Anatomy
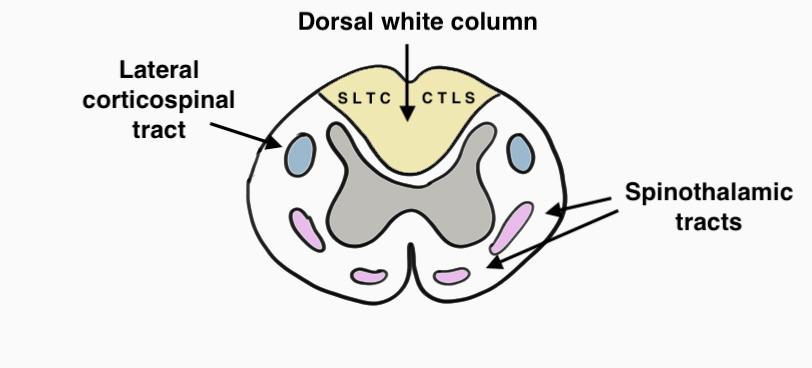
Dorsal Columns
- light touch, vibration & proprioception
- CTLS (cervical fibres central, sacral fibres lateral)
Lateral Corticospinal Tract
- motor tract
- CTLS (cervical central, sacral fibres peripheral)
Anterolateral Spinothalamic Tract
- pain & temperature
Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury Patterns
1. Central Cord Syndrome
- most common
- poor prognosis
- hyperextension injury
- Upper limb > Lower limb (as above, cervical fibres are central)
- distal > proximal
- sacral sparing (typically)
- due to the arrangement of fibres in dorsal column and anterior corticospinal
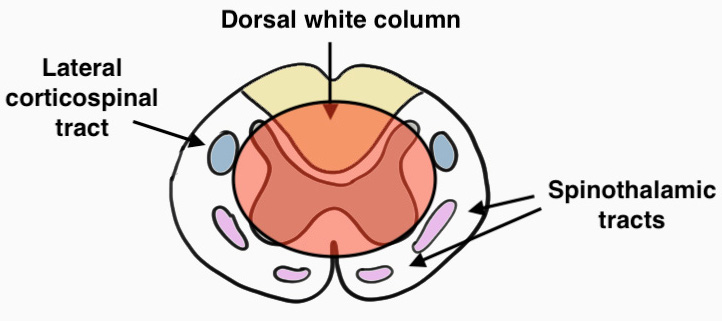
2. Anterior Cord Syndrome
- complete paralysis with dorsal column sparing
- anterior spinothalamic & lateral corticospinal tracts lost
- secondary to ischaemic event secondary to the anterior spinal artery
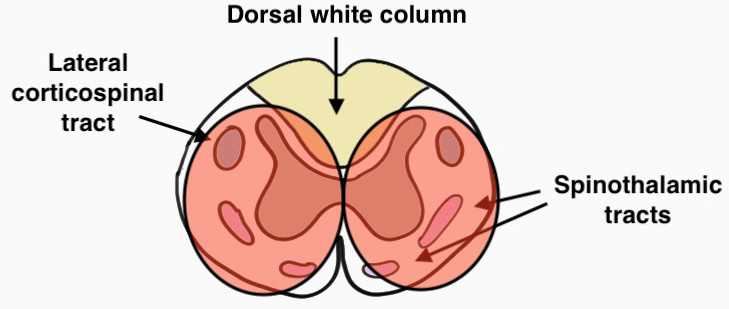
3. Brown-Sequard syndrome
- cord hemisection
- usually secondary to laceration
- ipsilateral dorsal columns & motor
- contralateral loss pain & temperature
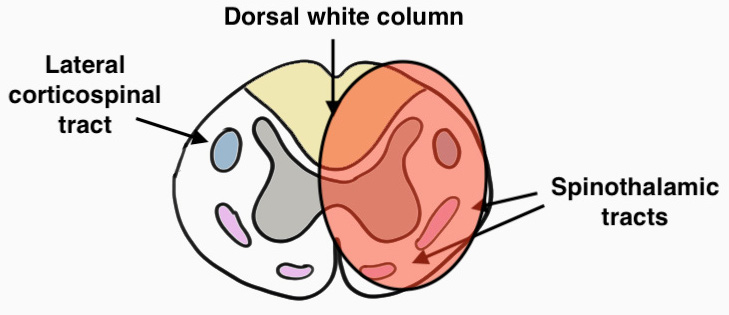
4. Posterior Cord Syndrome
- rare
- dorsal column loss only
- due to tumour / iatrogenic injury
5. Cauda equina syndrome
- injury below L1
- only nerve roots at this level
- lower motor nerve injury to lumbar and sacral nerve roots
- fecal incontinence + urinary incontinence
- nil anal tone or sensation
6. Conus medullaris injury
- cord ends at L1
- injury at this level
- T12 / L1 burst fracture most common cause
- lower motor neuron lower limb weakness
- upper motor neuron sacral lesions
- may have a spastic bladder which enables urination without catheterisation
Sacral Sparing
Triad of
- anal voluntary contraction
- perianal sensation
- FHL function
Indicates
- incomplete injury
- potential for recovery
- due to pial arteries on cord surface supplying small amount of tissue
Blood Supply
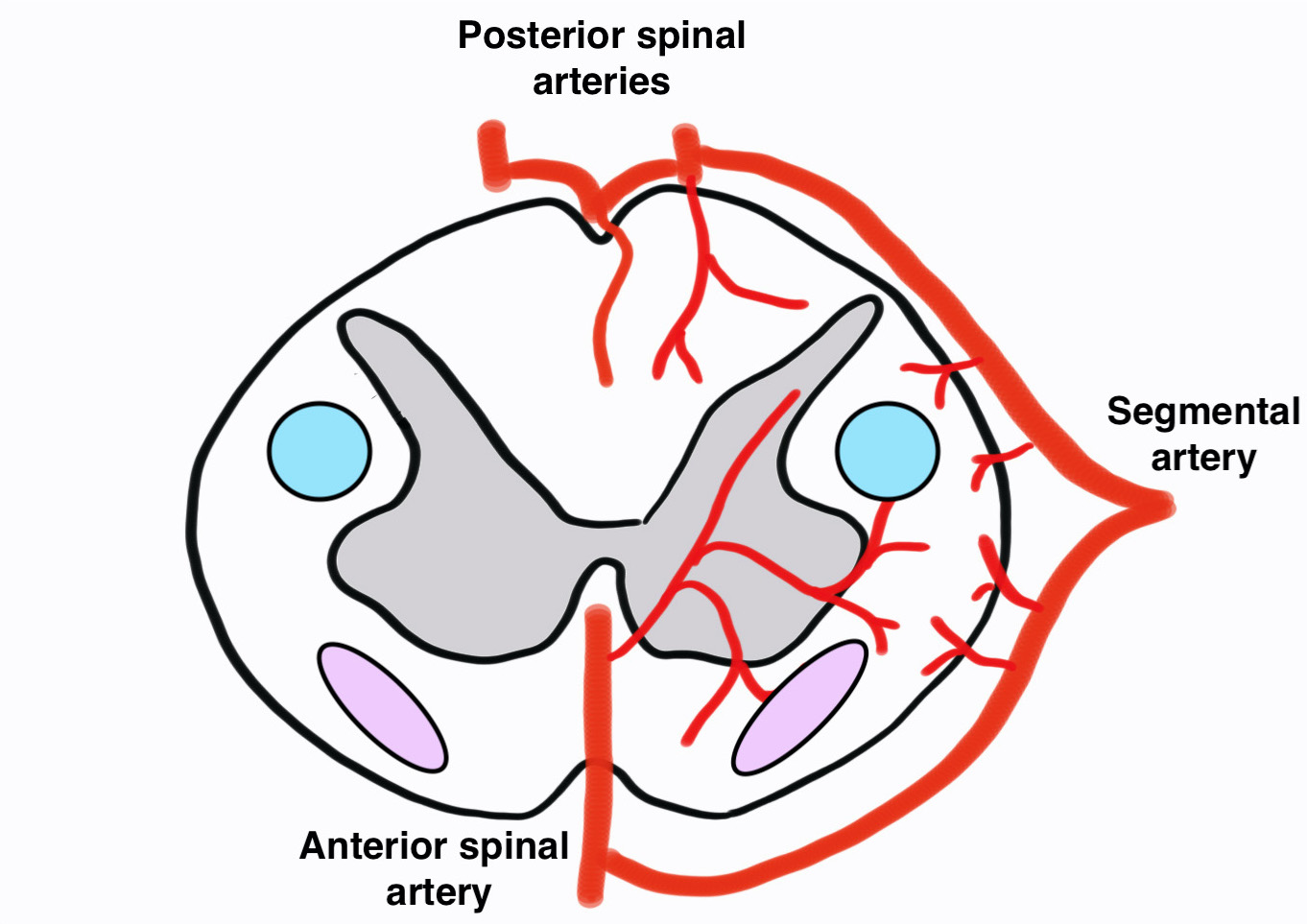
Anterior Spinal Artery
- arises from vertebral arteries at foramen magnum
- supplies the entire cord except for dorsal columns
- narrows and may become absent in thoracic region
Posterior Spinal Arteries
- paired
- originate from vertebral arteries
- smaller
Segmental Arteries
- average of 8 paired arteries
- may be single segmental supply between T4 and T8
- Artery of Adamkiewicz from left between T9-11 in 80% cases
