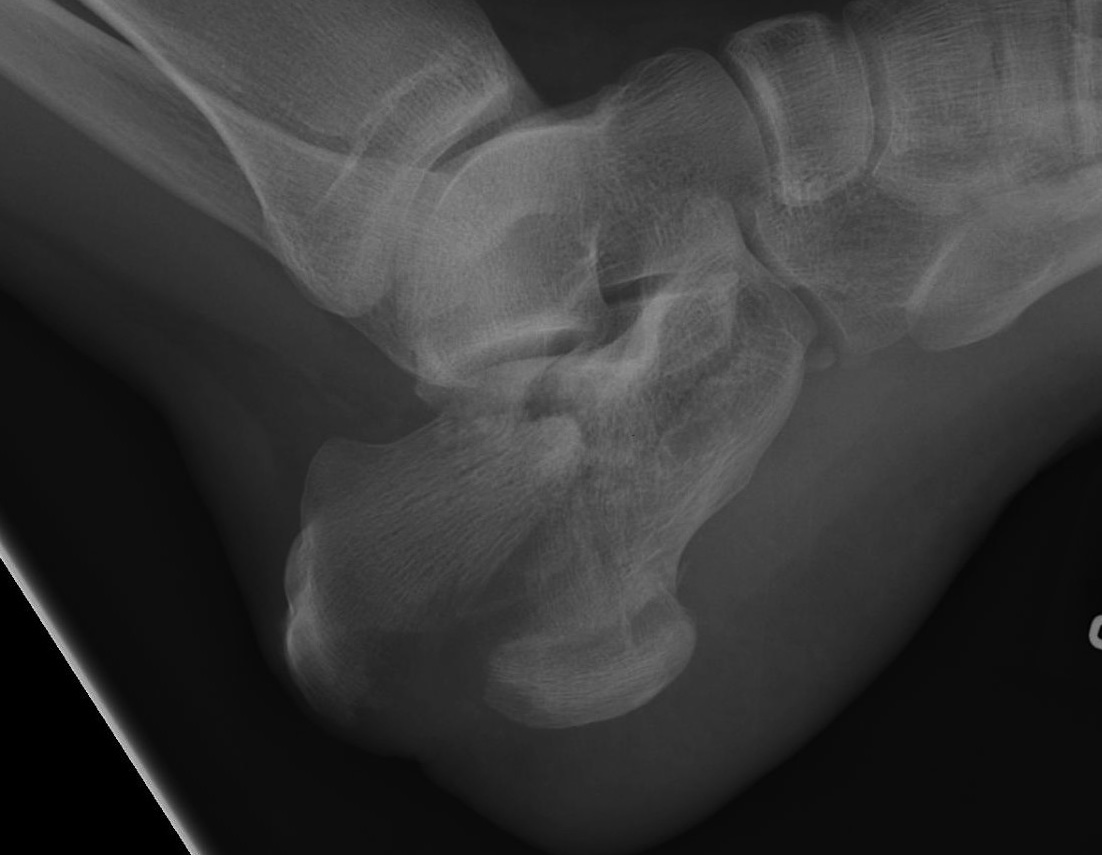
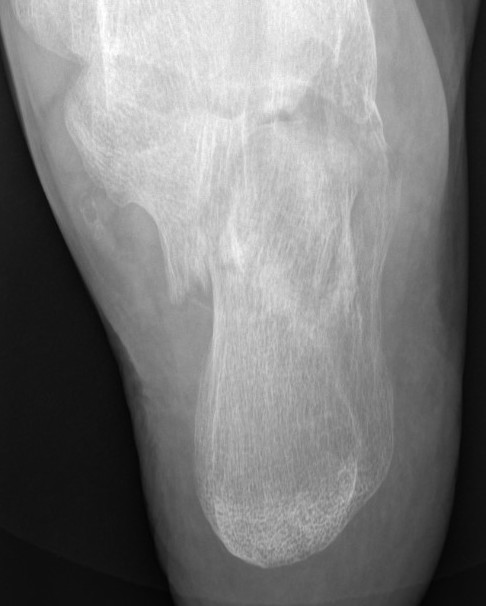
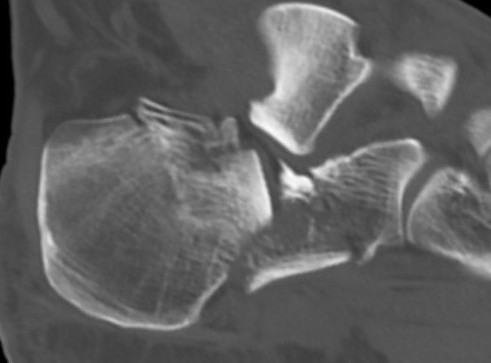
Anatomy
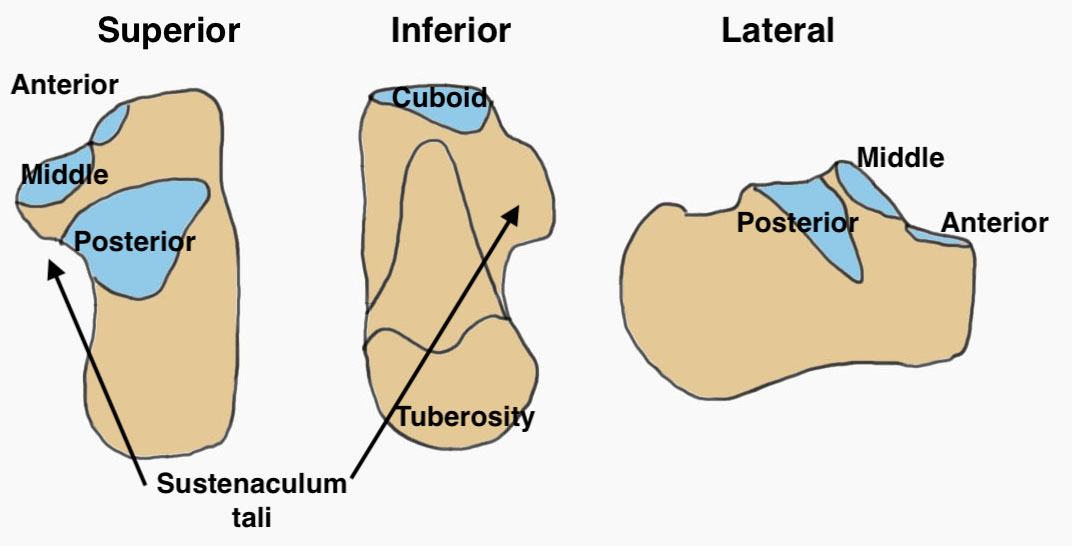
| Facets | Tuberosities | Process |
|---|---|---|
| Posterior facet / subtalar joint | Posterior - tendoachilles | Anterior - calcaneocuboid joint |
| Middle facet (sustenaculum tali) | Medial - adductor hallucis, plantar fascia | |
| Anterior facet | Lateral - abductor digiti minimi |
Etiology
Axial loading
- fall from height / motor vehicle accidents
- calcaneus driven up against talus
Epidemiology
Males < 40
10% bilateral
10% associated with lumbar spine fracture
Fracture patterns
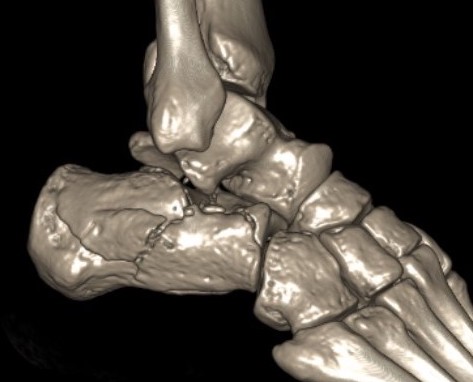
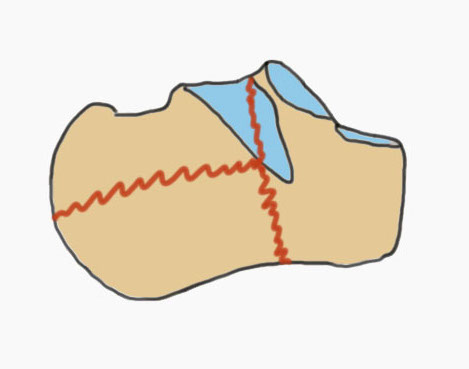
| Primary fracture line | Secondary fracture lines |
|---|---|
|
Lateral process of talus driven into crucial angle - starts at lateral wall near tarsal sinus - passes obliquely across posterior facet - exits at medial wall posterior to sustentaculum tali |
Passes immediately behind the posterior facet of the subtalar joint - exits posterior to posterior facet & anterior to tendoachilles insertion - creates thalamic portion containing posterior facet |
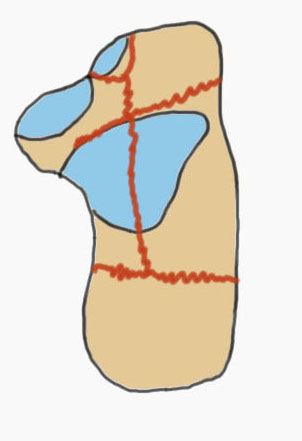
Common fracture fragments
| Sustenacular | Superolateral | Lateral wall | Posterior tuberosity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superomedial |
Lateral fragment of posterior facet
|
Tongue fracture | |
| Attached to talus by deltoid ligament | Thalamic fragement | Secondary fracture line exits below tendoachilles |
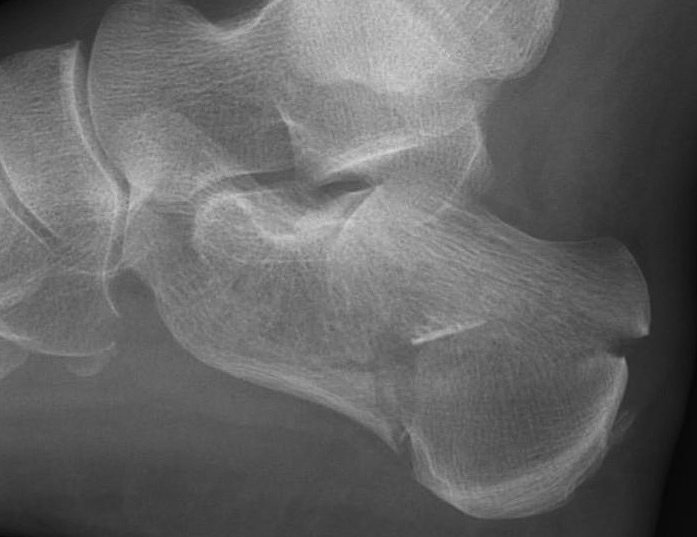
X-ray Views
| Lateral | Oblique view |
|---|---|
|
Bohler's angle Crucial angle of Guisane |
Calcaneocuboid joint |
 |
 |
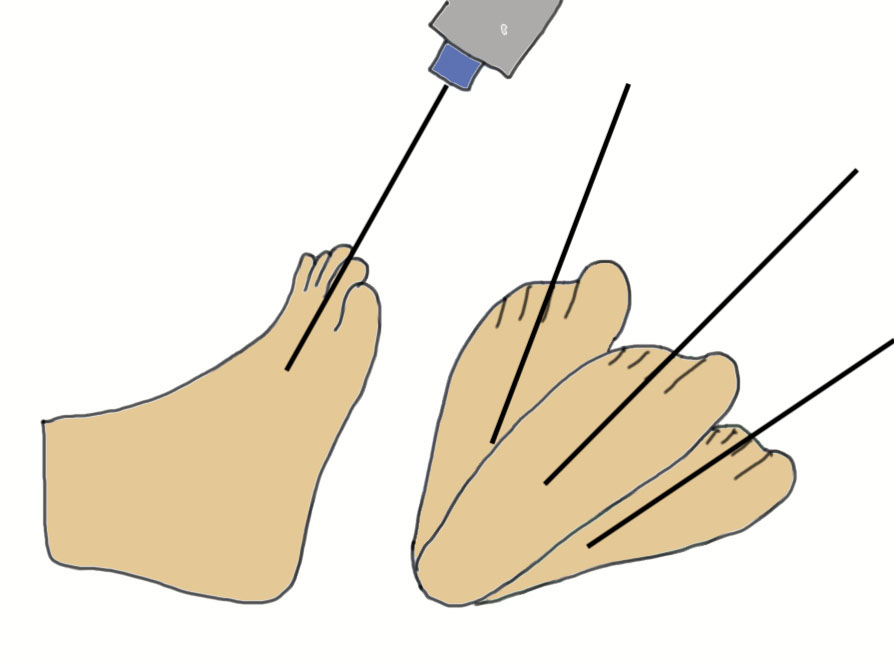
| Harris axial view | Broden's view |
|---|---|
|
45o axial of heel - normally hindfoot 10o of valgus - assess varus malalignment & heel width |
Internally rotate foot 45 degrees - ankle neutral initially - plantar flex the foot 10° increments from 10° to 40
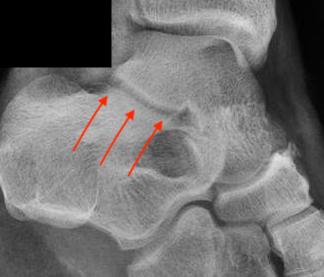
Useful intra-op to assess congruency of subtalar joint |
 |
  |
Xray Angles
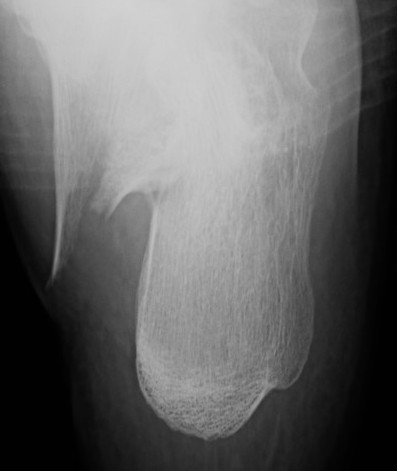
Bohler's angle (20-40°)
Lateral xray
Highest point anterior process - highest point on posterior facet - highest point on tuberosity
- represents the height of the calcaneus
- normal 20-40°
Angle of </=0° is associated with a poor outcome
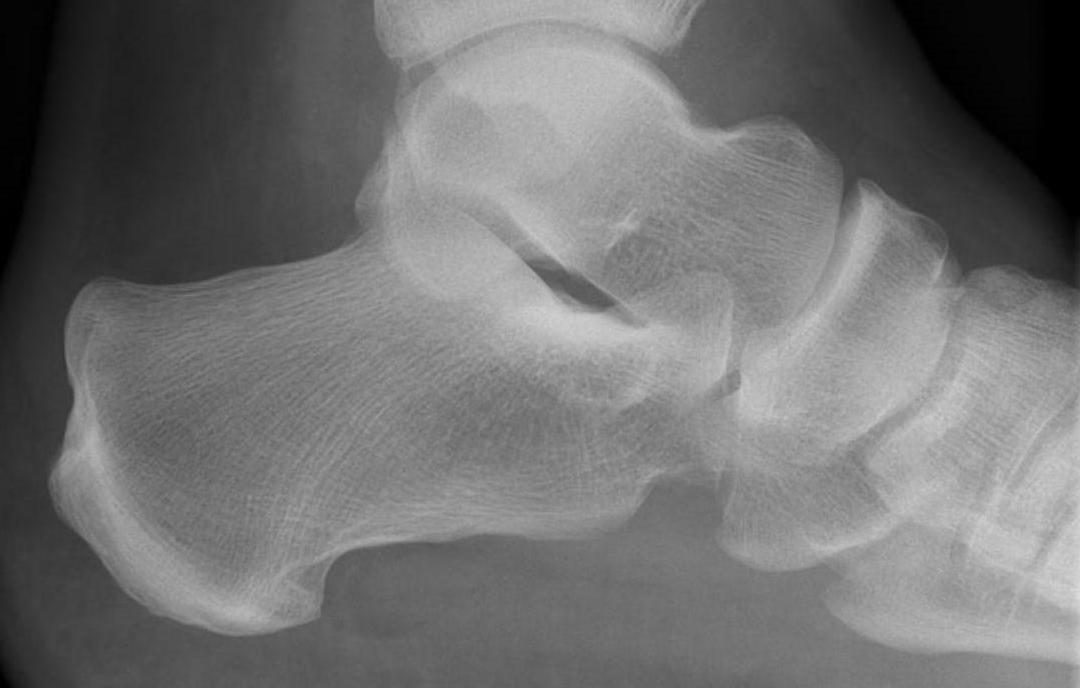
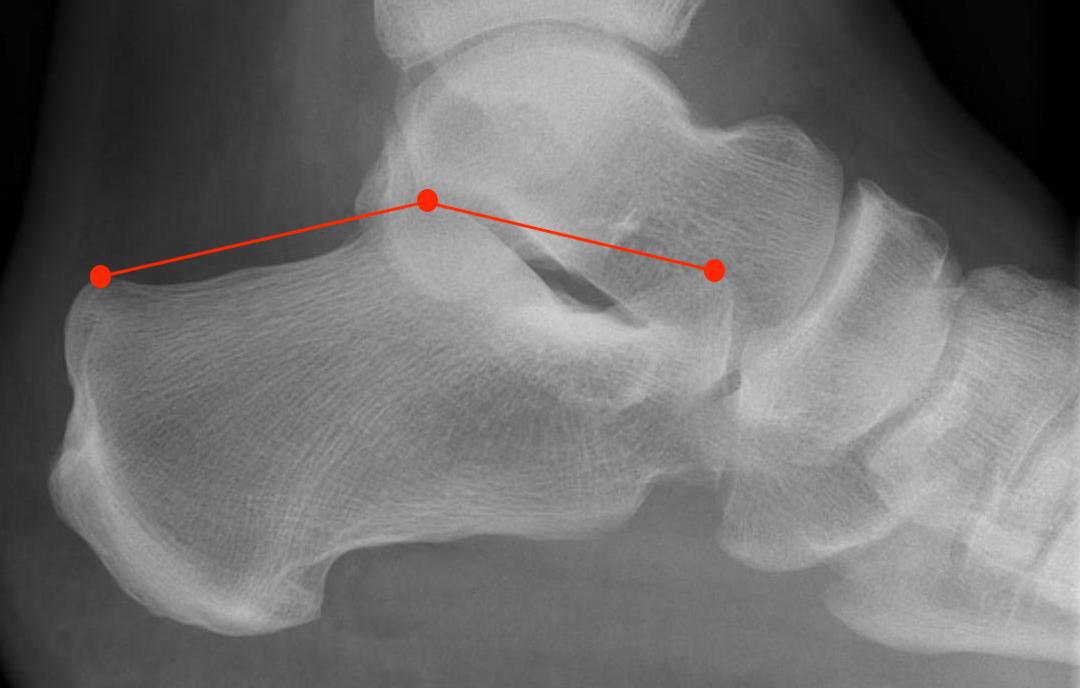
Normal Bohler's angle
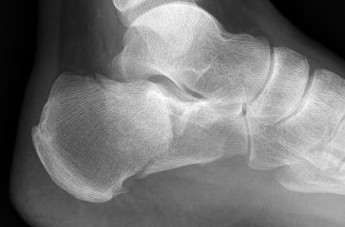
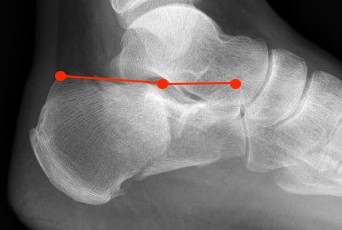
Calcaneal fracture with Bohler's angle < 0
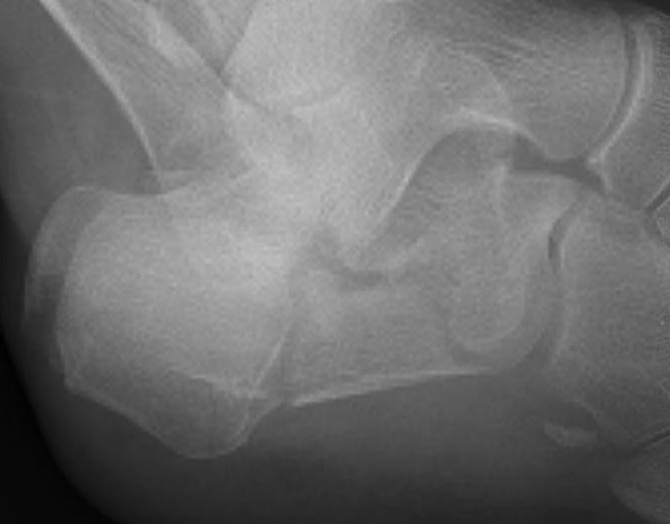
Crucial Angle Gissane (120-140°)
Lateral xray
Posterior facet of calcaneum - anterior process of calcaneum

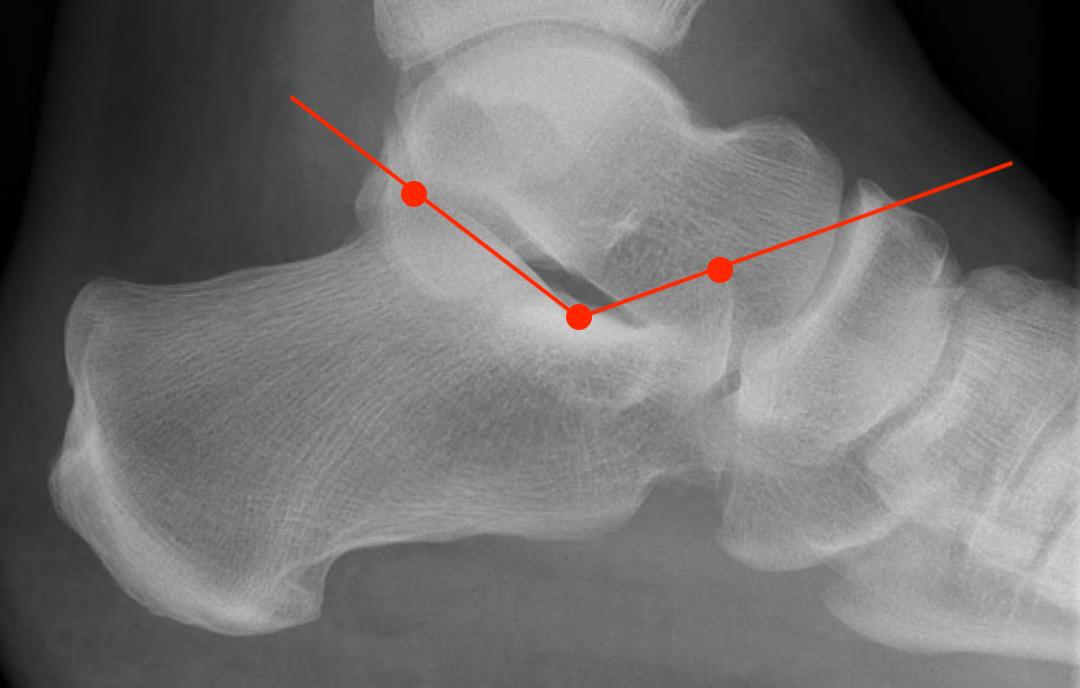
Normal angle of Gissane

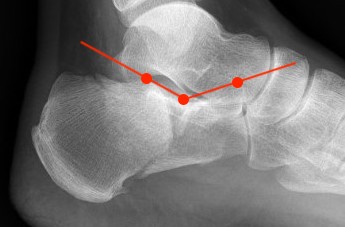
Reduced angle of Gissane after fracture
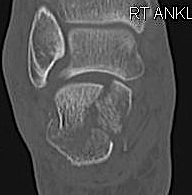
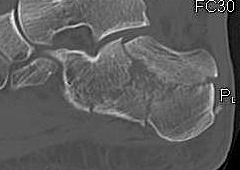
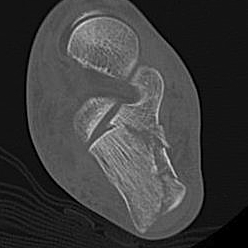
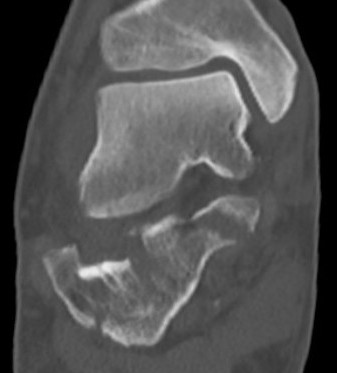
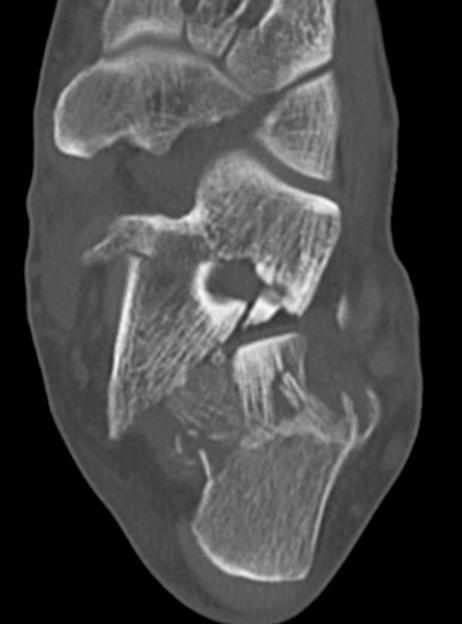
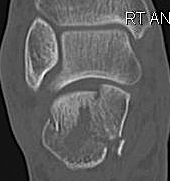
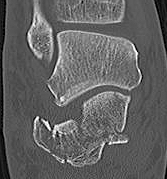
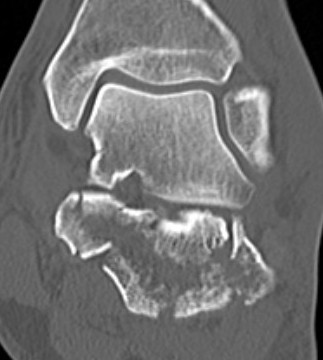
CT scan
| Coronal | Sagittal | Axial |
|---|---|---|
|
Posterior facet / number of fragments Sustenaculum tali Heel widening |
Bohlers angle Posterior facet depression / angulation |
Calcaneocuboid joint Sustenaculum tali |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
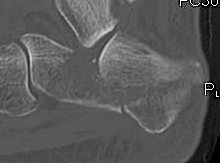
Sanders Coronal CT Classification
Posterior facet on coronal CT
- number of longitudinal fracture lines (Type II - IV)
- location of fractures (A: lateral, B: central, C: medial)
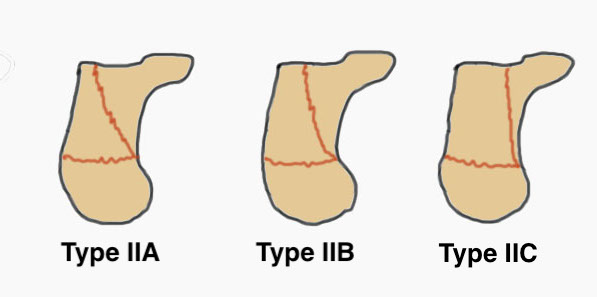
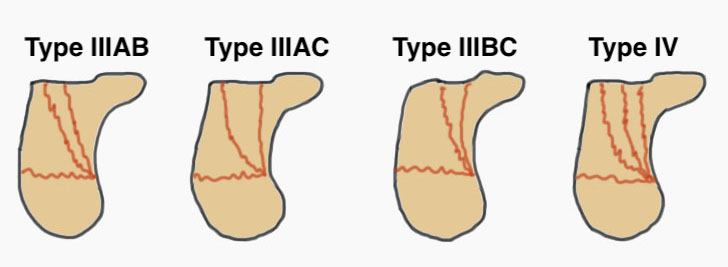
| Type I | Type II | Type III | Type IV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Undisplaced |
Two parts Displaced > 2 mm |
Three parts Displaced > 2 mm |
Highly comminuted |
| Non operative | ORIF | ORIF / fusion | Primary fusion |
 |
 |
 |
