Risk Factors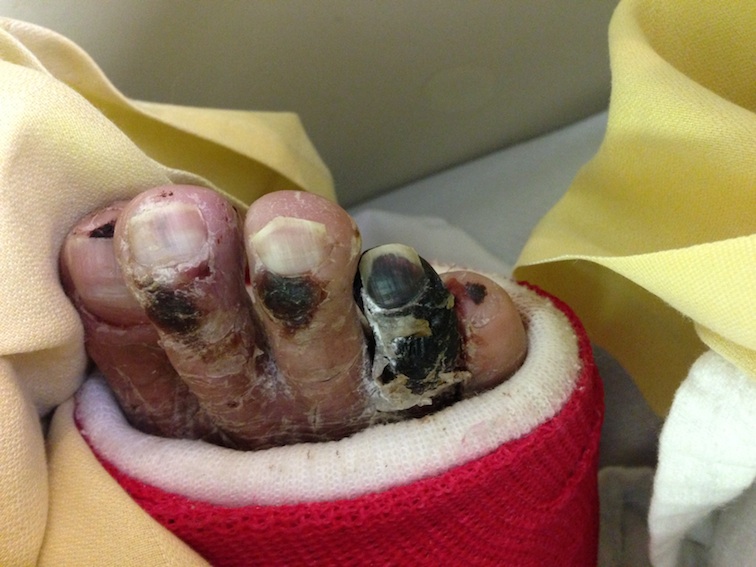
- DM > 10 years
- chronic hyperglycaemia
- impaired vision or joint mobility
- lack education
- increasing age
- previous amputation
Considerations
- blood flow
- soft tissue envelope
- deformities / Charcot collapse
- sensation
- contractures - Achilles tendon, knee, toe
- rehab goals
Selection of Level
Aim is to preserve foot
- BKA leads to contralateral BKA in 1/2 in 5 years
'Biologic Amputation Level'
- most distal functional amputation level with reasonable potential for wound healing
Technique
No tourniquet
Cover with IV Abs 10 days then oral until wound healing
2 stage procedure
No sharp corners on bone
Long plantar flap if available
- otherwise fish mouth
- tensionless flap
- sutures 8/52
- non constrictive dressings
Delay Weight bearing and prosthesis
Amputations
Toe
Try & leave base proximal phalanx
If complete toe amputation
- proximal to metatarsal neck
Hallux
- must stabilise sesamoids or they retract & expose base MT
2nd toe
- avoid because get severe hallux valgus
- may need to fuse 1st MTPJ
Ray
Most useful for 1st or 5th ray
- central ray resection takes a long time to heal if wound left open
- avoid multiple ray amputations
- often difficult to close wounds after ray amputation & may need to leave open rather than close under tension
Fifth ray
- racquet for toe and then straight lateral
- preserve base of fifth (P brevis)
Transmetatarsal amputation
Good
- toe filler only, no shoe modification
A. Lisfranc
- preserve base 5th MT
- leave PB attach
B. Chopart
- reattach T Ant and T Post to neck of talus
- post op cast in dorsiflexion
Late equinovarus
- percutaneous TA lengthening
- 2 medial and one lateral
- in theory leaves more intact laterally
- +/- lateral transfer of Tibialis Anterior
Boyd
Talectomy & calcaneotibial arthrodesis
- forward translation of the calcaneus
- similar flaps to Symes but longer
- Occasionally in children
- Poor in adults
Pirogoff
Talectomy & vertical osteotomy of calcaneus
- osteotomy thru midbody then forward rotation of calcaneum to appose tibial plafond
- good in kids, too long to unite / heal in elderly
Syme's
Ankle disarticulation preserving heel pad
Advantages
1. Able to go to toilet in night without prosthesis
- can ambulate short distances if need
2. Bulb makes the socket self suspending
Disadvantages
- cosmetically poor because stump is very wide
- many women unhappy with cosmesis
Partial Calcanectomy
Indication
- for non-healing heel ulcers associated with vascular insufficiency
- not so severe that wound won't heal
Technique
- ulcer excised & longitudinal incision proximal & distal
- T Achilles reflected
- all of posterior process of calcaneum excised
- this makes skin closure easy
- T Achilles can't be reattached & is left free
- patient must wear rigid AFO style partial foot prosthesis with cushion heel long term
Trans-tibial
Long posterior flap now standard
- previously always 6 inches from knee joint but trend now is to make as long as possible
- avoid distal 1/3 as poor soft tissue coverage & padding
Posterior flap length is equal to diameter of limb at level of bone cut plus 1cm
- fibula is cut 1-2cm shorter
- don't perform tibiofibular synostosis
- usually get painful non-union
- gastrocnemius myodesis