Epidemiology
10 - 30% of clavicle fractures
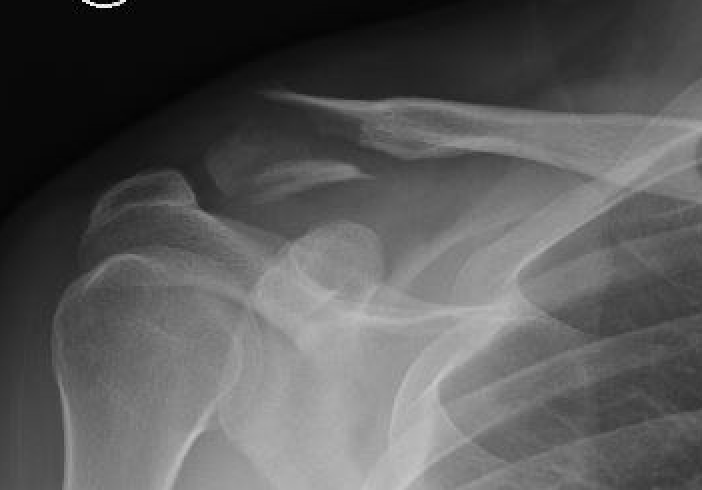
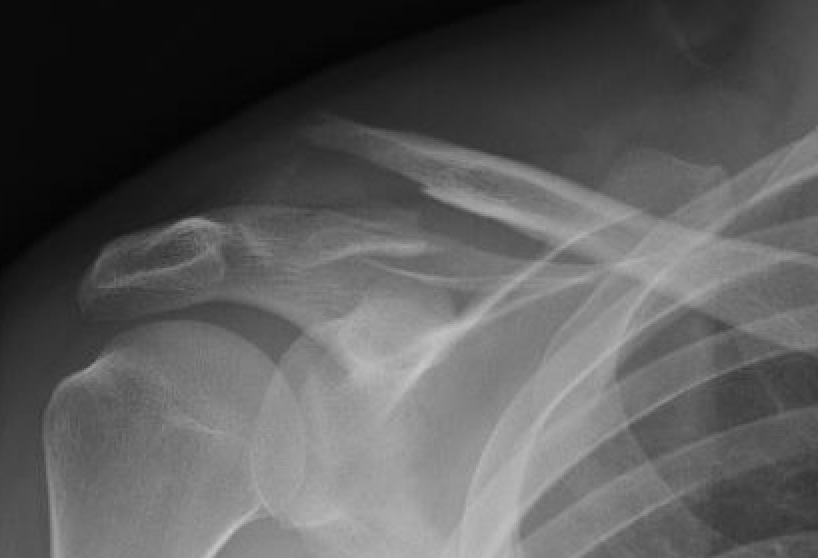
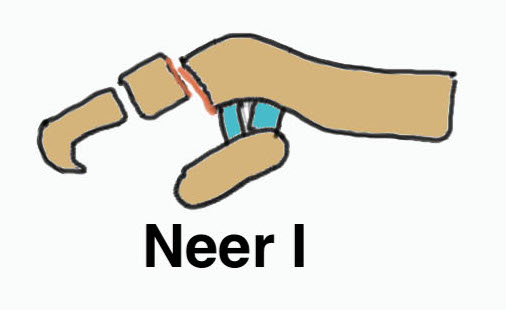
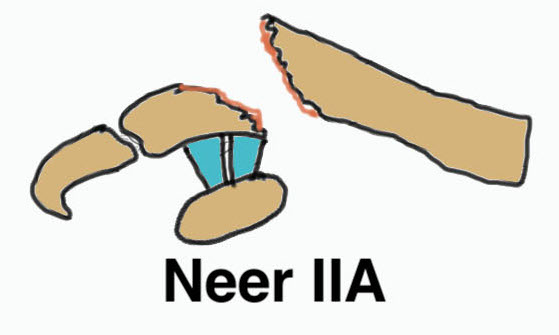
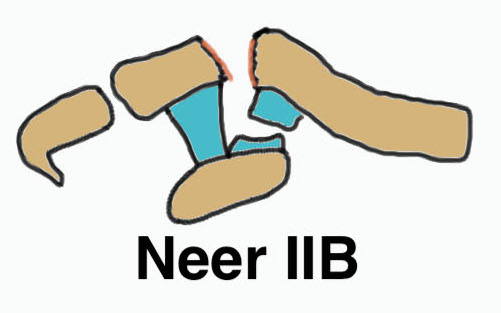
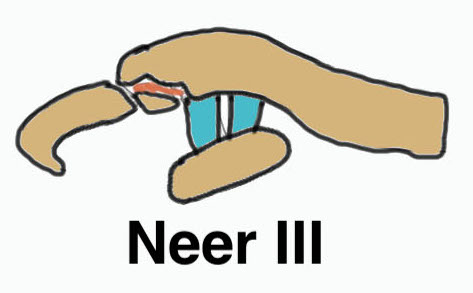
Neer Classification
 |
 |
 |
|
Fracture lateral to the CC ligaments Non displaced
|
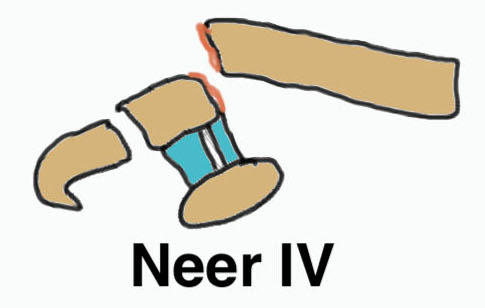
Fracture medial to the CC ligaments CCL ligaments attached to lateral fragment Medial fragment displaced superiorly |
Between conoid and trapezoid Conoid disrupted Trapezoid remains attached to the lateral fragment |
 |
 |
 |
|
Lateral to CC ligaments Intra-articular extension Stable |
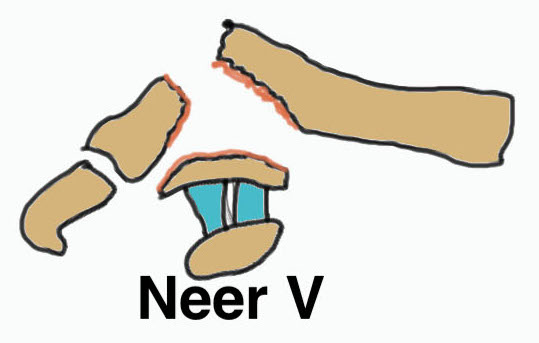
Periosteal sleeve disruption Pediatric Medial fragment displaced |
Comminuted Type II Medial fragment displaced |
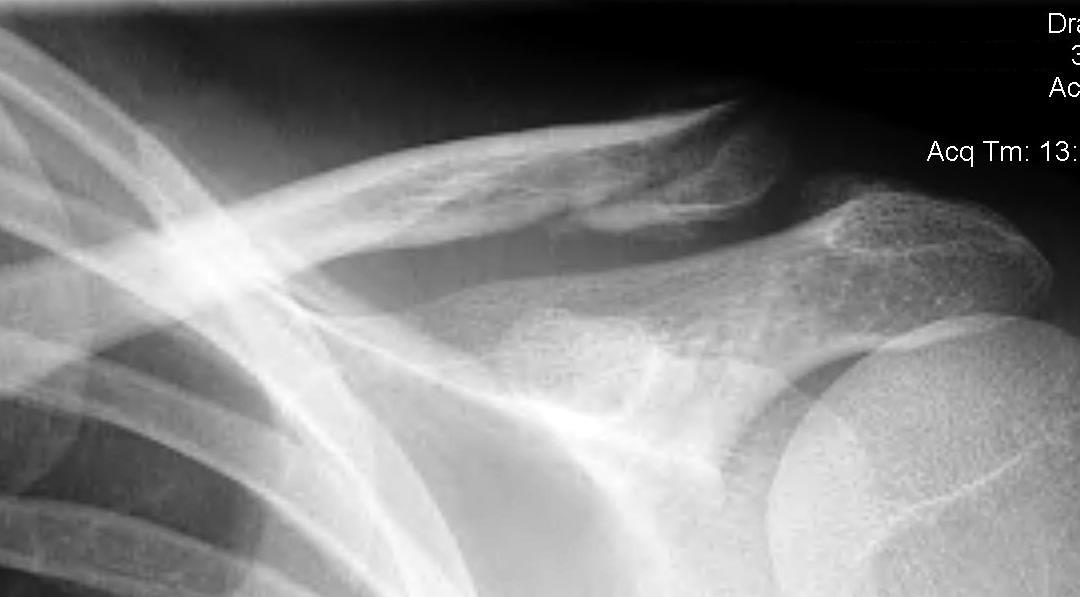
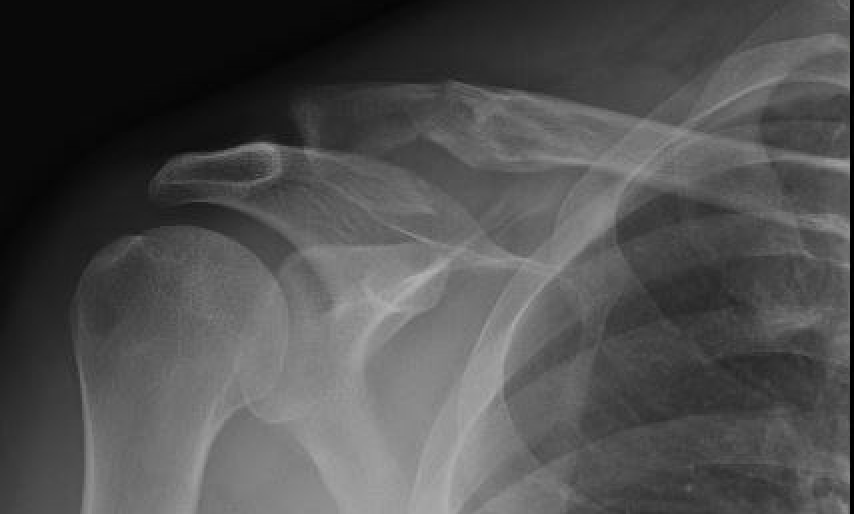
Type I
Type II
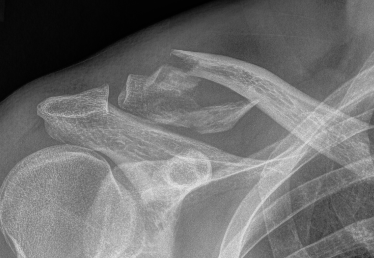
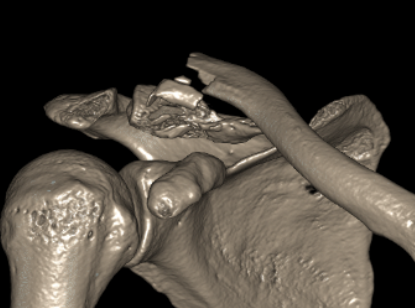
Type V
Nonunion
Robinson and Cairns JBJS Am 2004
- cohort of 100 displaced Type II fractures treated nonoperatively
- 11 had symptomatic nonunion
- 21 had asymptomatic nonunion
- reasonable outcome scores with nonunion
- recommended non operative treatment in middle aged / elderly
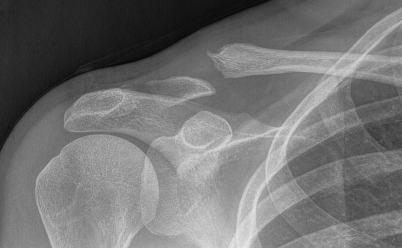
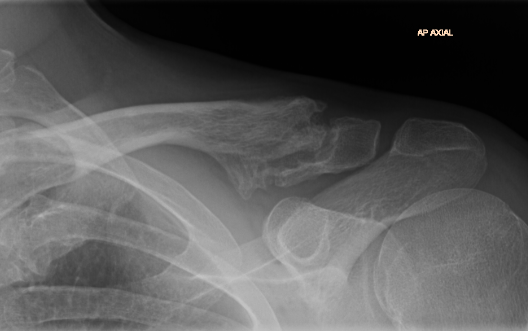
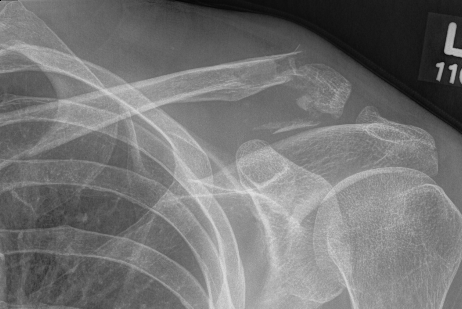
Operative Management
Indications
Displaced fracture in young people: Type II, Type V
Compound fractures
Skin compromise
Non union
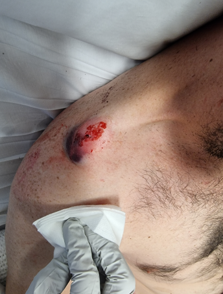
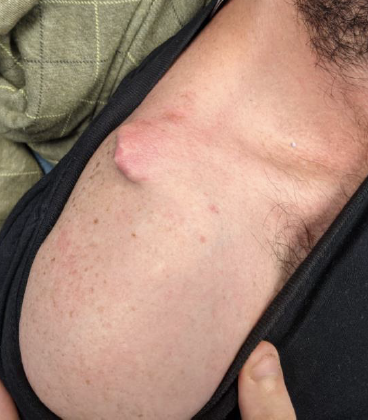
Options
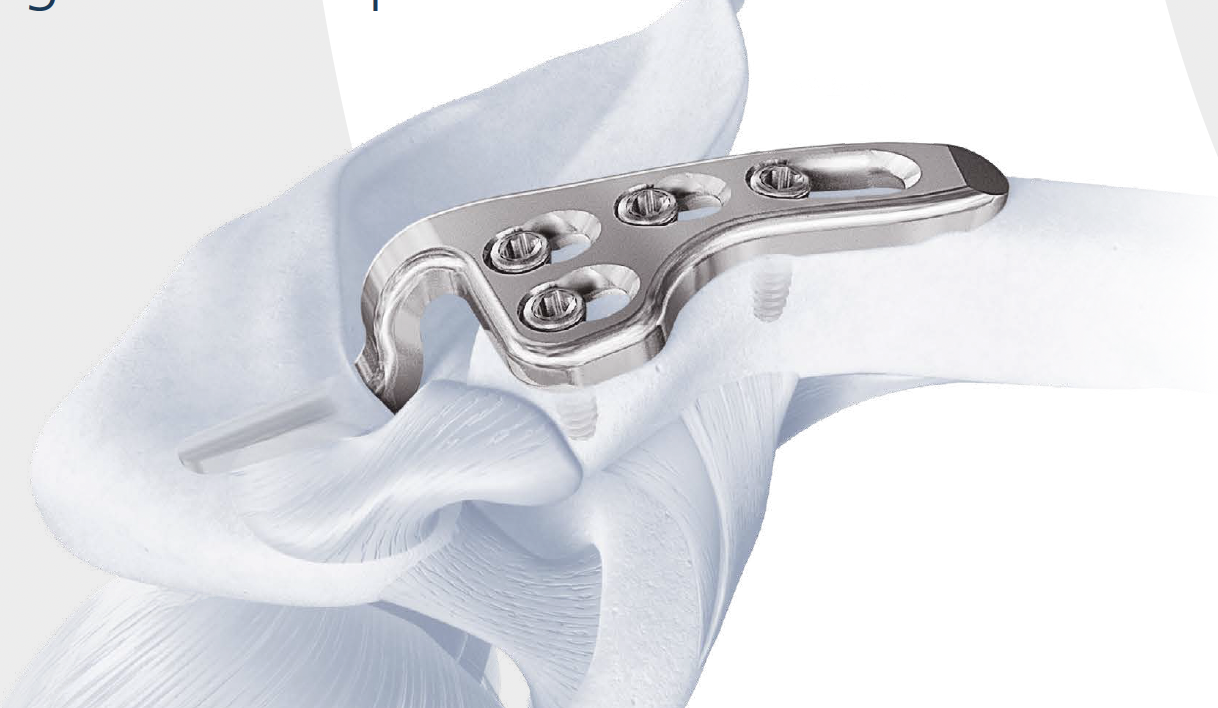
Dorsal locking plate +/- CC ligament reconstruction
Hook plate
Coracoclavicular fixation
Hook plate versus locking plate
- systematic review of 523 patients
- comparison hook plate and dorsal locking plate
- mean 3 year follow up
- no difference in outcome scores
- better reduction with hook plate
- increased nonunion with locking plate
- increased complications with hook plate
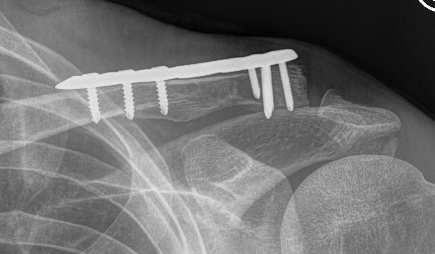
Dorsal locking plate +/- CCL reconstruction
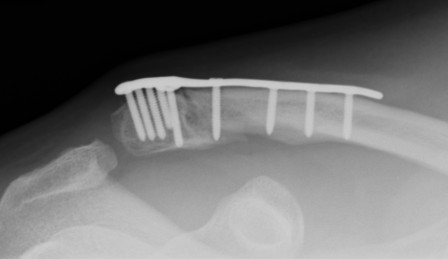

Advantage
No need to remove
Disadvantage
Lateral screws under significant tension and subsequently higher rate of screw/plate pull-out
Indication
Sufficient lateral bone to obtain fixation
Consider having hook plate available / supplement with coraco-clavicular fixation
Technique
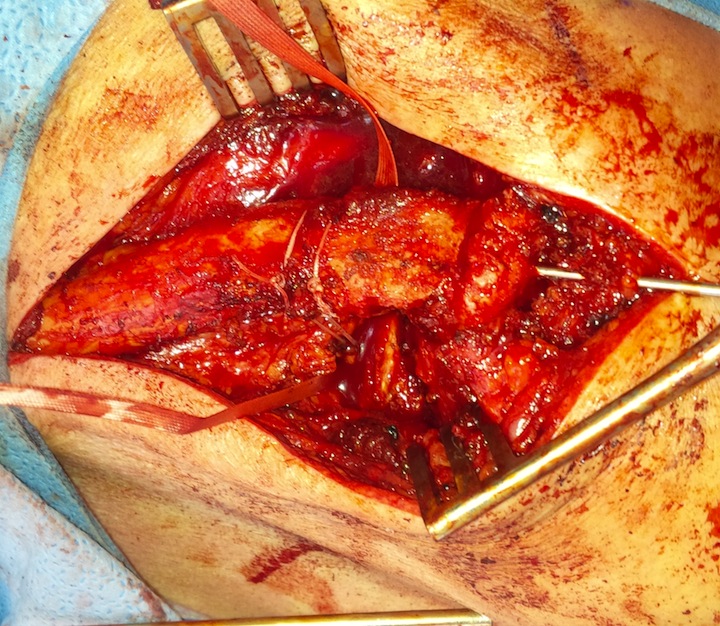
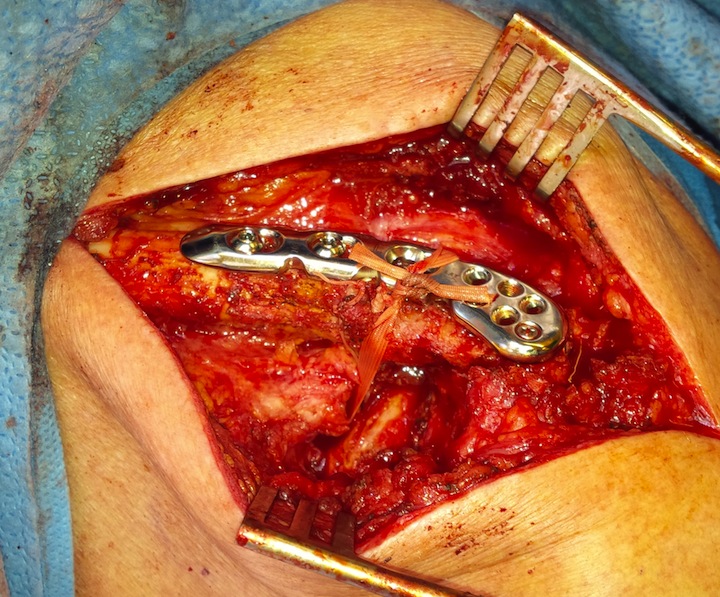
Dorsal locking plate with cerclage fibretape
Vumedi dorsal locking plate + CCL reconstruction
Lazy beach chair
- divide deltoid-trapezius fascia
- expose clavicle
- clean and reduce fracture
- plate fracture
- expose coracoid
- suture anchor / suspensory fixation / cerclage tape or graft
Results
- precontoured distal locking plate in 35 patients
- all united at mean of 4 months
- excellent outcomes scores
Xu et al BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2019
- 16 patients with locking plate versus 18 with plate + CC suture anchors
- shorter union time (14 v 16 weeks) and better outcomes (94 v 90 Constant) with suture anchors
Hook Plate
Advantage
Mechanically secure
Disadvantage
Needs to be removed
- subacromial impingement
- acromial erosion
- shoulder stiffness
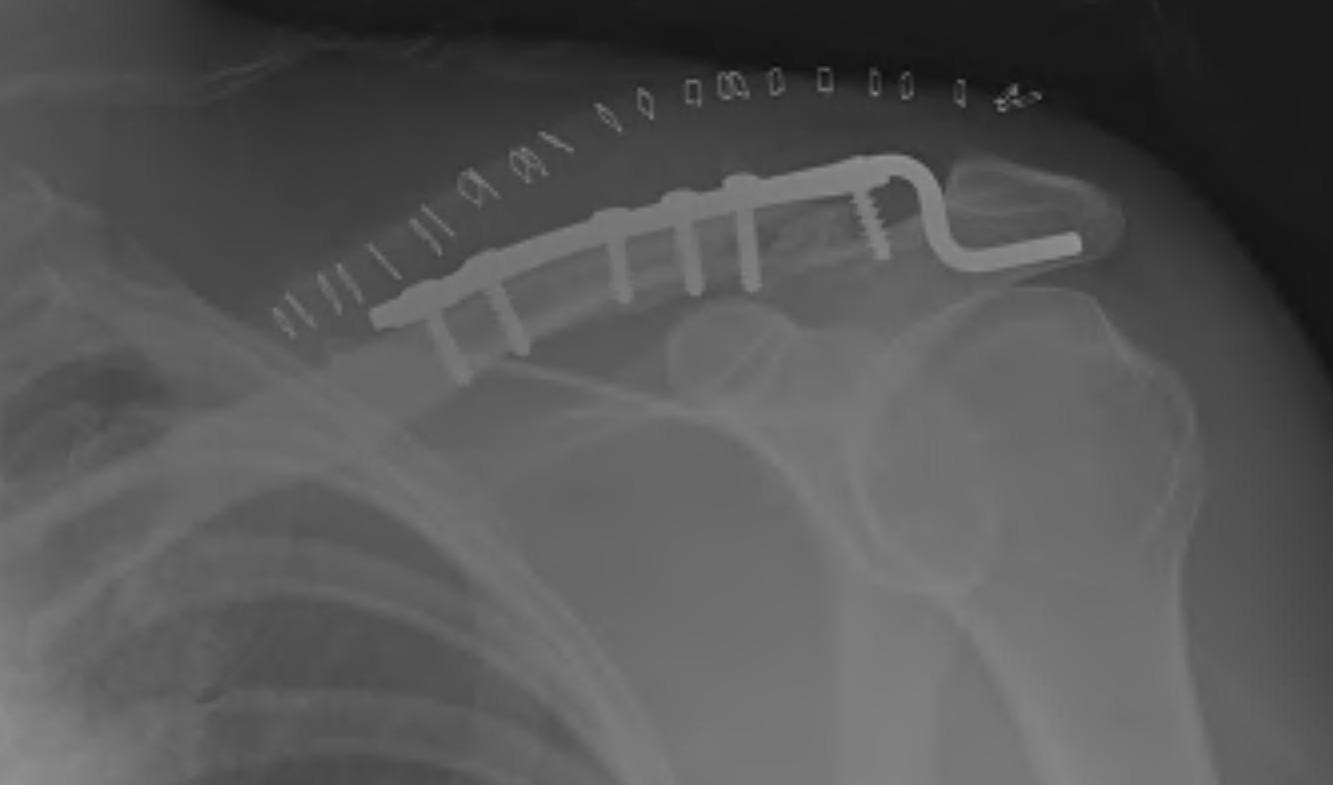
Technique

Synthes surgical technique PDF
AO surgery reference hook plate technique
Lazy beachchair
- tilt head away
- split delto-trapezius fascia to expose clavicle
- clean and reduce fracture
- detach trapezius from medial acromion to facilitate hook passage under acromion
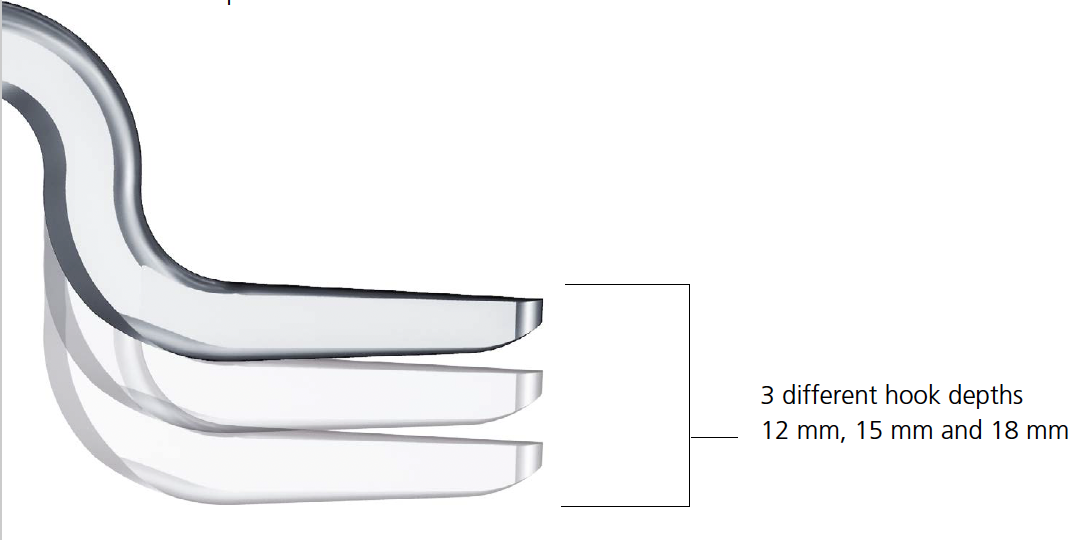
- trial different hook depths +/- image intensifier
- avoid over-reduction / insufficient hook depth increases risk of acromial erosion
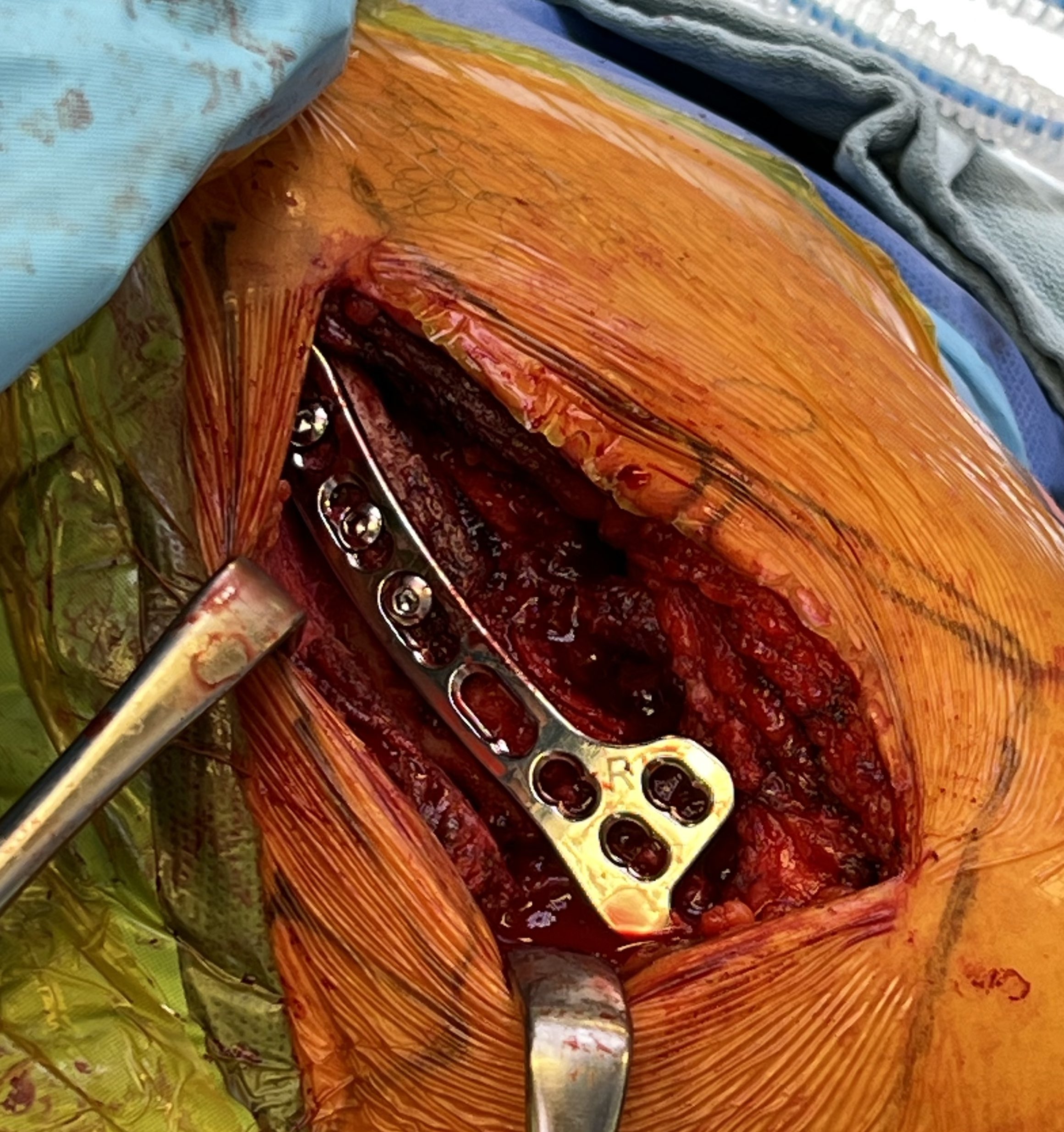
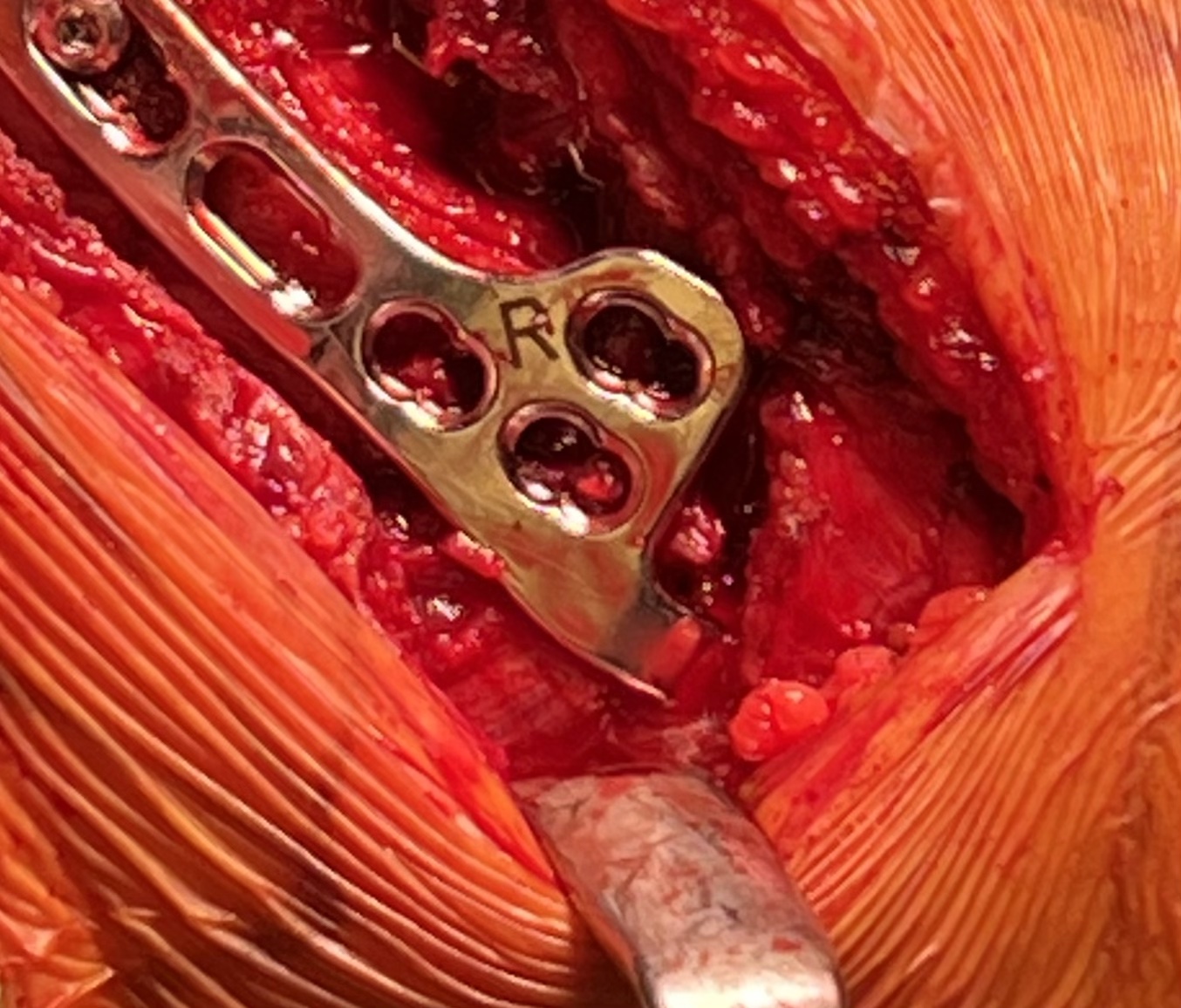
Results
- 36 patients with displaced distal clavicle fractures treated with hook plate
- 95% union rate
- mean time to union 3 months
- hook plate removed in 92%
- 2 patients presented with late falls and fractures medial to the plate
- 35 patients with displaced distal clavicle fractures treated with hook plate
- 100% union rates
- 23% shoulder stiffness
- 17% subacromial erosion
Complications
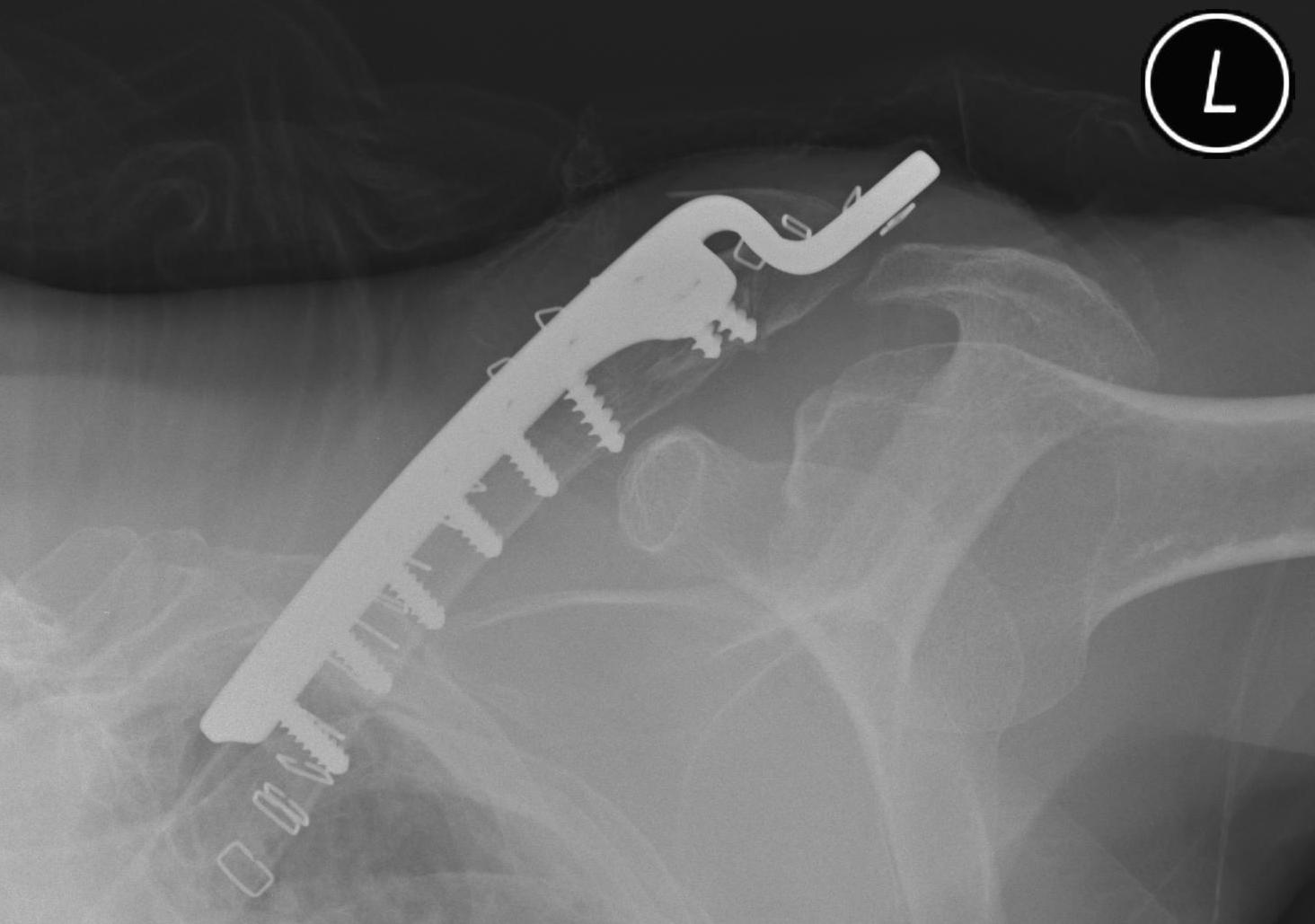
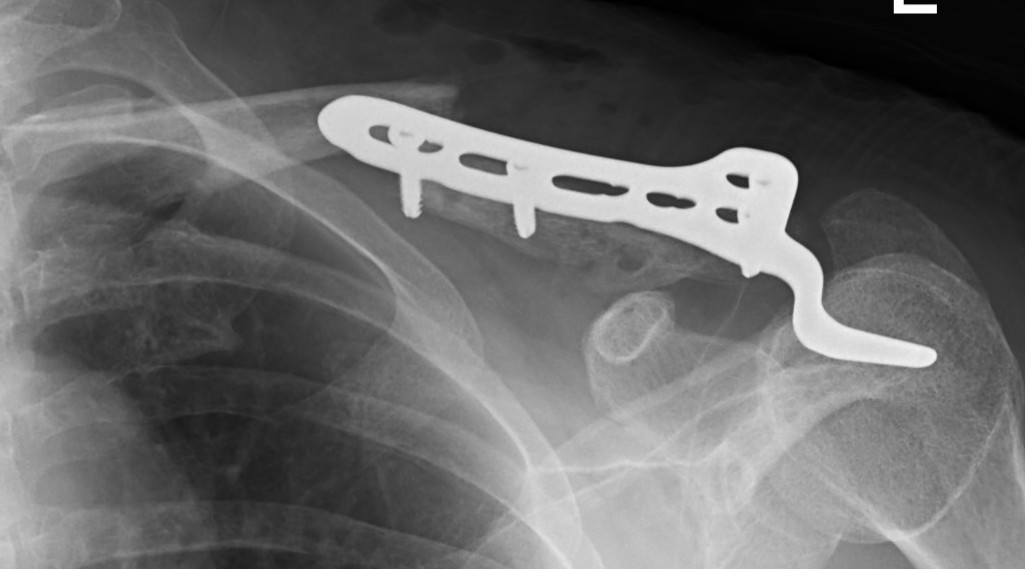
Hook not under acromion Periprosthetic fracture
Coracoclavicular reconstruction
Technique
Results
Malik et al Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2023
- systematic review of open CCL reconstruction in distal clavicle fractures
- 18 studies and 330 cases
- 98% union rate
- 7.6% complication rate
- systematic review of arthroscopic CCL reconstruction in distal clavicle fractures
- 14 studies
- union rate varied form 70% to 100%
Non-Union
Options
1. Large fragment - bone graft / ORIF
2. Small fragment - excise open / arthroscopic
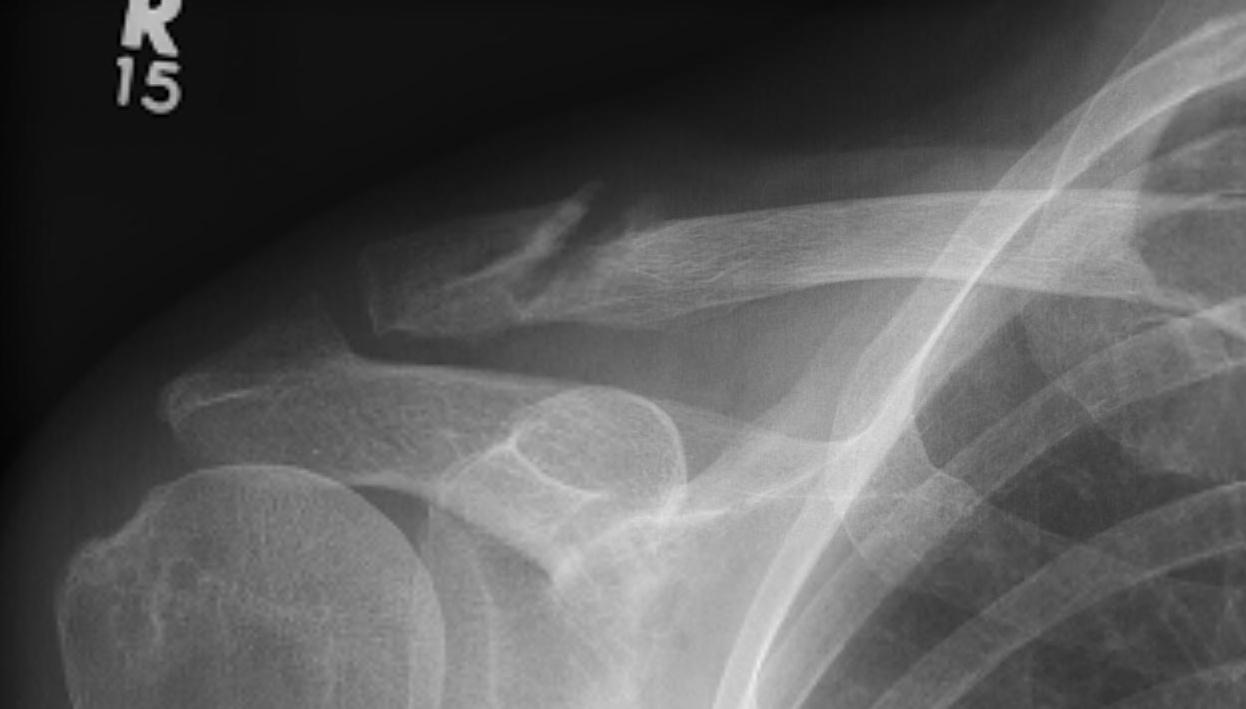
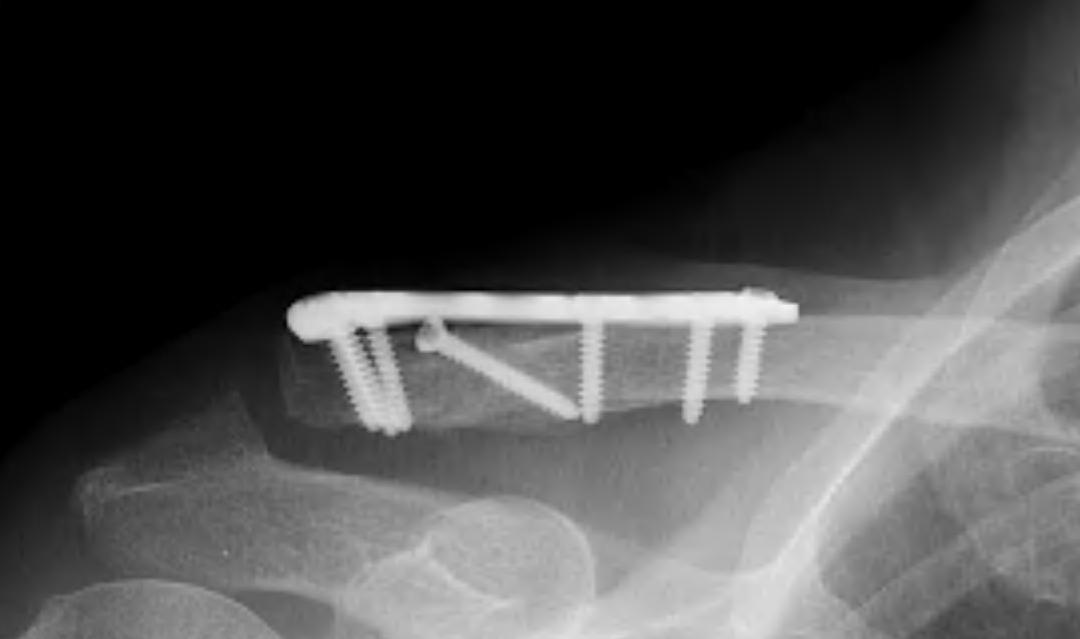
ORIF of nonunion with large distal fragment
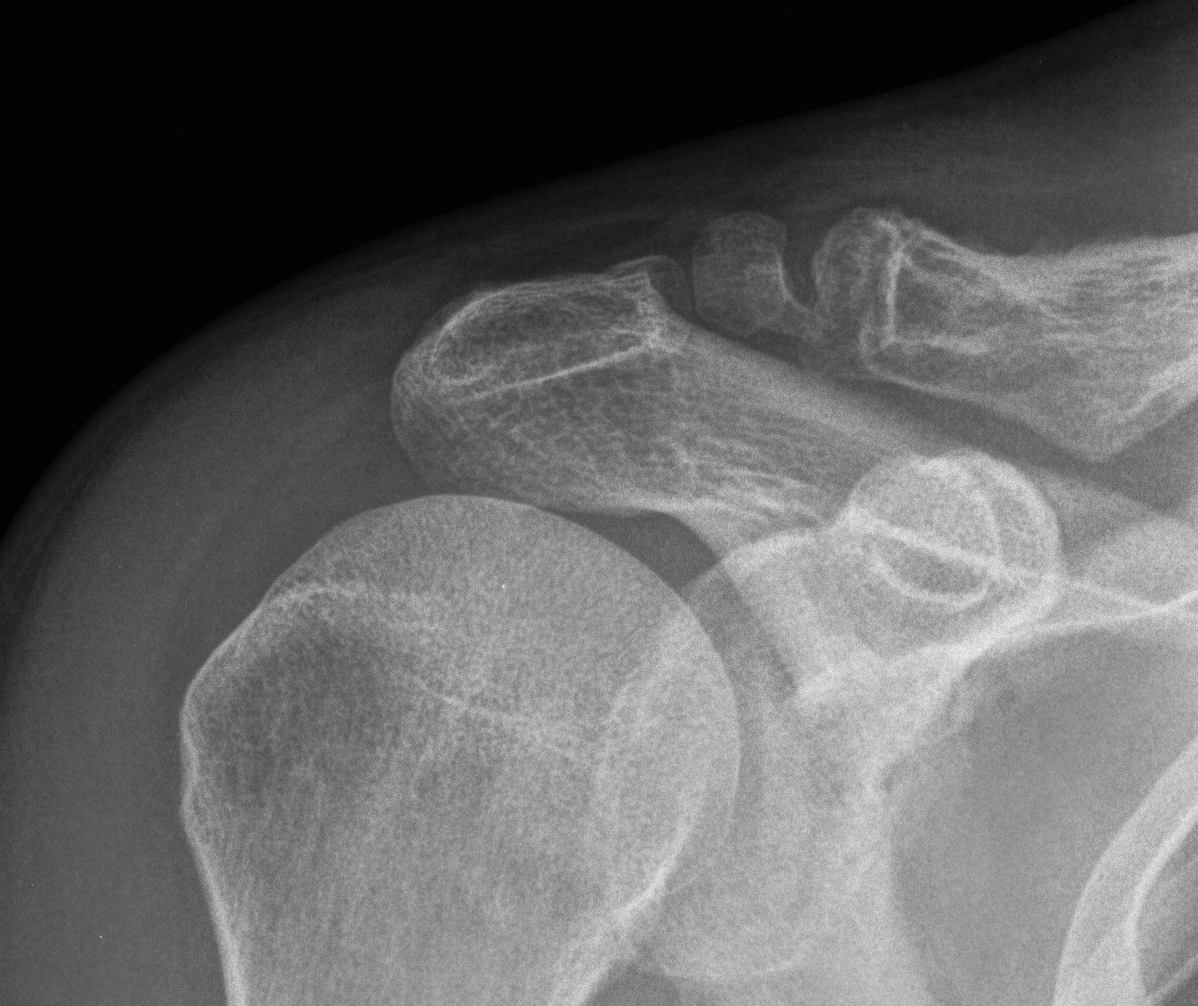
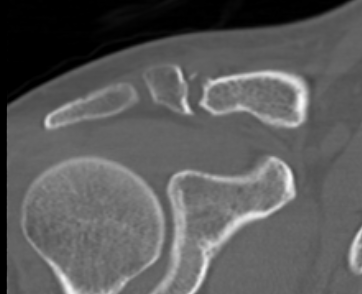
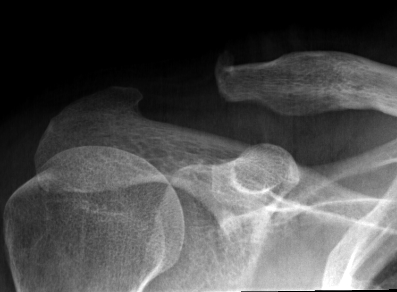
Open excision of small distal nonunion fragment