Definition
Hereditary Multiple Exostosis (HME)
Heritable skeletal dysplasia characterised by multiple osteochondromas
Epidemiology
1:50,000
Etiology
AD with variable penetrance (96%)
90% of HME associated with mutation in EXT1 or EXT2 gene
- part of proteoglycan synthesis
- requires a second genetic hit to create the disease
Malignant Transformation
Incidence
Fei J Bone Oncol 2018
- systematic review
- incidence of chondosarcoma 4%
- 75% between age 20 - 40
- 56% pelvis and proximal femur
Danger areas / central
- pelvis / proximal femur
- scapula / proximal humerus
Screening
Van der Woude et al Skeletal Radiol 2023
- total body MRI in 355 patients with HME
- 9/366 (2.5%) MRIs found suspicious lesions that ultimately were chondrosarcomas
- all in flat bones (pelvis / ribs / scapula)
Clinical
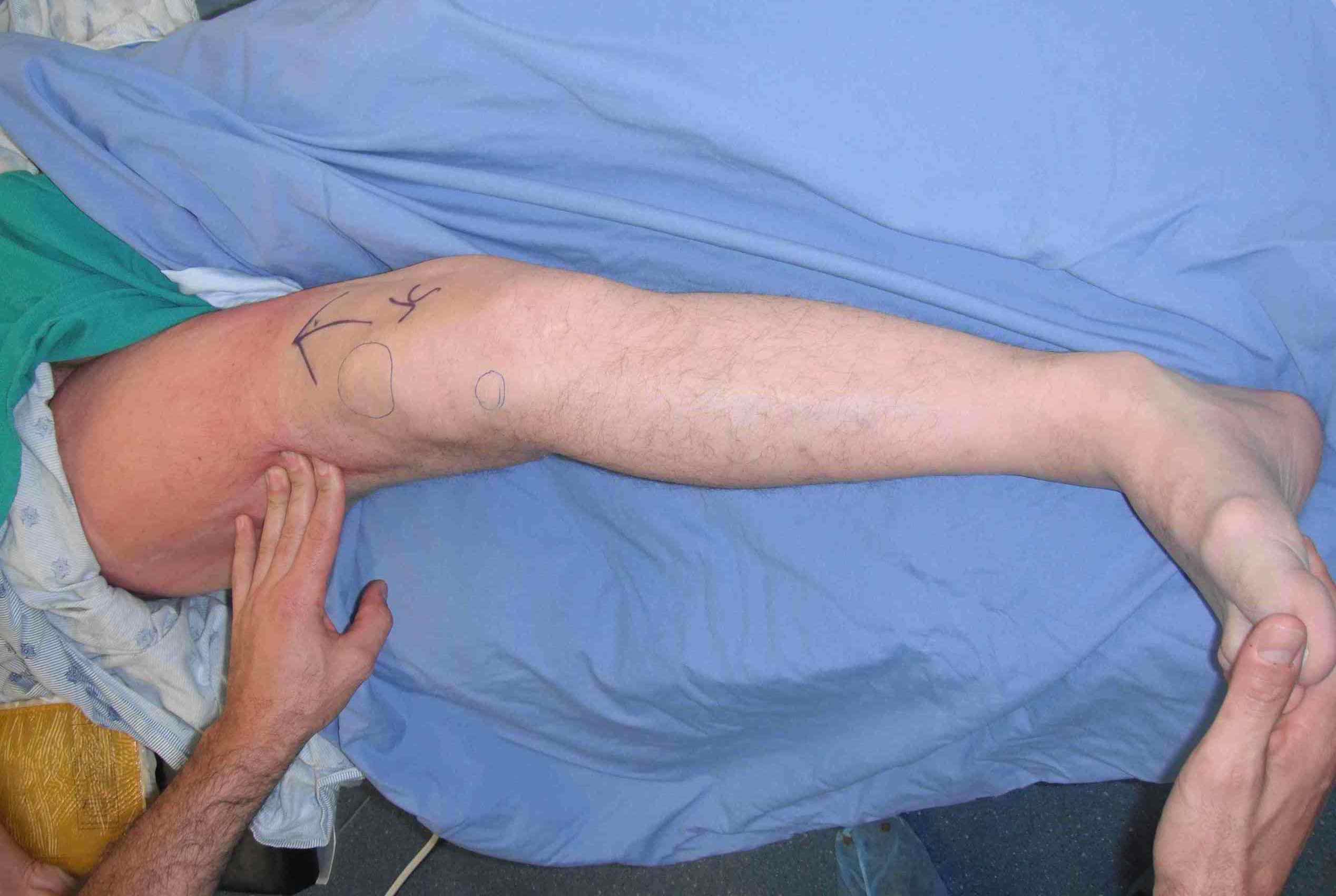
Commonly presents as skeletal deformity, such as Madelung deformity
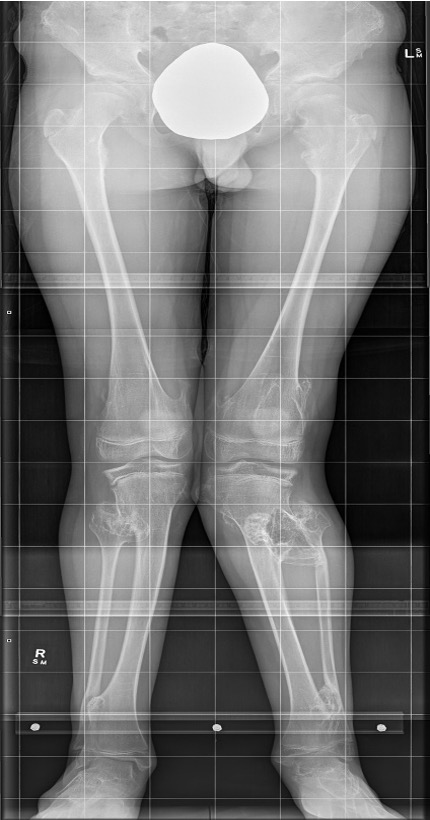
Lower limbs
- mildly short stature
- eg length discrepancies
- valgus knees / valgus ankle
- common peroneal compression
Upper limb
- scapular winging
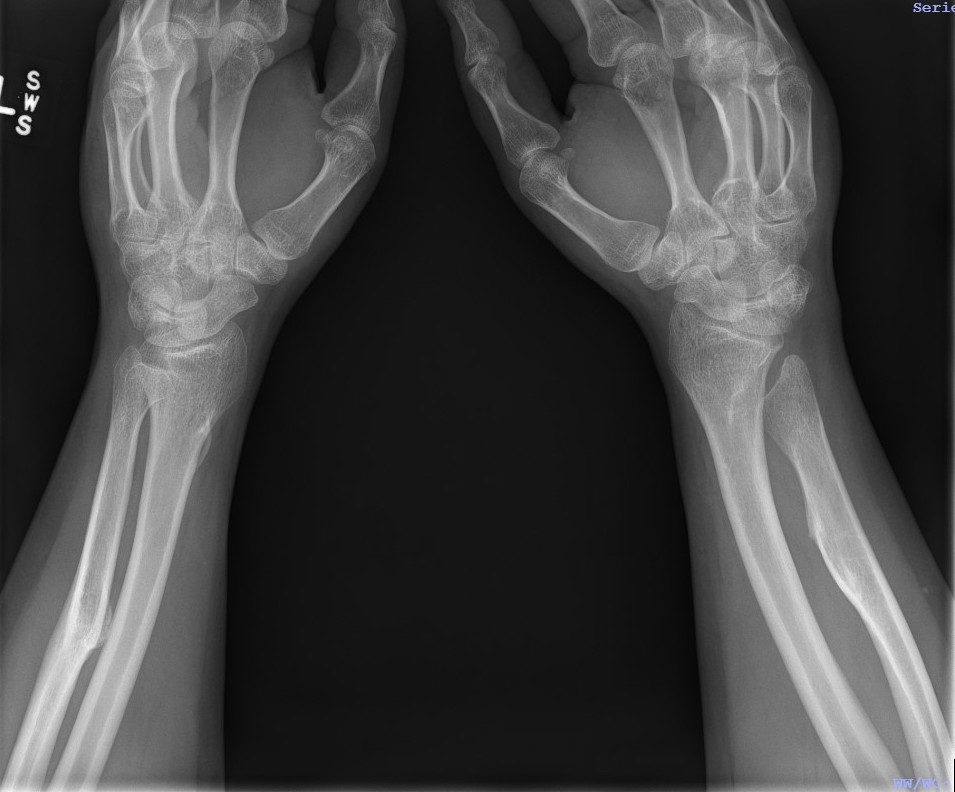
- forearm bowing / ulnar deviation of wrist / loss of pronation / supination
Spinal stenosis
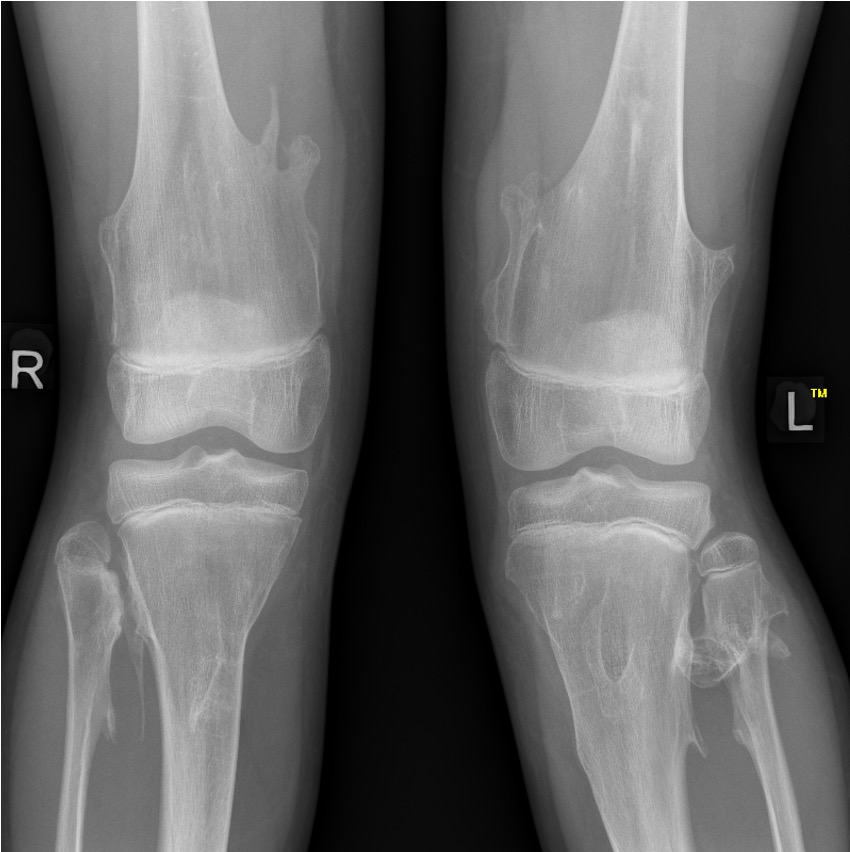
X-ray
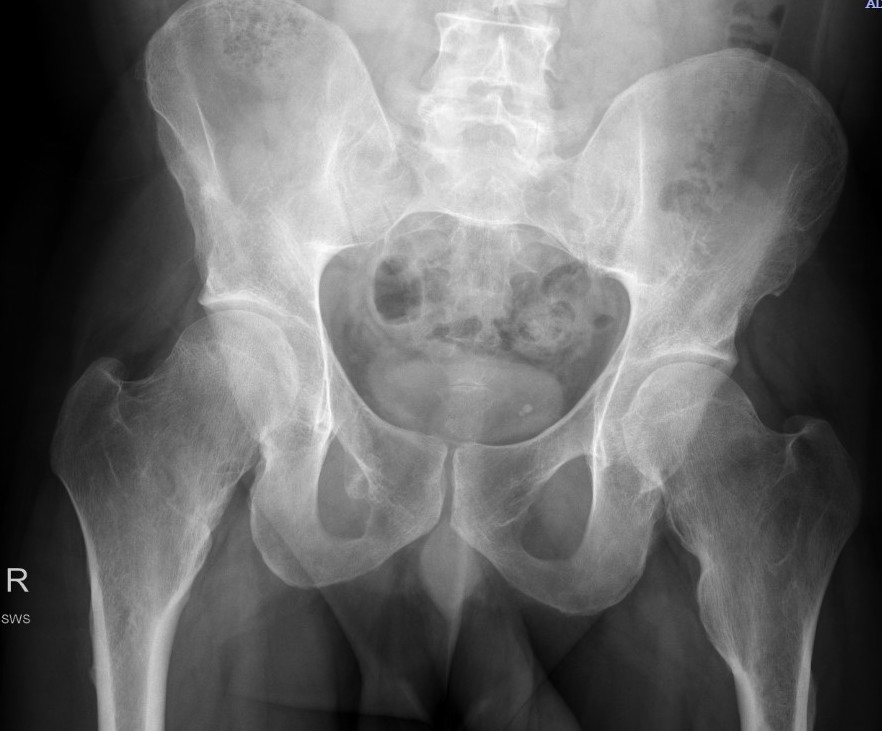
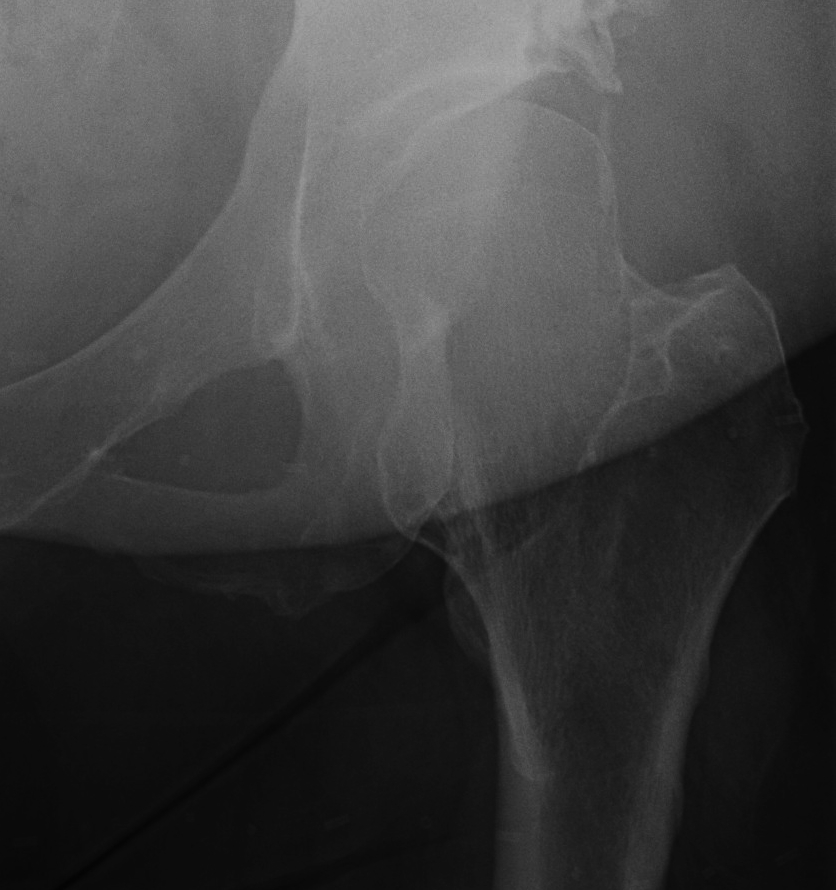
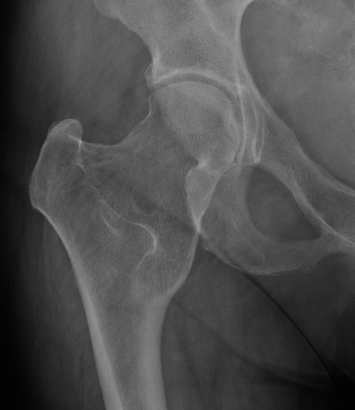
Hip
- coxa valga
- neck short & broad
Knee - genu valgum


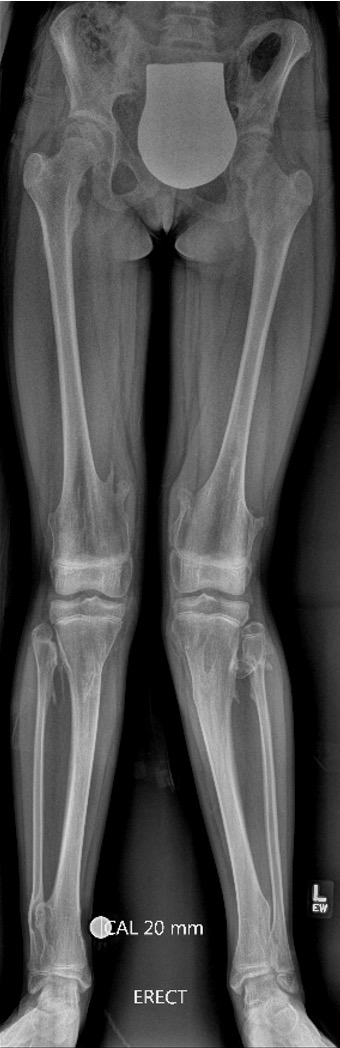
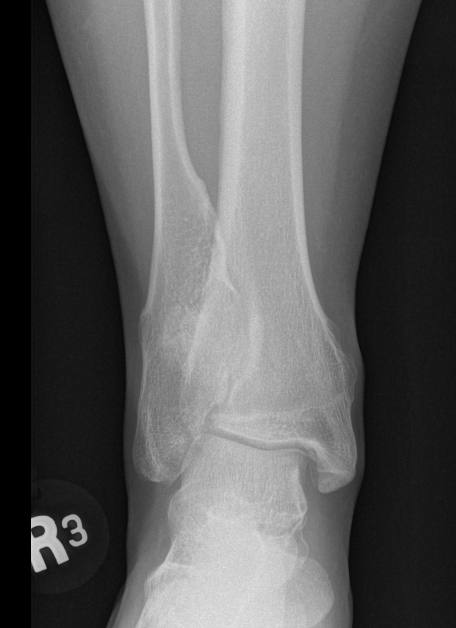
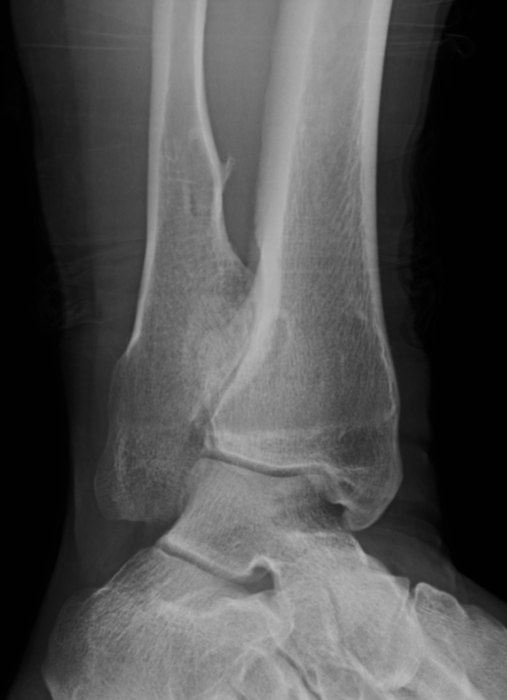
Ankle
- valgus
- fibular shortening with valgus distal tibia
- wedge-shaped distal tibial epiphysis
- leads to valgus talar tilt in abnormal mortise
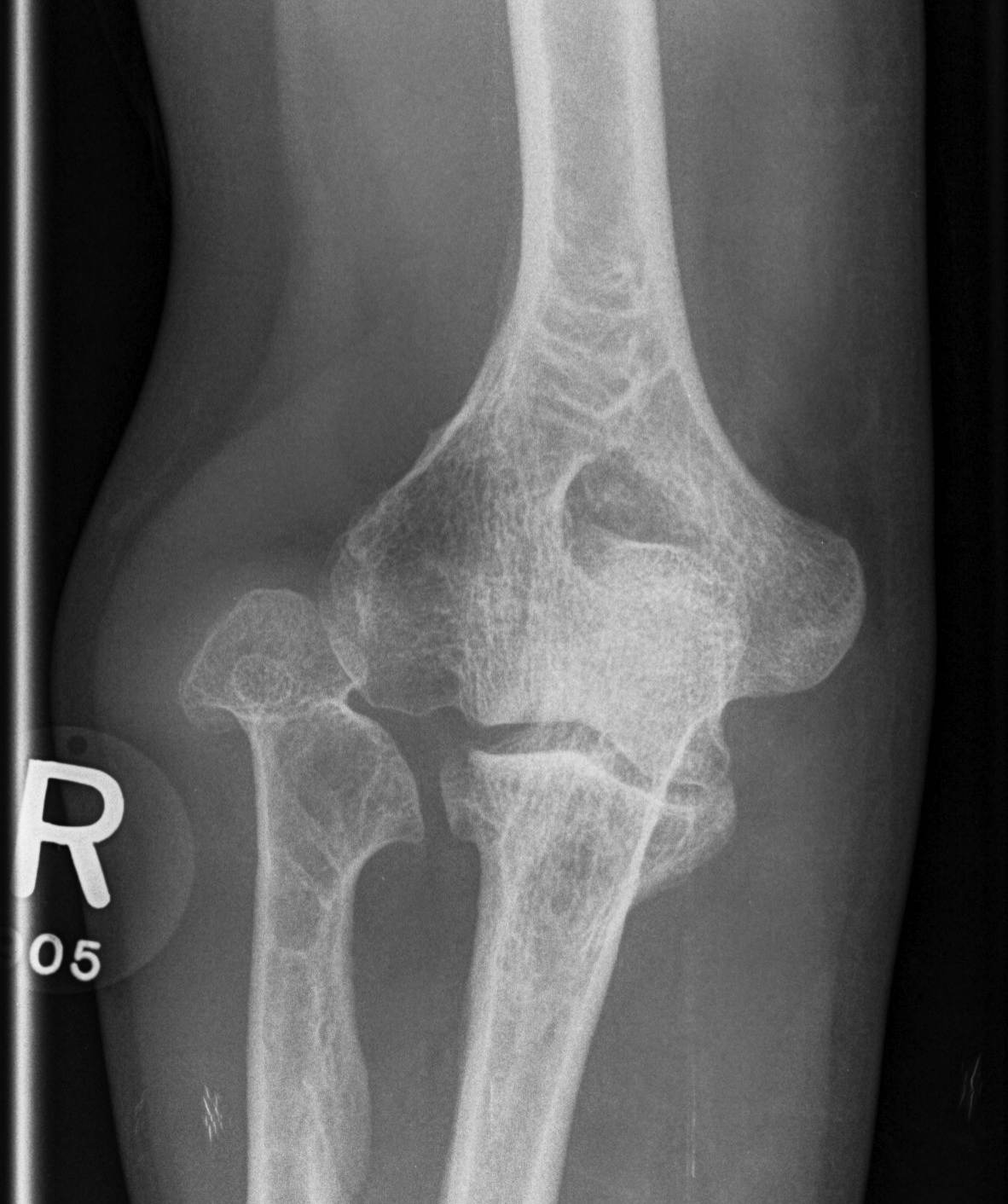
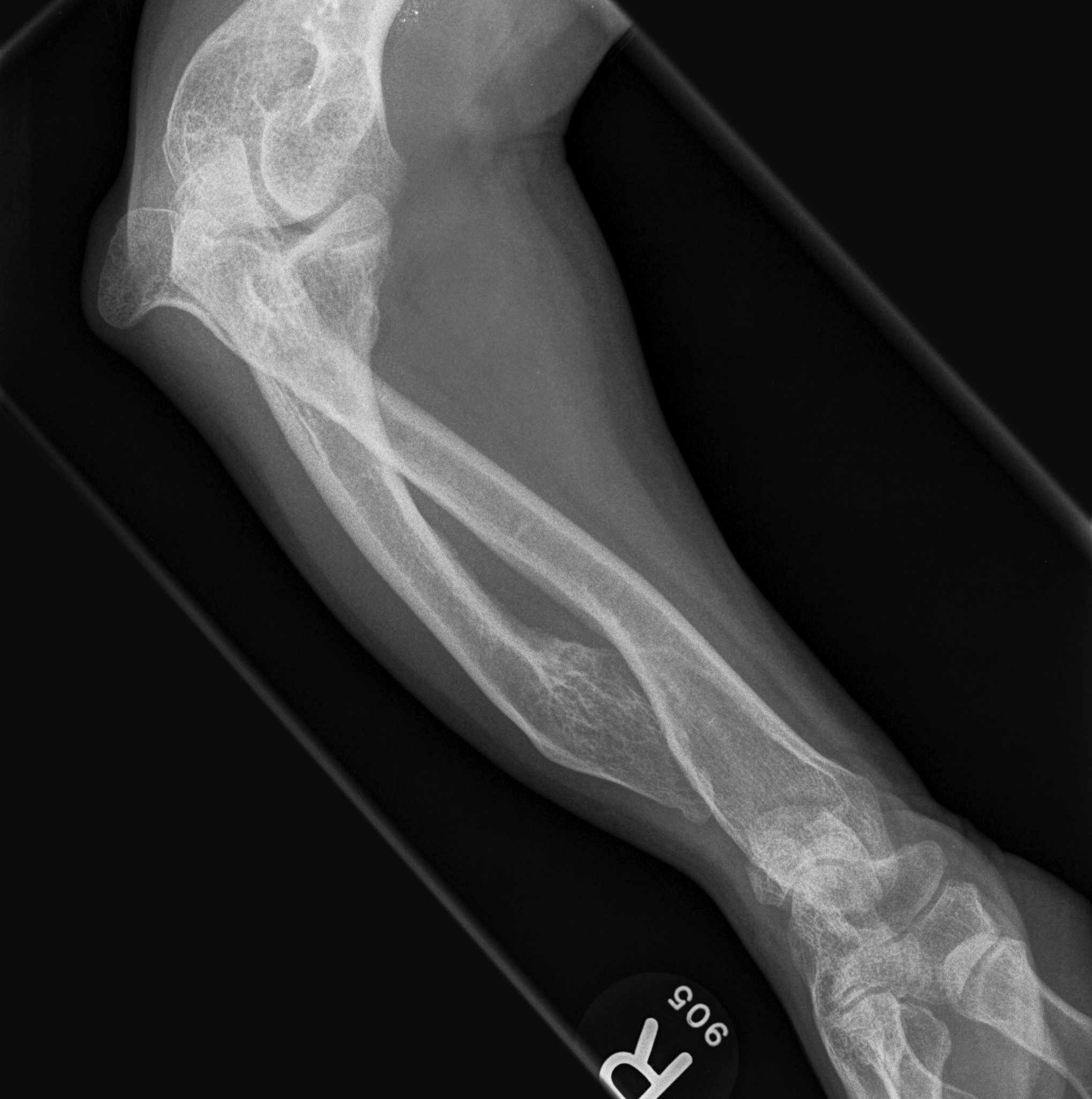
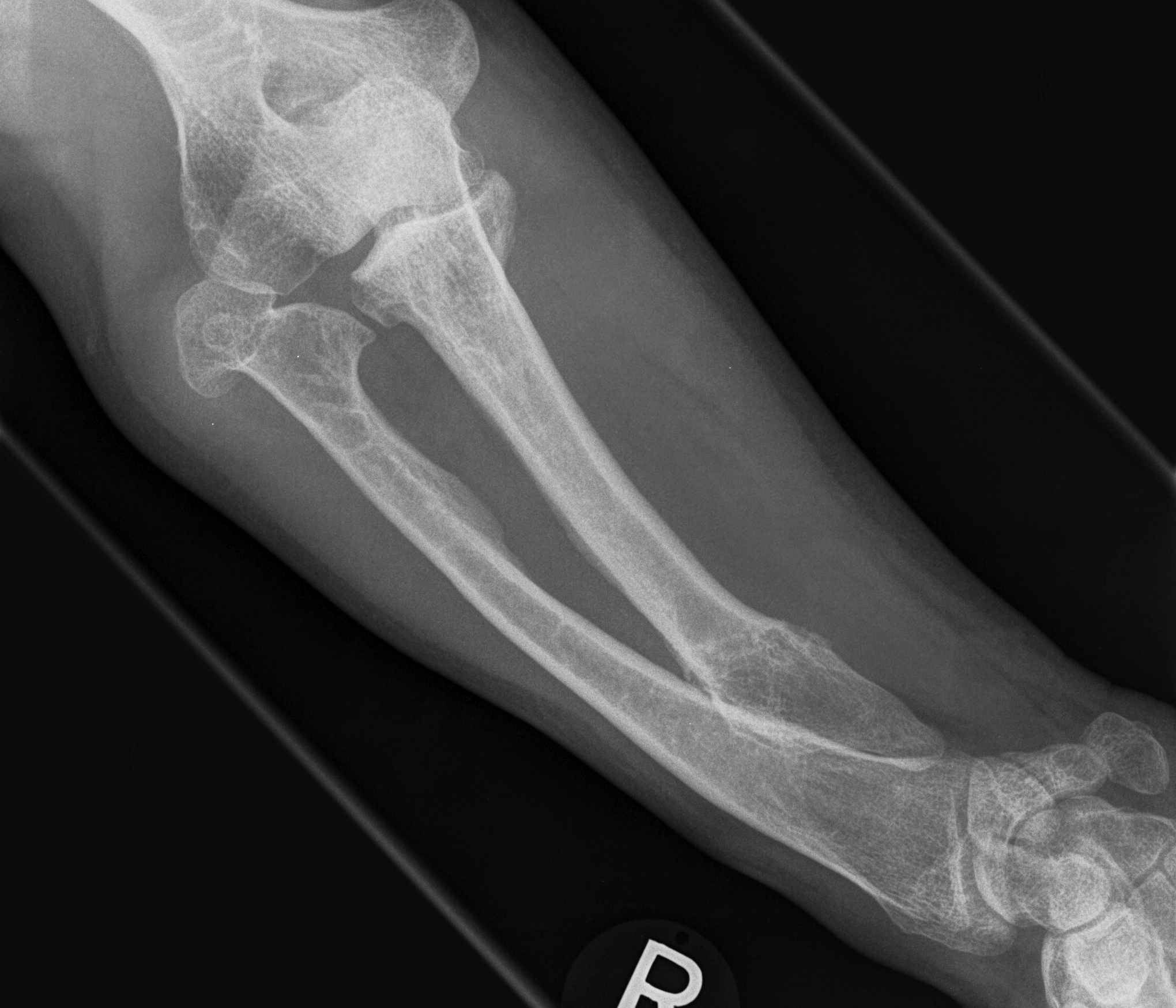
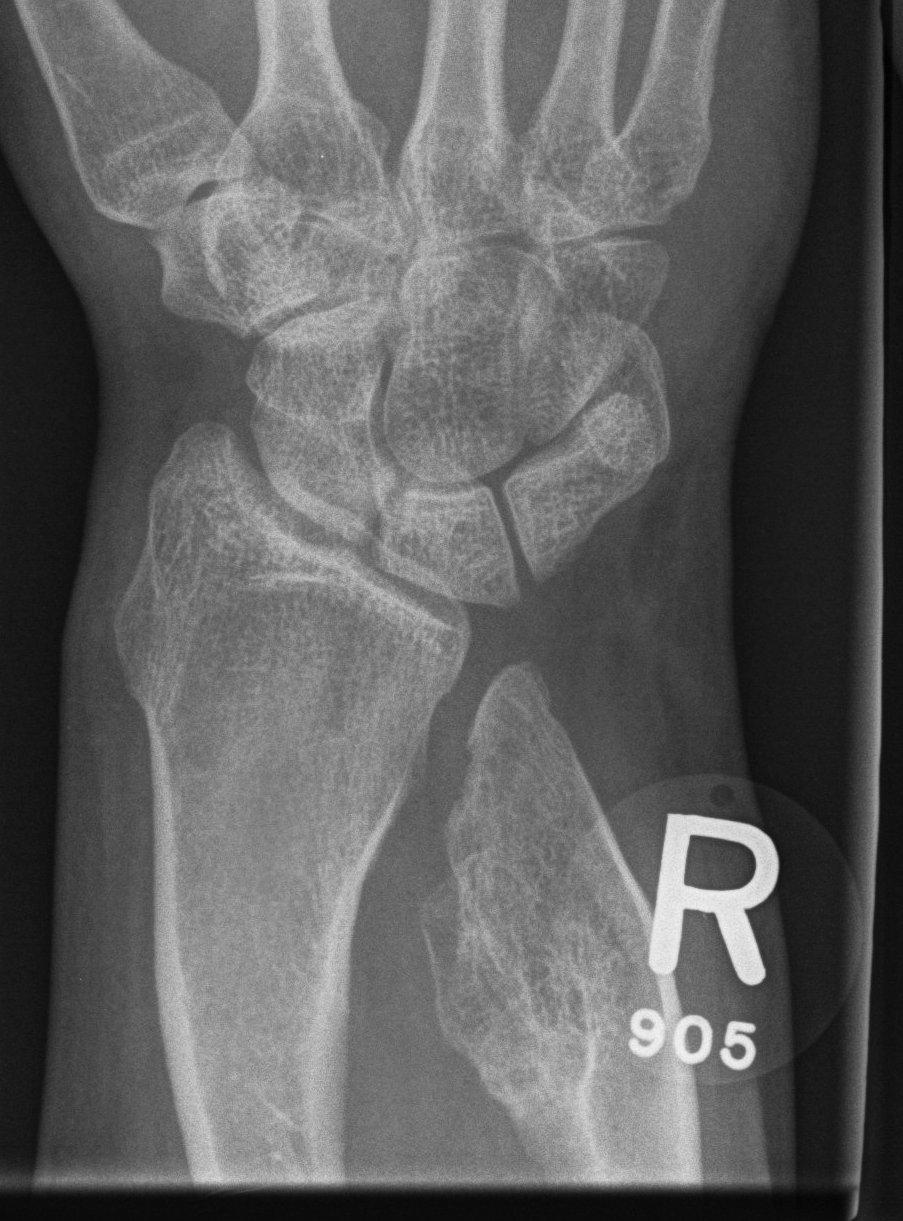
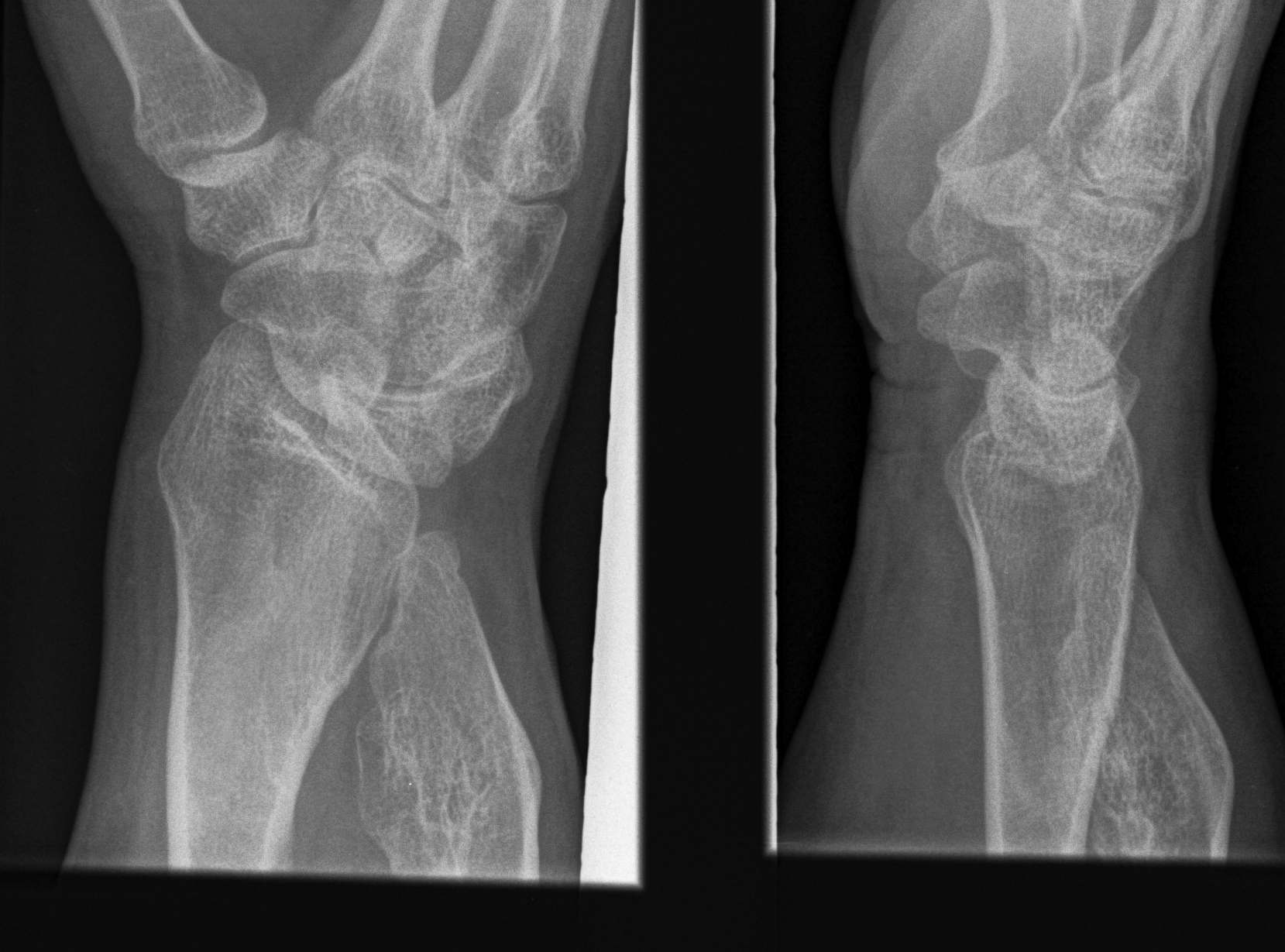
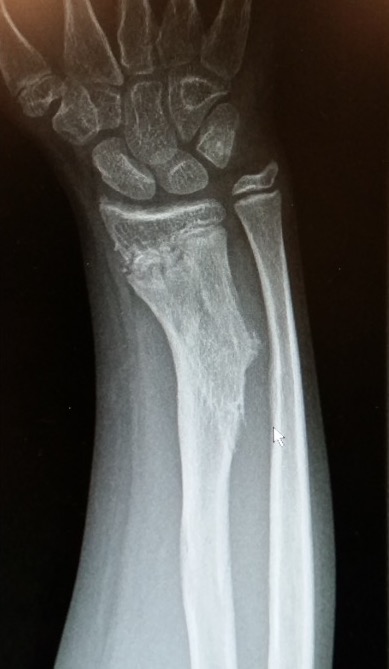
Forearm
- ulnar shortening / radial bowing / ulnar deviation of wrist
- can get radial head dislocation / carpal slip
Histology
Exostoses tend to be more disorganised with bosselated cartilage cap
Management
Surgical Indications
Symptomatic osteochondromas - nerve impingement
Biopsy suspicious lesions
Growth deformity - bowing / leg length discrepancy
Knee
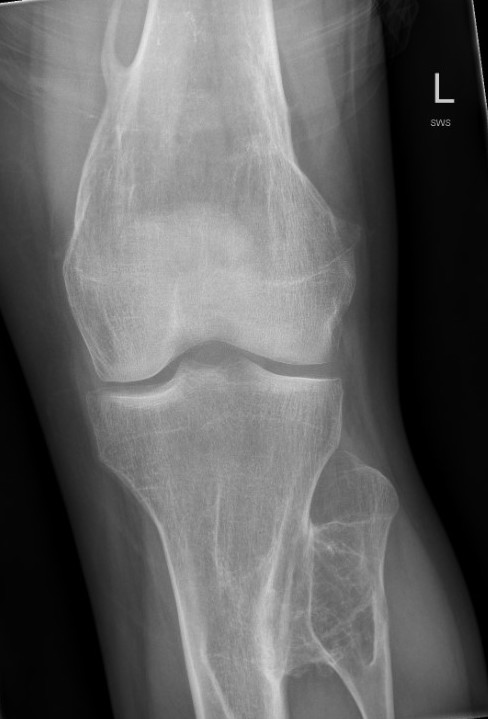
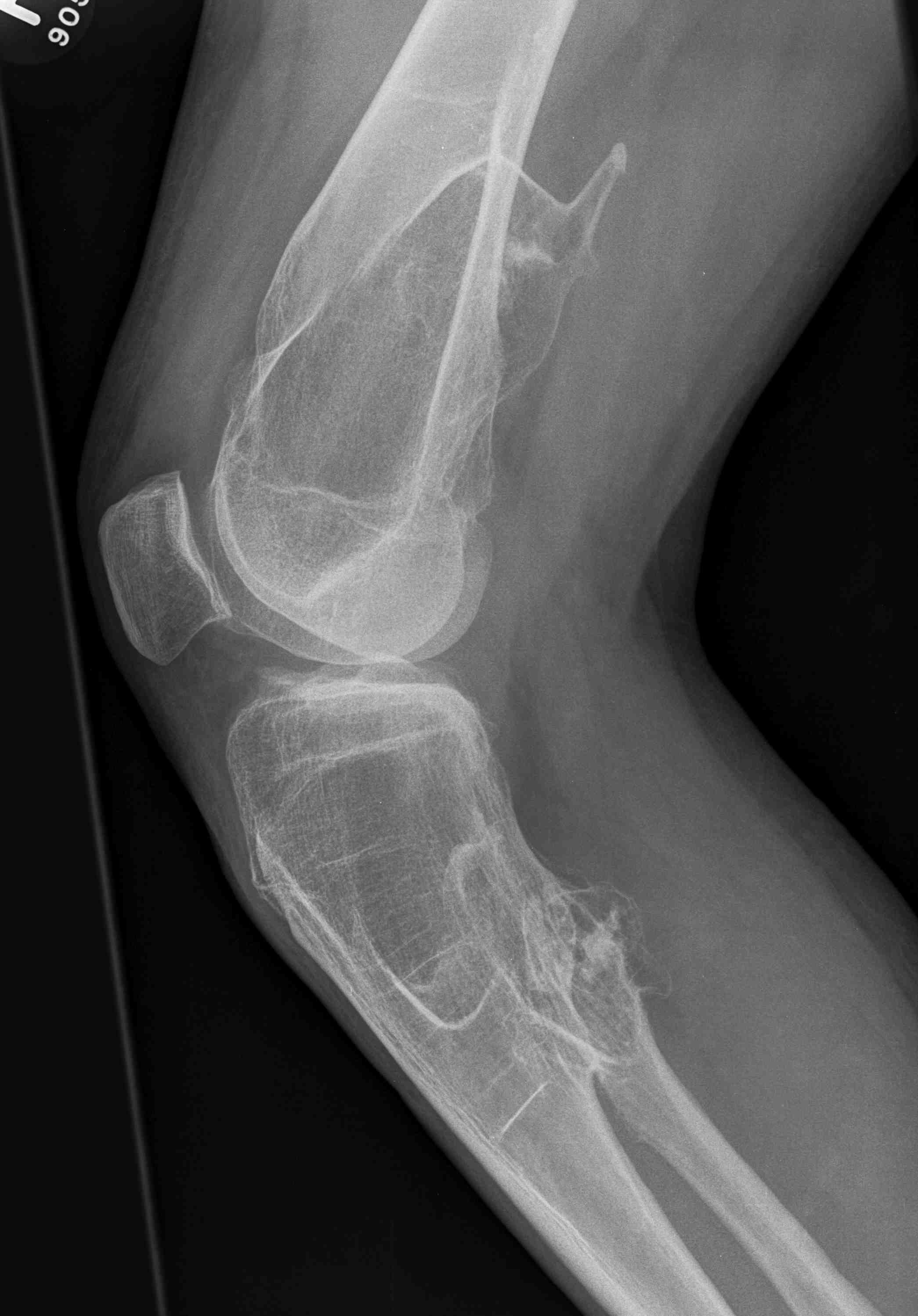
Incidence
- 172 patients with HME
- 90% had exostosis around the knee
- 20% had valgus deformity
- 15% had FFD deformity
Issues
1. Multiple case reports of pseudoaneuryms and vascular complications with knee osteochondromas
2. Excision of osteochondromas may cause rapidly developing deformity
Denduluri et al J Paediatri Orthop B 2016
- excision of medial proximal tibial osteochondroma in 3 patients with HME
- developed genu valgum as a result
Options
Guided growth / temporary hemi-epiphysiodesis
Osteotomy
Guided growth
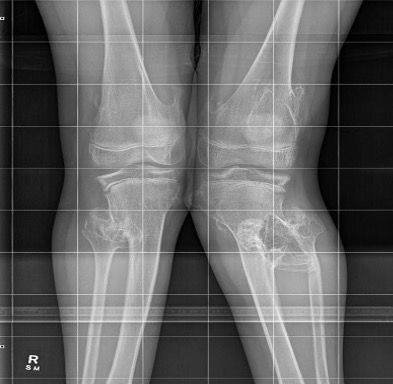
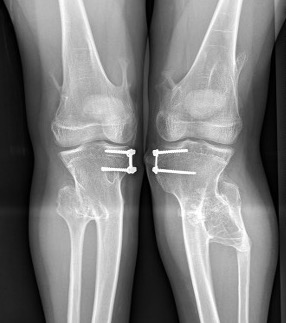
Kang et al J Paediatr Orthop 2017
- 15 cases of MHE with genu valgum
- treated with hemi-epiphyseal stapling
- 67% satisfactory corrections
- correction slower than idiopathic valgus correction (1.5 years v 1 year)
Osteotomy
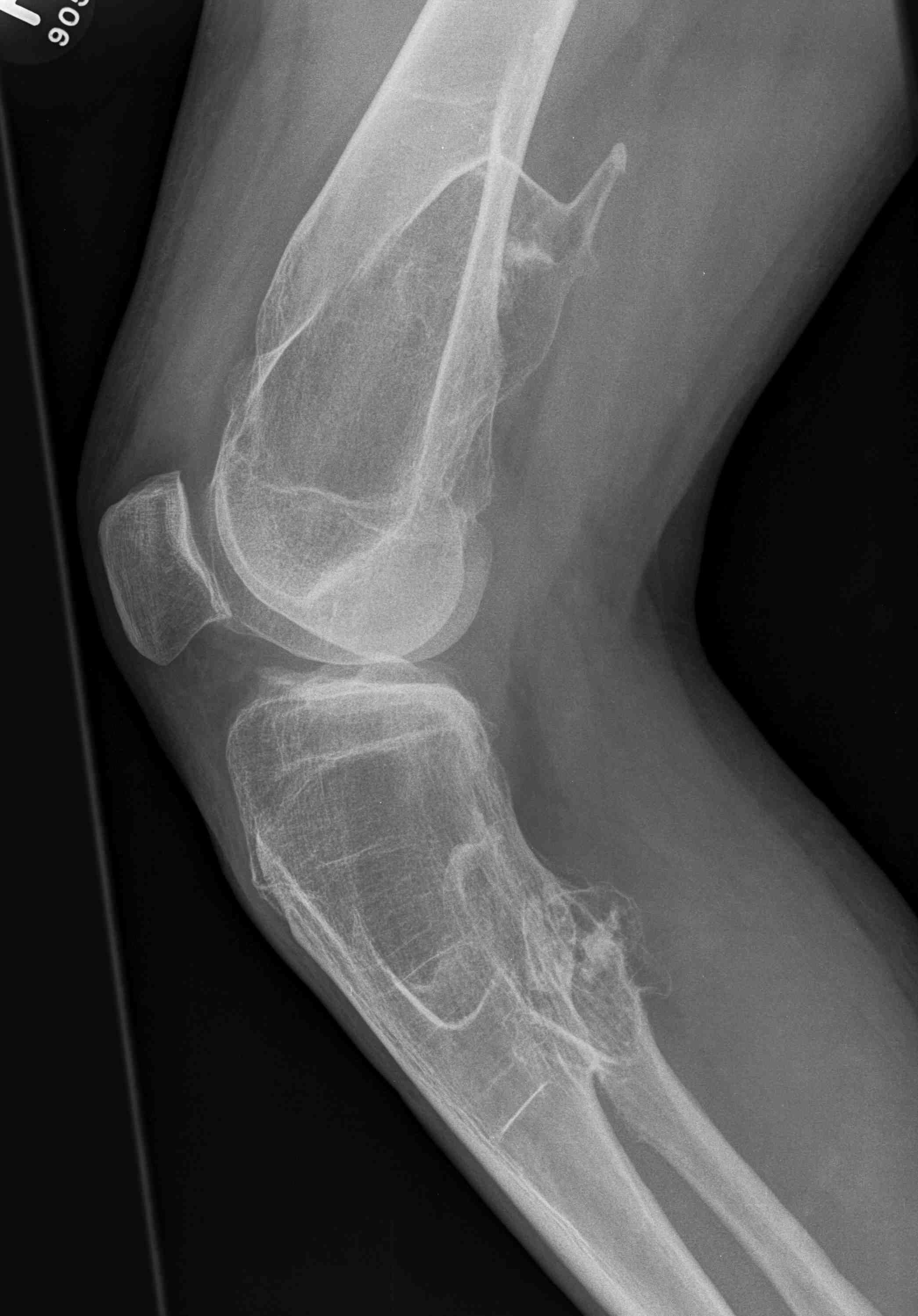
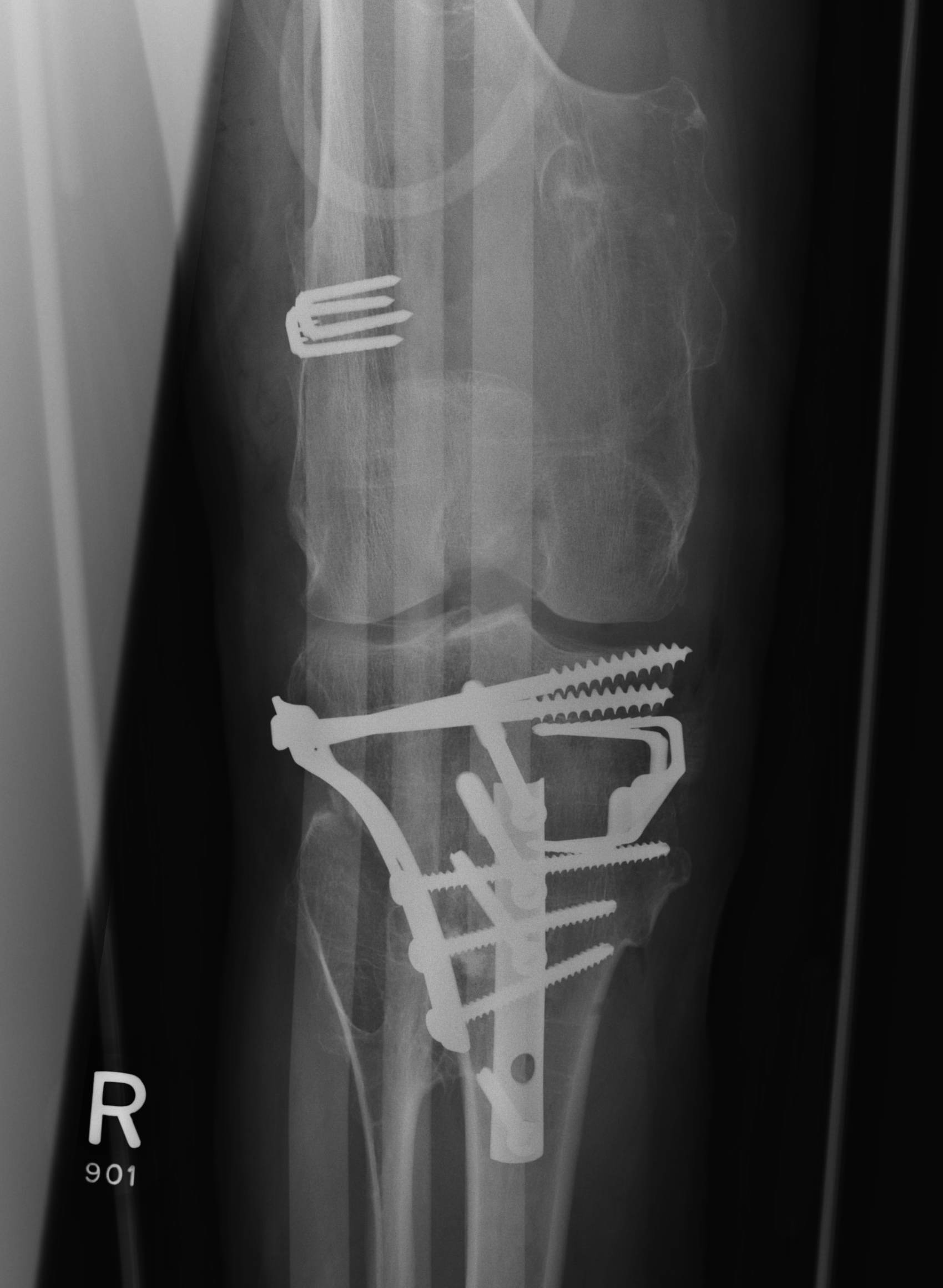
Ankle
Incidence
Zhang et al J Child Orthop 2021
- 61 children, mean age of 10
- 50% had ankle valgus
- correlates with osteochondromas lateral tibia / medial fibula
Surgical options
Guided growth
Osteotomy
Temporary screw epiphysiodesis
Rupprecht et al J Paediatr Orthop 2015
- 12 patients with HME and ankle valgus
- average age of 12, average tibio-talar tilt 13 degrees
- treated with temporary medial malleolar screw epiphysiodesis for 24 months
- excellent corrections
- 43% rebounded > 5 degrees after screw removal, treated by repeated eiphysiodesis
Ilizaroz / Osteotomy
Olfram et al J Orthop Traumatol 2008
- correction of ankle valgus in 5 patients ilizarov
- average correction 18 degrees
Hip
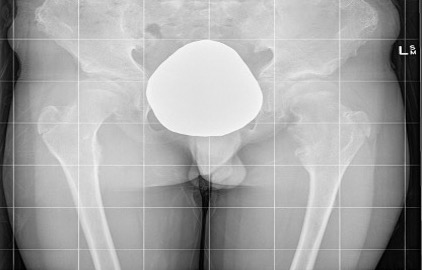
Issues
Coxa valga
Hip subluxation
Guided growth
Hung et al J Paediatr Orthop 2023
- 12 patients with HME and coxa valga / hip subluxation
- guided growth improved neck shaft angles and epiphyseal angles
Forearm


Incidence
Jo et al J Hand Surg Am
- 53 pediatric patients with HME
- 10% incidence of radial head dislocation
Issue
Prevent radial head dislocation / radial slip
? improve function
Options
Excision of local osteochondromas
Ulnar lengthening
Ulnar lengthening
Vogt et al J Paediatr Orthop 2011
- 12 children mean age of 10 with HME
- external fixator ulna lengthening
- no change on radial head dislocation / carpal slip
- no functional improvement except radial abduction
Li et al J Orthop Surg Res 2020
- 17 forearms mean age 10
- Ilizarov distraction osteogenesis of the ulna average 4 cm
- improved pronation and elbow flexion
- unable to reduce radial head dislocation
Spine
- 43 patients with HME evaluated with spine MRI
- 68% had spinal osteochondromas
- 27% had lesions encroaching on spinal canal
- all asymptomatic
