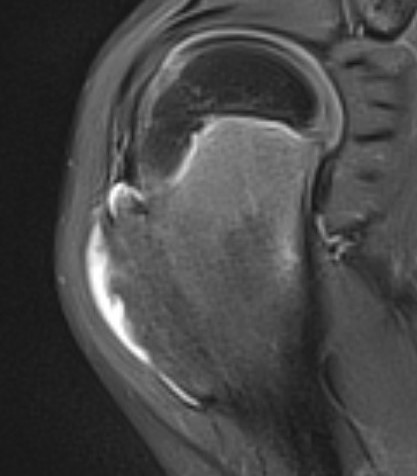
MRI
Cartilage cap iso-intense with hyaline cartilage

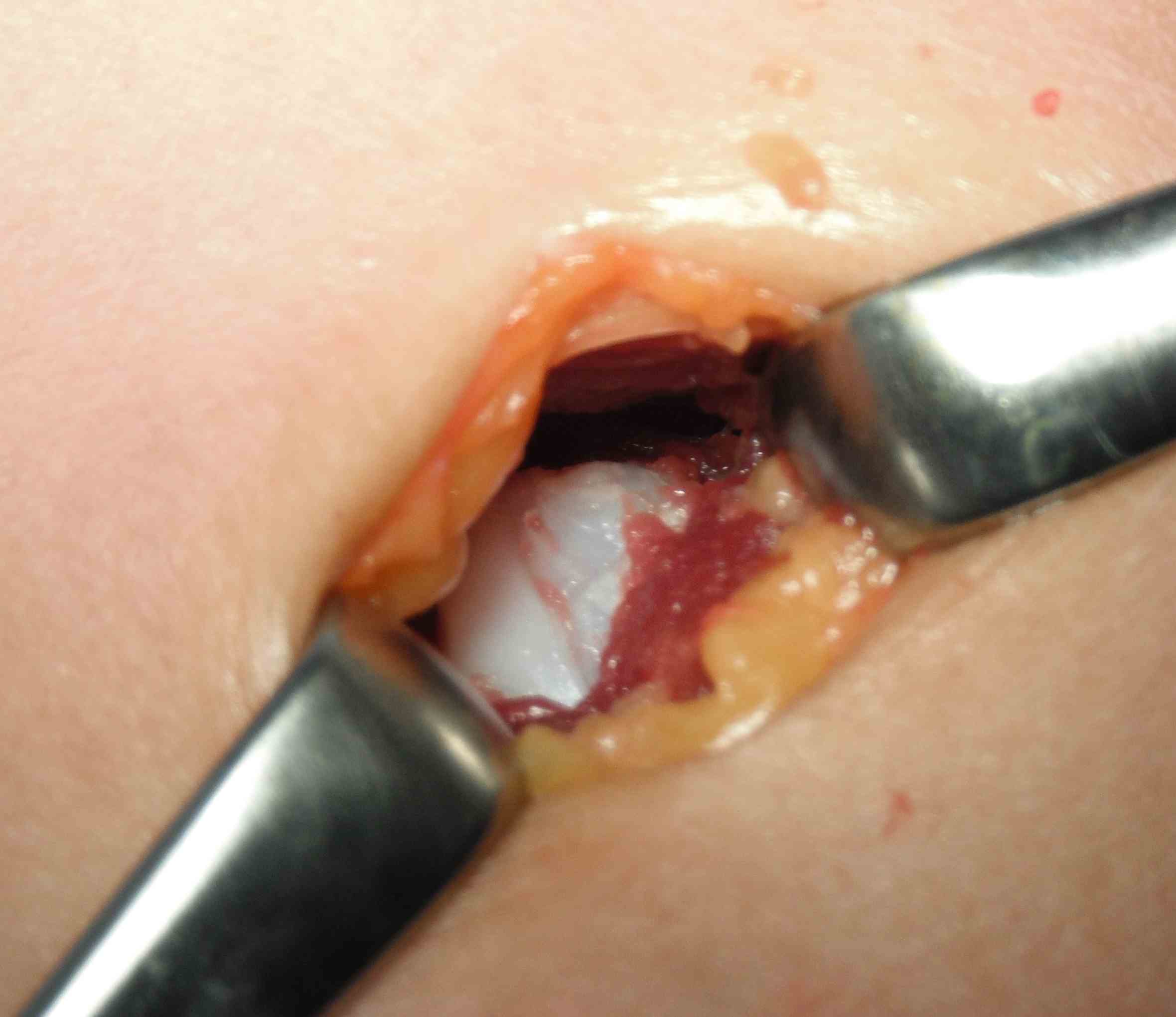
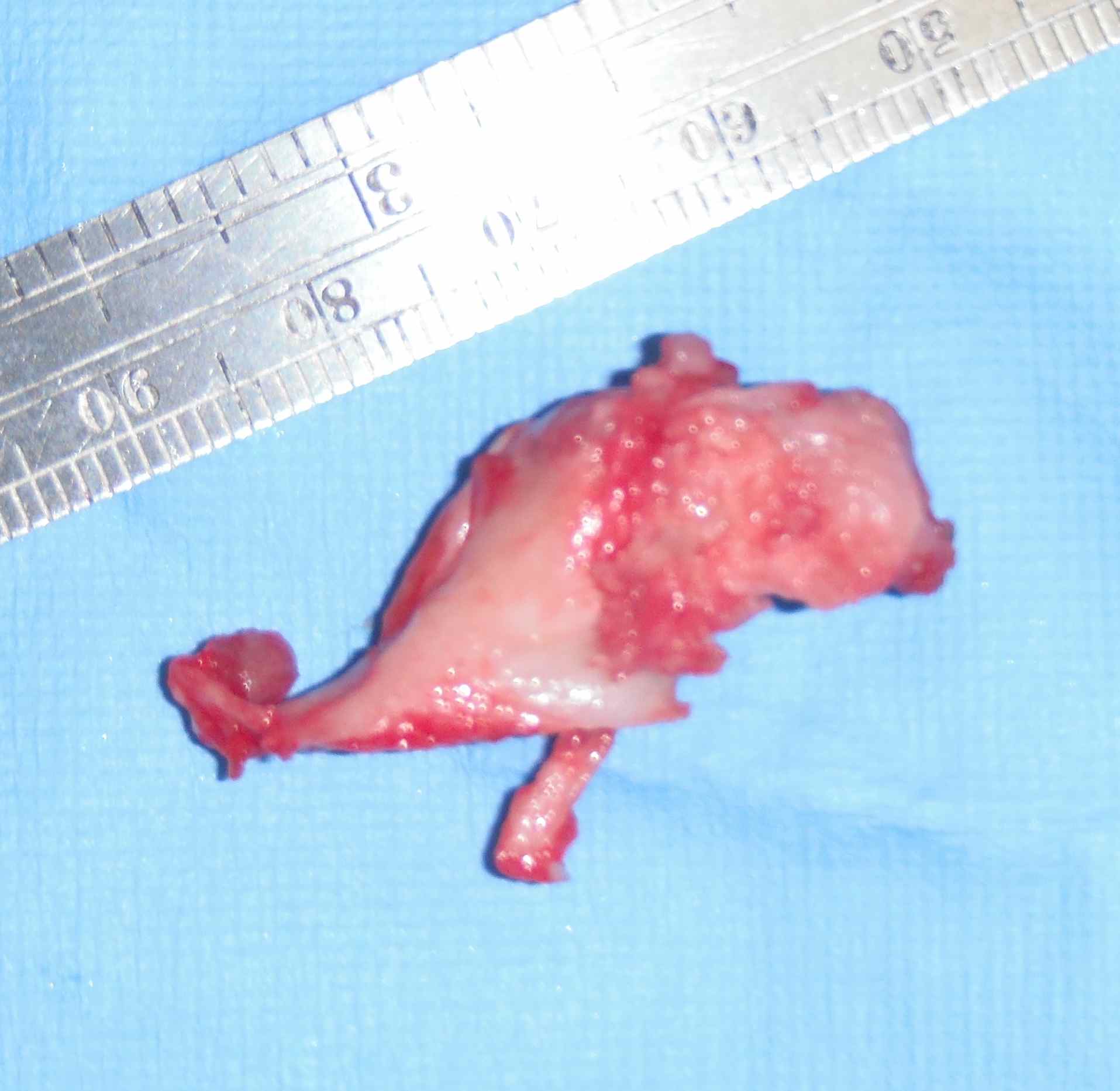
Pathology
Gross
- surface covered with irregular cartilage
- osteochondroma has cortical and medullary bone
Histology
- cap resembles disorganised physis
- irregular shaped underlying trabecular bone
- may contain calcified cartilage matrix
Management
Surgical Indications
1. Painful / symptomatic - bursitis / tendon impingement / neurovascular impingement
3. Restore joint motion
4. Correct deformity
5. Biopsy suspicious lesions
6. Central / pelvis / scapula - higher malignant transformation rate
Technique
Remove osteochondroma at the bony base
Results
About the knee
Typically causes bony mass or tendon impingement
- i.e. hamstring impingement at proximal medial tibia
- excision of solitary osteochondroma around knee in 264 patients < 20 years of age
- 65% pedunculated / 35% sessile
- distal femur > proximal tibia > proximal fibula
- recurrence in 3/264 (1%)
Proximal humerus

Bae et al J Pediatr Orthop 2014
- 31 patients with proximal humerus osteochondromas
- anterior / lateral / posterolateral debulked 92%
- posteromedial debulked 68%
- recurrence 2/31 (6.5%)
Ankle

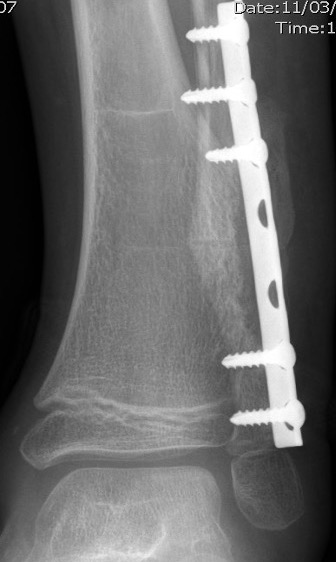
Causes valgus deformity
- 19 patients with solitary osteochondroma of distal tibia or fibula
- cause plastic deformity and pronation deformity
- distal tibia more symptomatic than distal fibula
- 4/19 recurred
Appy-Fedida et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2017
- trans-fibular approach for worsening valgus deformity in 10 cases
- good functional outcomes
- recurrence in 1 case
- 7/10 developed tibiofibular synostosis
Scapula
Typically on ventral surface
Causes winging / snapping with abduction
Prakash et al J Orthop Surg 2020
- medial parascapular approach to ventral osteochondroma
Talus