Cord injury patterns
Anatomy
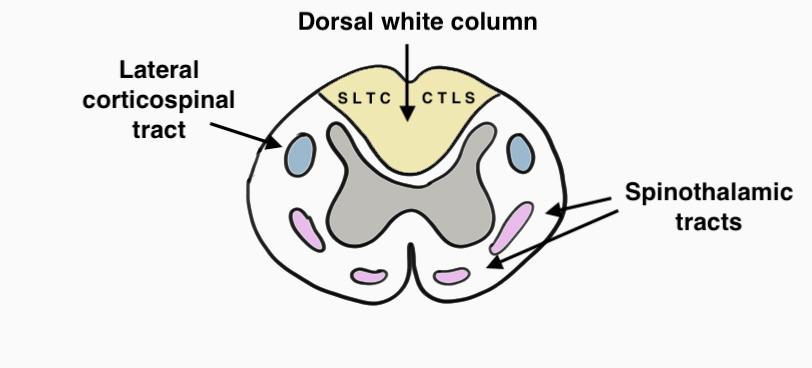
Dorsal Columns
- light touch, vibration & proprioception
- CTLS (cervical fibres central, sacral fibres lateral)
Lateral Corticospinal Tract
- motor tract

Dorsal Columns
- light touch, vibration & proprioception
- CTLS (cervical fibres central, sacral fibres lateral)
Lateral Corticospinal Tract
- motor tract
Fascicles of long, spiraling bundles
- tenocytes & Type I collagen
- synovial cells & fibroblasts present
Endotenon
- surrounds the individual collagen bundles
Epitenon
- fine fibrous outer layer, highly cellular, continuous with endotenon
- contains most of the blood vessels & capillaries
Second most common hindfoot after calcaneal fractures
Aviators Astragalus
Fall from height
- hyper-dorsiflexion injury
- neck of talus strikes the anterior tibia
More than half surface covered by articular cartilage
- medial articular wall straight
- lateral articular wall curves posteriorly
Rotational force incurred while joint partially flexed & extending
- caught between femoral & tibial condyles
- usually valgus & ER / varus & IR
3 Sesamoids may be present in great toe
- 2 almost always present on plantar aspect of MTPJ
- 1 may be present on plantar aspect of IPJ
MTPJ sesamoids most important
- embedded in FHB tendons
- held together by intersesamoid ligament & plantar plate
- each side of crista / inter-sesamoid ridge
- articulate with plantar facets of 1st MT
Tibial usually larger than fibula
Complete Lesion
- bulbocavernosus reflex present
- no cord function below lesion
- very poor prognosis for recovery
Incomplete Lesion
- bulbocavernosus reflex present
- some cord function below lesion
- good prognosis for recovery
Vertebral Canal narrowest at T8/9
- Also area of vascular watershed