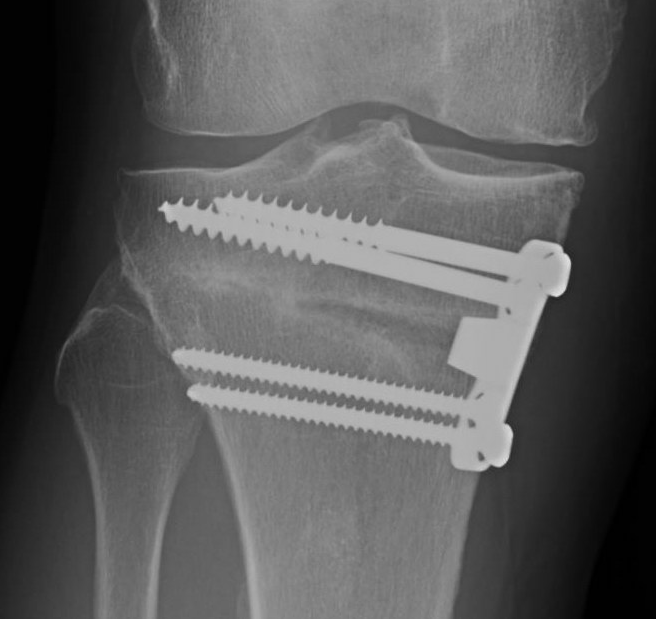
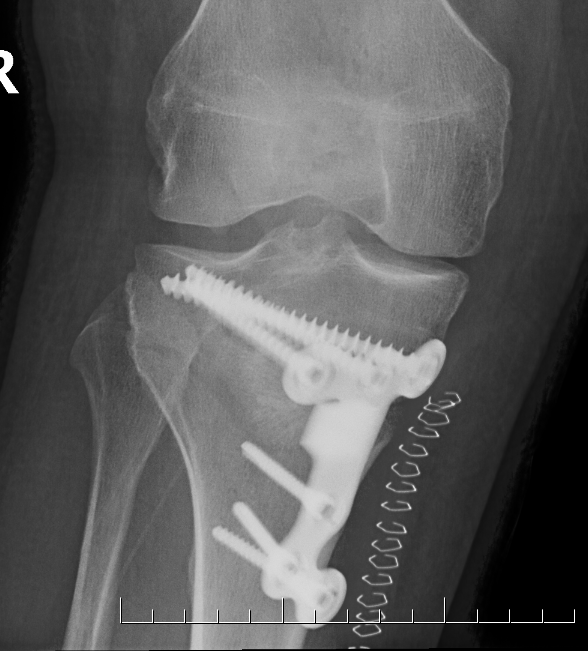
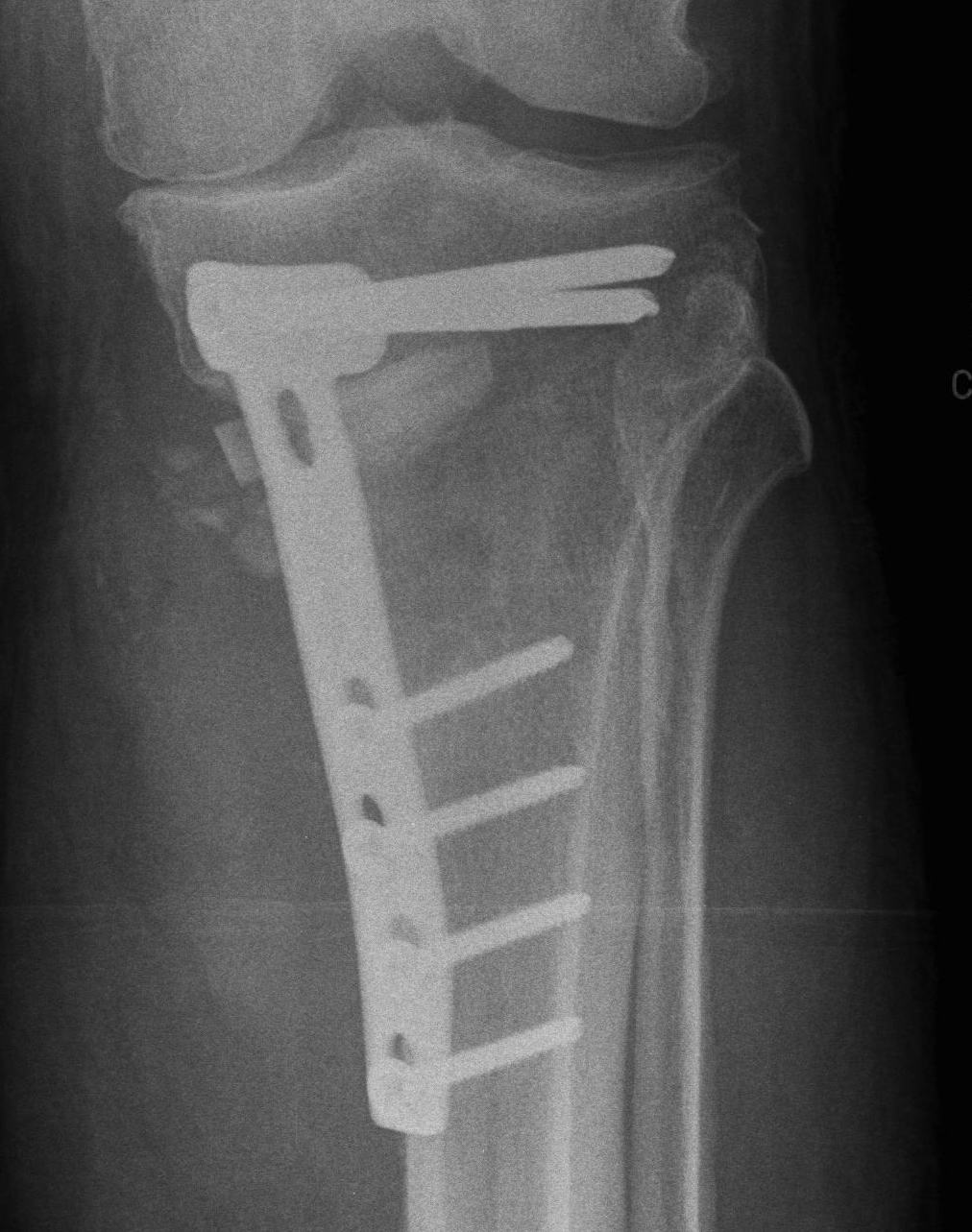
Medial opening wedge osteotomy
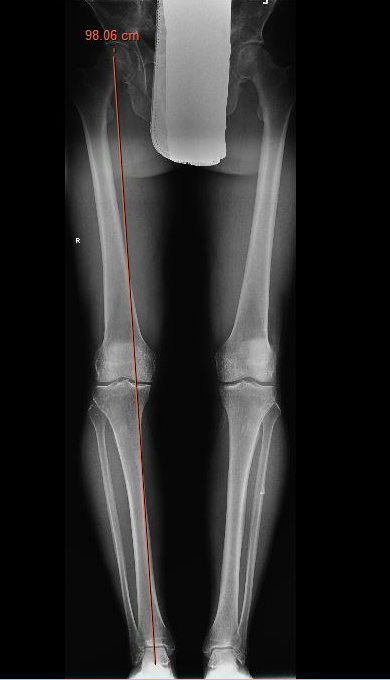
Equipment
Arthrex Locking Puddhu plate PDF
Arthrex ContourLock system PDF
Technique
Vumedi uniplanar Arthrex Puddhu plate technique
Vumedi uniplanar Arthrex Puddhu plate technique
Vumedi biplanar medial opening wedge
Vumedi biplanar medial opening wedge
Position
- patient supine on radiolucent table
Approach
- medial incision close to midline to incorporate into later TKA
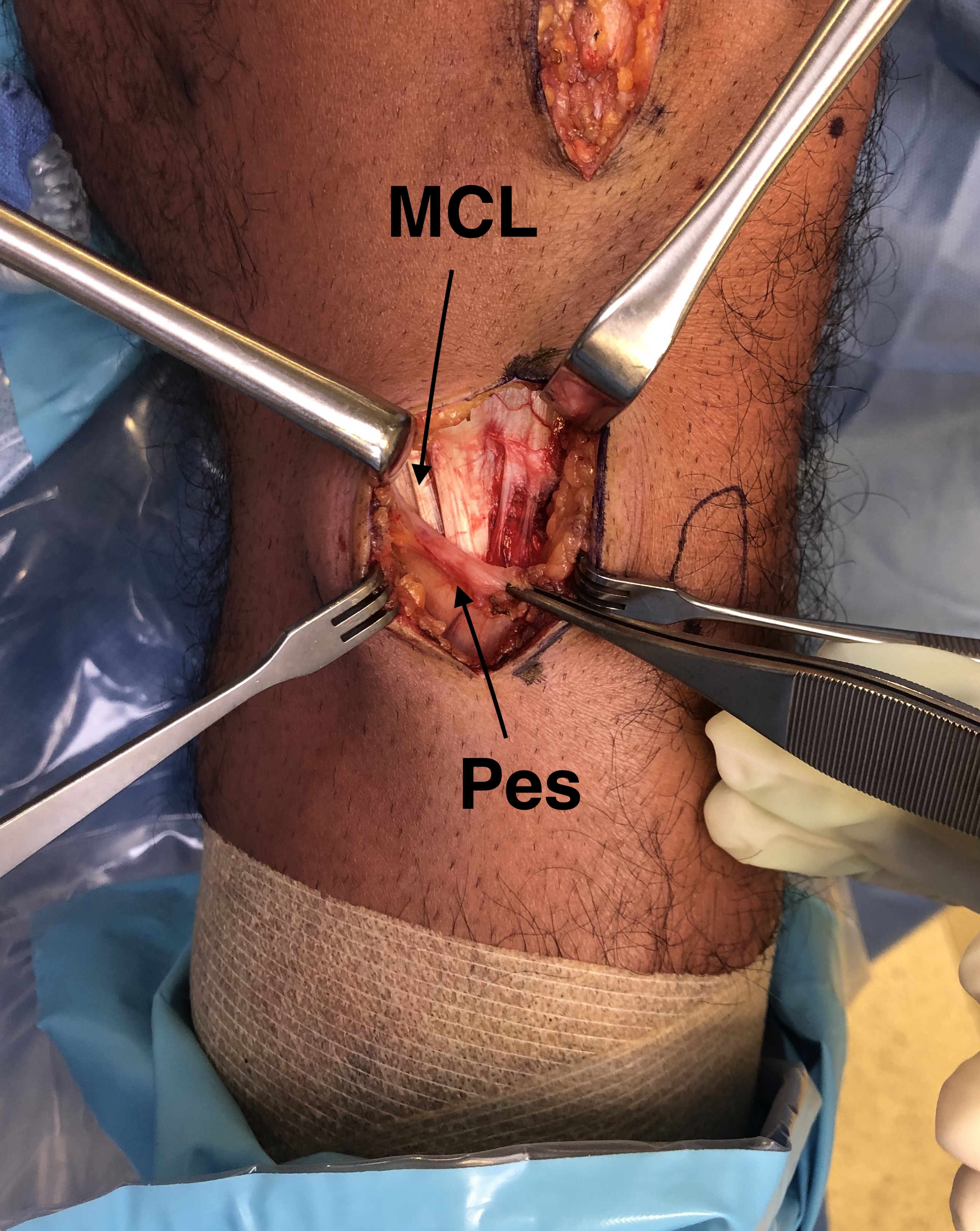
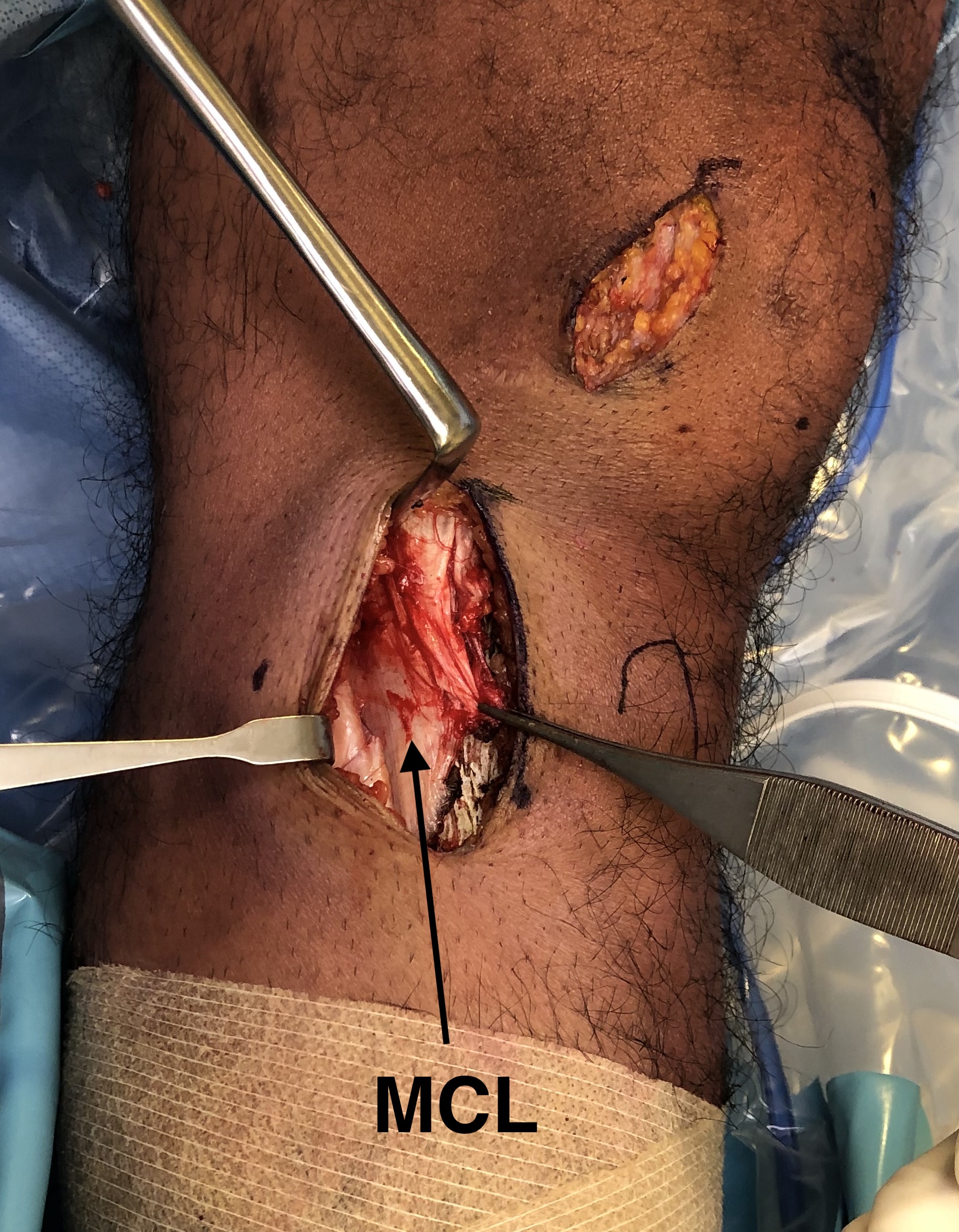
- between tibial tuberosity and MCL
- L shaped incision of sartorius fascia
- identify and elevate pes anserinus, as may have to slide plate under
- identify and elevate MCL posteriorly
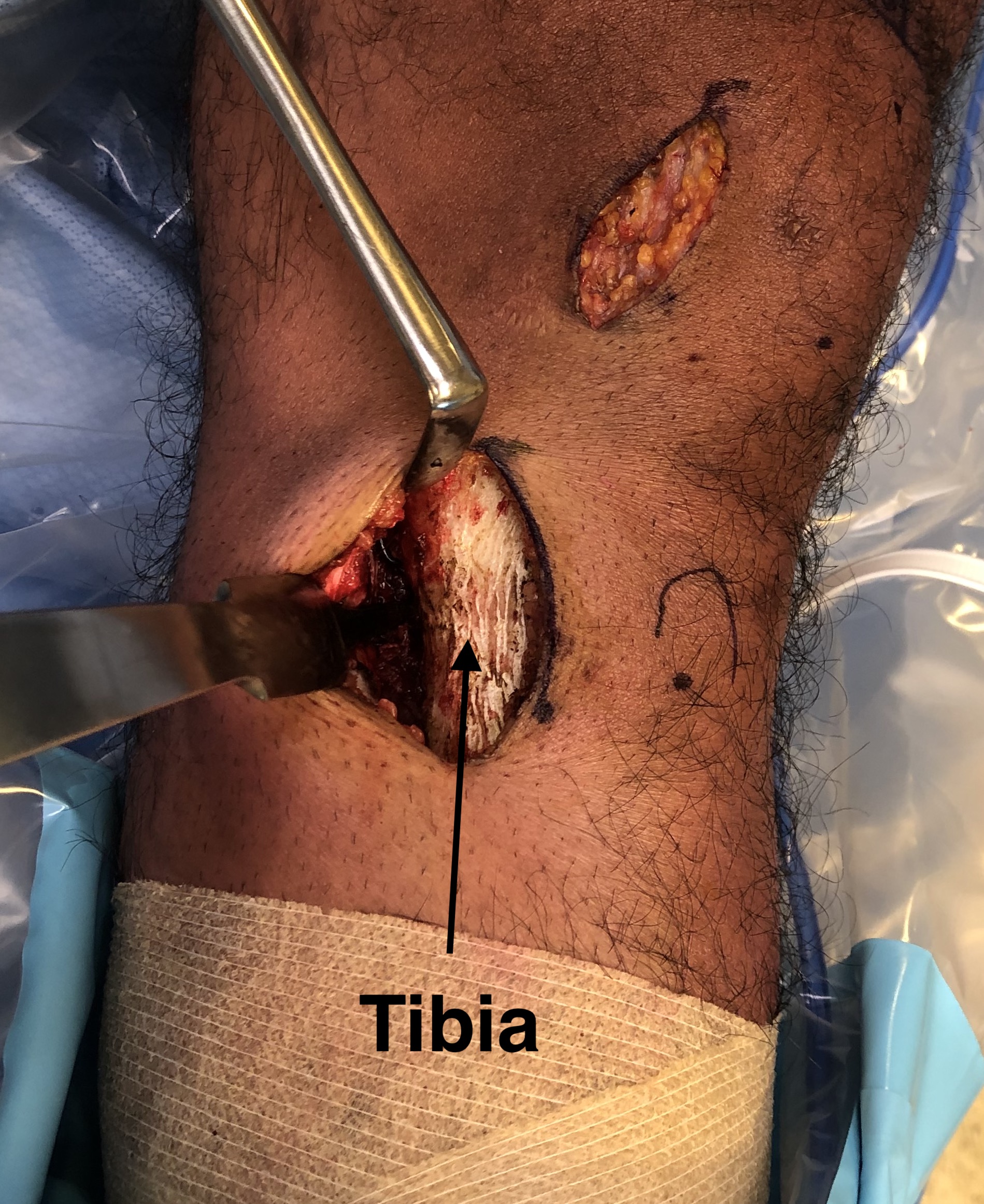
Exposure
- must expose and protect entire posterior tibia subperiosteally
- should be able to place finger entirely across tibia to proximal tibio-fibular joint
- must expose and protect patella tendon above tibial tuberosity
- place Langenbeck / Homan retractors anteriorly and posteriorly
Consider lateral hinge 2 mm K wire
- 10 mm from lateral cortex
- distal to proximal
Oblique Osteotomy
- entry is 4 cm distal to joint line
- osteotomy must pass above tibial tuberosity
- aiming for proximal third of the fibula head
- to 10 mm of lateral cortex to avoid lateral hinge fracture
- stay 2 cm below the tibial plateau to avoid intra-articular fracture
- ensure osteotomy is parallel to joint line to avoid altering slope
- ensure complete posterior cortex
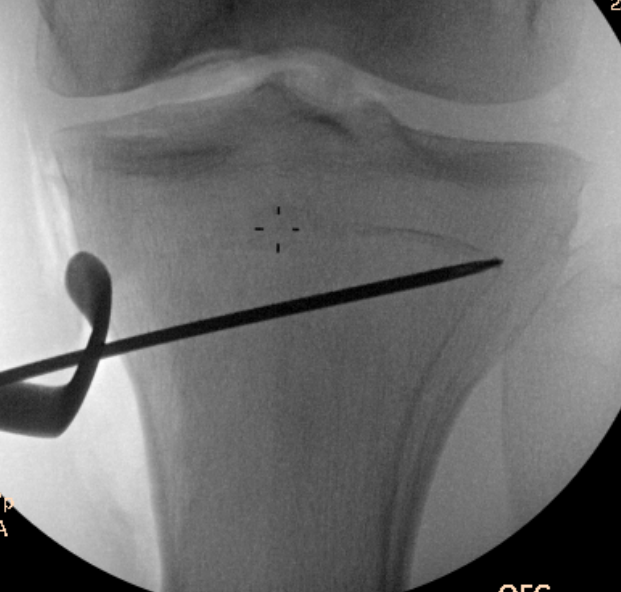
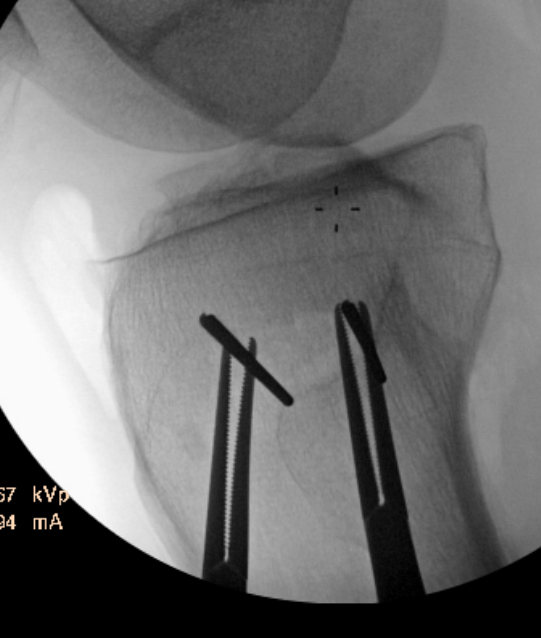
Guide pins for osteotomy and checking posterior slope
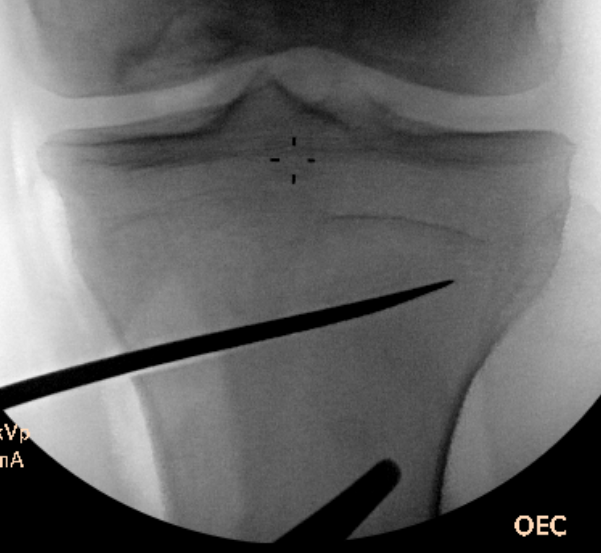
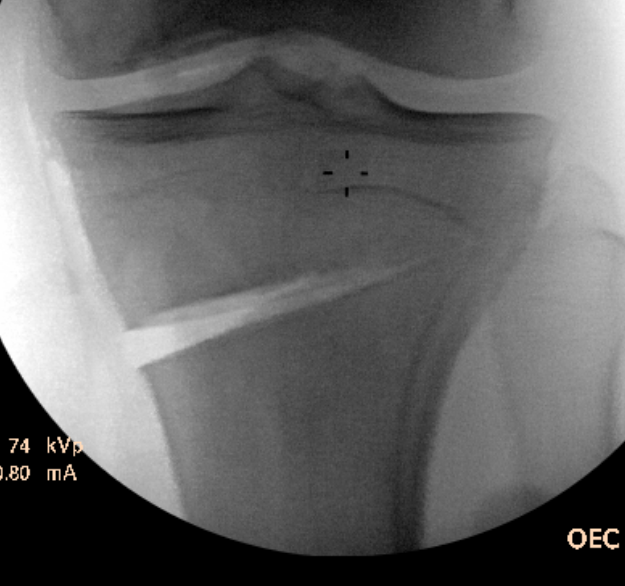
Osteotomy to within 1cm of the lateral cortex
Opening of wedge
- slow
- stacked osteotomes / lamina spreader / wedged osteotomes
- ensure no change of posterior slope on lateral
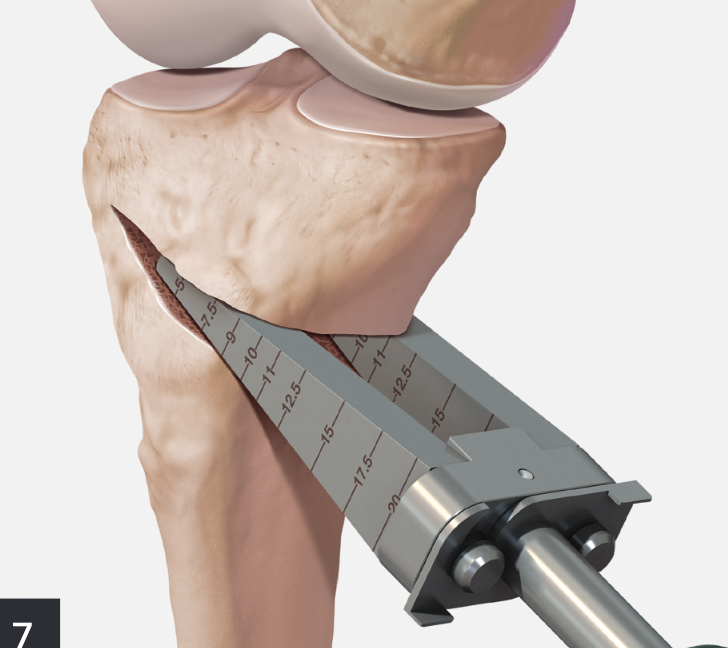
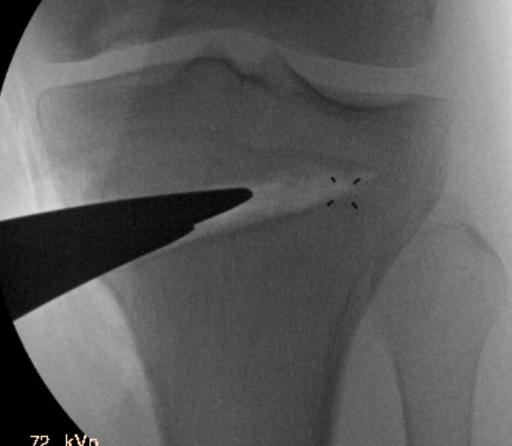
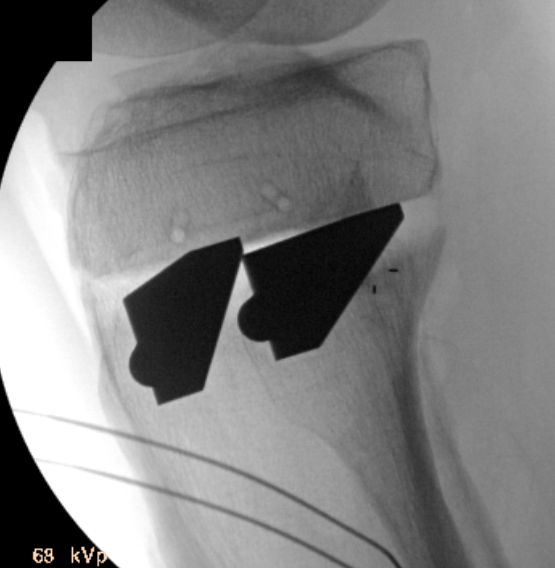
Arthrex wedged osteotomes
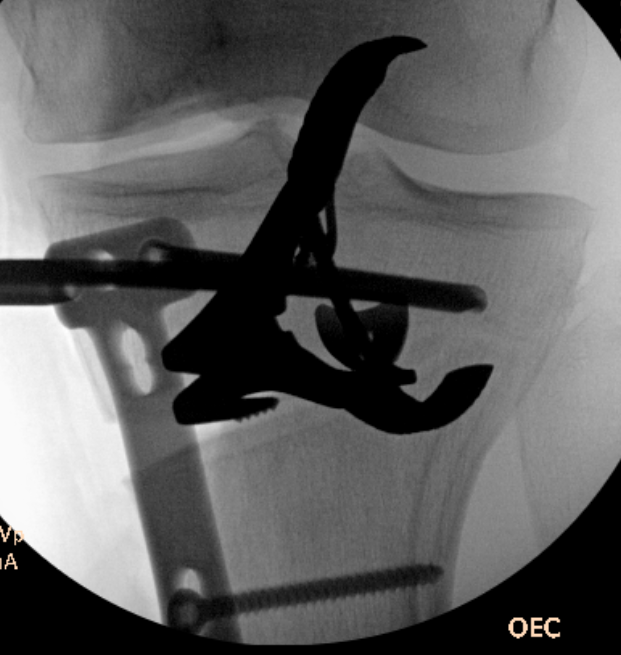
Opening osteotomy with laminar spreader
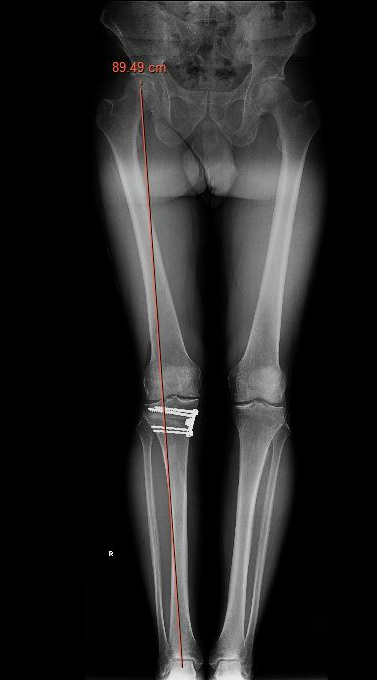
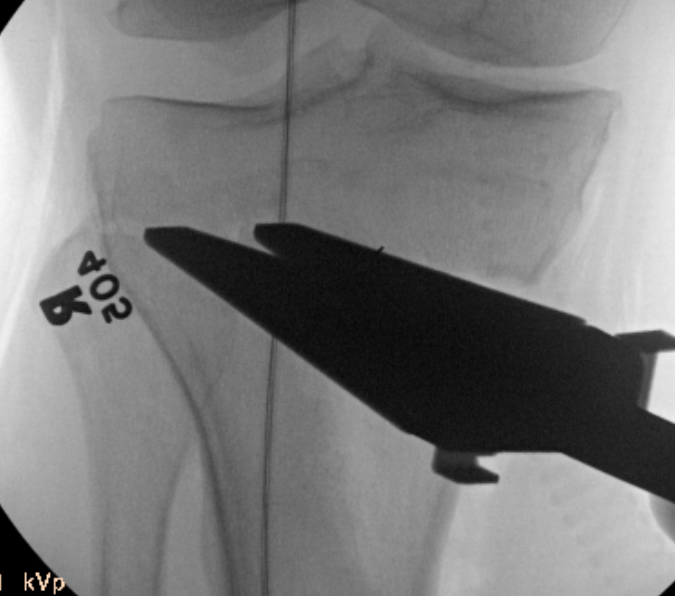
Check correct alignment with drop rod
- goal lateral tibial spine
- Fujisawa point / 62% of the tibial plateau / lateral tibial spine
Stabilisation
- locking plates
- +/- autograft / allograft / synthetic bone graft
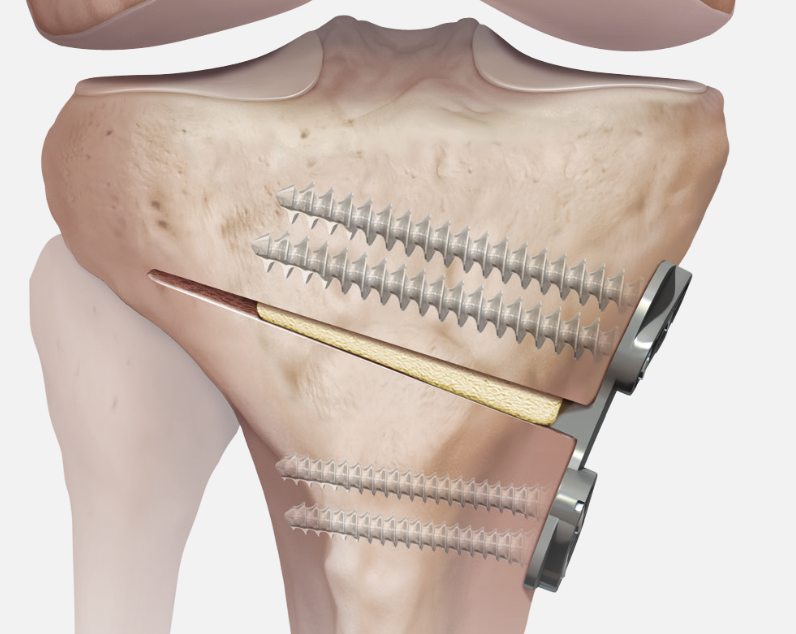
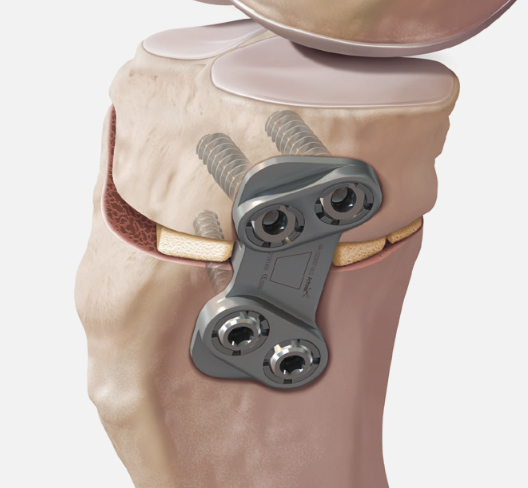
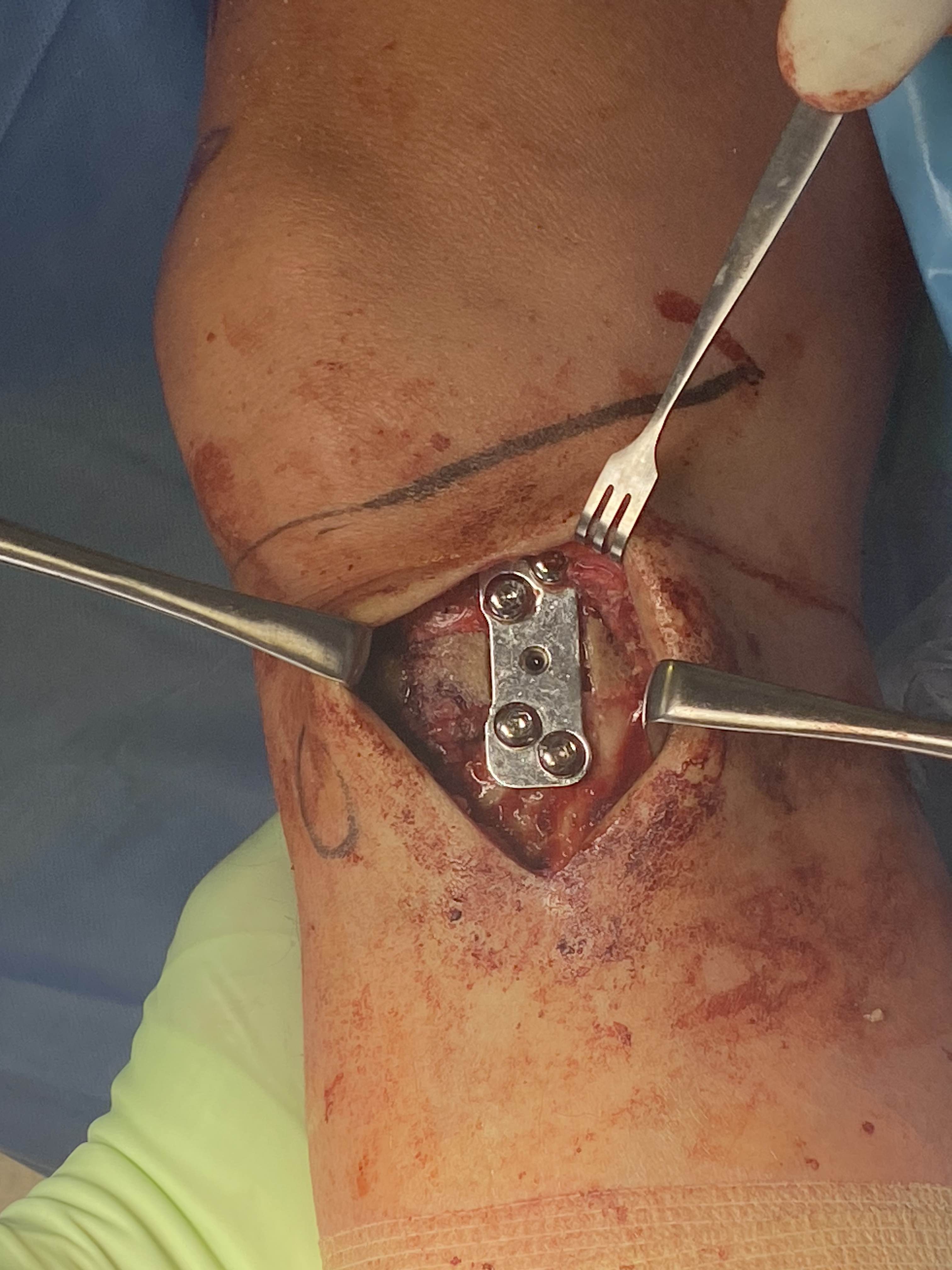

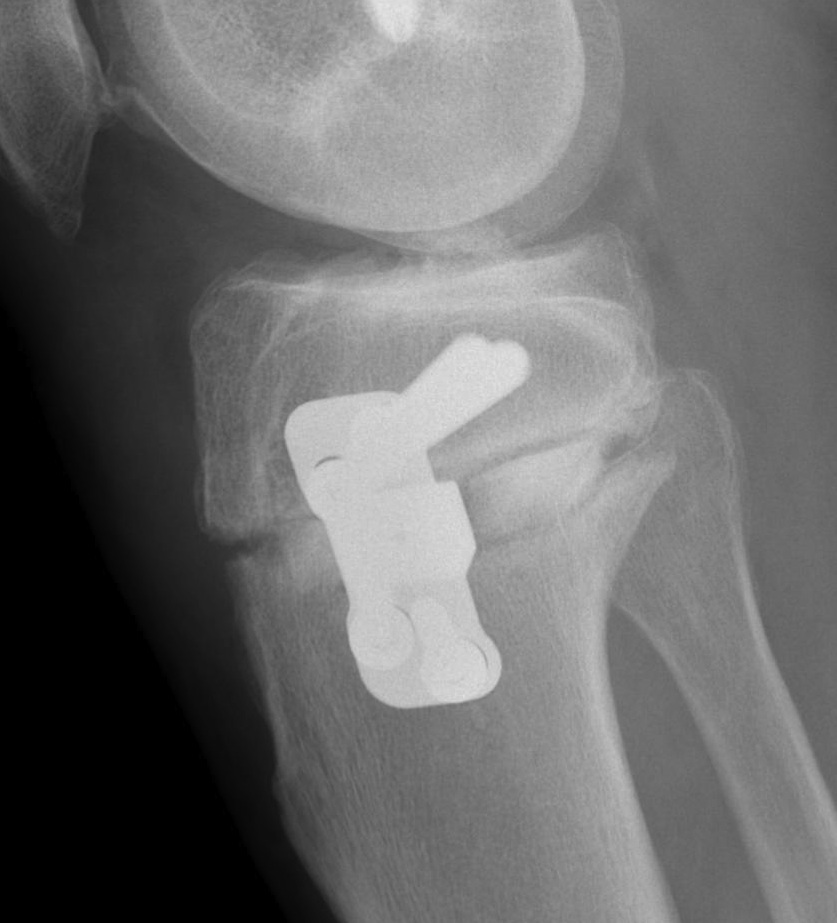
Arthrex Locking Puddhu plate PDF
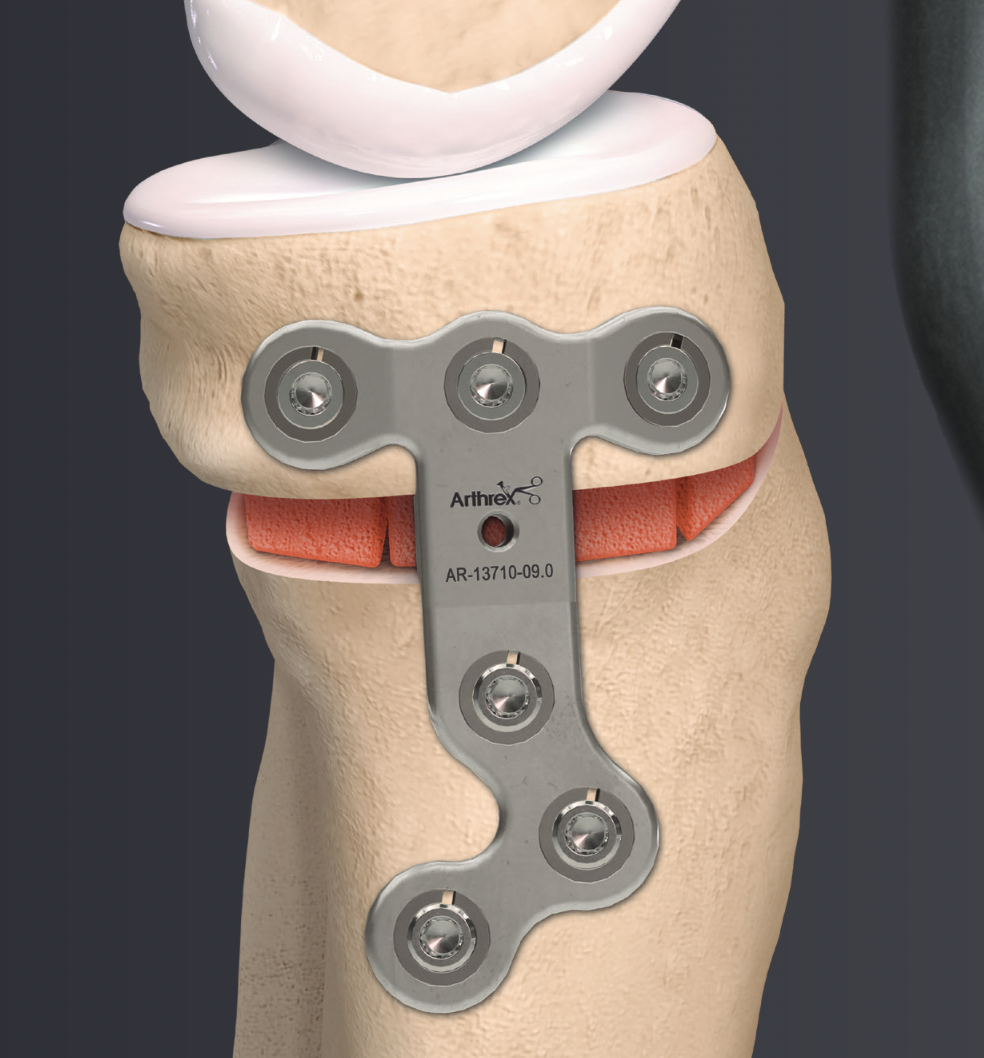

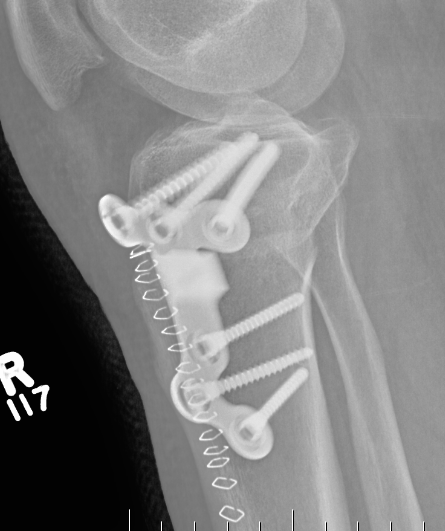
Arthrex ContourLock system PDF
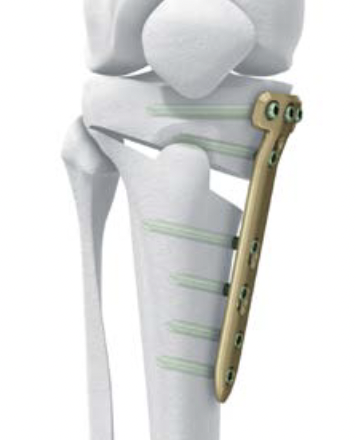
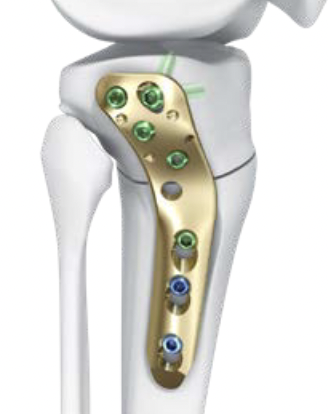
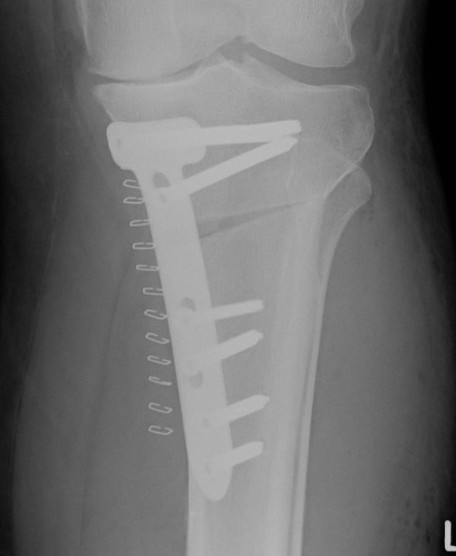
Biplanar medial opening wedge osteotomy
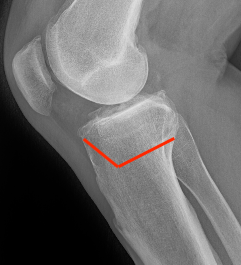
Retro-tubercle osteotomy
Advantage
- preserves patella tendon
- ? increases bony contact for healing
Disadvantage
- ? increases incidence of lateral hinge fracture
Complications
Infection 1%
Lateral hinge fracture 25%
Intra-articular fracture 3%
Delayed / nonunion
Compartment syndrome
Infection
- database of 822 osteotomies around the knee
- overall infection rate 2.8%
- superficial infection 1.6%
- deep infection 1.2%
- all successfully treated with debridement +/- plate removal
Lateral hinge fracture
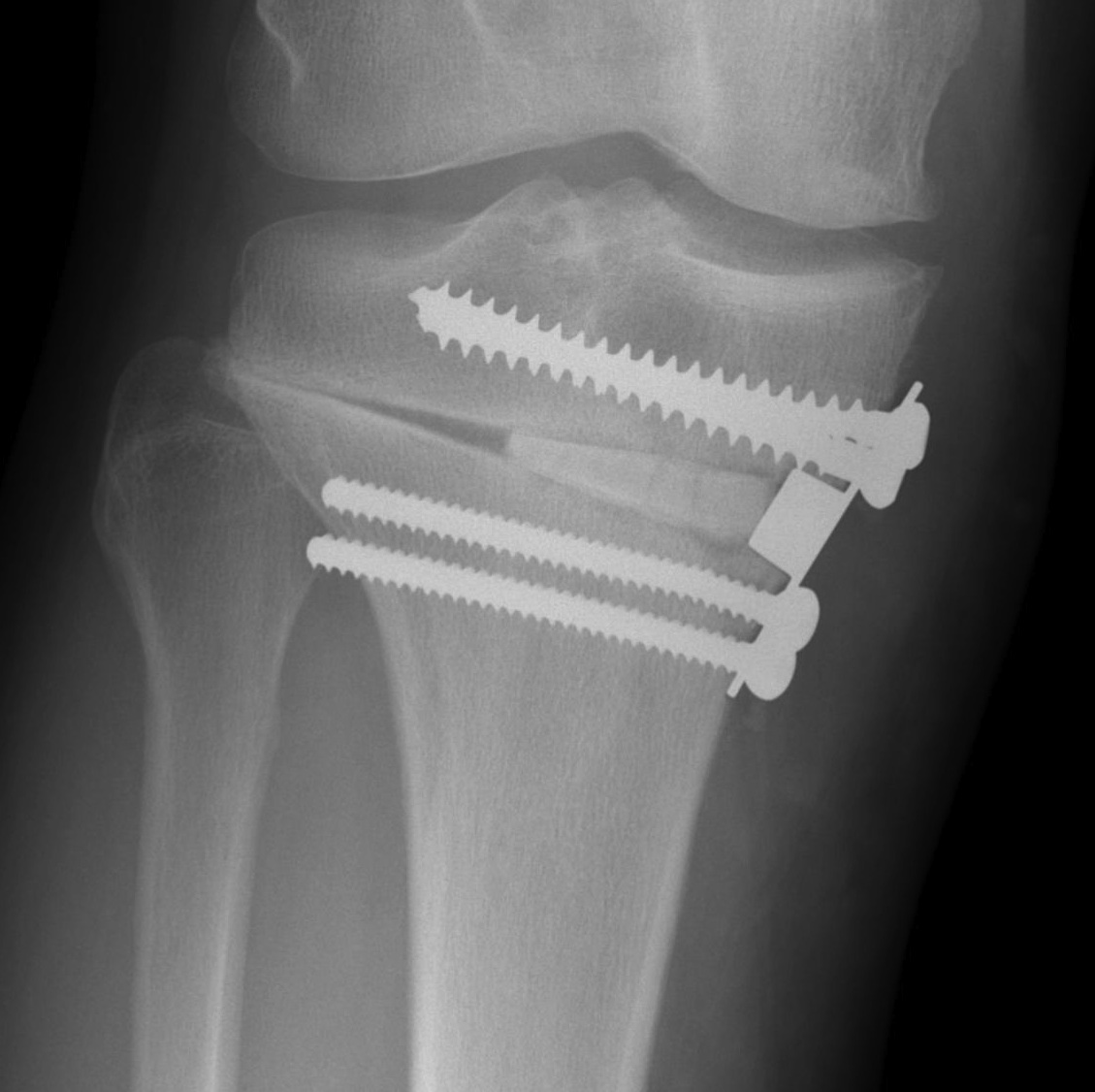
Type I hinge fracture
Definition
Extension of the osteotomy into far cortex
May be associated with instability / delayed union / nonunion
Incidence
- 48 opening wedge HTO
- xray: incidence lateral hinge fracture 15%
- CT: incidence lateral hinge fracture 50%
Causes
- systematic review hinge fracture after OW HTO
- incidence 25%
- increased with opening > 11 mm
- 55 lateral hinge fracture
- Type I associated with lateral distance < 6 mm
- Type II associated with lateral distance > 9 mm
Classification lateral hinge fracture after OW HTO
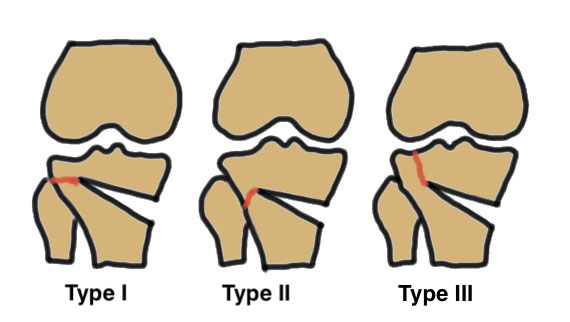
Takeuchi classfication
- type I: extend into lateral cortex above proximal tibio-fibular joint
- type II: extend into lateral cortex below proximal tibio-fibular joint
- type III: extend into lateral tibial plateau
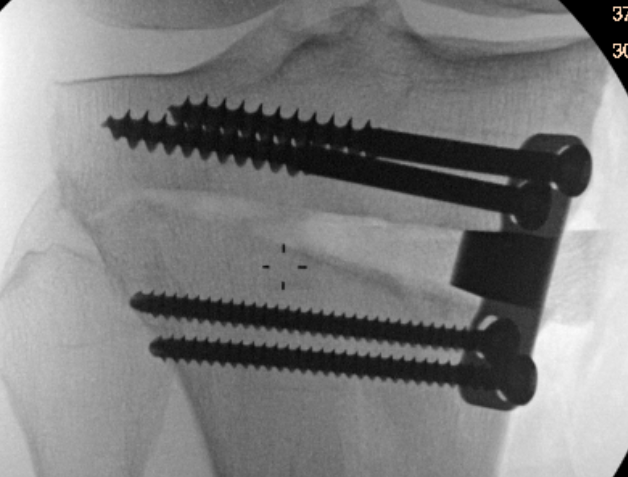
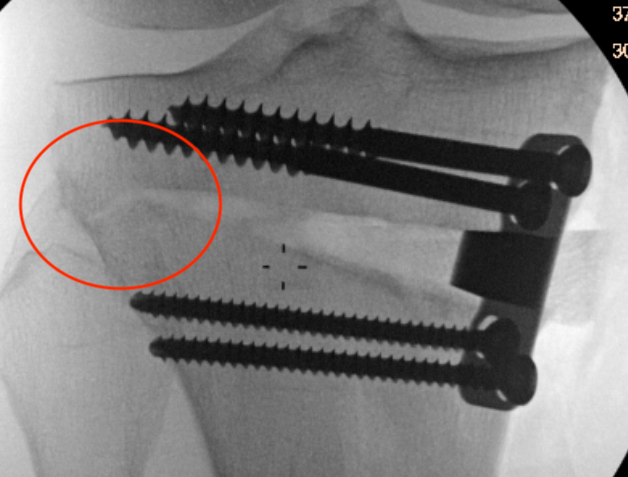
Type II hinge fracture
Delayed union / Nonunion
Nakamura et al Bone Joint J 2015
- 15 HTO with lateral hinge fracture
- increased delayed union with Type II
- increased delayed union / loss of position with Type III
Song et al Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2020
- 132 OW HTO
- 24% incidence lateral hinge fractures
- time to union no hinge fracture: 5 months
- time to union hinge fracture: 7 months
- no difference in outcome
Prevention
10 mm from lateral cortex
Aim for tibio-fibular joint
Slow correction
Lateral 2 mm K wire - inserted distal to proximal 10 mm from lateral cortex
? Biplanar osteotomy
- 206 OW HTO, 71 had lateral K wire
- no K wire: hinge fracture 40%
- K wire: hinge fracture 17%
- 59 uniplanar osteotomy versus 44 biplanar osteotomy
- uniplanar osteotomy: hinge fracture 12%, plate irritation 19%
- biplanar osteotomy: hinge fracture 27%, plate irritation 32%
Management
Type I: limit weight bearing 6 weeks
Type II / displacement: lateral plate
Instability
- place a Richards staple / plate over lateral fracture site
Intra-articular fracture
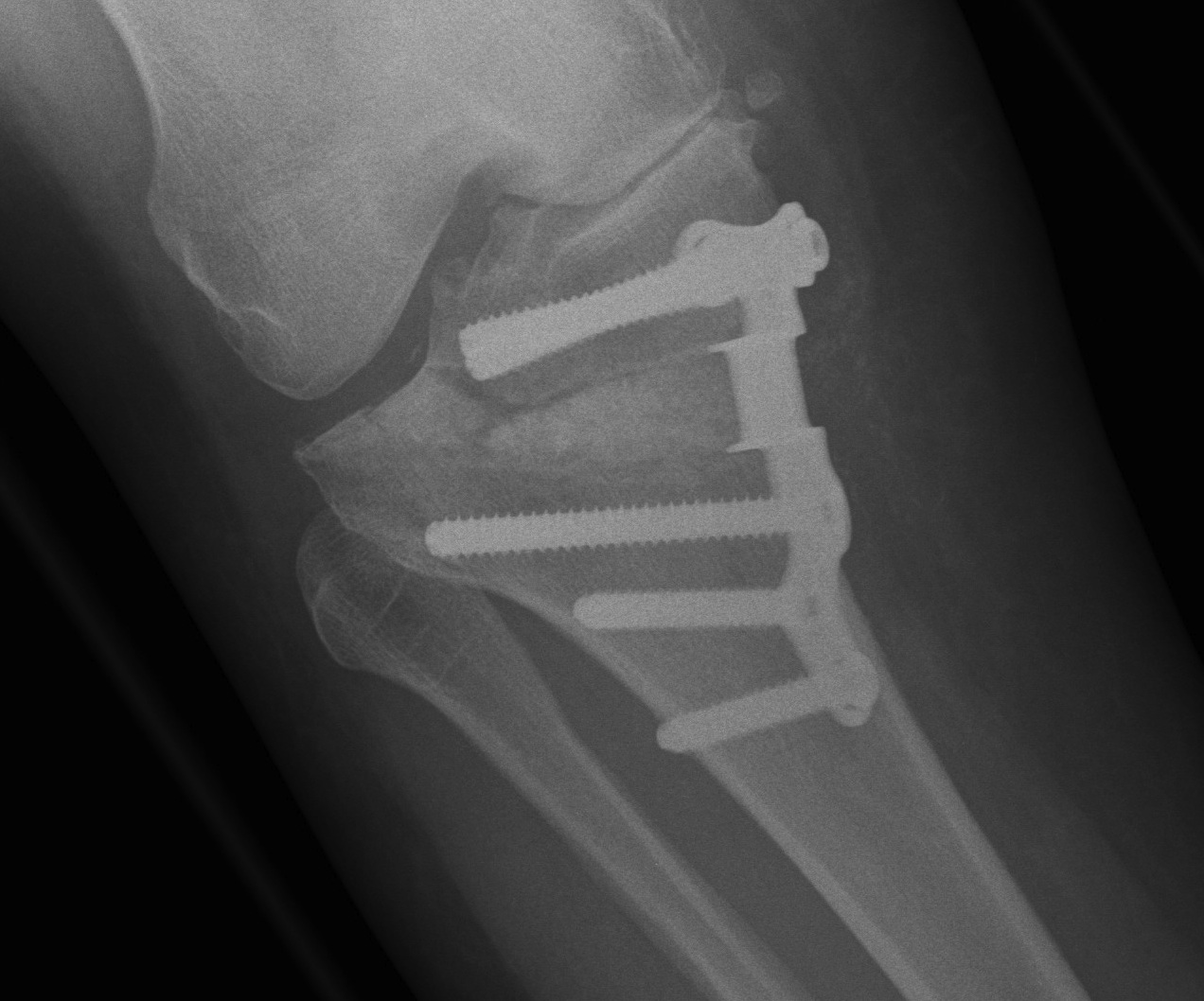
Incidence
- 323 OW HTO
- intra-articular lateral tibial plateau fractures 3%
Causes
- proximal fragment too thin
- osteotomy too short / trying to preserve far cortex for stability
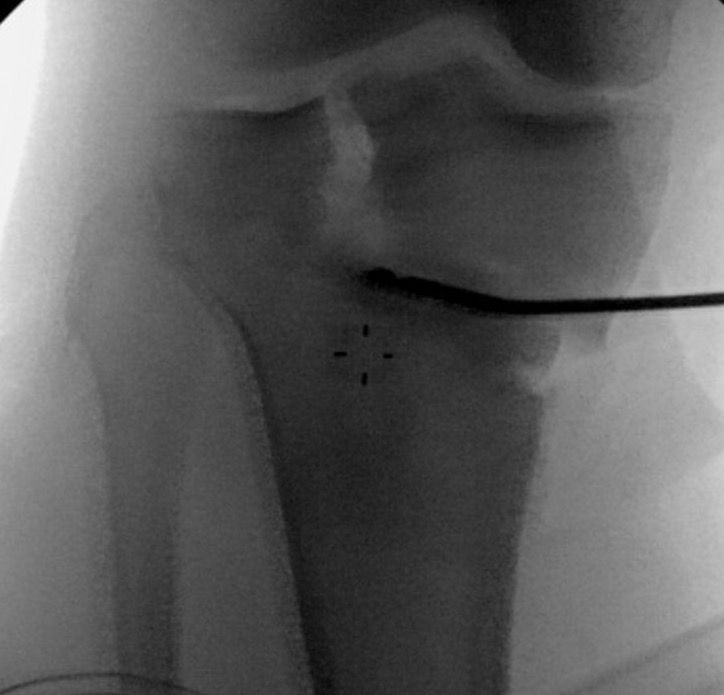
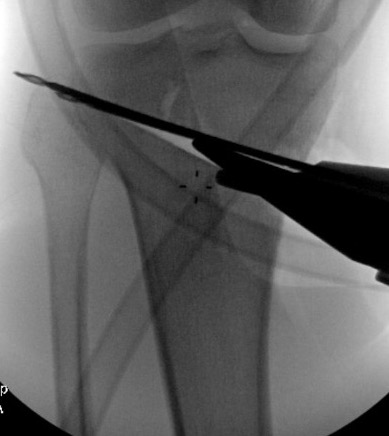
Osteotomy too close to articular surface
Prevention
- proximal fragment minimum 15 mm thick
- osteotomy within 10 mm of far cortex
- slow correction to allow stress relaxation
- ? keep in proximal K wires

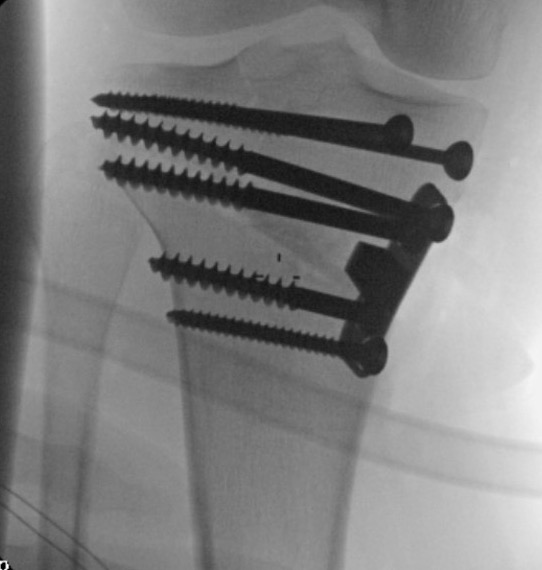
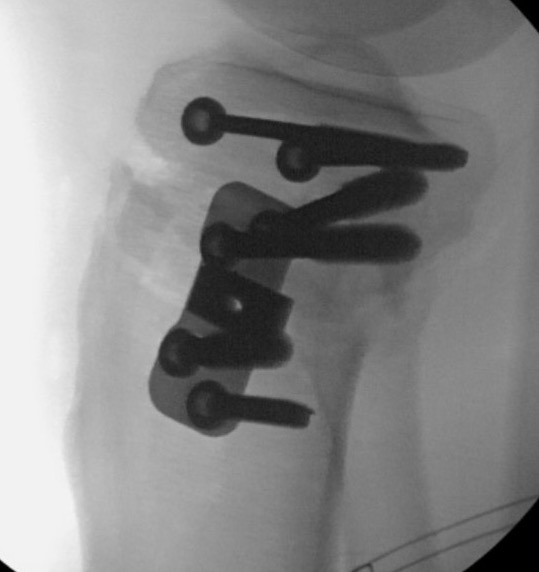
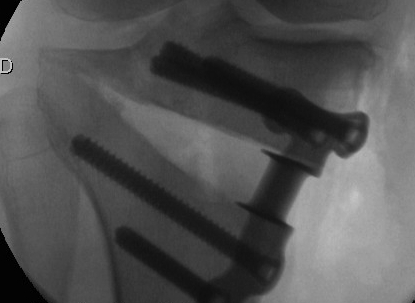
Non union
Bone grafting and locking plates
- systematic review of 3000 OW HTO
- autograft: delayed / nonunion 2.6%
- allograft: delayed / nonunion 4.6%
- synthetic bone graft: delayed / nonunion 4.5%
- non locking plates: delayed / nonunion 3.7%
- locking plates: delayed / nonunion 2.6%
Other
Undercorrection / loss of correction
DVT/PE
Patella baja
Compartment syndrome
Harware removal
