Definition
High ankle sprain - injury to the syndesmosis
Epidemiology
Mulcahey et al Orthop J Sports Med 2018
- 1200 ankle sprains in the NFL
- 34% high ankle sprain
- 6% required surgery
Mechanism Injury
Forced external rotation of dorsiflexed ankle
Collision sports - rugby / NFL / hockey
Anatomy
Fibrous joint
- interosseous crest / tibial incisura of the tibia to fibular
- Tillaux-Chaput tubercle anteriorly
- Volkmann tubercle posteriorly
Ligaments
- anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL)
- posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (PITFL)
- interosseous ligament (provides only 10% of strength)
Talar dome wider anteriorly
- fibula internally rotates 3–5 degrees with plantar flexion
- fibula externally rotates 3 - 5 degrees with dorsiflexion
Examination
| Significant swelling | AITFL tenderness | Squeeze test | External rotation |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Proximal swelling Beyond expected for sprain |
Focal tenderness at syndesmosis |
Compress tibia and fibular Stress syndesmosis Pain ++ |
Stabilize tibia ER the foot Pain ++ |
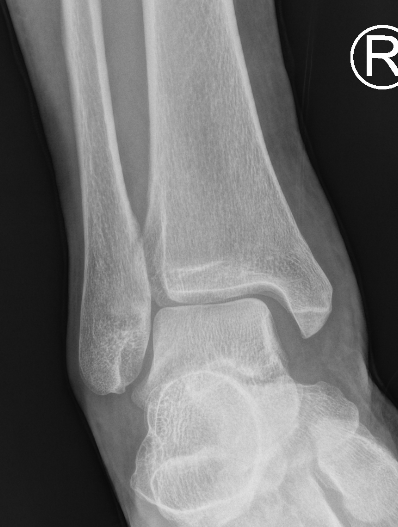
Xray
Associated fractures
- Weber C
- Maisonneuve
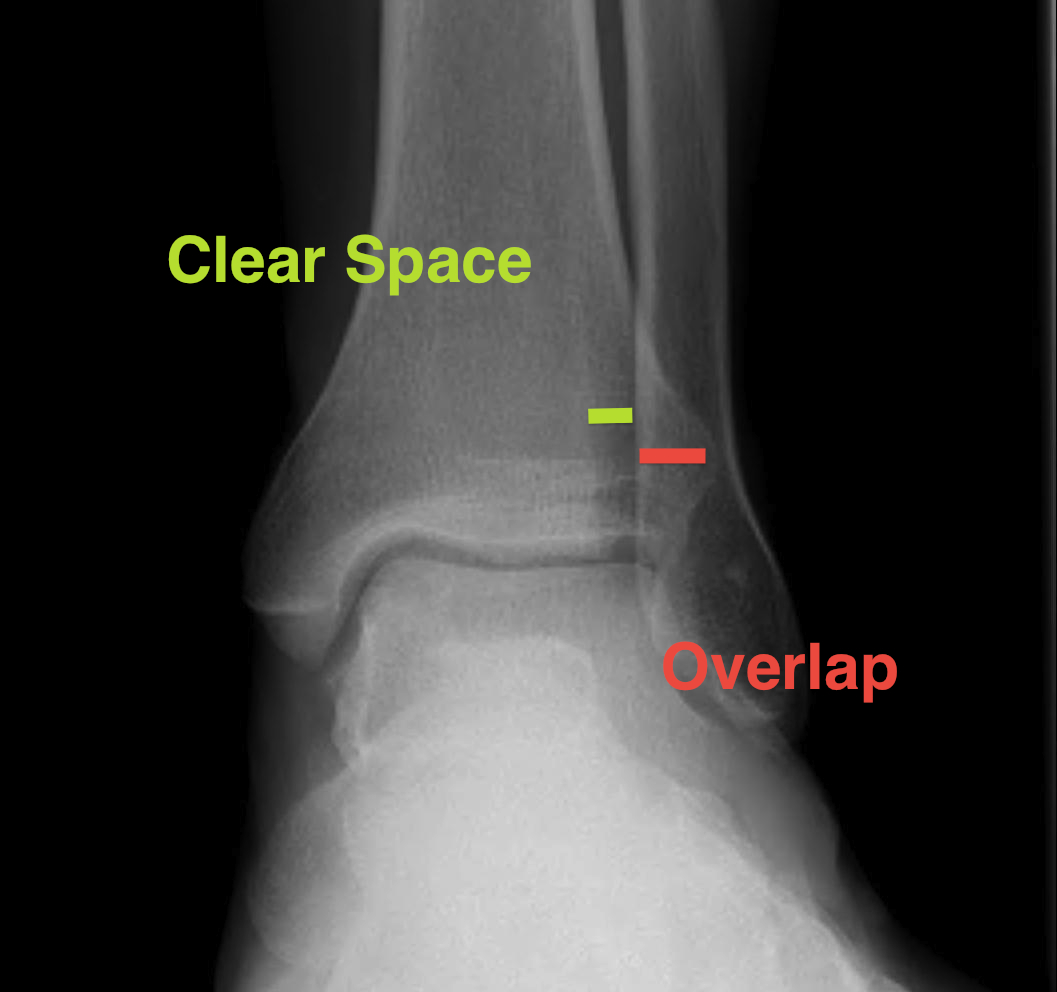
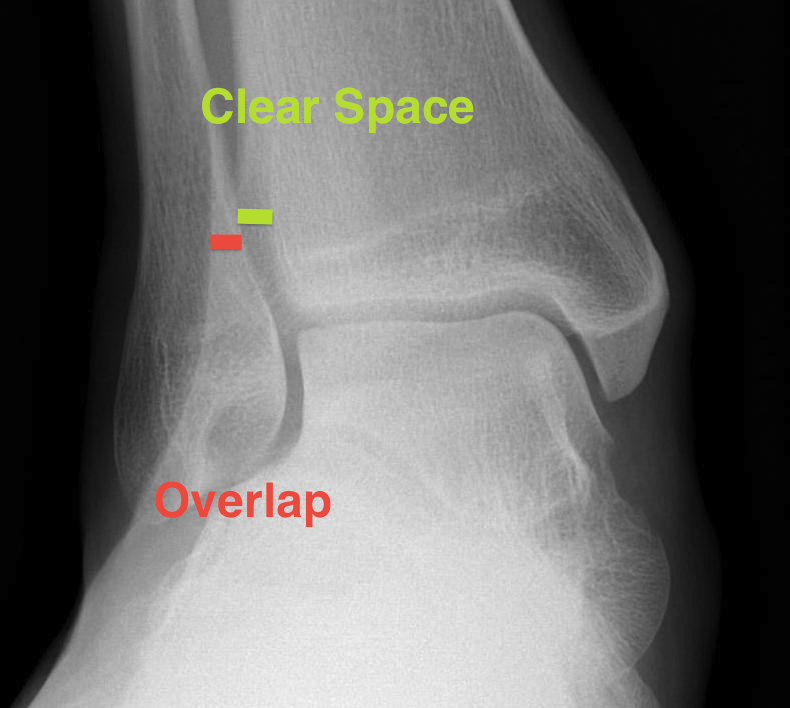
| Increased tibio-fibular Clear space | Overlap | Increased medial clear space |
|---|---|---|
|
Medial border of the fibula Lateral border of the posterior tibia (incisura fibularis) Measured 1 cm above the plafond |
Overlap of the fibula and the anterior tibial tubercle | Deltoid ligament injury |
| <5mm AP and mortise |
> 6 mm AP view > 1 mm mortise view |
Maisonneuve / proximal fibular injury |
 |
 |
 |
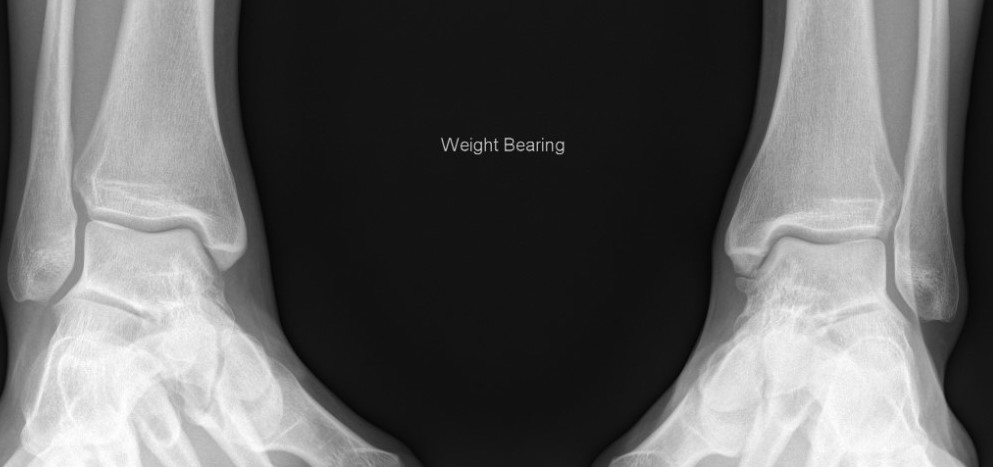
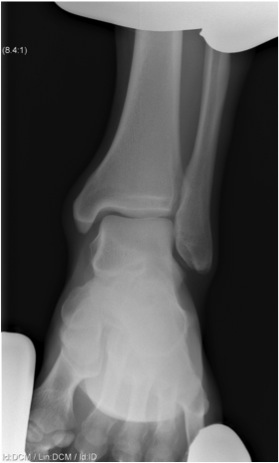
Lack of overlap and increased clear space on right
Clear isolated disruption to the syndesmosis
Stress xrays
Technique
- application of an external rotation and abduction force
- anesthesia is often required because of the painful nature of this examination
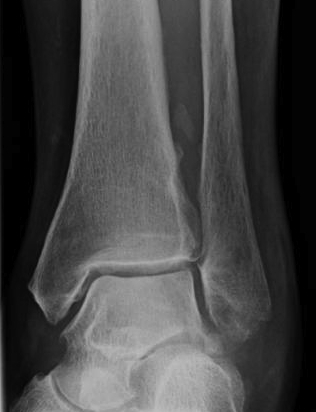
Chronic
Heterotopic ossification interosseous ligament
CT
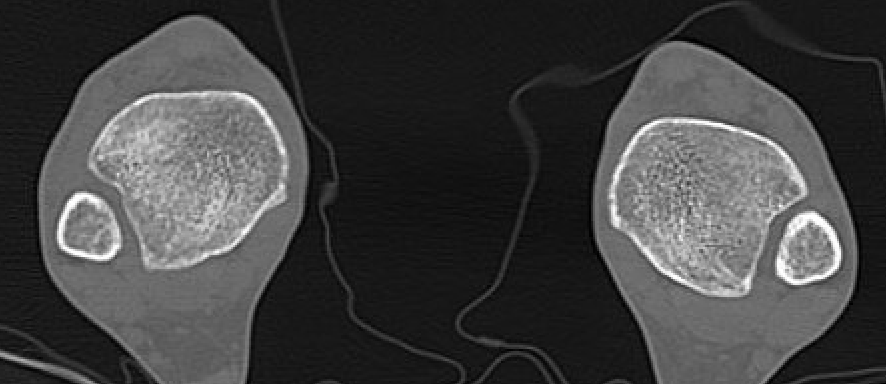
Normal bilateral axial CT
Bilateral axial CT
- compare to other side
- widening
- malrotation
- posterior malleolar fracture / Volkmann tubercle
- anterior tubercle / Tillaux-Chaput tubercle
Gifford's tibiofibular line (TFL)
- anterolateral fibula
- should be < 2 mm from tibia
< 4 mm Tibio-fibular gap
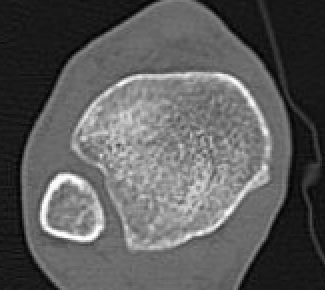
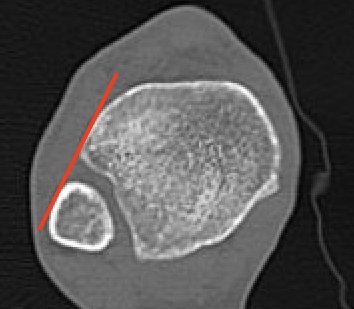
Normal Gifford's line and tibiofibular gap
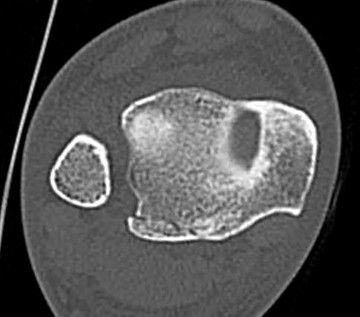
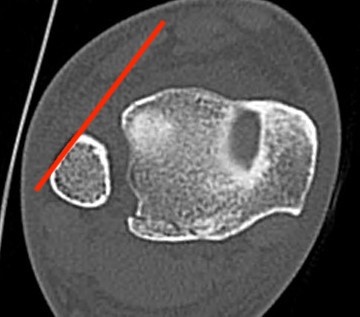
Abormal Gifford's line and increased tibiofibular gap with posterior malleolar fracture
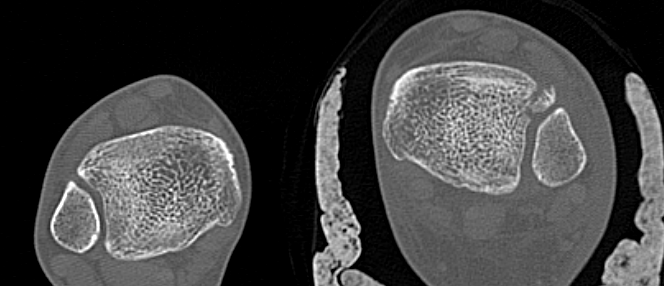
Tillaux-Chaput fracture on right with mild increased widening
MRI
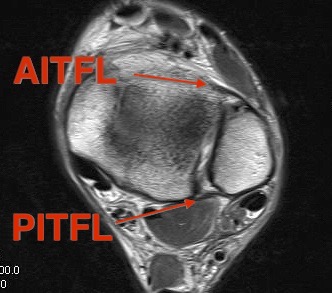
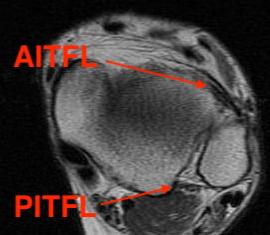
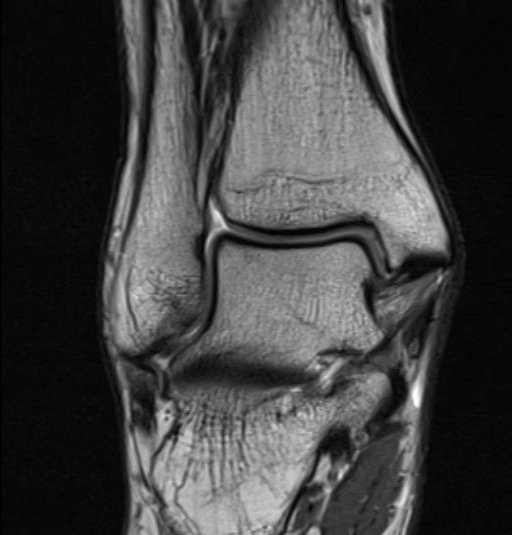
Normal anatomy
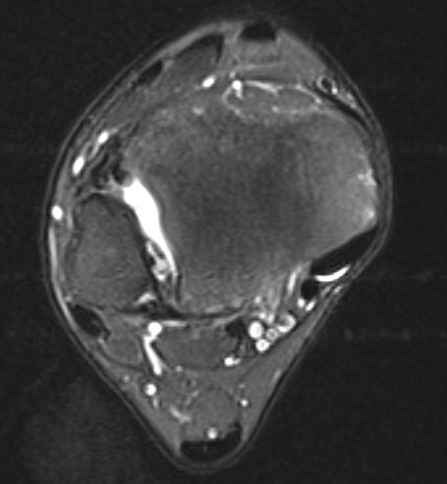
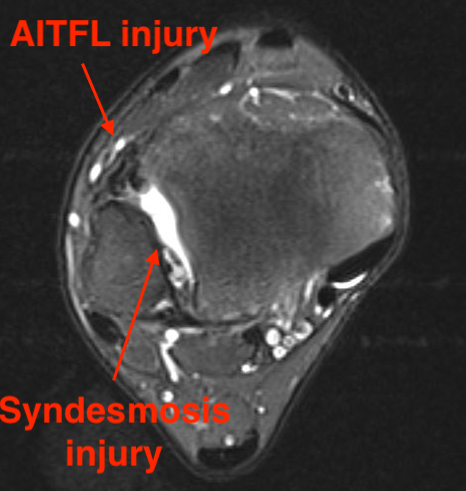
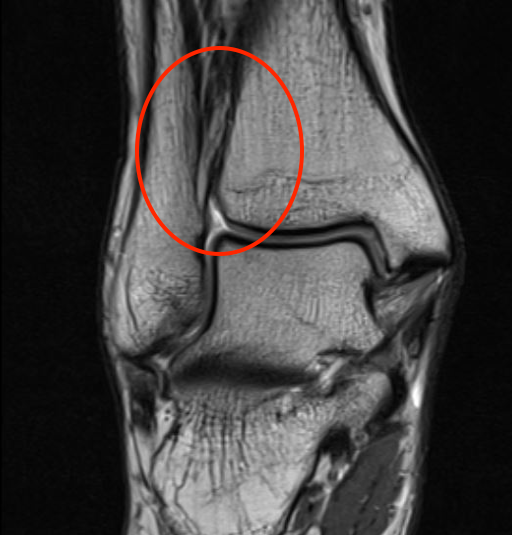
Tear of AITFL and syndesmotic injury with external rotation of the fibula
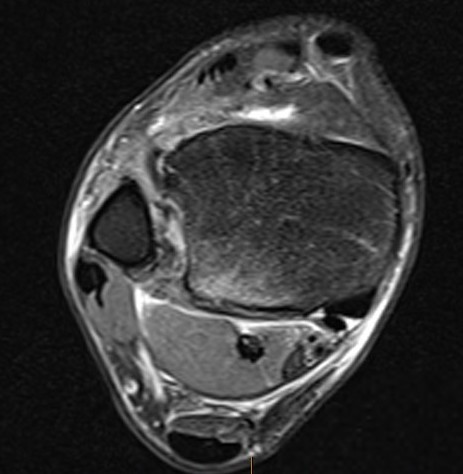
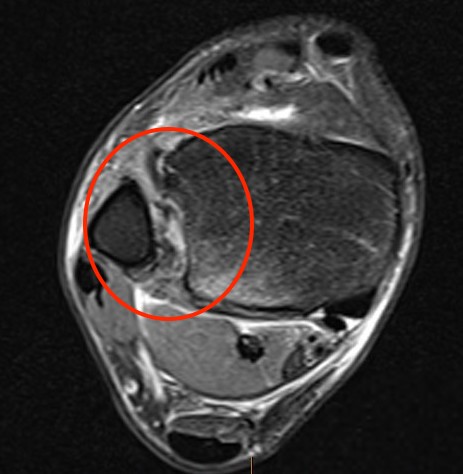
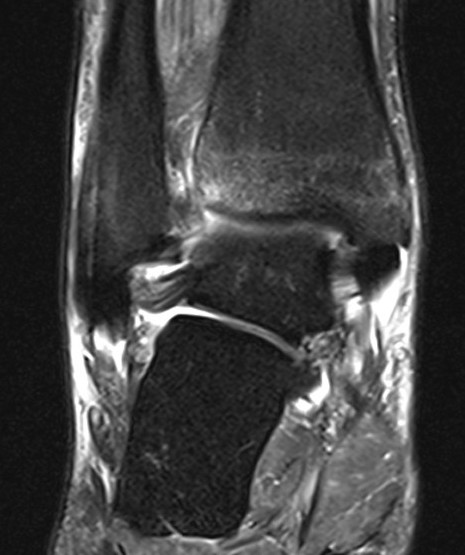
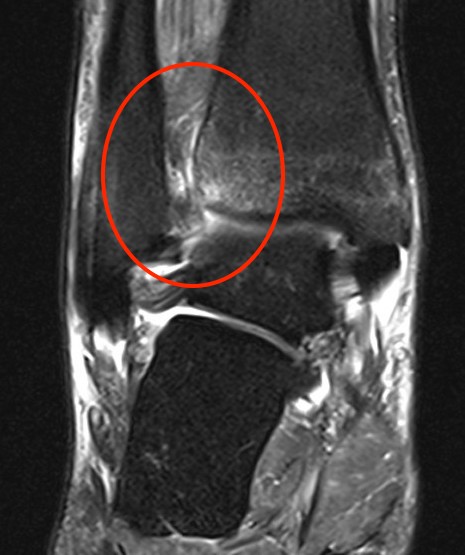
Tear of AITFL & PITFL with syndesmotic widening
Classification
Sikka MRI classification
Grade I: isolated AITFL
Grade II: AITFL + intra-osseous membrance
Grade III: AITFL + PITFL
Grade IV: AITFL + deltoid ligament
Arthroscopy
Inspect the syndesmosis with external rotation stress test
- widening > 2mm between tibia and fibula
- dynamic widening
- can also visualize AITFL and PITFL
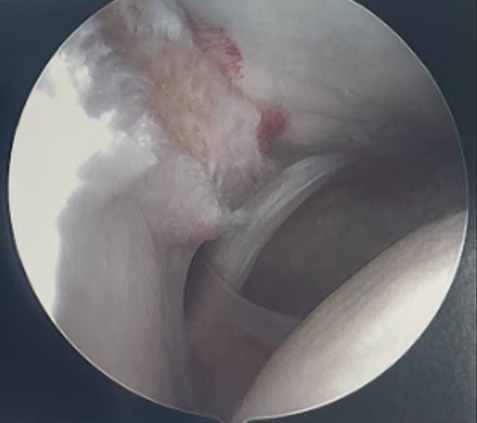
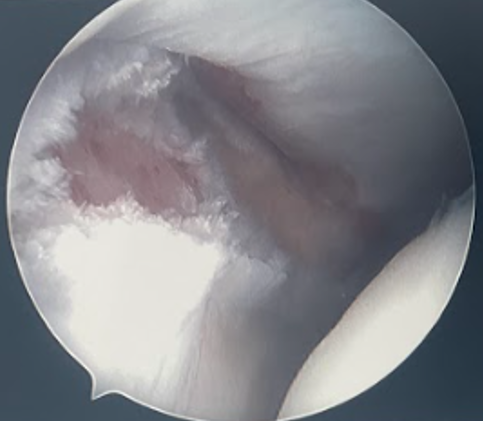
Disruption of the syndesmosis and widening with external rotation stress
Acute Syndesmotic Injuries
Nonoperative
Indication
No widening on xray / stress xray / CT
Grade I - isolated AITFL injury
Grade II - isolated AITFL injury + IOL
Operative
Indications
Widening
Dynamic widening
3 ligament injuries - AITFL+IOL+PITFL / ATIFL+IOL+PITFL
Reduction
Avoid malreduction
- arthroscopic visualization
- open reduction of syndesmosis via anterolateral approach
Spindler et al Foot Ankle Int 2024
- comparison of 2 ligament (AITFL+IOL) versus 3 ligament (AITFL+IOL+PITFL) injury
- 147 patients treated with suture button +/- screw
- increased malreduction with 3 ligament injury
Vumedi open reduction syndesmosis
Options
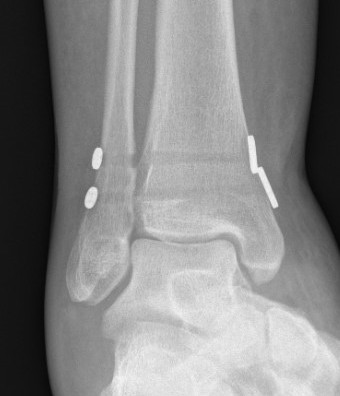
Screw fixation
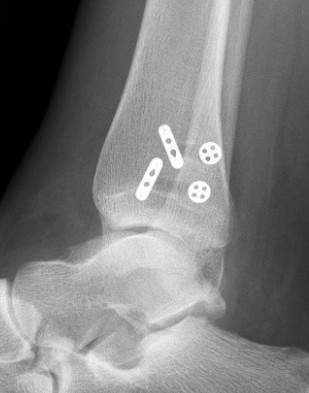
Suture button fixation
Results
Xu et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2021
- meta-analysis of 12 studies and 600 patients
- suture button had improved functional outcomes at 2 years
- suture button had reduced malreduction
- suture button had reduced implant failure / removal / irritation
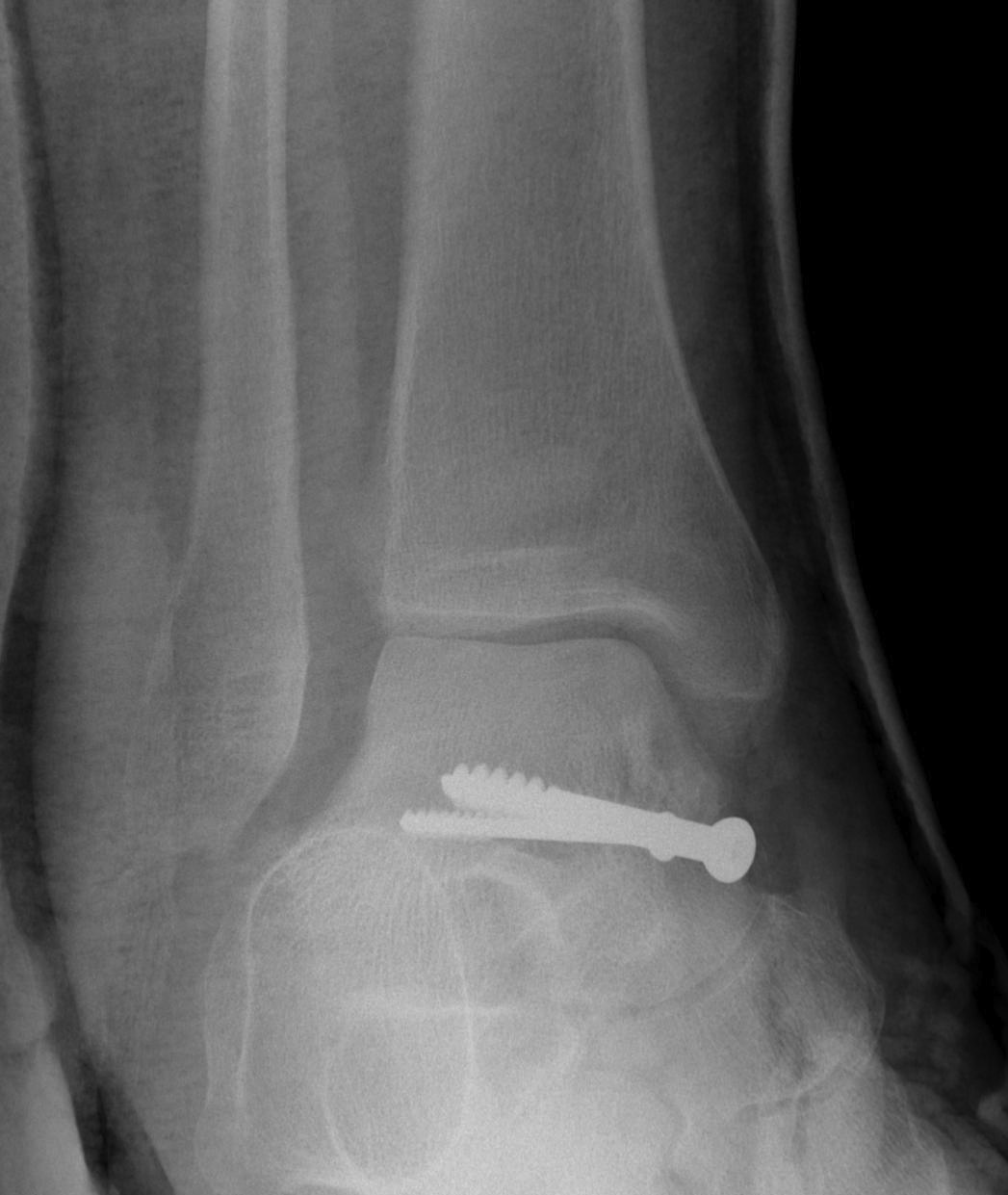
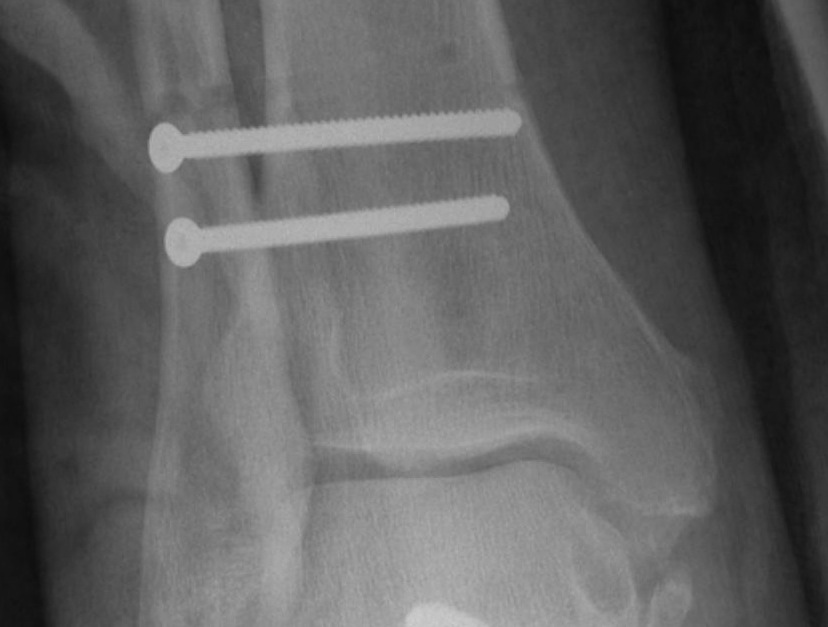
Screw fixation
Technique
AO surgery reference surgical technique
Open reduction of the distal tibio-fibular joint
Two screws
- level of syndesmosis (1.5 - 3 cm from joint)
- angle 30 degrees anterior
- 3 or 4 cortices
- 4 cortices probably more likely to break
- insert screws with ankle at neutral dorsiflexion
- consider removal at 4 - 6 months
Results
Sanders et al Bone Joint J 2021
- 150 patients RCT of routine screw removal versus on demand screw removal
- no functional difference at 1 year (or 4 years in later follow up study)
- increased complications with routine screw removal
Suture button fixation
Technique
Arthrex tightrope technique PDF
Arthrex surgical technique video
Open reduction of the tibio-fibular joint
Caution in length unstable fractures (consider fixing fibula first)
One or two suture buttons
- 1.5 - 3 cm above joint line
- angle 30 degrees anterior
- need to ensure entry point centered on fibula
- risk of saphenous nerve damage of medial side
- consider medial incision to identify and protect nerve
- talus at neutral dorsiflexion when tightening
Results
Hong et al Orthop J Sports Med 2023
- report of fibula fracture following suture button fixation in athletes
- spiral fractures / stress fractures
- associated with eccentric drill hole in fibular
Consider
- screw + suture button
- small lateral fibular plate to prevent skiving / fibular stress fracture
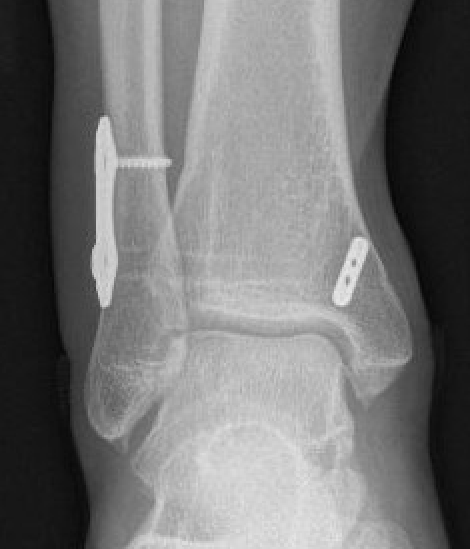
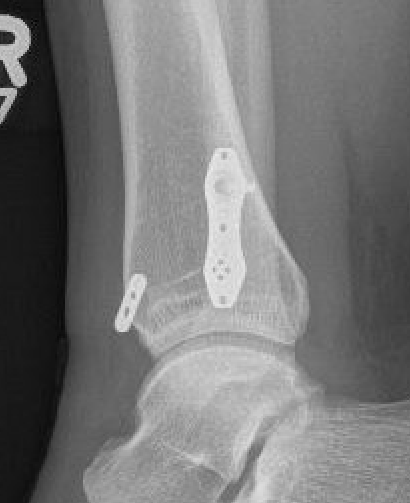
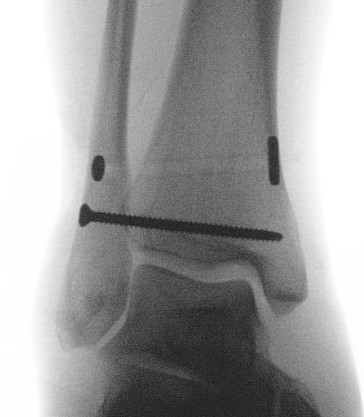
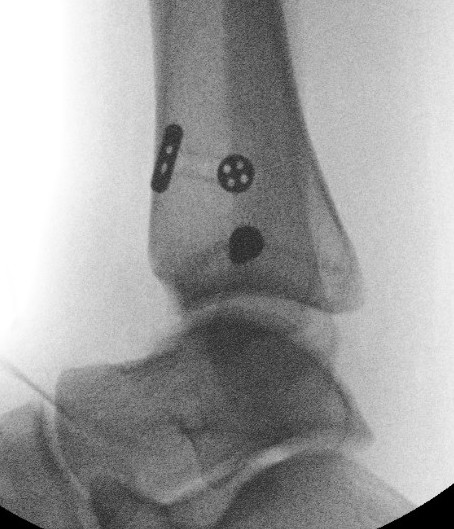
Chronic syndesmotic Injuries
Symptoms
Pain
Instability
Swelling
Signs
Tender syndesmosis
Pain on external rotation of the ankle with tibia fixed
Weight bearing rays / stress xrays / MRI
Look for signs of instability
Management
Arthroscopy and assess syndesmosis stability
Syndesmosis stable - debridement
Syndemosis unstable
- arthroscopic debridement
- + syndesmotic stabilization
- +/- AITFL repair +/- periosteal flap repair +/- ligament reconstruction
Technique
Vumedi syndesmosis ligament reconstruction
Arthroscopy techniques PDF syndesmosis ligament reconstruction
Results
- systematic review of autogenous ligament reconstruction for chronic instability
- 5 studies and 50 patients
- improvements in functional outcomes
Colcuc et al Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2016
- 32 chronic instability syndesmosis
- arthroscopic instability < 1.5mm: suture AITFL + screw + tightrope
- arthroscopic instability 1.5 - 2.5mm: periosteal flap + screw + tightrope
- arthroscopic instability > 2.5mm: plantaris ligament reconstruction + screw + tightrope